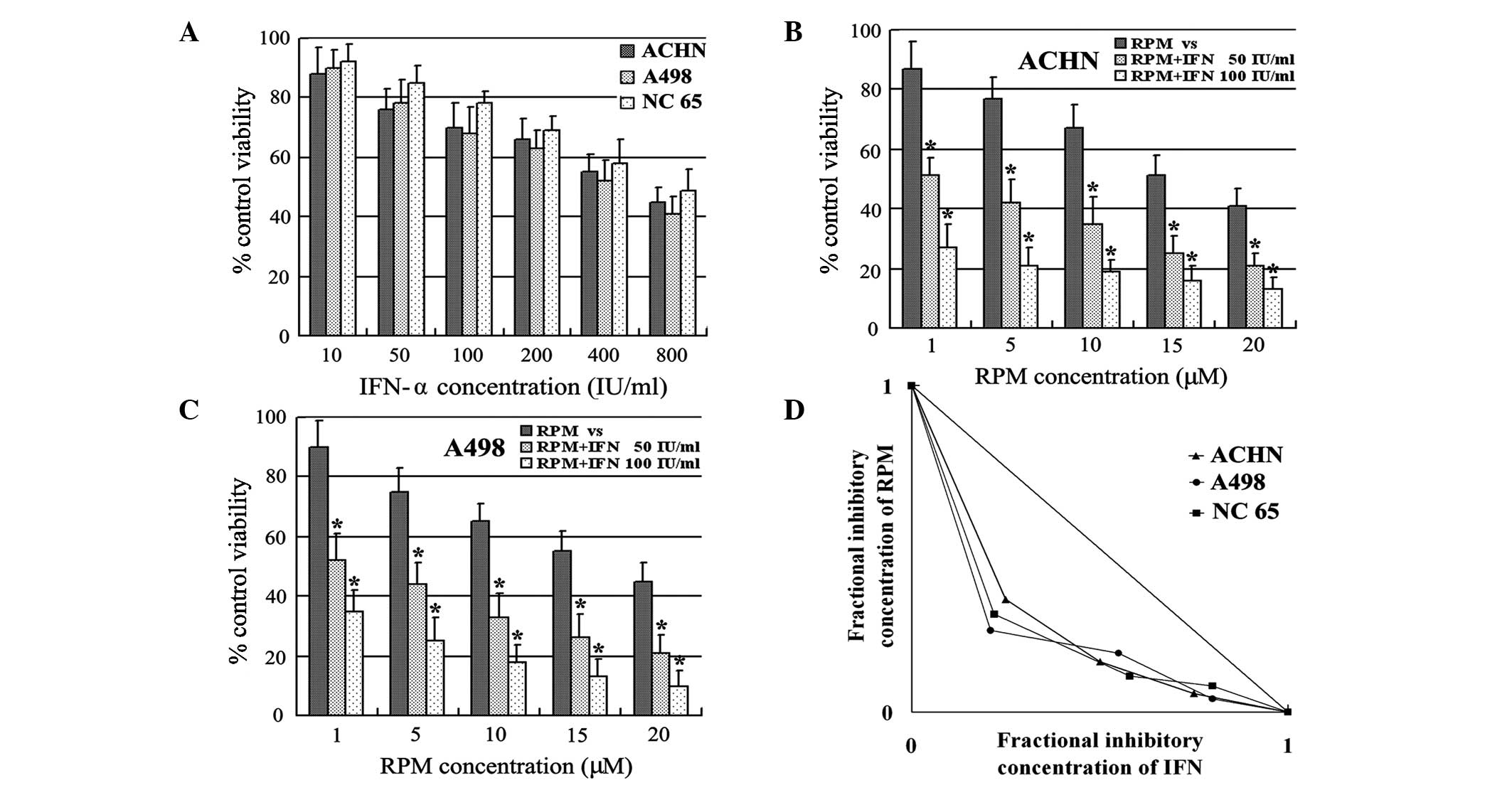
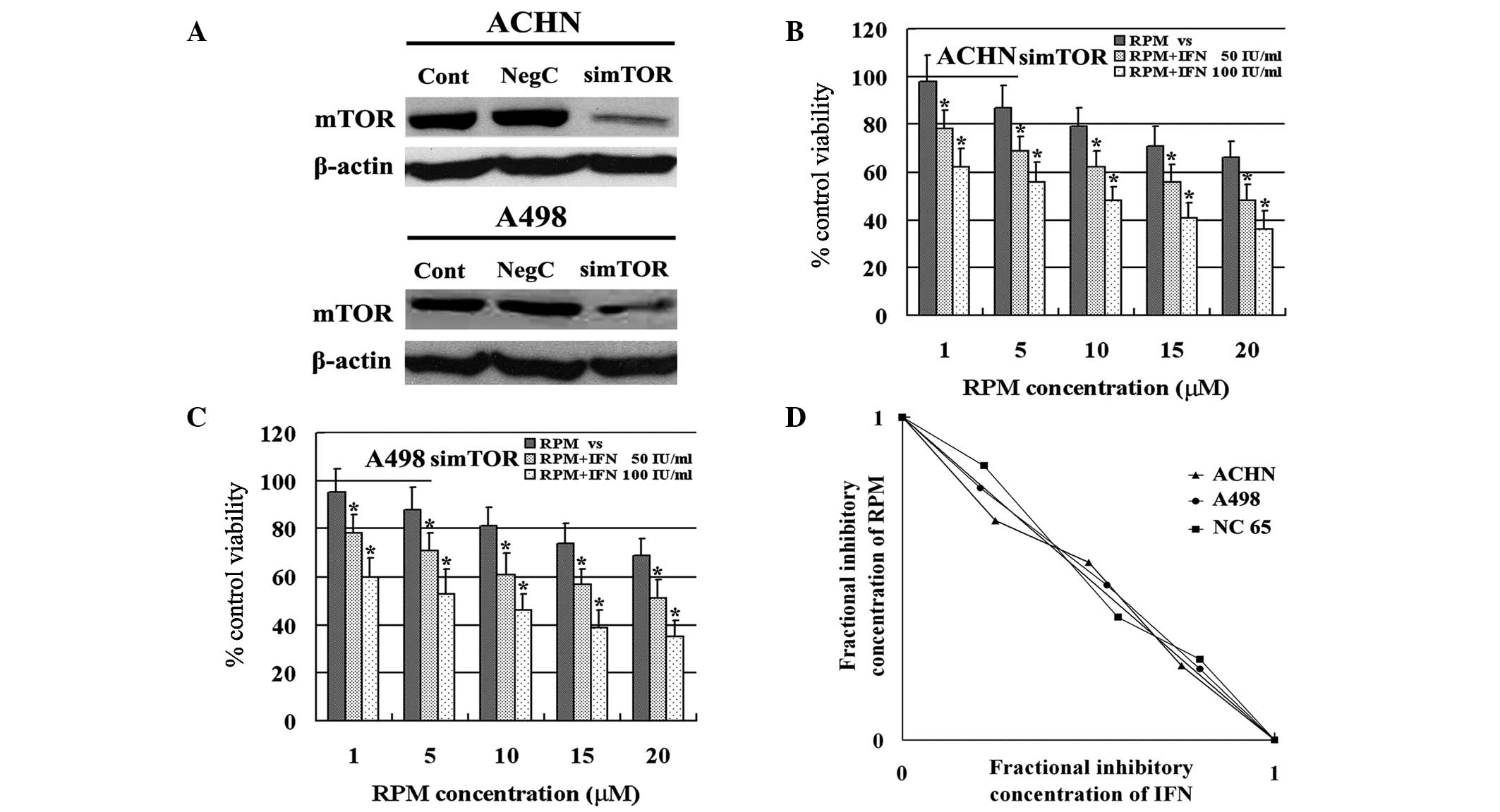
|
1
|
Pantuck AJ, Zisman A and Belldegrun AS:
The changing natural history of renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
166:1611–1623. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hartmann JT and Bokemeyer C: Chemotherapy
for renal cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 19:1541–1543.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hernberg M, Pyrhönen S and Muhonen T:
Regimens with or without interferon-alpha as treatment for
metastatic melanoma and renal cell carcinoma: an overview of
randomized trials. J Immunother. 22:145–154. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yanai Y, Horie S, Yamamoto K, et al:
Characterization of the antitumor activities of IFN-alpha8 on renal
cell carcinoma cells in vitro. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
21:1129–1136. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM and Stark GR:
Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to
IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science.
