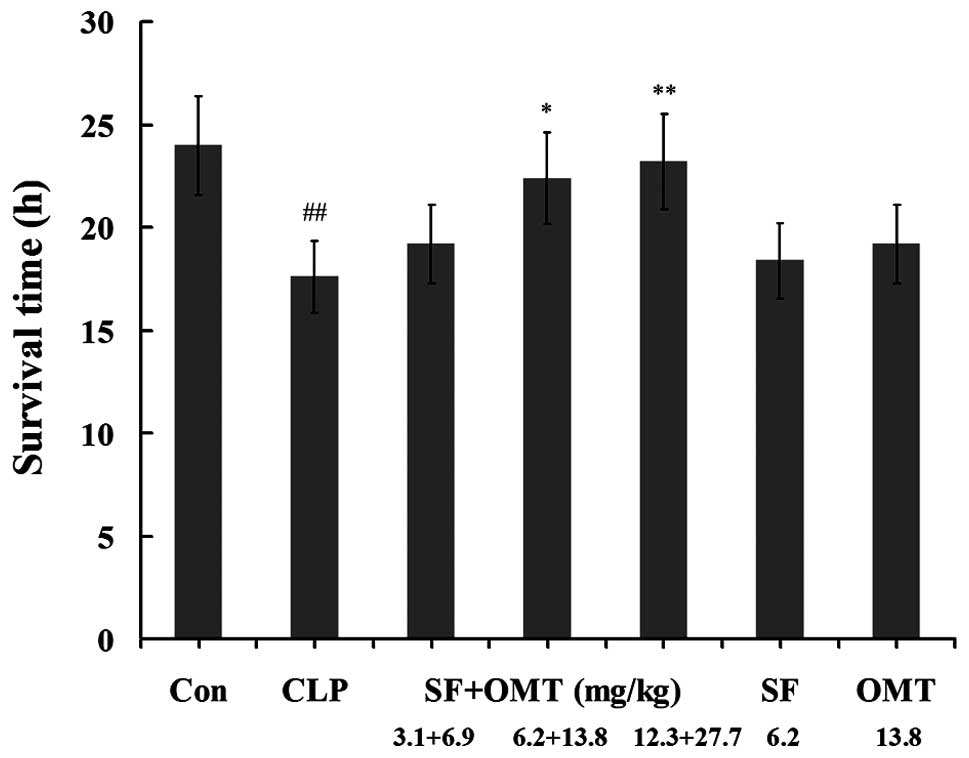
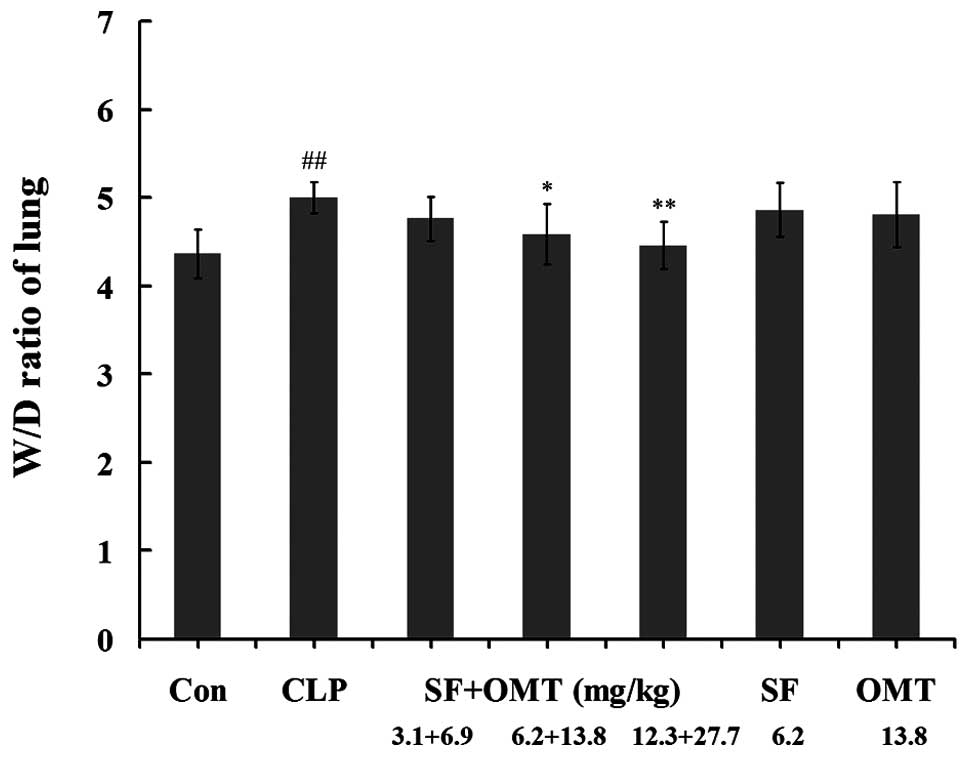
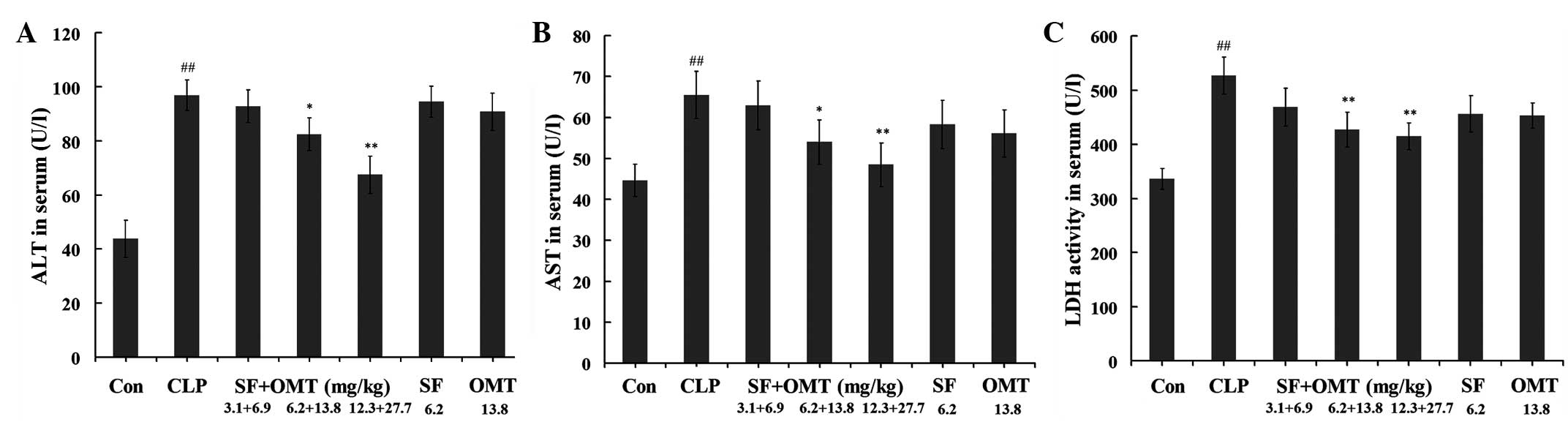
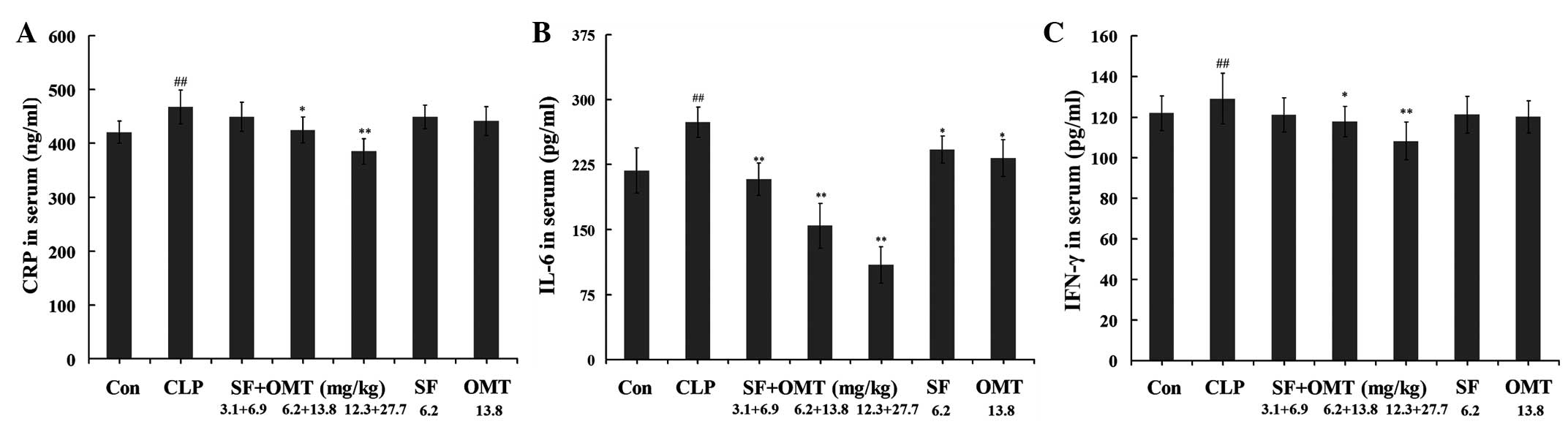
|
1
|
Mokart D, Capo C, Blache JL, Delpero JR,
Houvenaeghel G, Martin C and Mege JL: Early postoperative
compensatory anti-inflammatory response syndrome is associated with
septic complications after major surgical trauma in patients with
cancer. Br J Surg. 89:1450–1456. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bollaert PE, Charpentier C, Levy B,
Debouverie M, Audibert G and Larcan A: Reversal of late septic
shock with supraphysiologic doses of hydrocortisone. Crit Care Med.
