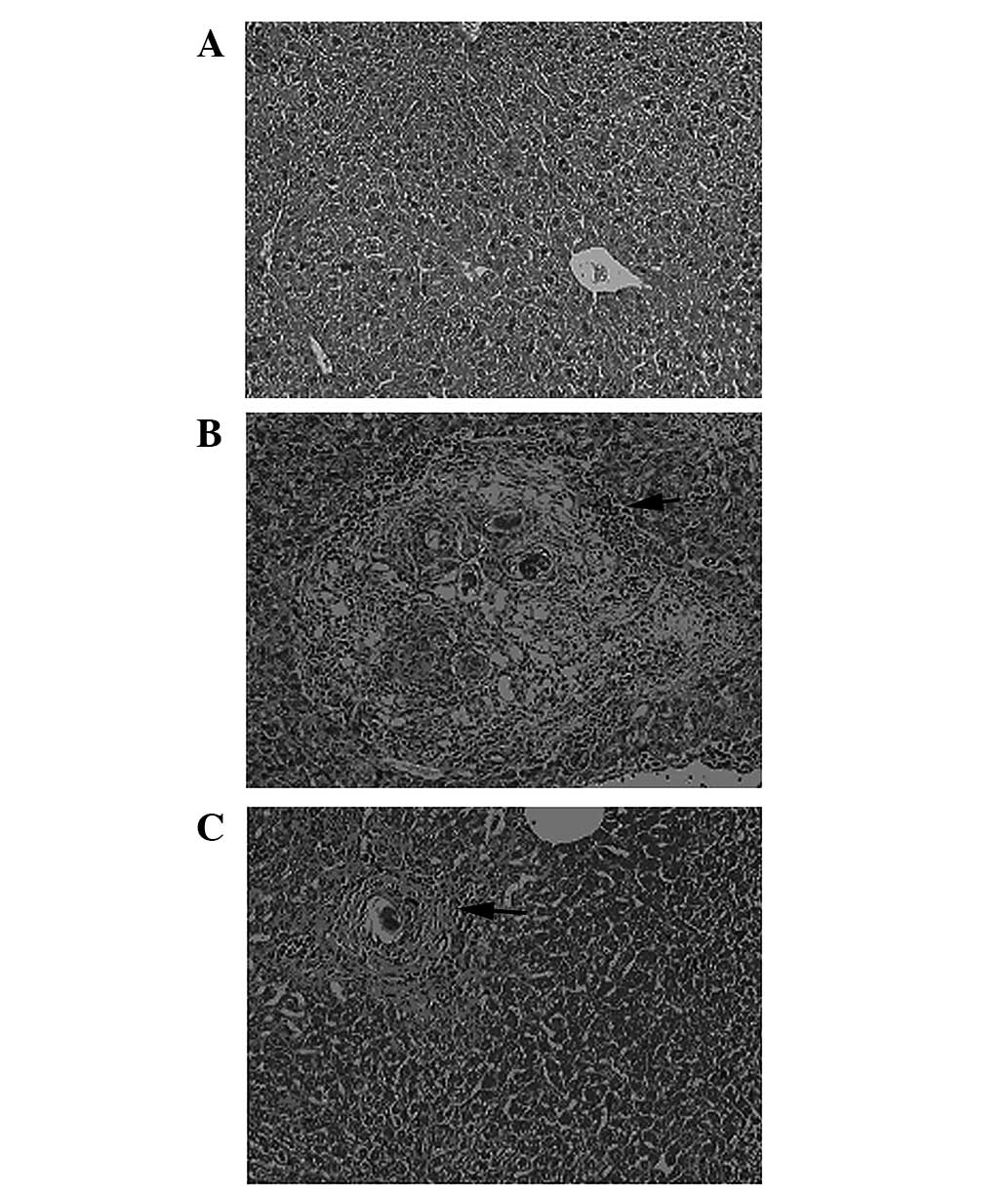
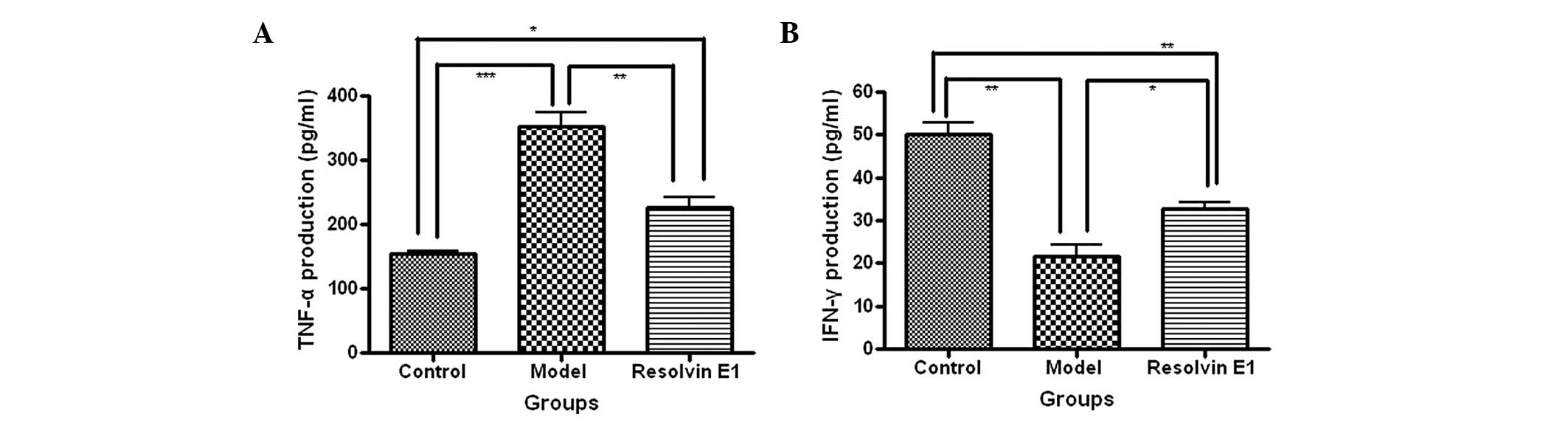
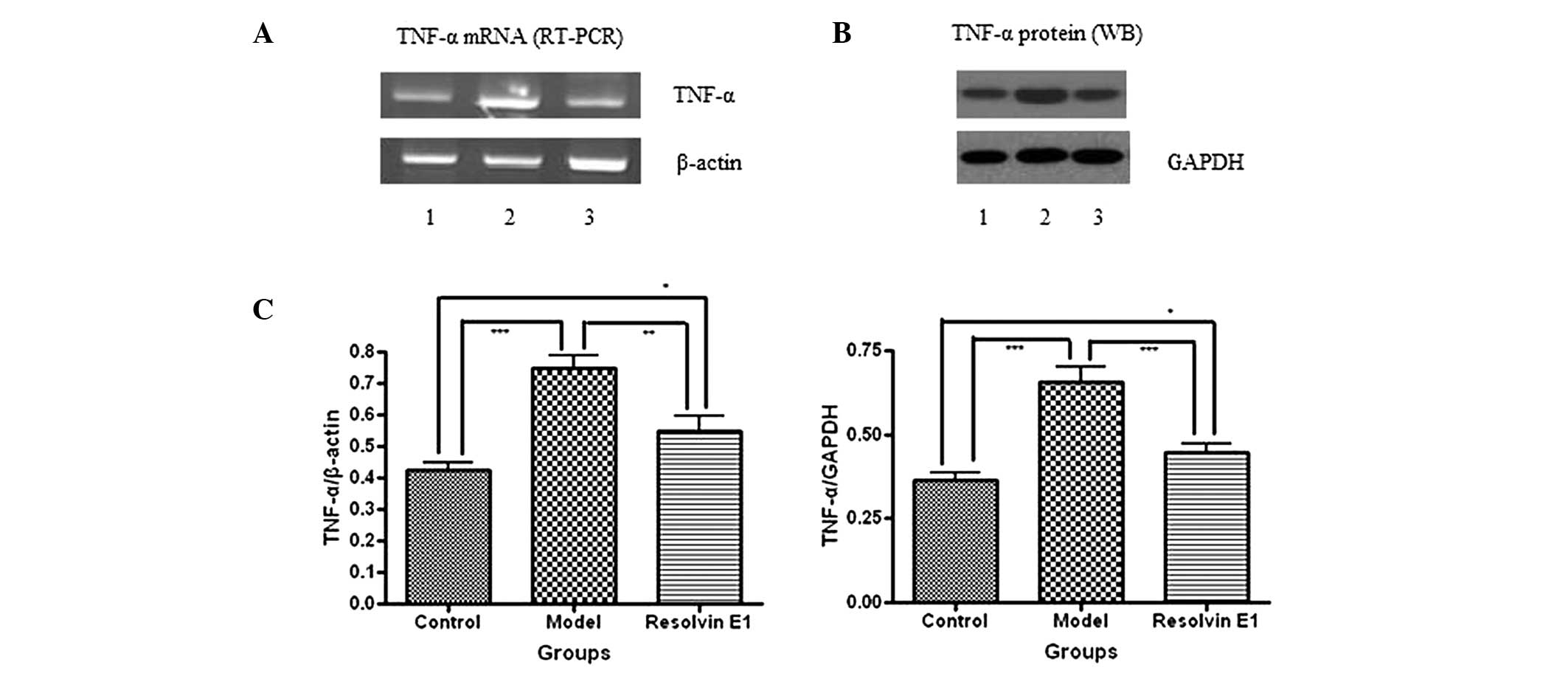
|
1
|
Wilson MS, Mentink-Kane MM, Pesce JT,
Ramalingam TR, Thompson R and Wynn TA: Immunopathology of
schistosomiasis. Immunol Cell Biol. 85:148–154. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chitsulo L, Engels D, Montresor A and
Savioli L: The global status of schistosomiasis and its control.
