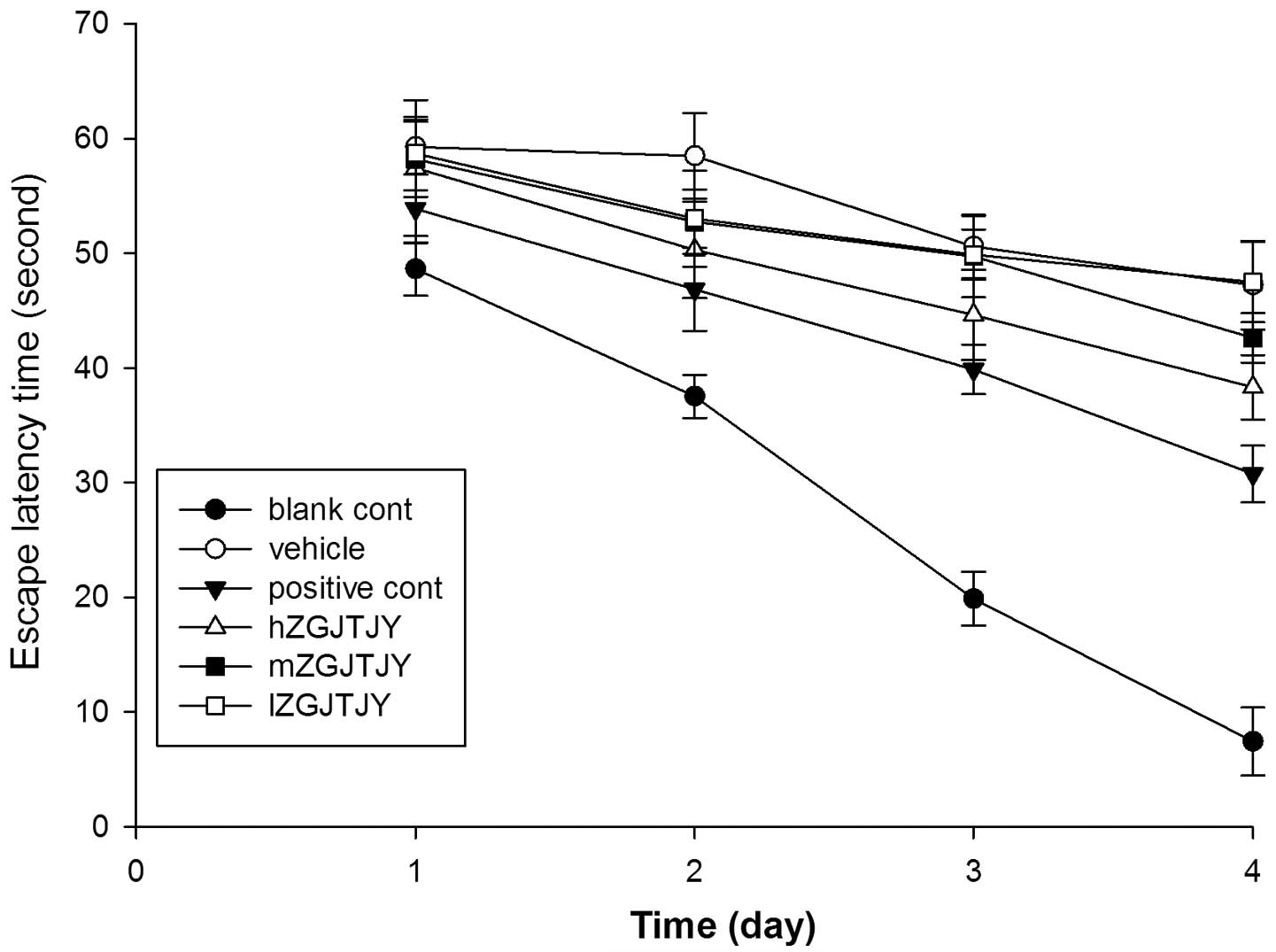
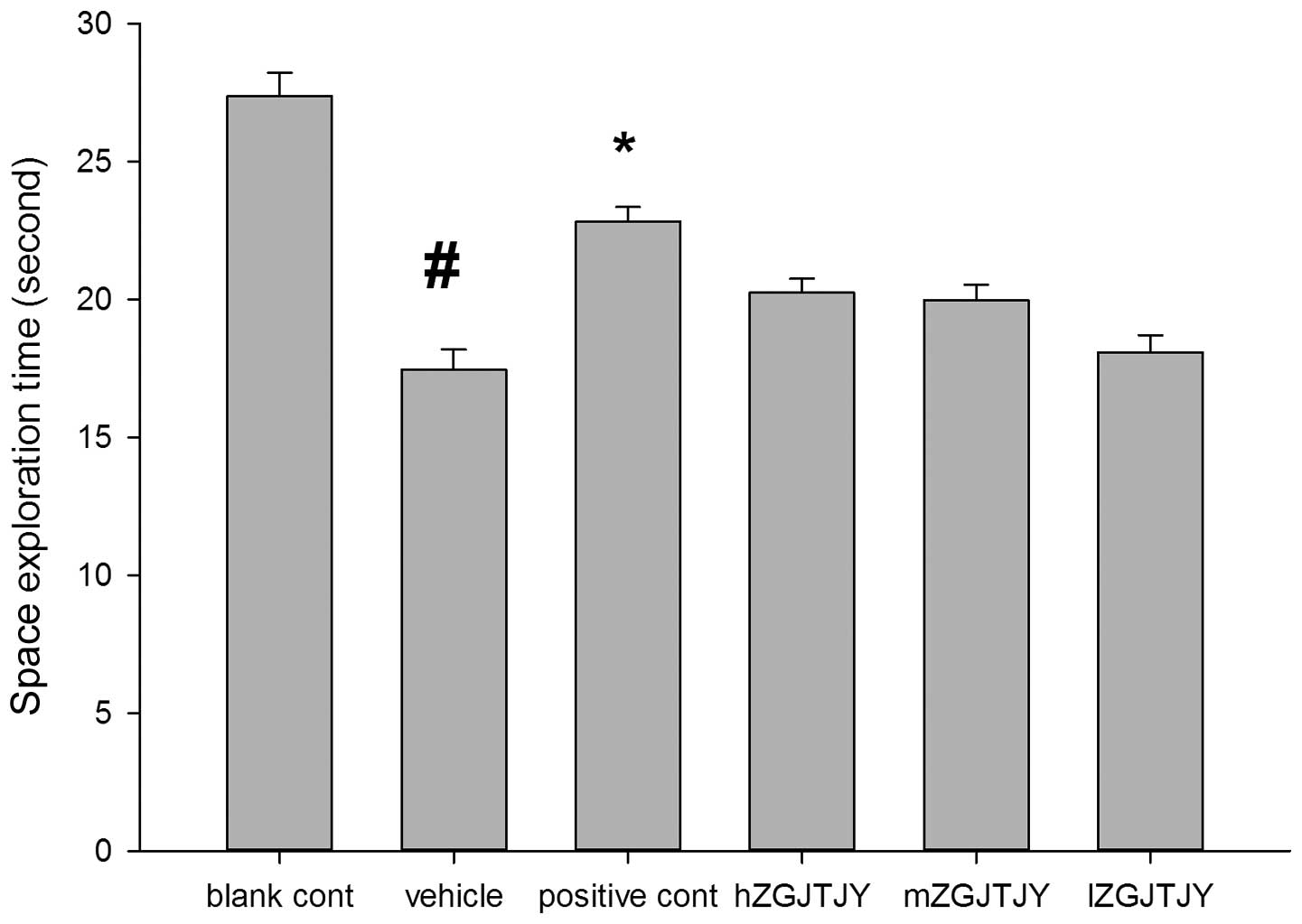
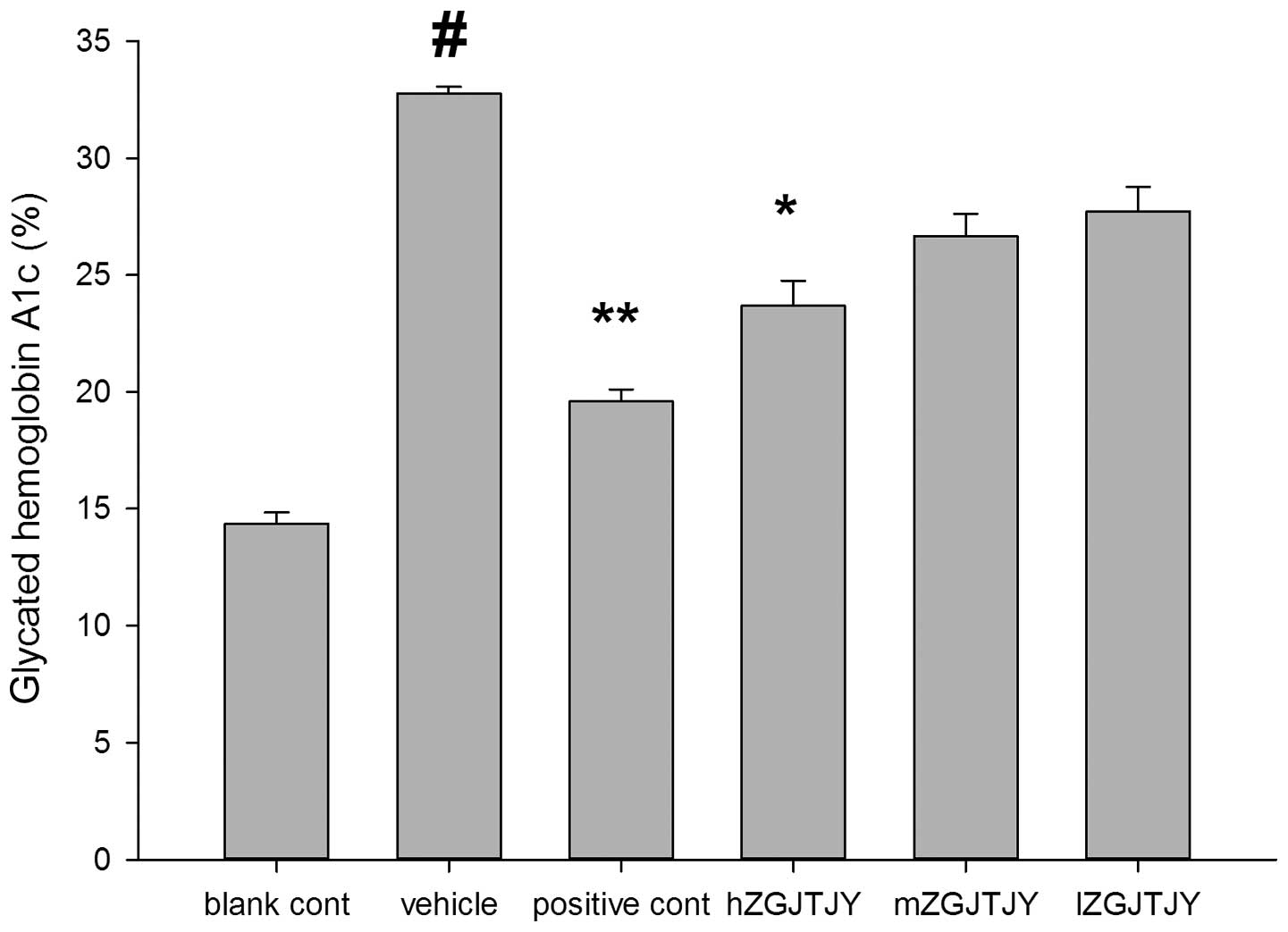
|
1
|
Lavergne F and Jay TM: A new strategy for
antidepressant prescription. Front Neurosci. 4:1922010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fujitsuka N, Asakawa A, Hayashi M, et al:
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors modify physiological
gastrointestinal motor activities via 5-HT2c receptor and acyl
ghrelin. Biol Psychiatry. 65:748–759. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT
and Murray CJ: Global and regional burden of disease and risk
factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data.
