Spandidos Publications style
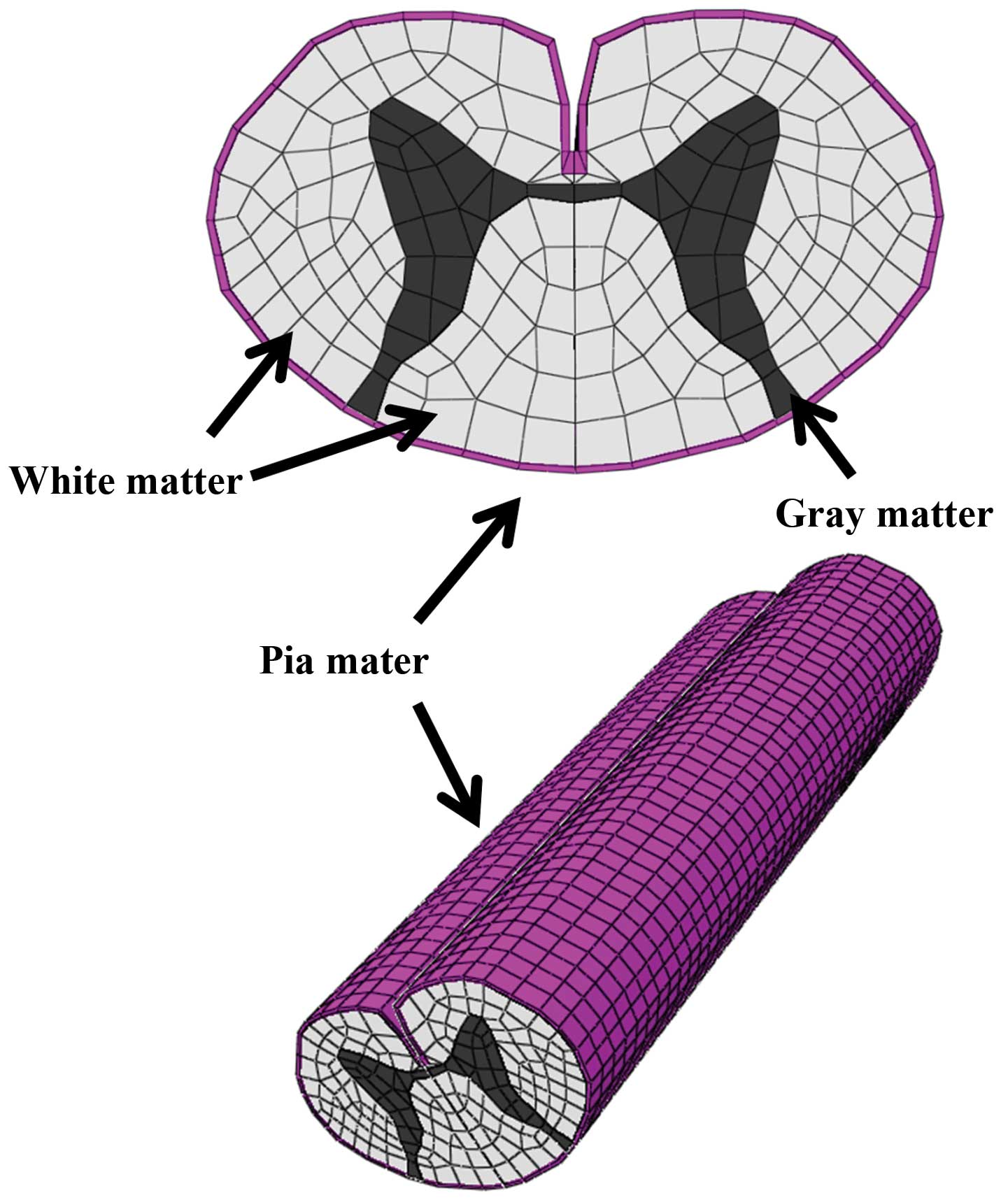
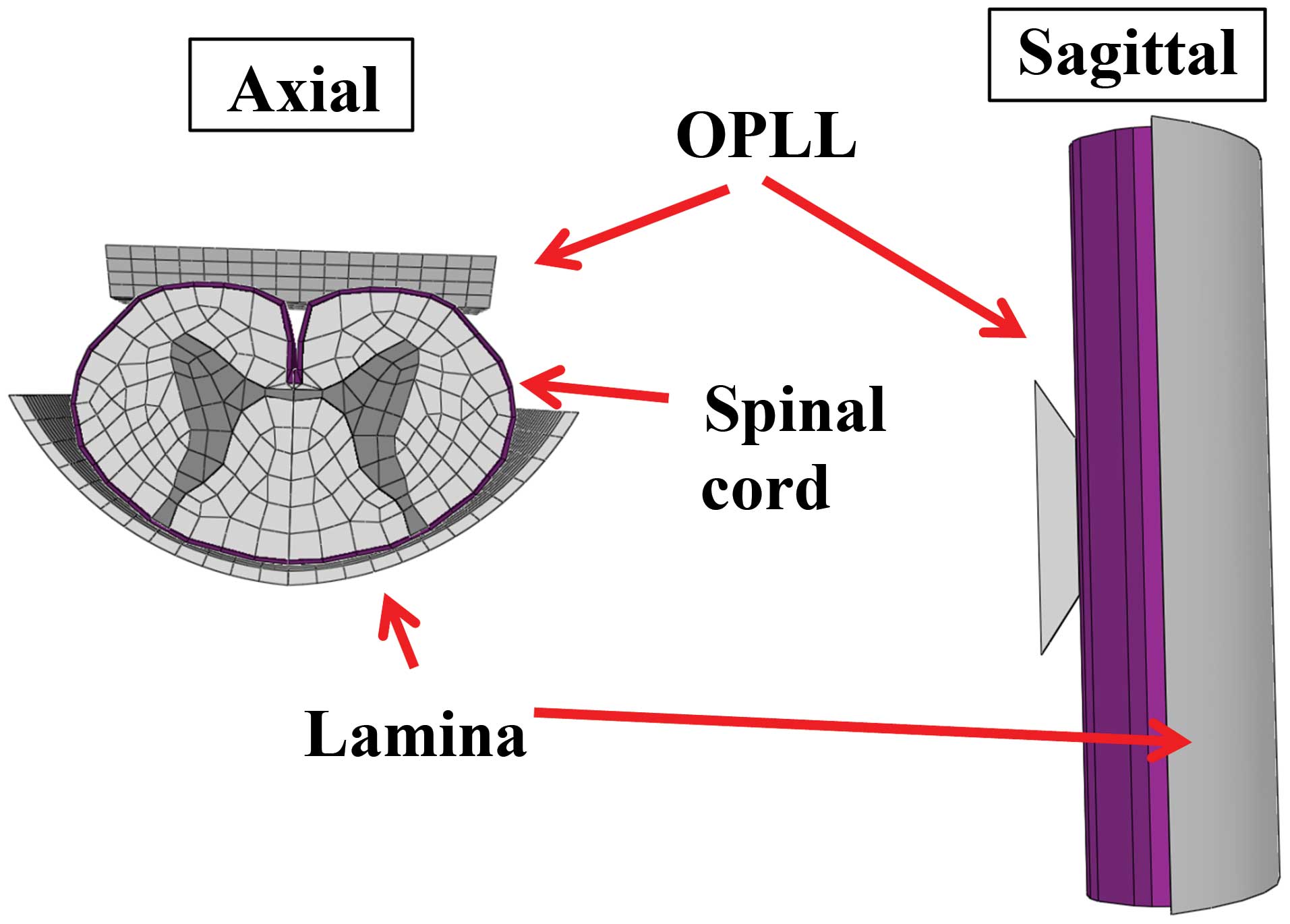
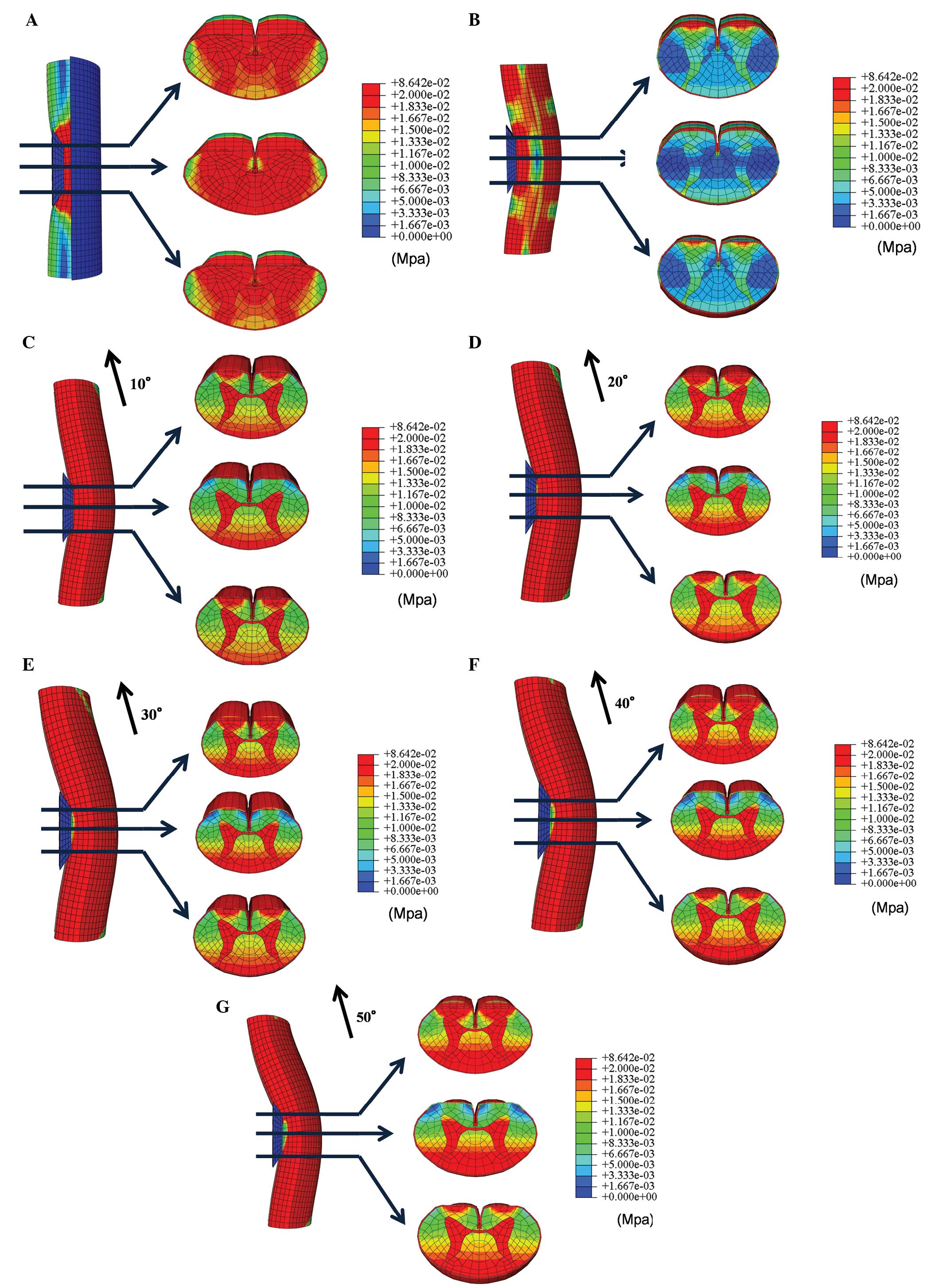
Nishida N, Kanchiku T, Kato Y, Imajo Y, Yoshida Y, Kawano S and Taguchi T: Biomechanical analysis of cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Effects of posterior decompression and kyphosis following decompression. Exp Ther Med 7: 1095-1099, 2014.
APA
Nishida, N., Kanchiku, T., Kato, Y., Imajo, Y., Yoshida, Y., Kawano, S., & Taguchi, T. (2014). Biomechanical analysis of cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Effects of posterior decompression and kyphosis following decompression. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 7, 1095-1099. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1557
MLA
Nishida, N., Kanchiku, T., Kato, Y., Imajo, Y., Yoshida, Y., Kawano, S., Taguchi, T."Biomechanical analysis of cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Effects of posterior decompression and kyphosis following decompression". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 7.5 (2014): 1095-1099.
Chicago
Nishida, N., Kanchiku, T., Kato, Y., Imajo, Y., Yoshida, Y., Kawano, S., Taguchi, T."Biomechanical analysis of cervical myelopathy due to ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament: Effects of posterior decompression and kyphosis following decompression". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 7, no. 5 (2014): 1095-1099. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1557