264:1415–1421. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rathmell WK and Godley PA: Recent updates
in renal rell carcinoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 22:250–256. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kremer CL, Klein RR, Mendelson J, et al:
Expression of mTOR signaling pathway markers in prostate cancer
progression. Prostate. 66:1203–1212. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hashemolhosseini S, Nagamine Y, Morley SJ,
Desrivières S, Mercep L and Ferrari S: Rapamycin inhibition of the
G1 to S transition is mediated by effects on cyclin D1 mRNA and
protein stability. J Biol Chem. 273:14424–14429. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nozawa H, Watanabe T and Nagawa H:
Phosphorylation of ribosomal p70 S6 kinase and rapamycin
sensitivity in human colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 251:105–113.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ruvinsky I, Sharon N, Lerer T, et al:
Ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation is a determinant of cell size
and glucose homeostasis. Genes Dev. 19:2199–2211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seufferlein T and Rozengurt E: Rapamycin
inhibits constitutive p70s6k phosphorylation, cell proliferation,
and colony formation in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res.
56:3895–3897. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Grewe M, Gansauge F, Schmid RM, Adler G
and Seufferlein T: Regulation of cell growth and cyclin D1
expression by the constitutively active FRAP-p70s6K pathway in
human pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 59:3581–3587.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cho D, Signoretti S, Regan M, Mier JW and
Atkins MB: The role of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors in
the treatment of advanced renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
13:758s–763s. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luan FL, Ding R, Sharma VK, Chon WJ,
Lagman M and Suthanthiran M: Rapamycin is an effective inhibitor of
human renal cancer metastasis. Kidney Int. 63:917–926. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Y, Frankel A, Radvanyi LG, Penn LZ,
Miller RG and Mills GB: Rapamycin enhances apoptosis and increases
sensitivity to cisplatin in vitro. Cancer Res. 55:1982–1988.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Masiello D, Mohi MG, McKnight NC, et al:
Combining an mTOR antagonist and receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitors for the treatment of prostate cancer. Cancer Biol Ther.
6:195–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu WZ, Sun HC, Shen YF, et al: Interferon
alpha 2a down-regulates VEGF expression through PI3 kinase and MAP
kinase signaling pathways. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 131:169–178.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Costa LJ, Gemmill RM and Drabkin HA:
Upstream signaling inhibition enhances rapamycin effect on growth
of kidney cancer cells. Urology. 69:596–602. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Linehan WM, Lerman MI and Zbar B:
Identification of the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene. Its role in
renal cancer. JAMA. 273:564–570. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kaelin WG Jr: Molecular basis of the VHL
hereditary cancer syndrome. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:673–682. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guba M, von Breitenbuch P, Steinbauer M,
et al: Rapamycin inhibits primary and metastatic tumor growth by
antiangiogenesis: involvement of vascular endothelial growth
factor. Nat Med. 8:128–135. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Treins C, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Murdaca J,
Monthouël-Kartmann MN and Van Obberghen E: Regulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 activity and expression of HIF
hydroxylases in response to insulin-like growth factor I. Mol
Endocrinol. 19:1304–1317. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu YT, Shang D, Akatsuka S, et al:
Chronic oxidative stress causes amplification and overexpression of
ptprz1 protein tyrosine phosphatase to activate beta-catenin
pathway. Am J Pathol. 171:1978–1988. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Berenbaum MC: A method for testing for
synergy with any number of agents. J Infect Dis. 137:122–130. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hattori K and Akaza H: New combination
chemotherapy in urological cancers. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho.