Acta Trop. 2000.77:41–51
|
|
3
|
Pearce EJ and MacDonald AS: The
immunobiology of schistosomiasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:499–511. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fabre V, Wu H, PondTor S, Coutinho H,
Acosta L, Jiz M, Olveda R, Cheng L, White ES, Jarilla B, McGarvey
ST, Friedman JF and Kurtis JD: Tissue inhibitor of
matrix-metalloprotease-1 predicts risk of hepatic fibrosis in human
Schistosoma japonicum infection. J Infect Dis. 203:707–714.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zou WL, Yang Z, Zang YJ, Li DJ, Liang ZP
and Shen ZY: Inhibitory effects of prostaglandin E1 on activation
of hepatic stellate cells in rabbits with schistosomiasis.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 6:176–181. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Iredale JP: Models of liver fibrosis:
exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid
organ. J Clin Invest. 117:539–548. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohira T, Arita M, Omori K, Recchiuti A,
Van Dyke TE and Serhan CN: Resolvin E1 receptor activation signals
phosphorylation and phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 285:3451–3461. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
WHO Expert Committee. Prevention and
control of schistosomiasis and soil-transmitted helminthiasis.
World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 912:2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Collins C, Xu J and Tang S:
Schistosomiasis control and the health system in P.R. China. Infect
Dis Poverty. 1:82012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gryseels B, Polman K, Clerinx J and
Kestens L: Human schistosomiasis. Lancet. 368:1106–1118. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coutinho HM, Acosta LP, Wu HW, McGarvey
ST, Su L, Langdon GC, Jiz MA, Jarilla B, Olveda RM, Friedman JF and
Kurtis JD: Th2 cytokines are associated with persistent hepatic
fibrosis in human Schistosoma japonicum infection. J Infect
Dis. 195:288–295. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
MacDonald TT: Decoy receptor springs to
life and eases fibrosis. Nat Med. 12:13–14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fichtner-Feigl S, Strober W, Kawakami K,
Puri PK and Kitani A: IL-13 signaling through the IL-13alpha2
receptor is involved in induction of TGF-beta1 production and
fibrosis. Nat Med. 12:99–106. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bonnard P, Remoué F, Schacht AM, Pialoux G
and Riveau G: Association between serum cytokine profiles and
schistosomiasisrelated hepatic fibrosis: infection by
Schistosoma japonicum versus S. mansoni. J Infect
Dis. 193:748–750. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Henri S, Chevillard C, Mergani A, Paris P,
Gaudart J, Camilla C, Dessein H, Montero F, Elwali NE, Saeed OK,
Magzoub M and Dessein AJ: Cytokine regulation of periportal
fibrosis in humans infected with Schistosoma mansoni:
IFN-gamma is associated with protection against fibrosis and
TNF-alpha with aggravation of disease. J Immunol. 169:929–936.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Booth M, Mwatha JK, Joseph S, Jones FM,
Kadzo H, Ireri E, Kazibwe F, Kemijumbi J, Kariuki C, Kimani G, Ouma
JH, Kabatereine NB, Vennervald BJ and Dunne DW: Periportal fibrosis
in human Schistosoma mansoni infection is associated with low
IL-10, low IFN-gamma, high TNF-alpha, or low RANTES, depending on
age and gender. J Immunol. 172:1295–1303. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Serhan CN, Clish CB, Brannon J, Colgan SP,
Chiang N and Gronert K: Novel functional sets of lipid-derived
mediators with antiinflammatory actions generated from omega-3
fatty acids via cyclooxygenase 2-nonsteroidal antiinflammatory
drugs and transcellular processing. J Exp Med. 192:1197–1204. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Serhan CN, Hong S, Gronert K, Colgan SP,
Devchand PR, Mirick G and Moussignac RL: Resolvins: a family of
bioactive products of omega-3 fatty acid transformation circuits
initiated by aspirin treatment that counter proinflammation
signals. J Exp Med. 196:1025–1037. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Serhan CN: Resolution phase of
inflammation: novel endogenous anti-inflammatory and proresolving
lipid mediators and pathways. Annu Rev Immunol. 25:101–137. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Connor KM, SanGiovanni JP, Lofqvist C,
Aderman CM, Chen J, Higuchi A, Hong S, Pravda EA, Majchrzak S,
Carper D, Hellstrom A, Kang JX, Chew EY, Salem N Jr, Serhan CN and
Smith LE: Increased dietary intake of omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty
acids reduces pathological retinal angiogenesis. Nat Med.
13:868–873. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schwab JM, Chiang N, Arita M and Serhan
CN: Nature. 447:869–874. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|