Lancet. 367:1747–1757. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ning G and Bloomgarden Z: Diabetes in
China: prevalence, diagnosis, and control. J Diabetes. 5:3722013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shaw JE, Sicree RA and Zimmet PZ: Global
estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 87:4–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin CH, Lee YY, Liu CC, Chen HF, Ko MC and
Li CY: Urbanization and prevalence of depression in diabetes.
Public Health. 126:104–111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ali S, Stone MA, Peters JL, Davies MJ and
Khunti K: The prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with
Type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabet Med.
23:1165–1173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barnard KD, Skinner TC and Peveler R: The
prevalence of co-morbid depression in adults with Type 1 diabetes:
systematic literature review. Diabet Med. 23:445–448. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Katon W, Russo J, Lin EH, et al: Diabetes
and poor disease control: is comorbid depression associated with
poor medication adherence or lack of treatment intensification?
Psychosom Med. 71:965–972. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Egede LE and Ellis C: Diabetes and
depression: global perspectives. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
87:302–312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schram MT, Baan CA and Pouwer F:
Depression and quality of life in patients with diabetes: a
systematic review from the European depression in diabetes (EDID)
research consortium. Curr Diabetes Rev. 5:112–119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Erenmemisoglu A, Ozdogan UK, Saraymen R
and Tutus A: Effect of some antidepressants on glycaemia and
insulin levels of normoglycaemic and alloxan-induced hyperglycaemic
mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 51:741–743. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goodnick PJ: Use of antidepressants in
treatment of comorbid diabetes mellitus and depression as well as
in diabetic neuropathy. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 13:31–41. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee HJ, Lee SY, Kim JH, et al: Depressive
mood and quality of life in functional gastrointestinal disorders:
differences between functional dyspepsia, irritable bowel syndrome
and overlap syndrome. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 32:499–502. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kim HS, Rhee PL, Park J, et al:
Gender-related differences in visceral perception in health and
irritable bowel syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:468–473.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tang HS: Study on relative problems of
acupuncture and moxibustion for treatment of simple obesity.
Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 28:522–524. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Salpeter SR, Buckley NS, Kahn JA and
Salpeter EE: Meta-analysis: Metformin treatment in persons at risk
for diabetes mellitus. Am J Med. 121:149–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Selvin E, Bolen S, Yeh HC, et al:
Cardiovascular outcomes in trials of oral diabetes medications: a
systematic review. Arch Intern Med. 168:2070–2080. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Srinivasan K, Viswanad B, Asrat L, Kaul CL
and Ramarao P: Combination of high-fat diet-fed and low-dose
streptozotocin-treated rat: a model for type 2 diabetes and
pharmacological screening. Pharmacol Res. 52:313–320. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Willner P: Validity, reliability and
utility of the chronic mild stress model of depression: a 10-year
review and evaluation. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 134:319–329.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wong TP, Howland JG, Robillard JM, et al:
Hippocampal long-term depression mediates acute stress-induced
spatial memory retrieval impairment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:11471–11476. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cassano P and Fava M: Depression and
public health: an overview. J Psychosom Res. 53:849–857. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cassileth BR, Lusk EJ, Strouse TB, et al:
Psychosocial status in chronic illness. A comparative analysis of
six diagnostic groups. N Engl J Med. 311:506–511. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Noël PH, Williams JW Jr, Unützer J, et al:
Depression and comorbid illness in elderly primary care patients:
impact on multiple domains of health status and well-being. Ann Fam
Med. 2:555–562. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu Y, Barish PA, Pan J, Ogle WO and
O’Donnell JM: Animal models of depression and neuroplasticity:
assessing drug action in relation to behavior and neurogenesis.
Methods Mol Biol. 829:103–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yan HC, Cao X, Das M, Zhu XH and Gao TM:
Behavioral animal models of depression. Neurosci Bull. 26:327–337.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|