27:382–387. 2000.(In Japanese).
|
|
26
|
Zhang JF, Liu JJ, Lu MQ, et al: Rapamycin
inhibits cell growth by induction of apoptosis on hepatocellular
carcinoma cells in vitro. Transpl Immunol. 17:162–168. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bukowski RM: Metastatic renal cell
carcinoma: role of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors. Clin
Genitourin Cancer. 5:359–361. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Amato RJ, Jac J, Mohammad T and Saxena S:
Pilot study of rapamycin in patients with hormone-refractory
prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 6:97–102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang Z, Zhou J, Fan J, et al: Effect of
rapamycin alone and in combination with sorafenib in an orthotopic
model of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
14:5124–5130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huynh H, Chow PK, Palanisamy N, et al:
Bevacizumab and rapamycin induce growth suppression in mouse models
of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 49:52–60. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi Y and August DA: A new trick for an
old drug: mTOR inhibitor rapamycin augments the effect of
fluorouracil on hepatocellular carcinoma by inducing cell
senescence. Cancer Biol Ther. 7:397–398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pectasides D, Pectasides E, Papaxoinis G,
et al: Combination chemotherapy with docetaxel, vinorelbine and
estramustine phosphate in metastatic androgen-resistant prostate
cancer: a single institution experience. Anticancer Res.
29:769–775. 2009.
|
|
33
|
Vaishampayan UN, Marur S, Heilbrun LK, et
al: Phase II trial of capecitabine and weekly docetaxel for
metastatic castrate resistant prostate cancer. J Urol. 182:317–323.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hou G, Xue L, Lu Z, Fan T, Tian F and Xue
Y: An activated mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines and inhibition of the pathway by
rapamycin and siRNA against mTOR. Cancer Lett. 253:236–248. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fan QW and Weiss WA: Inhibition of
PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling in glioblastoma by mTORC1/2 inhibitors.
Methods Mol Biol. 821:349–359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fingar DC, Salama S, Tsou C, Harlow E and
Blenis J: Mammalian cell size is controlled by mTOR and its
downstream targets S6K1 and 4EBP1/eIF4E. Genes Dev. 16:1472–1487.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rosner M and Hengstschläger M:
Nucleocytoplasmic localization of p70 S6K1, but not of its isoforms
p85 and p31, is regulated by TSC2/mTOR. Oncogene. 30:4509–4522.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Terzis G, Spengos K, Mascher H, Georgiadis
G, Manta P and Blomstrand E: The degree of p70 S6k and S6
phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle in response to resistance
exercise depends on the training volume. Eur J Appl Physiol.
110:835–843. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pullen N and Thomas G: The modular
phosphorylation and activation of p70s6k. FEBS Lett. 410:78–82.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hinnebusch AG: Translational homeostasis
via eIF4E and 4E-BP1. Mol Cell. 46:717–719. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tait S, Dutta K, Cowburn D, Warwicker J,
Doig AJ and McCarthy JE: Local control of a disorder-order
transition in 4E-BP1 underpins regulation of translation via eIF4E.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:17627–17632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pause A, Belsham GJ, Gingras AC, et al:
Insulin-dependent stimulation of protein synthesis by
phosphorylation of a regulator of 5′-cap function. Nature.
371:762–767. 1994.
|
|
43
|
Perier A, Fregni G, Wittnebel S, et al:
Mutations of the von Hippel-Lindau gene confer increased
susceptibility to natural killer cells of clear-cell renal cell
carcinoma. Oncogene. 30:2622–2632. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|