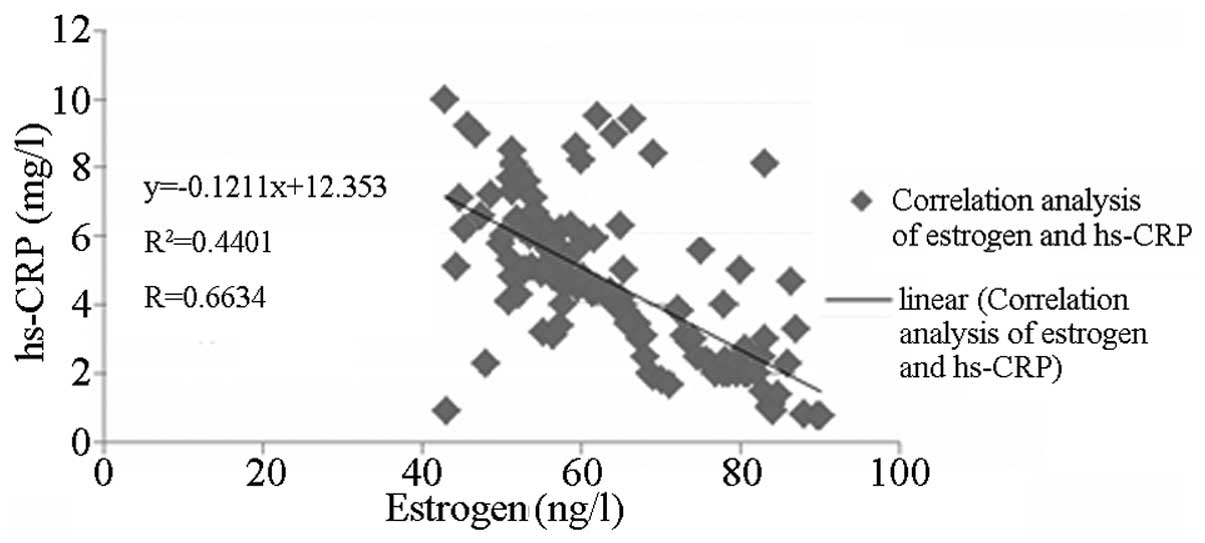
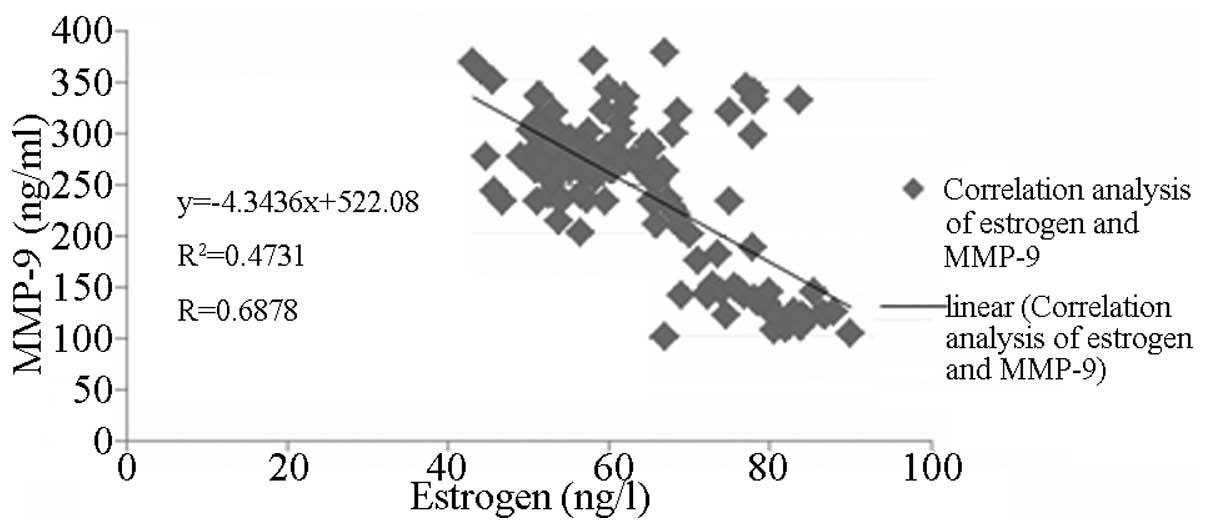
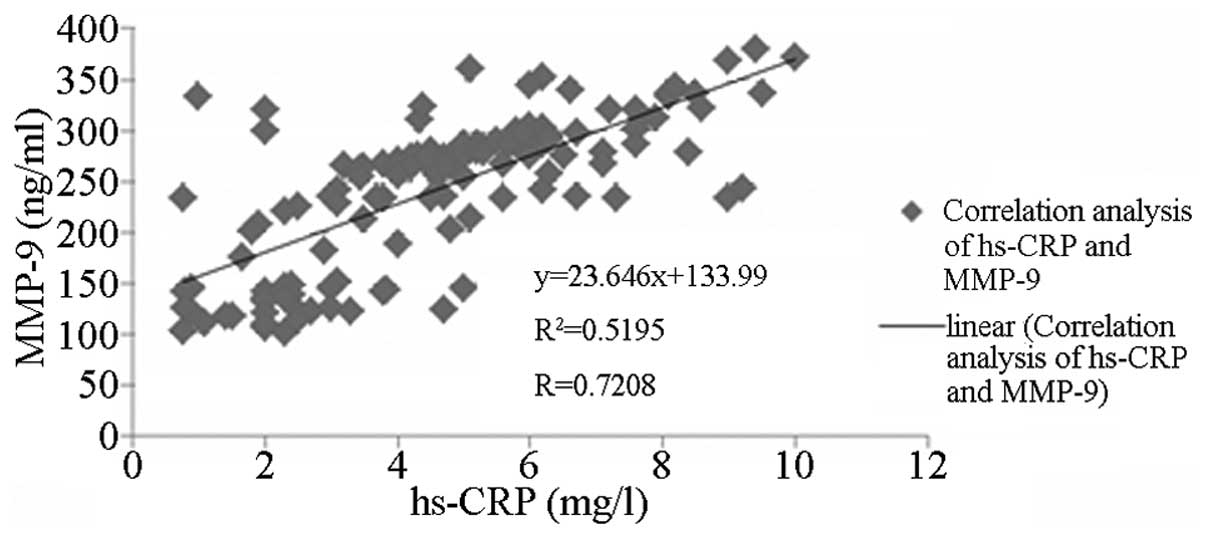
|
1
|
Harutyunyan M, Gøtze JP, Winkel P, et al:
Serum YKL-40 predicts long-term mortality in patients with stable
coronary disease: a prognostic study within the CLARICOR trial.
