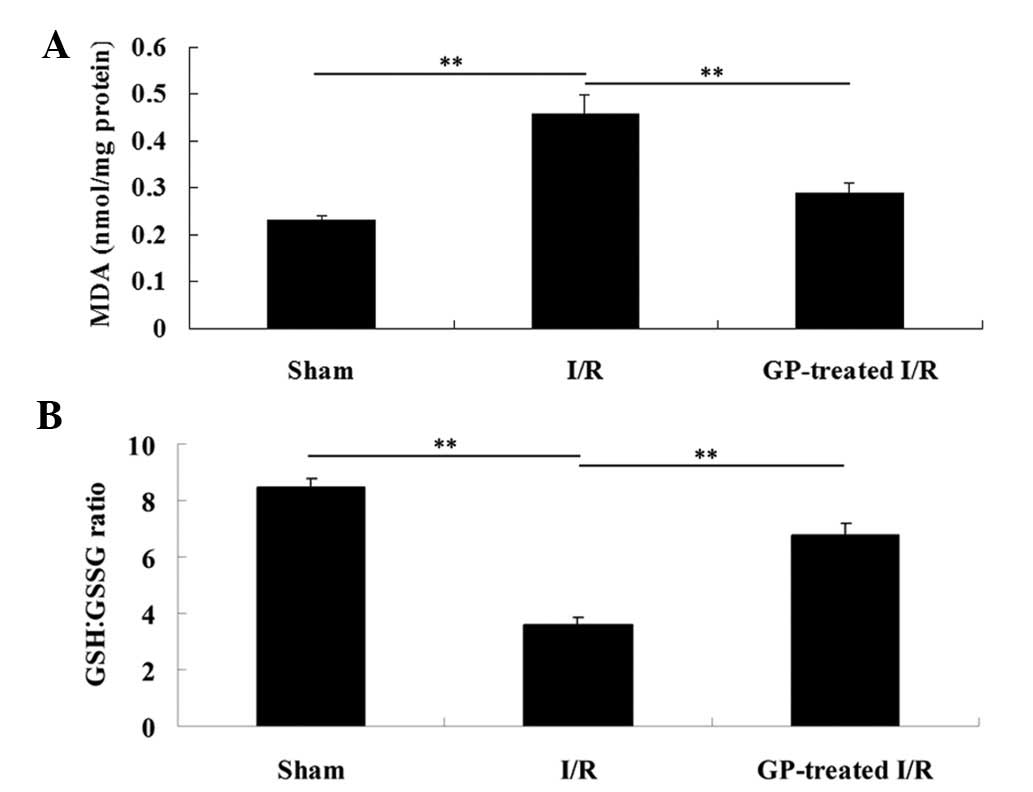
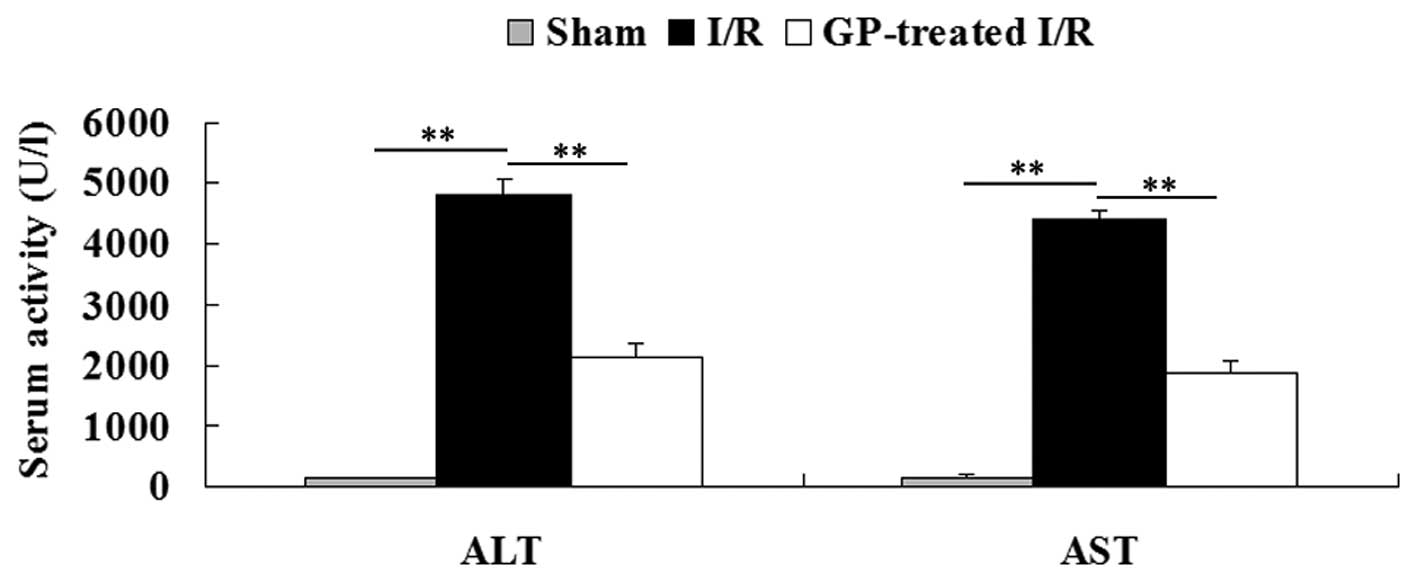
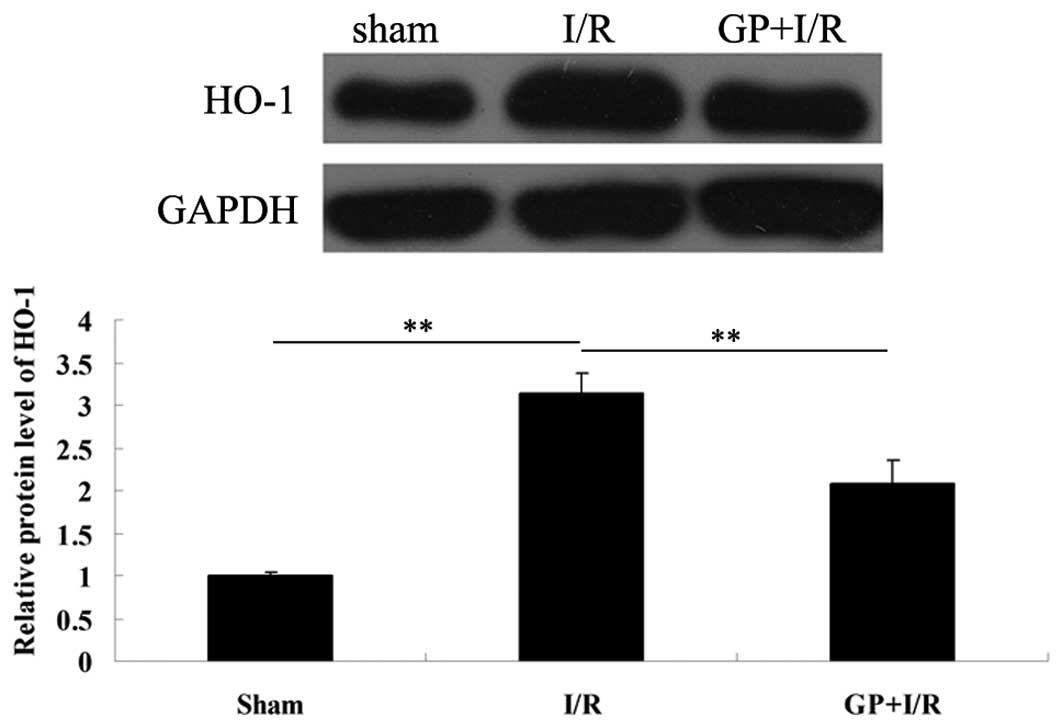
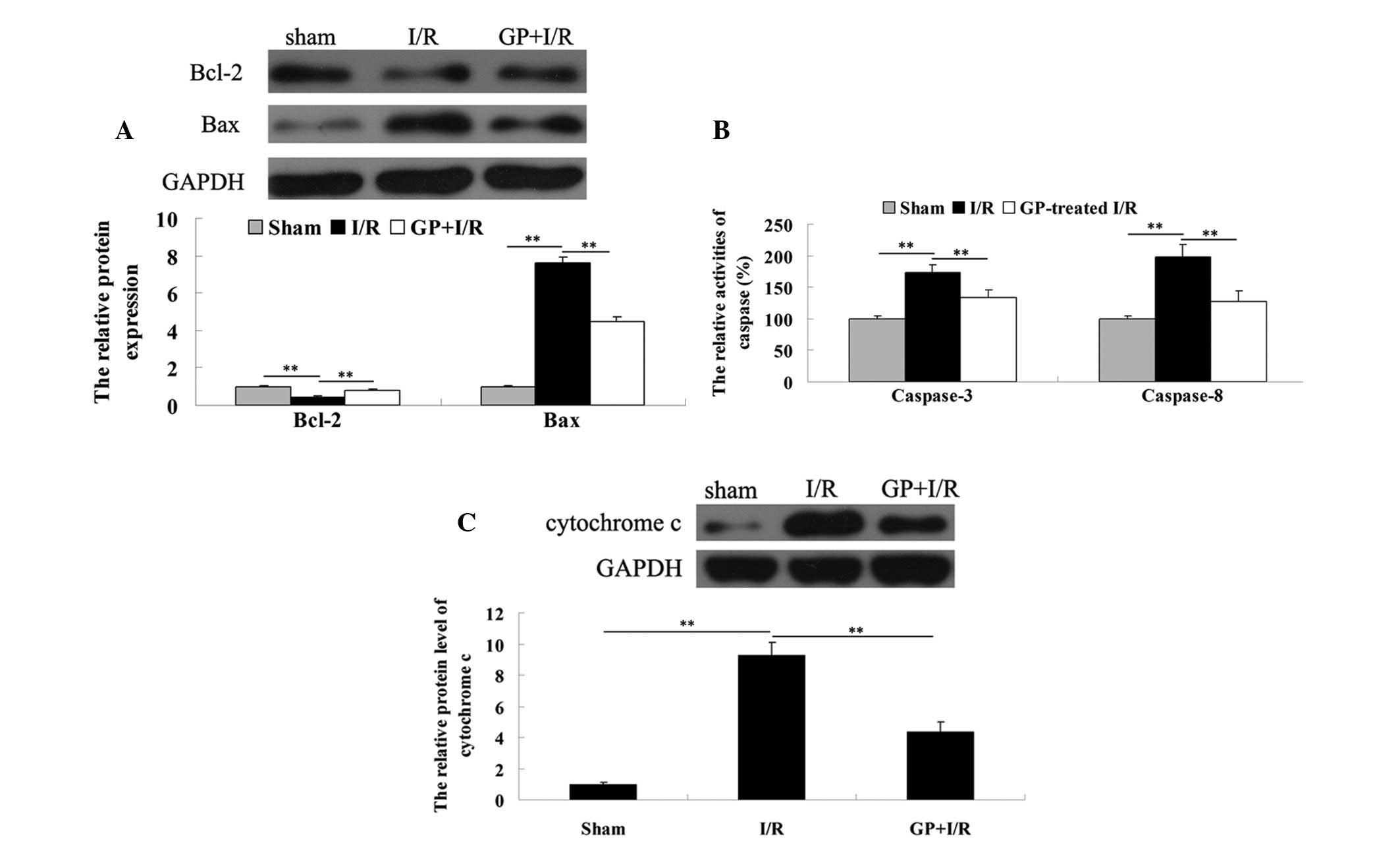
|
1
|
Mendes-Braz M, Elias-Miró M,
Jiménez-Castro MB, Casillas-Ramírez A, Ramalho FS and Peralta C:
The current state of knowledge of hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
injury based on its study in experimental models. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2012:2986572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yu HC, Bai L, Yue SQ, et al: Notch signal
protects non-parenchymal cells from ischemia/reperfusion injury in
vitro by repressing ROS. Ann Hepatol. 12:815–821. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang A, Chi X, Luo G, et al: Mast cell
stabilization alleviates acute lung injury after orthotopic
autologous liver transplantation in rats by downregulating
inflammation. PLoS One. 8:e752622013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Niu Y, Yan W, Lv J, Yao W and Yu LL:
Characterization of a novel polysaccharide from tetraploid
Gynostemma pentaphyllum makino. J Agric Food Chem.
61:4882–4889. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qin R, Zhang J, Li C, et al: Protective
effects of gypenosides against fatty liver disease induced by high
fat and cholesterol diet and alcohol in rats. Arch Pharm Res.
