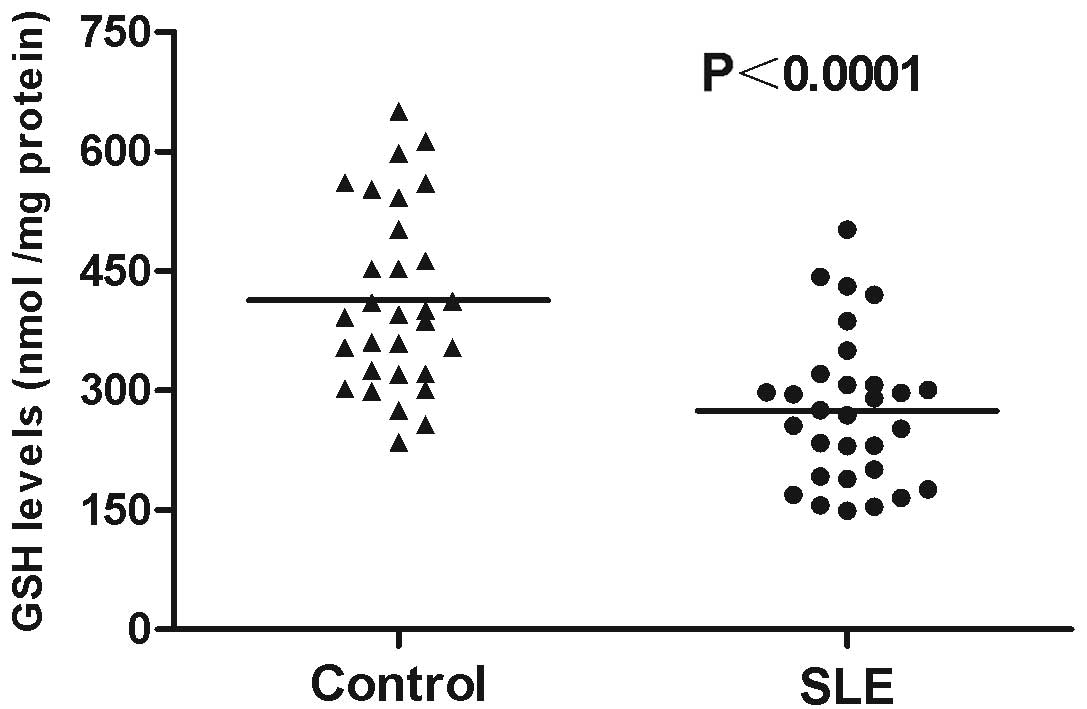
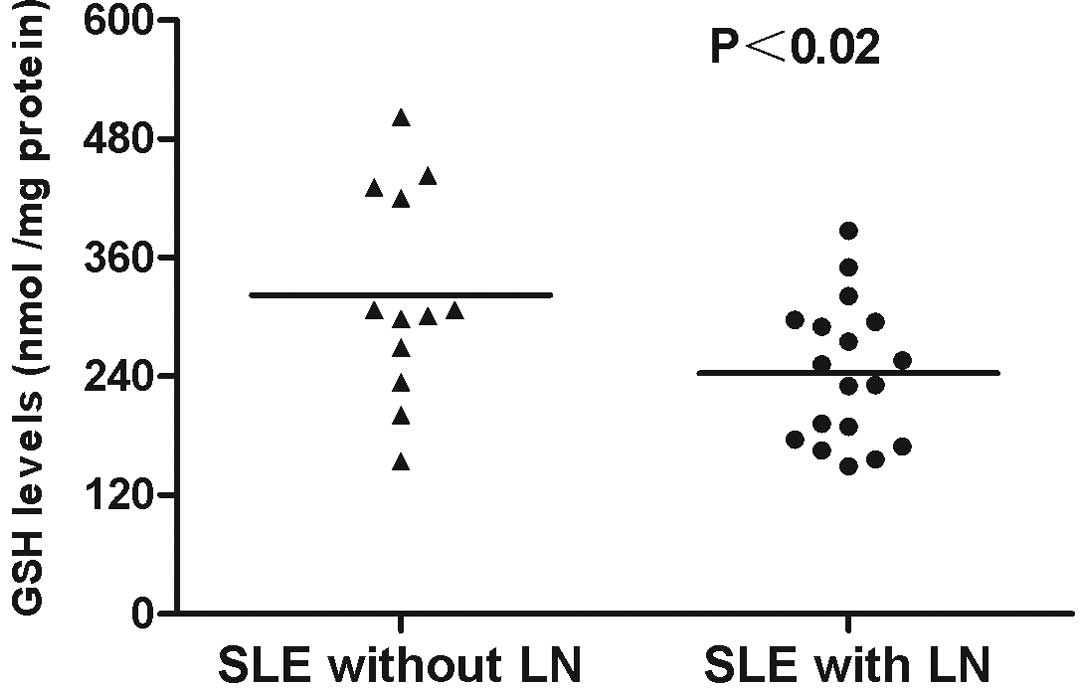
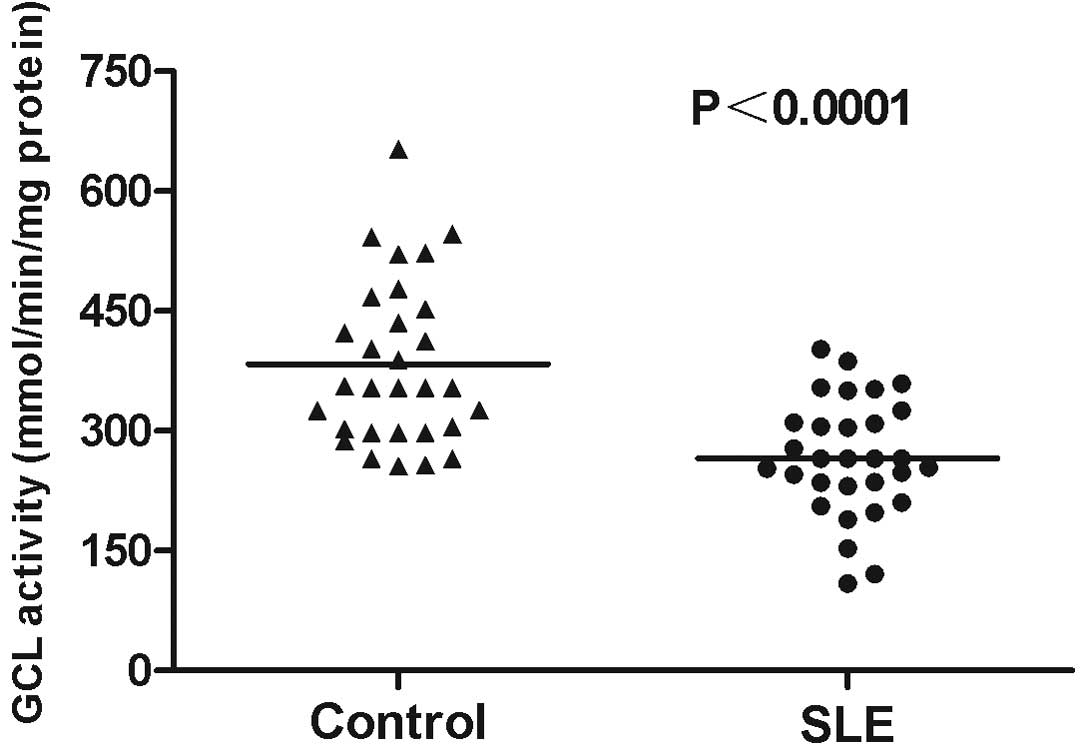
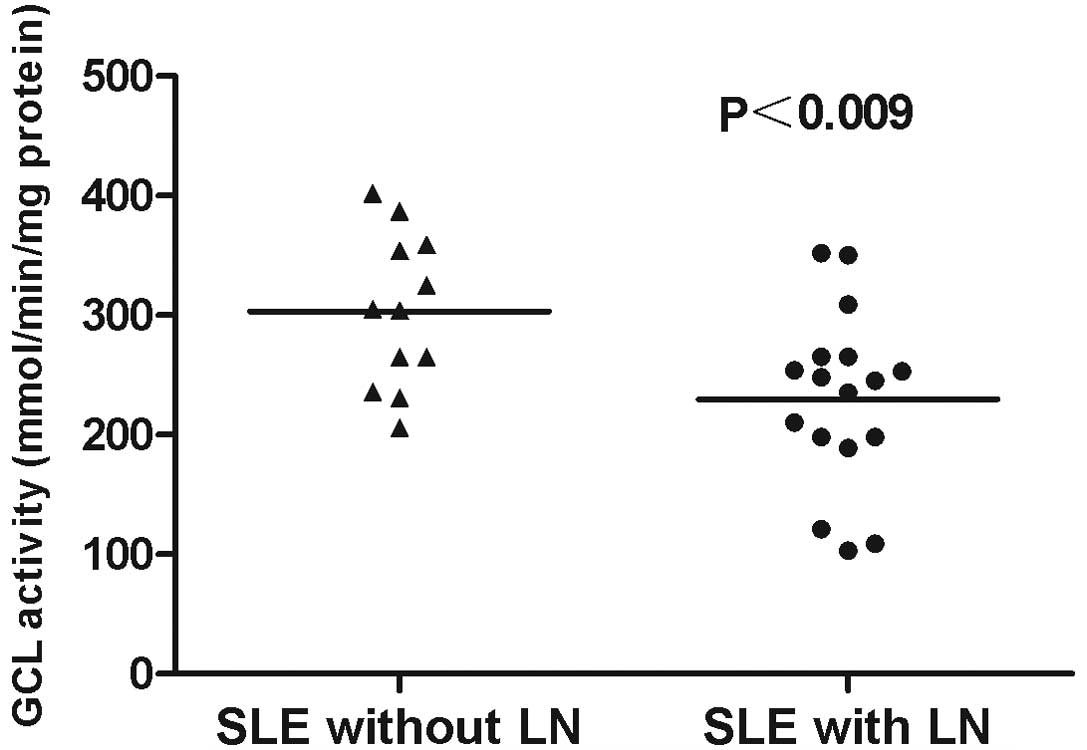
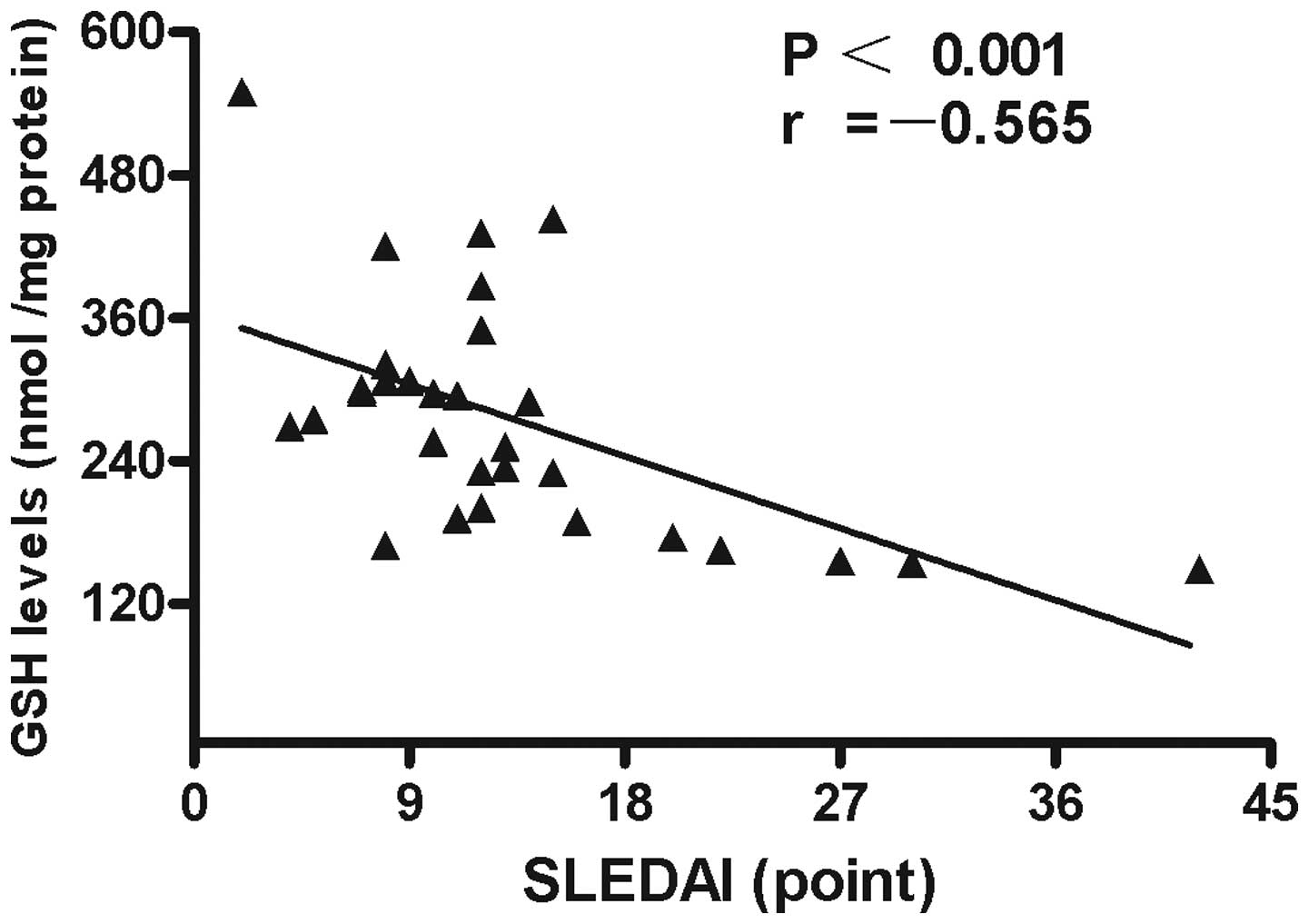
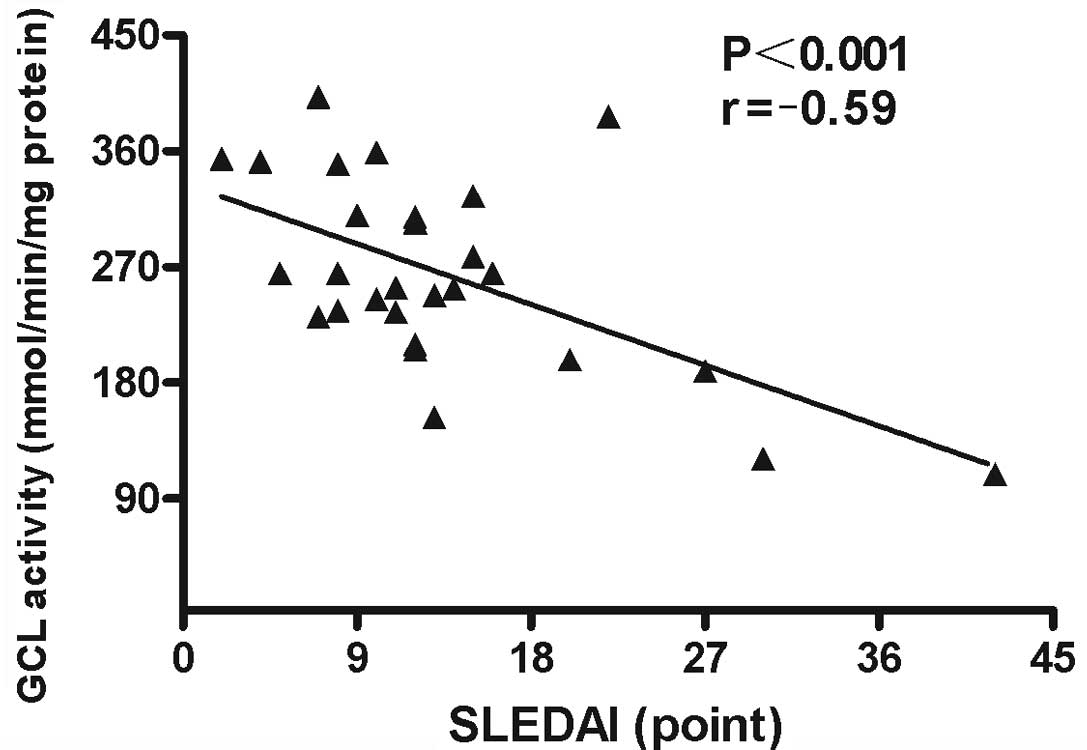
|
1
|
Shah D, Aggarwal A, Bhatnagar A, et al:
Association between T lymphocyte sub-sets apoptosis and peripheral
blood mononuclear cells oxidative stress in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Free Radic Res. 45:559–567. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gordon C: Long-term complications of
systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 41:1095–1100.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mansour RB, Lassoued S, Gargouri B, et al:
Increased levels of autoantibodies against catalase and superoxide
dismutase associated with oxidative stress in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J
Rheumatol. 37:103–108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kurien BT and Scofield RH: Free radical
mediated peroxidative damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Life
Sci. 73:1655–1666. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Munoz LE, Gaipl US and Herrmann M:
Predictive value of anti-dsDNA autoantibodies: importance of the
assay. Autoimmun Rev. 7:594–597. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li J, Ayene R, Ward KM, et al: Glucose
deprivation increases nuclear DNA repair protein Ku and resistance
to radiation induced oxidative stress in human cancer cells. Cell
Biochem Funct. 27:93–101. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Townsend DM, Tew KD and Tapiero H: The
importance of glutathione in human disease. Biomed Pharmacother.
57:145–155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gambhir JK, Lali P and Jain AK:
Correlation between blood antioxidant levels and lipid peroxidation
in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem. 30:351–355. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pastore A, Federici G, Bertini E and
Piemonte F: Analysis of glutathione: implication in redox and
detoxification. Clin Chim Acta. 333:19–39. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Burek CL and Rose NR: Autoimmune
thyroiditis and ROS. Autoimmun Rev. 7:530–537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Griffiths HR: Is the generation of
neo-antigenic determinants by free radicals central to the
development of autoimmune rheumatoid disease? Autoimmun Rev.
7:544–549. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Perricone C, De Carolis C and Perricone R:
Glutathione: a key player in autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev.
8:697–701. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fernandez D and Perl A: Metabolic control
of T cell activation and death in SLE. Autoimmun Rev. 8:184–189.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dimitrov JD, Vassilev TL, Andre S, et al:
Functional variability of antibodies upon oxidative processes.
Autoimmun Rev. 7:574–578. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Crane FL and Low H: Reactive oxygen
species generation at the plasma membrane for antibody control.
