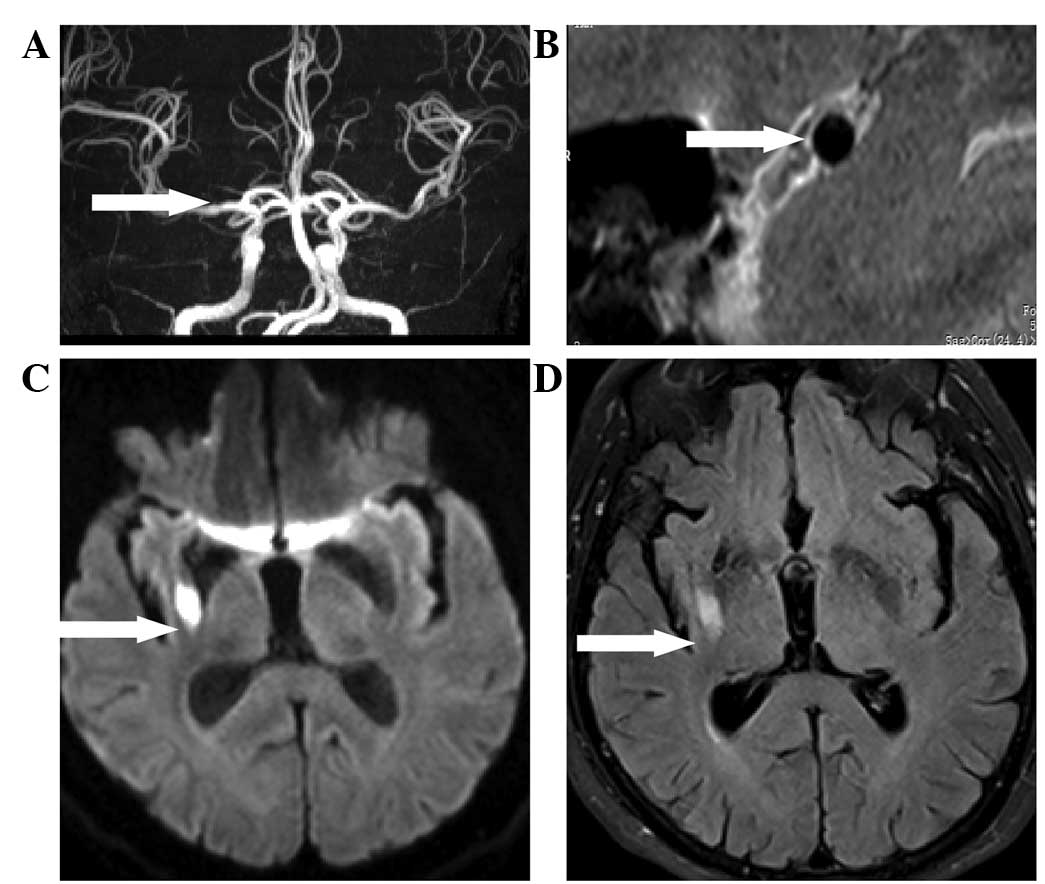
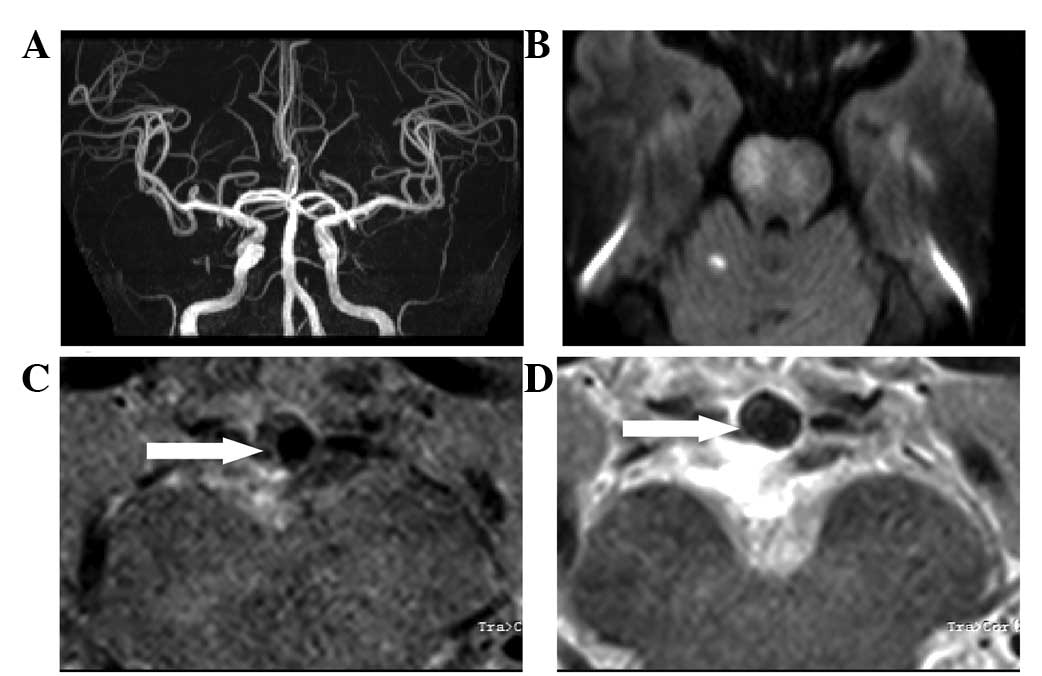
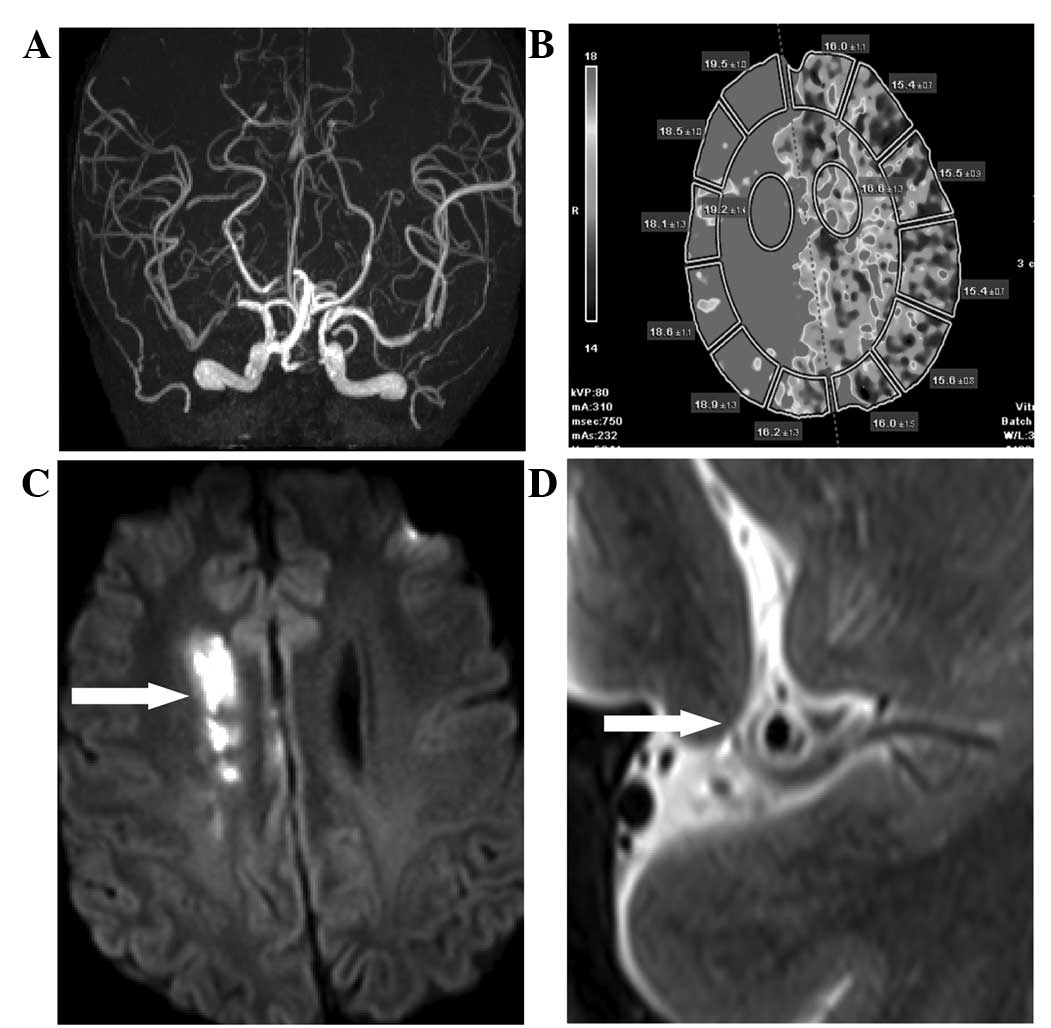
|
1
|
Pu Y, Liu L, Wang Y, et al; Chinese
IntraCranial AtheroSclerosis (CICAS) Study Group. Geographic and
sex difference in the distribution of intracranial atherosclerosis
in China. Stroke. 44:2109–2114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rincon F, Sacco RL, Kranwinkel G, et al:
Incidence and risk factors of intracranial atherosclerotic stroke:
the Northern Manhattan Stroke Study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 28:65–71.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shi MC, Wang SC, Zhou HW, et al:
Compensatory remodeling in symptomatic middle cerebral artery
atherosclerotic stenosis: a high-resolution MRI and microemboli
monitoring study. Neurol Res. 34:153–158. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E, et al: From
vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: a call for new definitions
and risk assessment strategies: Part I. Circulation. 108:1664–1672.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu WH, Li ML, Gao S, et al: In vivo
high-resolution MR imaging of symptomatic and asymptomatic middle
cerebral artery atherosclerotic stenosis. Atherosclerosis.