35:1241–1250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang G, Zhao Z, Gao L, et al: Gypenoside
attenuates white matter lesions induced by chronic cerebral
hypoperfusion in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 99:42–51. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang GL, Deng JP, Wang BH, et al:
Gypenosides improve cognitive impairment induced by chronic
cerebral hypoperfusion in rats by suppressing oxidative stress and
astrocytic activation. Behav Pharmacol. 22:633–644. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chen JC, Tsai CC, Chen LD, Chen HH and
Wang WC: Therapeutic effect of gypenoside on chronic liver injury
and fibrosis induced by CCl4 in rats. Am J Chin Med. 28:175–185.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi G, Zhang L, Xie WL, Chen XY and Li JS:
Protective effect of gypenosides on DNA and RNA of rat neurons in
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
21:1193–1196. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang SC, Shi Q, Feng YN and Fang J:
Tissue-protective effect of glutamine on hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury via induction of heme oxygenase-1.
Pharmacology. 91:59–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Aktan F, Henness S, Roufogalis BD and
Ammit AJ: Gypenosides derived from Gynostemma pentaphyllum
suppress NO synthesis in murine macrophages by inhibiting iNOS
enzymatic activity and attenuating NF-kappaB-mediated iNOS protein
expression. Nitric Oxide. 8:235–242. 2003.
|
|
12
|
Chen JC, Chung JG and Chen LD: Gypenoside
induces apoptosis in human Hep3B and HA22T tumour cells. Cytobios.
100:37–48. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Farmer EE and Mueller MJ: ROS-mediated
lipid peroxidation and RES-activated signaling. Annu Rev Plant
Biol. 64:429–450. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi Y, Pulliam DA, Liu Y, et al: Reduced
mitochondrial ROS, enhanced antioxidant defense, and distinct
age-related changes in oxidative damage in muscles of long-lived
Peromyscus leucopus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
304:R343–R355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amaral S, Redmann K, Sanchez V, Mallidis
C, Ramalho-Santos J and Schlatt S: UVB irradiation as a tool to
assess ROS-induced damage in human spermatozoa. Andrology.
1:707–714. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng Q, Li X, Peng J, Duan X, Fu Q and Hu
Y: Effect of gypenosides on DMN-induced liver fibrosis in rats.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 37:505–508. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Kim J, Kim HY and Lee SM: Protective
effects of geniposide and genipin against hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
21:132–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sass G, Barikbin R and Tiegs G: The
multiple functions of heme oxygenase-1 in the liver. Z
Gastroenterol. 50:34–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhong Z and Lemasters JJ: Role of free
radicals in failure of fatty liver grafts caused by ethanol.
Alcohol. 34:49–58. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dinnen RD, Mao Y, Qiu W, et al:
Redirecting apoptosis to aponecrosis induces selective cytotoxicity
to pancreatic cancer cells through increased ROS, decline in ATP
levels, and VDAC. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:2792–2803. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shamas-Din A, Kale J, Leber B and Andrews
DW: Mechanisms of action of Bcl-2 family proteins. Cold Spring Harb
Perspect Biol. 5:a0087142013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Renault TT, Teijido O, Antonsson B, Dejean
LM and Manon S: Regulation of Bax mitochondrial localization by
Bcl-2 and Bcl-x(L): keep your friends close but your enemies
closer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:64–67. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Renault TT and Manon S: Bax: Addressed to
kill. Biochimie. 93:1379–1391. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou F, Yang Y and Xing D: Bcl-2 and
Bcl-xL play important roles in the crosstalk between autophagy and
apoptosis. FEBS J. 278:403–413. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McIlwain DR, Berger T and Mak TW: Caspase
functions in cell death and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Biol. 5:a0086562013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Appelqvist H, Wäster P, Eriksson I,
Rosdahl I and Ollinger K: Lysosomal exocytosis and caspase-8
mediated apoptosis in UVA-irradiated keratinocytes. J Cell Sci.
126:5578–5584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qin Y, Vanden Hoek TL, Wojcik K, et al:
Caspase-dependent cytochrome c release and cell death in chick
cardiomyocytes after simulated ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 286:H2280–H2286. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kale J, Liu Q, Leber B and Andrews DW:
Shedding light on apoptosis at subcellular membranes. Cell.
151:1179–1184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zakeri Z and Lockshin RA: Cell death:
history and future. Adv Exp Med Biol. 615:1–11. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bernardi P and Rasola A: Calcium and cell
death: the mitochondrial connection. Subcell Biochem. 45:481–506.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|