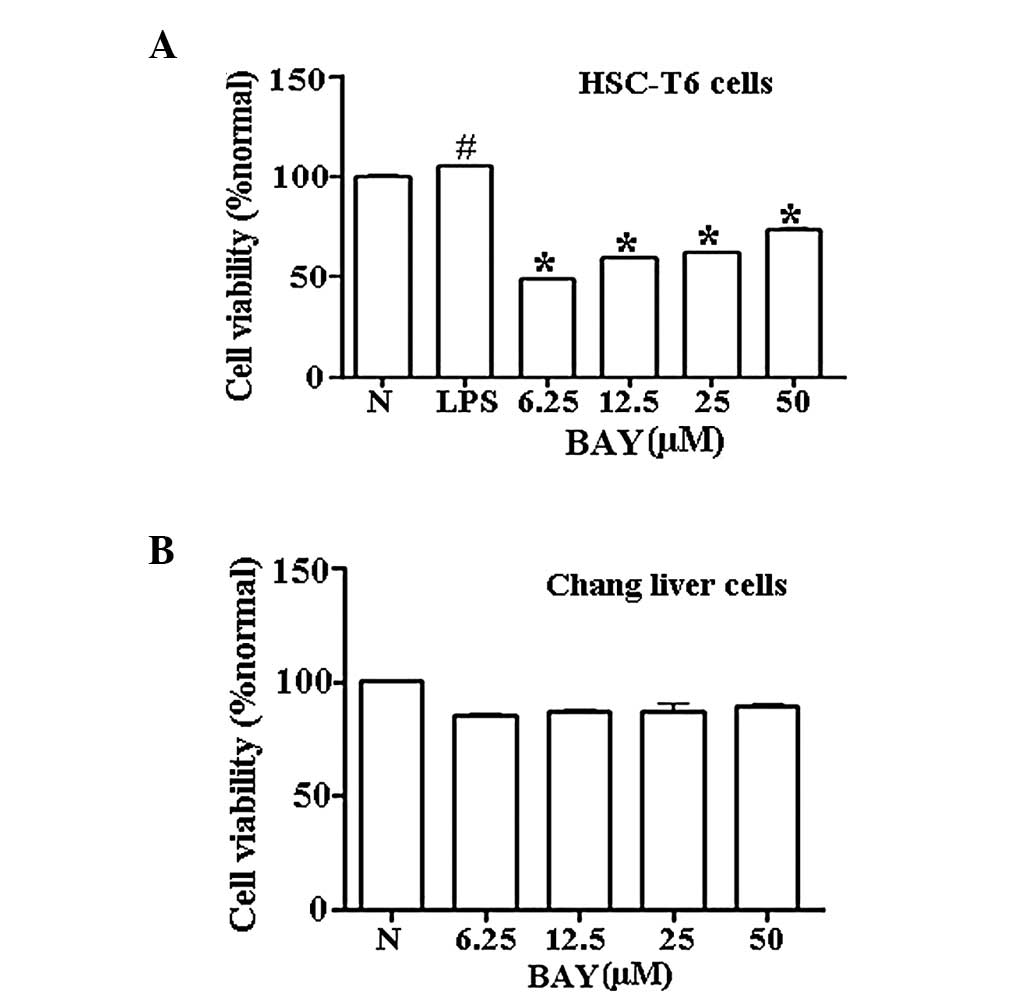
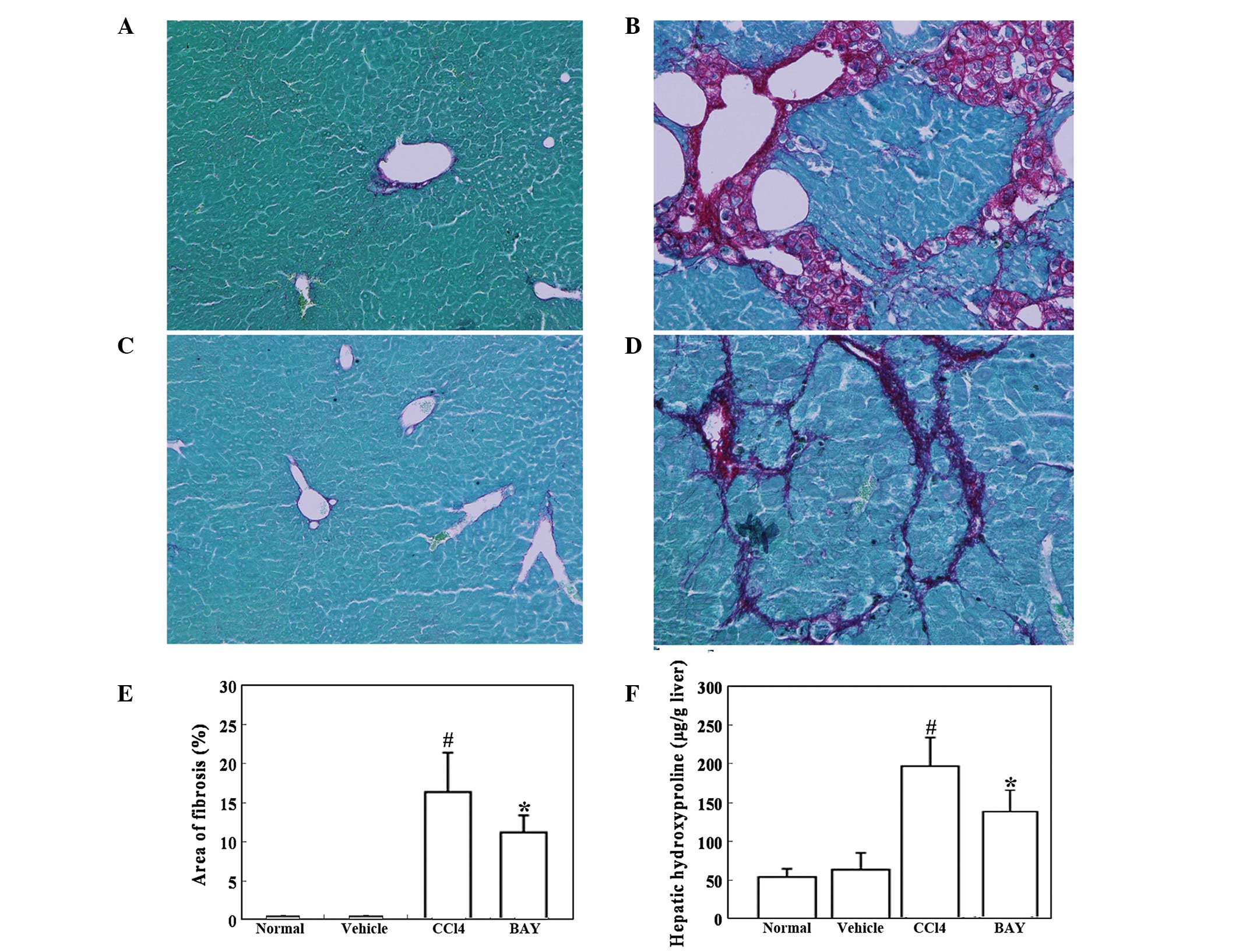
|
1
|
Friedman SL: Mechanisms of hepatic
fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 134:1655–1669. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiao J, Friedman SL and Aloman C: Hepatic
fibrosis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 25:223–229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bataller R and Brenner DA: Liver fibrosis.
J Clin Invest. 115:209–218. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Friedman SL: Reversibility of hepatic
fibrosis and cirrhosis - is it all hype? Nat Clin Pract
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:236–237. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tangkijvanich P and Yee HF Jr: Cirrhosis -
can we reverse hepatic fibrosis? Eur J Surg Suppl. 587:100–112.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Povero D, Busletta C, Novo E, et al: Liver
fibrosis: a dynamic and potentially reversible process. Histol
Histopathol. 25:1075–1091. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schuppan D and Kim YO: Evolving therapies
for liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 123:1887–1901. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gressner AM and Weiskirchen R: Modern
pathogenetic concepts of liver fibrosis suggest stellate cells and
TGF-beta as major players and therapeutic targets. J Cell Mol Med.
10:76–99. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R, Breitkopf K
and Dooley S: Roles of TGF-beta in hepatic fibrosis. Front Biosci.