Autoimmun Rev. 7:518–522. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grisham MB: Reactive oxygen species in
immune responses. Free Radic Biol Med. 36:1479–1480. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hassan SZ, Gheita TA, Kenawy SA, et al:
Oxidative stress in systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid
arthritis patients: relationship to disease manifestations and
activity. Int J Rheum Dis. 14:325–331. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kurien BT and Scofield RH: Autoimmunity
and oxidatively modified autoantigens. Autoimmun Rev. 7:567–573.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang CS, Chang LS, Anderson ME and
Meister A: Catalytic and regulatory properties of the heavy subunit
of rat kidney gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. J Biol Chem.
268:19675–19680. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McConnachie LA, Mohar I, Hudson FN, et al:
Glutamate cysteine ligase modifier subunit deficiency and gender as
determinants of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice.
Toxicol Sci. 99:628–636. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dalton TP, Dieter MZ, Yang Y, et al:
Knockout of the mouse glutamate cysteine ligase catalytic subunit
(Gclc) gene: Embryonic lethal when homozygous, and proposed model
for moderate glutathione deficiency when heterozygous. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 279:324–329. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kasuno K, Nakamura H, Ono T, et al:
Protective roles of thioredoxin, a redox-regulating protein, in
renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 64:1273–1282. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maurice MM, Nakamura H, Gringhuis S, et
al: Expression of the thioredoxin-thioredoxin reductase system in
the inflamed joints of patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Arthritis Rheum. 42:2430–2439. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, et
al: Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus
patients The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis
Rheum. 35:630–640. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hawker G, Gabriel S, Bombardier C, et al:
A reliability study of SLEDAI: a disease activity index for
systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol. 20:657–660.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen CN, Brown-Borg HM, Rakoczy SG, et al:
Aging impairs the expression of the catalytic subunit of glutamate
cysteine ligase in soleus muscle under stress. J Gerontol A Biol
Sci Med Sci. 65:129–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shah D, Sah S and Nath SK: Interaction
between glutathione and apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus.
Autoimmun Rev. 12:741–751. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ortona E, Margutti P, Matarrese P, et al:
Redox state, cell death and autoimmune diseases: a gender
perspective. Autoimmun Rev. 7:579–584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ziegler DM: Role of reversible
oxidation-reduction of enzyme thiols-disulfides in metabolic
regulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 54:305–329. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maher P: The effects of stress and aging
on glutathione metabolism. Ageing Res Rev. 4:288–314. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kasahara Y, Iwai K, Yachie A, et al:
Involvement of reactive oxygen intermediates in spontaneous and
CD95 (Fas/APO-1)-mediated apoptosis of neutrophils. Blood.
89:1748–1753. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hammond CL, Madejczyk MS and Ballatori N:
Activation of plasma membrane reduced glutathione transport in
death receptor apoptosis of HepG2 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
195:12–22. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Messina JP and Lawrence DA: Cell cycle
progression of glutathione-depleted human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells is inhibited at S phase. J Immunol.
143:1974–1981. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Franco R, Panayiotidis MI and Cidlowski
JA: Glutathione depletion is necessary for apoptosis in lymphoid
cells independent of reactive oxygen species formation. J Biol
Chem. 282:30452–30465. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ballatori N, Krance SM, Notenboom S, et
al: Glutathione dysregulation and the etiology and progression of
human diseases. Biol Chem. 390:191–214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shah D, Kiran R, Wanchu A and Bhatnagar A:
Oxidative stress in systemic lupus erythematosus: relationship to
Th1 cytokine and disease activity. Immunol Lett. 129:7–12. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Túri S, Németh I, Torkos A, et al:
Oxidative stress and antioxidant defense mechanism in glomerular
diseases. Free Radic Biol Med. 22:161–168. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nakamura H, De Rosa SC, Yodoi J, et al:
Chronic elevation of plasma thioredoxin: inhibition of chemotaxis
and curtailment of life expectancy in AIDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:2688–2693. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jikimoto T, Nishikubo Y, Koshiba M, et al:
Thioredoxin as a biomarker for oxidative stress in patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Immunol. 38:765–772. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|