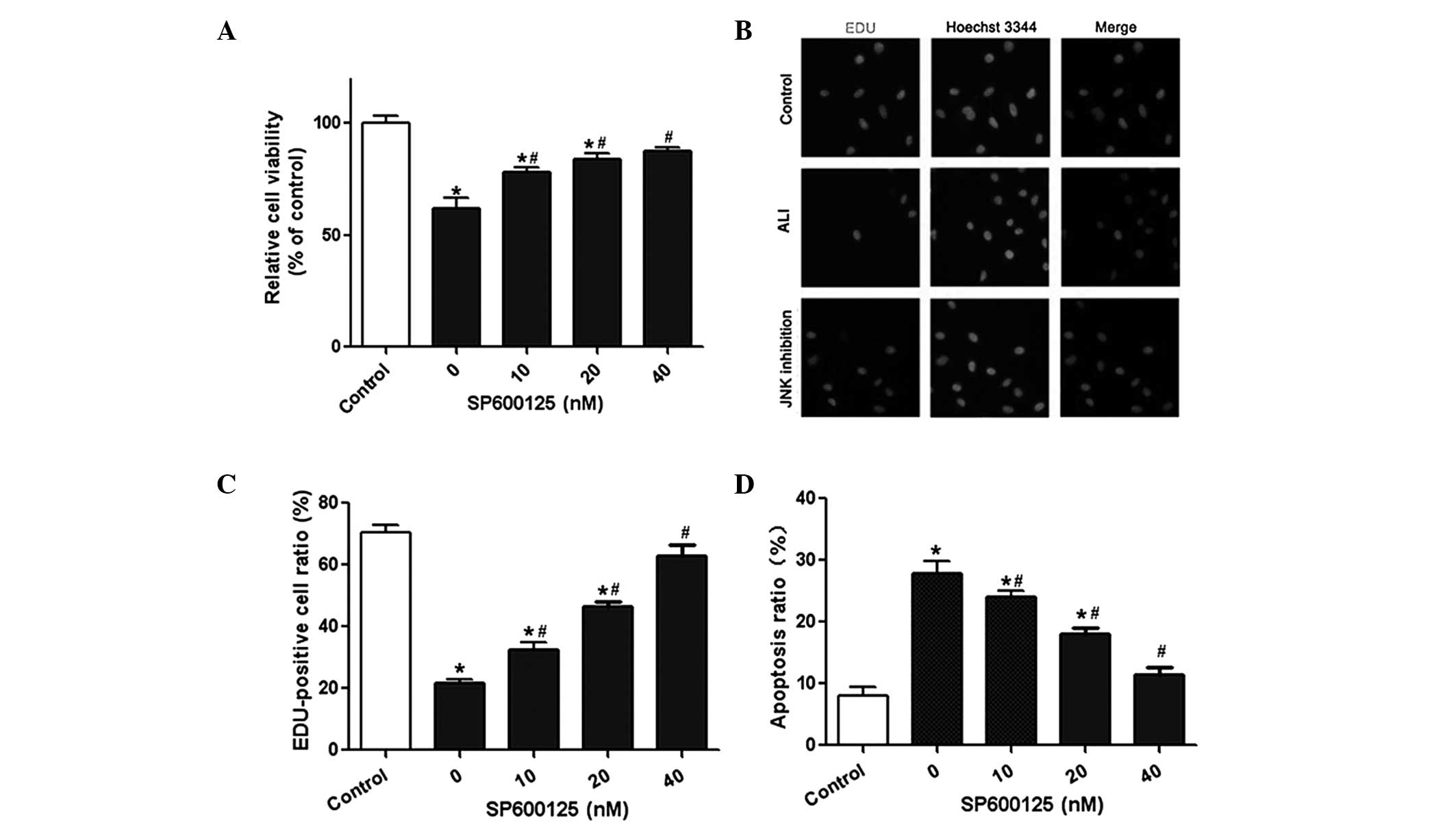
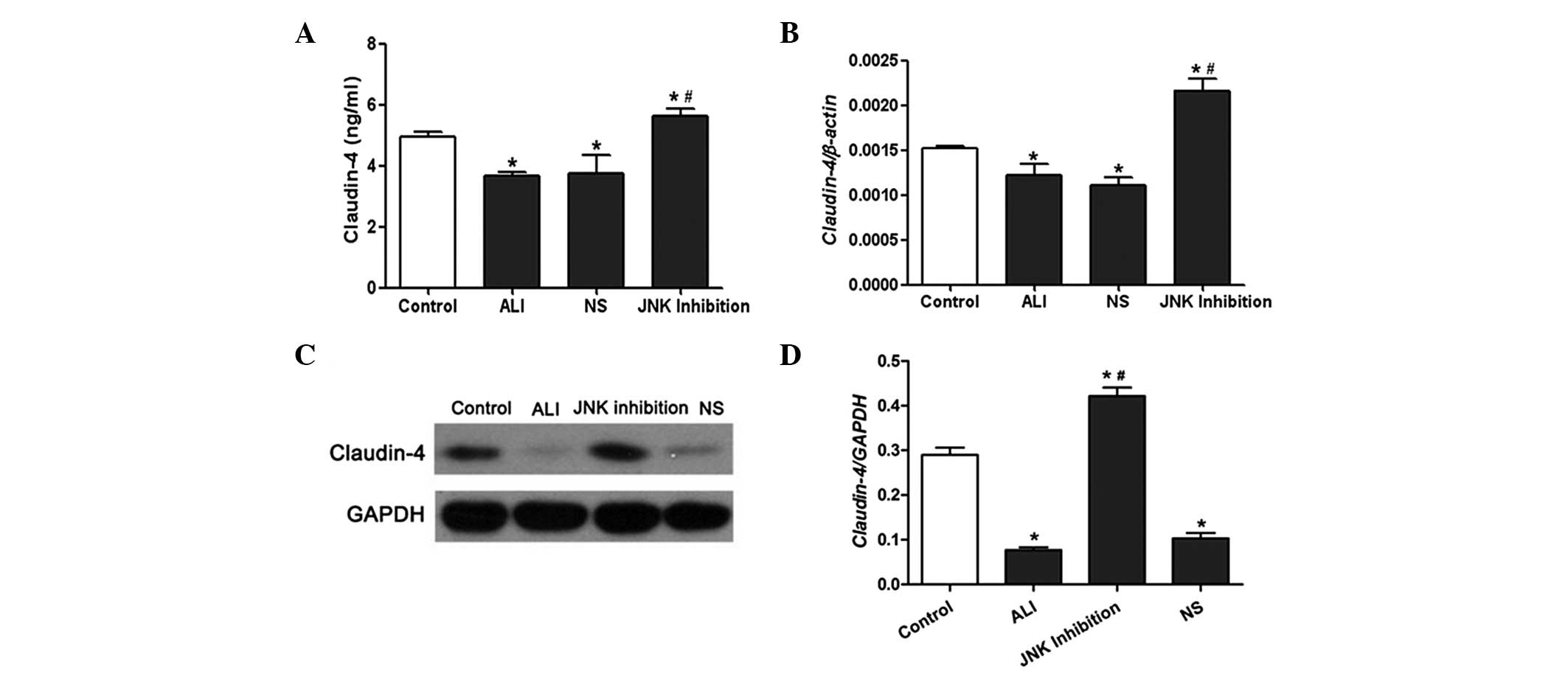
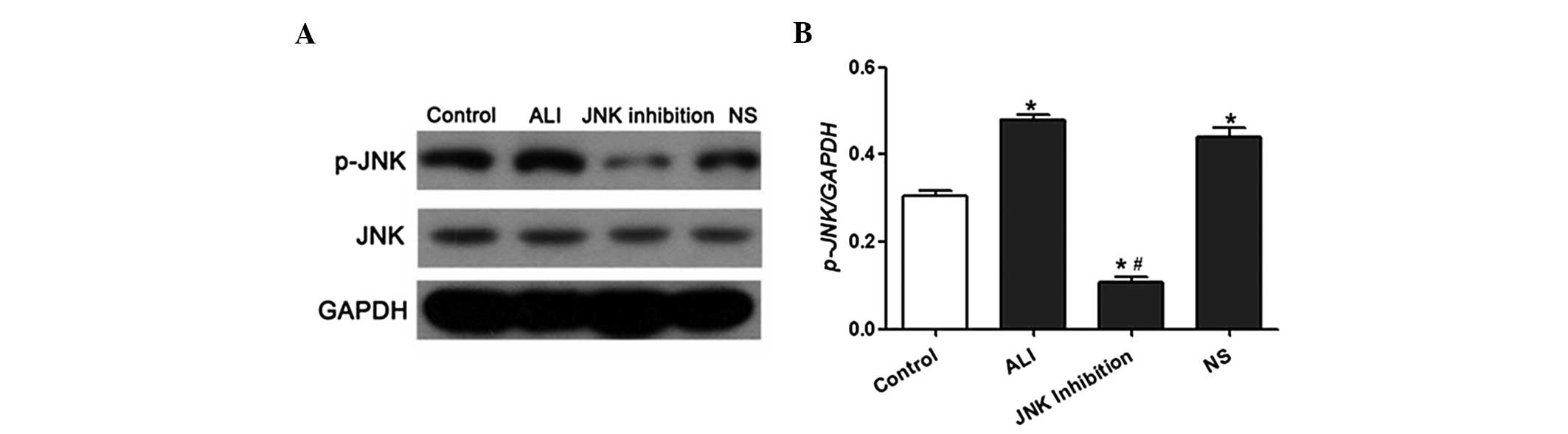