Immunobiology. 218:945–951. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Falcone C, Lucibello S, Mazzucchelli I, et
al: Galectin-3 plasma levels and coronary artery disease: a new
possible biomarker of acute coronary syndrome. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 24:905–913. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sakamoto Y, Muramatsu T, Tsukahara R, Ito
Y, Ishimori H, Hirano K and Nakano M: A case achieved successful
revascularization to severe ischemic coronary artery disease after
endovascular recanalization with infrarenal aortic occlusion.
Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 27:93–98. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Oh JE, Kim YW, Park SY and Kim JY:
Estrogen rather than progesterone cause constipation in both female
and male mice. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 17:423–426. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seo SM, Baek SH, Jeon HK, et al:
Correlations between the level of high-sensitivity c-reactive
protein and cardiovascular risk factors in korean adults with
cardiovascular disease or diabetes mellitus: the CALLISTO study. J
Atheroscler Thromb. 20:616–622. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yabluchanskiy A, Ma Y, Iyer RP, Hall ME
and Lindsey ML: Matrix metalloproteinase-9: Many shades of function
in cardiovascular disease. Physiology (Bethesda). 28:391–403.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Duellman T, Warren CL, Peissig P, Wynn M
and Yang J: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 genotype as a potential
genetic marker for abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ Cardiovasc
Genet. 5:529–537. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miller VM, Petterson TM, Jeavons EN, et
al: Genetic polymorphisms associated with carotid artery
intima-media thickness and coronary artery calcification in women
of the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study. Physiol Genomics.
45:79–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rashidinejad H, Hosseini SM, Moazenzadeh
M, Azimzadeh BS, Mirzaeipour F, Fakhreddini K and Sheikhvatan M:
Relationship between serum level of high-sensitive C-reactive
protein and extension of myocardial involvement in patients with
acute myocardial infarction. Rom J Intern Med. 50:211–215.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Golovkin AS, Matveeva VG, Grigor’ev EV,
Baĭrakova IuV, Shukevich DL, Velikanova EA and Barbarash OL:
Postoperative dynamic changes in matrix metalloproteinase levels in
patients with coronary artery bypass graft procedure complications.
Kardiologiia. 52:4–7. 2012.(In Russian).
|
|
11
|
Salama MM, Morad AR, Saleh MA, Sabri NA,
Zaki MM and ElSafady LA: Resistance to low-dose aspirin therapy
among patients with acute coronary syndrome in relation to
associated risk factors. J Clin Pharm Ther. 37:630–636. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kehl DW, Iqbal N, Fard A, Kipper BA, De La
Parra Landa A and Maisel AS: Biomarkers in acute myocardial injury.
Transl Res. 159:252–264. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cristell N, Cianflone D, Durante A, et al:
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein is within normal levels at the
very onset of first ST-segment elevation acute myocardial
infarction in 41% of cases: a multiethnic case-control study. J Am
Coll Cardiol. 58:2654–2661. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Akhtar N, Adil MM, Ahmed W,
Habib-ur-Rehman and Shahs MA: The role of leukocyte counts in
patients with unstable angina pectoris or myocardial infarction;
prognostic significance and correlation with plasma brain
natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels. J Pak Med Assoc. 61:51–54.
2011.
|
|
15
|
Huang G, Wang D, Zeb I, et al:
Intra-thoracic fat, cardiometabolic risk factors, and subclinical
cardiovascular disease in healthy, recently menopausal women
screened for the Kronos Early Estrogen Prevention Study (KEEPS).
Atherosclerosis. 221:198–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Mirhosseini SJ, Forouzannia SK,
Ali-Hassan-Sayegh S, Ravan HV, Abdollahi MH and Mozayan MR:
Preoperative C-reactive protein can predict early clinical outcomes
following elective off-pump CABG surgery in patients with severe
left ventricle dysfunction. Saudi J Anaesth. 6:327–331. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Crăciunescu I, Serban M, Iancu M, et al:
Changes in plasma levels of MMP-9, MMP-7 and their inhibitors in
patients with coronary artery disease. Rom J Intern Med.
48:141–149. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park JP, Lee BK, Shim JM, Kim SH, Lee CW,
Kang DH and Hong MK: Relationship between multiple plasma
biomarkers and vulnerable plaque determined by virtual histology
intravascular ultrasound. Circ J. 74:332–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Datta S, Iqbal Z and Prasad KR: Comparison
between serum hsCRP and LDL cholesterol for search of a better
predictor for ischemic heart disease. Indian J Clin Biochem.
26:210–213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|