7:d793–d807. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gressner OA and Gressner AM: Connective
tissue growth factor: a fibrogenic master switch in fibrotic liver
diseases. Liver Int. 28:1065–1079. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Robinson SM and Mann DA: Role of nuclear
factor kappaB in liver health and disease. Clin Sci (Lond).
118:691–705. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao Q, Wang XY, Zhou J and Fan J: Cell
line misidentification: the case of the Chang liver cell line.
Hepatology. 54:1894–1895. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hao ZM, Cai M, Lv YF, Huang YH and Li HH:
Oral administration of recombinant adeno-associated virus-mediated
bone morphogenetic protein-7 suppresses CCl(4)-induced hepatic
fibrosis in mice. Mol Ther. 20:2043–2051. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kar S, Ukil A and Das PK: Cystatin cures
visceral leishmaniasis by NF-κB-mediated proinflammatory response
through co-ordination of TLR/MyD88 signaling with p105-TpI2-ERK
pathway. Eur J Immunol. 41:116–127. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhao J, Zhang H, Huang Y, et al:
Bay11–7082 attenuates murine lupus nephritis via inhibiting NLRP3
inflammasome and NF-κB activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 17:116–122.
2013.
|
|
16
|
Luedde T and Schwabe RF: NF-κB in the
liver - linking injury, fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:108–118. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Bonacchi A, Petrai I, Defranco RM, et al:
The chemokine CCL21 modulates lymphocyte recruitment and fibrosis
in chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology. 125:1060–1076.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, et
al: TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat Med.
13:1324–1332. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Seki E, De Minicis S, Gwak GY, et al: CCR1
and CCR5 promote hepatic fibrosis in mice. J Clin Invest.
119:1858–1870. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miura K, Kodama Y, Inokuchi S, et al:
Toll-like receptor 9 promotes steatohepatitis by induction of
interleukin-1beta in mice. Gastroenterology. 139:323–334. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duffield JS, Forbes SJ, Constandinou CM,
et al: Selective depletion of macrophages reveals distinct,
opposing roles during liver injury and repair. J Clin Invest.
115:56–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Son G, Iimuro Y, Seki E, Hirano T, Kaneda
Y and Fujimoto J: Selective inactivation of NF-kappaB in the liver
using NF-kappaB decoy suppresses CCl4-induced liver
injury and fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
293:G631–G639. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Paik YH, Schwabe RF, Bataller R, Russo MP,
Jobin C and Brenner DA: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates inflammatory
signaling by bacterial lipopolysaccharide in human hepatic stellate
cells. Hepatology. 37:1043–1055. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hellerbrand C, Jobin C, Iimuro Y, Licato
L, Sartor RB and Brenner DA: Inhibition of NFkappaB in activated
rat hepatic stellate cells by proteasome inhibitors and an IkappaB
super-repressor. Hepatology. 27:1285–1295. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oakley F, Teoh V, Ching-A-Sue G, et al:
Angiotensin II activates I kappaB kinase phosphorylation of RelA at
Ser 536 to promote myofibroblast survival and liver fibrosis.
Gastroenterology. 136:2334–2344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schwabe RF, Schnabl B, Kweon YO and
Brenner DA: CD40 activates NF-kappa B and c-Jun N-terminal kinase
and enhances chemokine secretion on activated human hepatic
stellate cells. J Immunol. 166:6812–6819. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Elsharkawy AM, Wright MC, Hay RT, et al:
Persistent activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in cultured rat
hepatic stellate cells involves the induction of potentially novel
Rel-like factors and prolonged changes in the expression of IkappaB
family proteins. Hepatology. 30:761–769. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kluwe J, Pradere JP, Gwak GY, et al:
Modulation of hepatic fibrosis by c-Jun-N-terminal kinase
inhibition. Gastroenterology. 138:347–359. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cushing TD, Metz DP, Whittington DA and
McGee LR: PI3Kδ and PI3Kγ as targets for autoimmune and
inflammatory diseases. J Med Chem. 55:8559–8581. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Jackson LN, Larson SD, Silva SR, et al:
PI3K/Akt activation is critical for early hepatic regeneration
after partial hepatectomy. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
294:G1401–G1410. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|