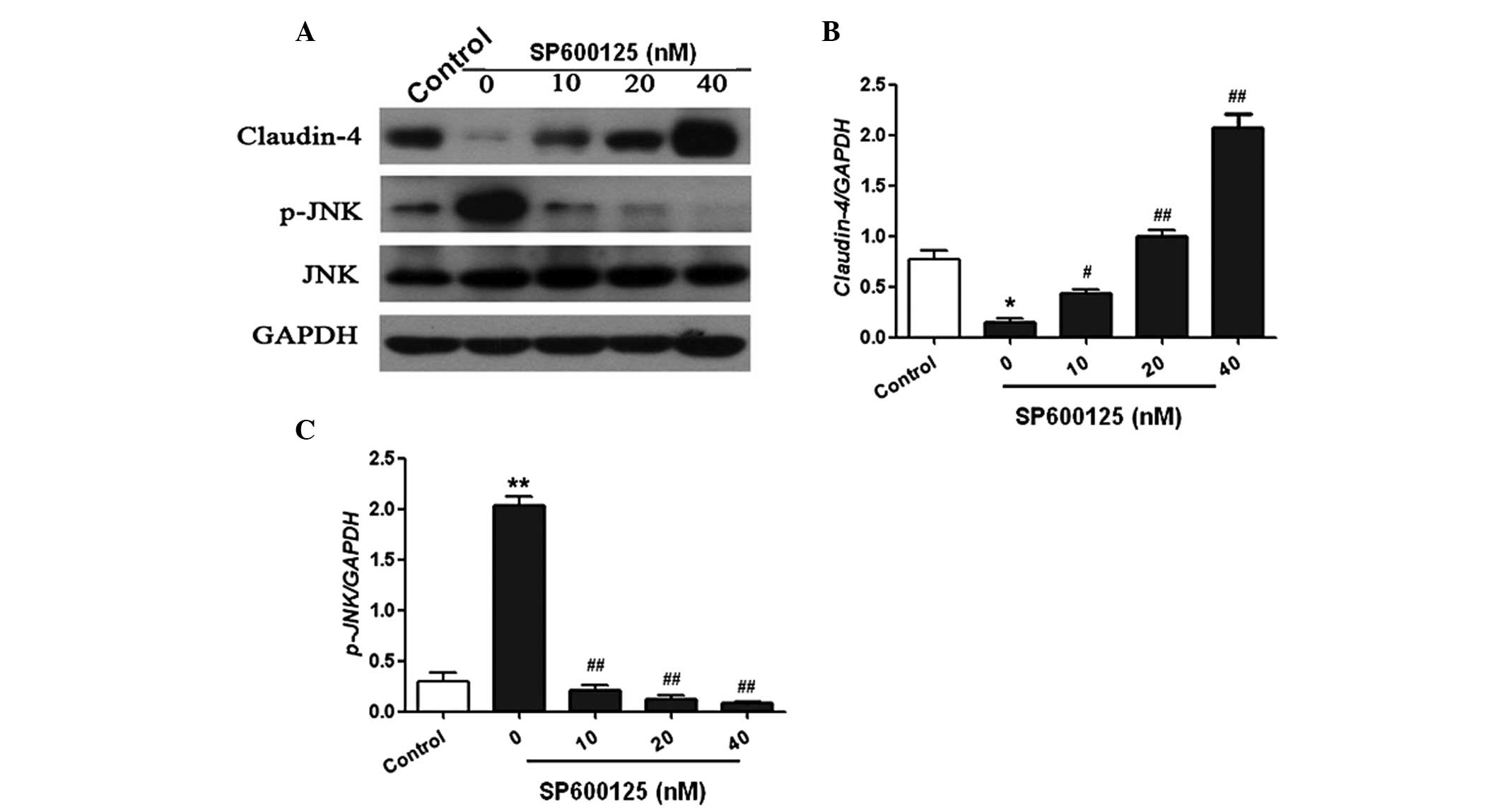
|
1
|
Yang B, Huang W, Han J and Liang Z: Study
of the role of epidermal growth factor on lung fluid transport in
rabbits with acute lung injury caused by endotoxin. Exp Ther Med.