26:645–650. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Baddour LM, Yu VL, Klugman KP, et al;
International Pneumococcal Study Group. Combination antibiotic
therapy lowers mortality among severely ill patients with
pneumococcal bacteremia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 170:440–444.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schlichting D and McCollam JS: Recognizing
and managing severe sepsis: a common and deadly threat. South Med
J. 100:594–600. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan X, Sun Y, Miao N, et al: The
synergistic anti-inflammatory effect of the combination of sodium
ferulate and oxymatrine and its modulation on
inflammation-associated mediators in RAW 264.7 cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 137:1477–1485. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu H, Sun Y, Gao Y, Chen F, Xu M and Liu
Z: The analgesic effect and mechanism of the combination of sodium
ferulate and oxymatrine. Neurochem Res. 35:1368–1375. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yuan X, Wang Y, Du D, Hu Z, Xu M, Xu M and
Liu Z: The effects of the combination of sodium ferulate and
oxymatrine on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice.
Inflammation. 35:1161–1168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baker CC, Chaudry IH, Gaines HO and Baue
AE: Evaluation of factors affecting mortality rate after sepsis in
a murine cecal ligation and puncture model. Surgery. 94:331–335.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Standage SW, Caldwell CC, Zingarelli B and
Wong HR: Reduced peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α
expression is associated with decreased survival and increased
tissue bacterial load in sepsis. Shock. 37:164–169. 2012.
|
|
10
|
Elstner EF and Heupel A: Inhibition of
nitrite formation from hydroxylammoniumchloride: a simple assay for
superoxide dismutase. Anal Biochem. 70:616–620. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N and Yagi K: Assay for
lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction.
Anal Biochem. 95:351–358. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Huang Y, Piao Y, Nagaoka K, Watanabe
G, Taya K and Li C: Protective effects of nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2 on whole body heat stress-induced oxidative
damage in the mouse testis. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 11:232013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wei Q, Ren X, Jiang Y, Jin H, Liu N and Li
J: Advanced glycation end products accelerate rat vascular
calcification through RAGE/oxidative stress. BMC Cardiovasc Disord.
13:132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang BH and Ou-Yang JP: Pharmacological
actions of sodium ferulate in cardiovascular system. Cardiovascuar
Drug Rev. 23:161–172. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Srinivasan M, Sudheer AR and Menon VP:
Ferulic acid: therapeutic potential through its antioxidant
property. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 40:92–100. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen XS, Wang GJ, Cai X, et al: Inhibition
of hepatitis B virus by oxymatrine in vivo. World J Gastroenterol.
7:49–52. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu GL, Yao L, Rao SY, Gong ZN, Zhang SQ
and Yu SQ: Attenuation of acute lung injury in mice by oxymatrine
is associated with inhibition of phosphorylated p53
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Ethnopharmacol. 98:177–183.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brooks HF, Osabutey CK, Moss RF, Andrews
PL and Davies DC: Caecal ligation and puncture in the rat mimics
the pathophysiological changes in human sepsis and causes
multiorgan dysfunction. Metab Brain Dis. 22:353–373. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Remick D, Manohar P, Bolgos G, Rodriguez
J, Moldawer L and Wollenberg G: Blockade of tumor necrosis factor
reduces lipopolysacharide lethality, but not the lethality of cecal
ligation and puncture. Shock. 4:89–95. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kosaka J, Morimatsu H, Takahashi T, et al:
Effects of biliverdin administration on acute lung injury induced
by hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation in rats. PLoS One.