212:507–511. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ma N, Jiang WJ, Lou X, et al: Arterial
remodeling of advanced basilar atherosclerosis: a 3-tesla MRI
study. Neurology. 75:253–258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bodle JD, Feldmann E, Swartz RH, Rumboldt
Z, Brown T and Turan TN: High-resolution magnetic resonance
imaging: an emerging tool for evaluating intracranial arterial
disease. Stroke. 44:287–292. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Niizuma K, Shimizu H, Takada S and
Tominaga T: Middle cerebral artery plaque imaging using 3-Tesla
high-resolution MRI. J Clin Neurosci. 15:1137–1141. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ryu CW, Jahng GH, Kim EJ, Choi WS and Yang
DM: High resolution wall and lumen MRI of the middle cerebral
arteries at 3 tesla. Cerebrovasc Dis. 27:433–442. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao S, Wang YJ, Xu AD, et al: Chinese
ischemic stroke subclassification. Front Neurol. 2:62011.
|
|
11
|
Turan TN, Maidan L, Cotsonis G, et al;
Warfarin-Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease Investigators.
Failure of antithrombotic therapy and risk of stroke in patients
with symptomatic intracranial stenosis. Stroke. 40:505–509. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JM, Jung KH, Sohn CH, Moon J, Han MH
and Roh JK: Middle cerebral artery plaque and prediction of the
infarction pattern. Arch Neurol. 69:1470–1475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arenillas JF and Alvarez-Sabin J: Basic
mechanisms in intracranial large-artery atherosclerosis: advances
and challenges. Cerebrovasc Dis. 20(Suppl 2): 75–83. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yazdani SK, Vorpahl M, Ladich E and
Virmani R: Pathology and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaque:
identification, treatment options, and individual patient
differences for prevention of stroke. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc
Med. 12:297–314. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cai JM, Hatsukami TS, Ferguson MS, Small
R, Polissar NL and Yuan C: Classification of human carotid
atherosclerotic lesions with in vivo multicontrast magnetic
resonance imaging. Circulation. 106:1368–1373. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kampschulte A, Ferguson MS, Kerwin WS, et
al: Differentiation of intraplaque versus juxtaluminal
hemorrhage/thrombus in advanced human carotid atherosclerotic
lesions by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation.
110:3239–3244. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Larose E, Yeghiazarians Y, Libby P, et al:
Characterization of human atherosclerotic plaques by intravascular
magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation. 112:2324–2331. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lam WW, Wong KS, So NM, Yeung TK and Gao
S: Plaque volume measurement by magnetic resonance imaging as an
index of remodeling of middle cerebral artery: correlation with
transcranial color Doppler and magnetic resonance angiography.
Cerebrovasc Dis. 17:166–169. 2004.
|
|
19
|
Gao T, Zhang Z, Yu W, Zhang Z and Wang Y:
Atherosclerotic carotid vulnerable plaque and subsequent stroke: a
high-resolution MRI study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 27:345–352. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mono ML, Karameshev A, Slotboom J, et al:
Plaque characteristics of asymptomatic carotid stenosis and risk of
stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis. 34:343–350. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lindsay AC, Biasiolli L, Lee JM, et al:
Plaque features associated with increased cerebral infarction after
minor stroke and TIA: a prospective, case-control, 3-T carotid
artery MR imaging study. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 5:388–396. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pantoni L and Garcia JH: Pathogenesis of
leukoaraiosis: a review. Stroke. 28:652–659. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arenillas JF, Molina CA, Chacón P, et al:
High lipoprotein (a), diabetes, and the extent of symptomatic
intracranial atherosclerosis. Neurology. 63:27–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thomas GN, Lin JW, Lam WW, et al:
Albuminuria is a marker of increasing intracranial and extracranial
vascular involvement in Type 2 diabetic Chinese patients.
Diabetologia. 47:1528–1534. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kwan MW, Mak W, Cheung RT and Ho SL:
Ischemic stroke related to intracranial branch atheromatous disease
and comparison with large and small artery diseases. J Neurol Sci.
303:80–84. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|