4:611–614. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vincent JL, Sakr Y and Ranieri VM:
Epidemiology and outcome of acute respiratory failure in intensive
care unit patients. Crit Care Med. 31:S296–S299. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhou GJ, Jiang SY, Zhang M, et al:
Evaluation of the inflammatory response in a two-hit acute lung
injury model using [18F]FDG microPET. Exp Ther Med. 6:894–898.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kolliputi N and Waxman AB: IL-6
cytoprotection in hyperoxic acute lung injury occurs via suppressor
of cytokine signaling-1-induced apoptosis signal-regulating
kinase-1 degradation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 40:314–324. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mutlu GM and Budinger GR: Incidence and
outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 354:416–417. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meade MO, Cook DJ, Guyatt GH, et al:
Ventiliation Study Investigators: Ventilation strategy using low
tidal volumes, recruitment maneuvers, and high positive
end-expiratory pressure for acute lung injury and acute respiratory
distress syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA.
299:637–645. 2008.
|
|
7
|
Sio SW, Ang SF, Lu J, et al: Substance P
upregulates cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E metabolite by
activating ERK1/2 and NF-kappaB in a mouse model of burn-induced
remote acute lung injury. J Immunol. 185:6265–6276. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Liu F, Liu H, et al: Urinary
trypsin inhibitor attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by blocking the activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase. Inflamm Res. 60:569–575. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ong E, Gao XP, Predescu D, et al: Role of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-gamma in mediating lung neutrophil
sequestration and vascular injury induced by E. coli sepsis.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 289:L1094–L1103. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee N, Maurange C, Ringrose L and Paro R:
Suppression of Polycomb group proteins by JNK signalling induces
transdetermination in Drosophila imaginal discs. Nature.
438:234–237. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gavrilescu LC, Molnár Á, Murray L, et al:
Retraction for Zhong et al. GCK is essential to systemic
inflammation and pattern recognition receptor signaling to JNK and
p38. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:51342012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han YH, Kim SZ, Kim SH and Park WH:
Enhancement of propyl gallate-induced calf pulmonary arterial
endothelial cell death by MEK and JNK inhibitors. Mol Med Rep.
2:825–830. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nacken W, Ehrhardt C and Ludwig S: Small
molecule inhibitors of the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) possess
antiviral activity against highly pathogenic avian and human
pandemic influenza A viruses. Biol Chem. 393:525–534. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yeste-Velasco M, Folch J, Casadesús G, et
al: Neuroprotection by c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase inhibitor SP600125
against potassium deprivation-induced apoptosis involves the Akt
pathway and inhibition of cell cycle reentry. Neuroscience.
159:1135–1147. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, et al:
SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:13681–13686. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu T, Wang DX, Zhang W, et al:
Andrographolide protects against LPS-induced acute lung injury by
inactivation of NF-κB. PLoS One. 8:e564072013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suresh R, Kupfer Y and Tessler S: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 343:660–661. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shaham S: Apoptosis: a process with a
(beta)NAC for complexity. Cell. 114:659–661. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inoue S, MacFarlane M, Harper N, et al:
Histone deacetylase inhibitors potentiate TNF-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in lymphoid
malignancies. Cell Death Differ. 11(Suppl 2): S193–S206. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lee SJ and Lim KT: Inhibitory effect of
ZPDC glycoprotein on the expression of inflammation-related
cytokines through p38 MAP kinase and JNK in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflamm Res.
58:184–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar A, Byun HS, Bittman R and Saba JD:
The sphingolipid degradation product trans-2-hexadecenal induces
cytoskeletal reorganization and apoptosis in a JNK-dependent
manner. Cell Signal. 23:1144–1152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim BW, Koppula S, Kim IS, et al:
Anti-neuroinflammatory activity of Kamebakaurin from Isodon
japonicus via inhibition of c-Jun NH2-terminal
kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in
activated microglial cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 116:296–308.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han Z, Boyle DL, Chang L, et al: c-Jun
N-terminal kinase is required for metalloproteinase expression and
joint destruction in inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Invest.
108:73–81. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee HS, Kim HJ, Moon CS, et al: Inhibition
of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase or extracellular
signal-regulated kinase improves lung injury. Respir Res. 5:232004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cording J, Berg J, Käding N, et al: In
tight junctions, claudins regulate the interactions between
occludin, tricellulin and marvelD3, which, inversely, modulate
claudin oligomerization. J Cell Sci. 126:554–564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wray C, Mao Y, Pan J, et al: Claudin-4
augments alveolar epithelial barrier function and is induced in
acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
297:L219–L227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lipschutz JH, Li S, Arisco A and Balkovetz
DF: Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 control claudin-2
expression in Madin-Darby canine kidney strain I and II cells. J
Biol Chem. 280:3780–3788. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Van Itallie C, Rahner C and Anderson JM:
Regulated expression of claudin-4 decreases paracellular
conductance through a selective decrease in sodium permeability. J
Clin Invest. 107:1319–1327. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rokkam D, Lafemina MJ, Lee JW, et al:
Claudin-4 levels are associated with intact alveolar fluid
clearance in human lungs. Am J Pathol. 179:1081–1087. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|