8:e636062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shahshahani MM, Azizahari S, Soori T, et
al: Hepatotoxicity and liver enzyme alteration in patients with
immunobullous diseases receiving immunosuppressive therapy. J
Dermatol. 38:1153–1157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Singab AN, Youssef DT, Noaman E and Kotb
S: Hepatoprotective effect of flavonol glycosides rich fraction
from Egyptian Vicia calcarata Desf. against
CCl4-induced liver damage in rats. Arch Pharm Res.
28:791–798. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Márquez-Velasco R, Martínez-Velázquez AX,
Amezcua-Guerra LM, et al: Enhanced survival from CLP-induced sepsis
following late administration of low doses of anti-IFNγ F(ab’)2
antibody fragments. Inflamm Res. 60:947–953. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Latifi SQ, O’Riordan MA, Levine AD and
Stallion A: Persistent elevation of serum interleukin-6 in
intraabdominal sepsis identifies those with prolonged length of
stay. J Pediatr Surg. 39:1548–1552. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Imamura T, Tanaka S, Yoshida H, et al:
Significance of measurement of high sensitivity C-reactive protein
in acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 37:935–938. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Memiş D, Gursoy O, Tasdogan M, et al: High
C-reactive protein and low cholesterol levels are prognostic
markers of survival in severe sepsis. J Clin Anesth. 19:186–191.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ballou SP and Lozanski G: Induction of
inflammatory cytokine release from cultured human monocytes by
C-reactive protein. Cytokine. 4:361–368. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cermak J, Key NS, Bach RR, Balla J, Jacob
HS and Vercellotti GM: C-reactive protein induces human peripheral
blood monocytes to synthesize tissue factor. Blood. 82:513–520.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lausevic Z, Lausevic M,
Trbojevic-Stankovic J, Krstic S and Stojimirovic B: Predicting
multiple organ failure in patients with severe trauma. Can J Surg.
51:97–102. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Calandra T, Gerain J, Heumann D, et al:
High circulating levels of interleukin-6 in patients with septic
shock: Evolution during sepsis, prognostic value, and interplay
with other cytokines. The Swiss-Dutch J5 Immunoglobulin Study
Group. Am J Med. 91:23–29. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gårdlund B, Sjölin J, Nilsson A, et al:
Plasma levels of cytokines in primary septic shock in humans:
correlation with disease severity. J Infect Dis. 172:296–301.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Coyle P, Philcox JC and Rofe AM:
Metallothionein induction in cultured rat hepatocytes by arthritic
rat serum, activated macrophages, interleukin-6, interleukin-11 and
leukaemia inhibitory factor. Inflamm Res. 44:475–481. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tao JY, Zheng GH, Zhao L, et al:
Anti-inflammatory effects of ethyl acetate fraction from
Melilotus suaveolens Ledeb on LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7
cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 123:97–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
de Lima TH, Sass N, Mattar R, Moron AF,
Torloni MR, Franchim CS and Daher S: Cytokine gene polymorphisms in
preeclampsia and eclampsia. Hypertens Res. 32:565–569.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Su F, Wang Z, Cai Y, Remmelink M and
Vincent JL: Beneficial effects of ethyl pyruvate in septic shock
from peritonitis. Arch Surg. 142:166–171. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Berg RM, Møller K and Bailey DM:
Neuro-oxidative-nitrosative stress in sepsis. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 31:1532–1544. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Perše M, Injac R and Erman A: Oxidative
status and lipofuscin accumulation in urothelial cells of bladder
in aging mice. PLoS One. 8:e596382013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gong WH, Zheng WX, Wang J, Chen SH, Pang
B, Hu XM and Cao XL: Coexistence of hyperlipidemia and acute
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion induces severe liver damage in a rat
model. World J Gastroenterol. 18:4934–4943. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fakurazi S, Sharifudin SA and Arulselvan
P: Moringa oleifera hydroethanolic extracts effectively
alleviate acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in experimental rats
through their antioxidant nature. Molecules. 17:8334–8350. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sunil C, Duraipandiyan V, Ignacimuthu S
and Al-Dhabi NA: Antioxidant, free radical scavenging and liver
protective effects of friedelin isolated from Azima
tetracantha Lam. leaves. Food Chem. 139:860–865. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|