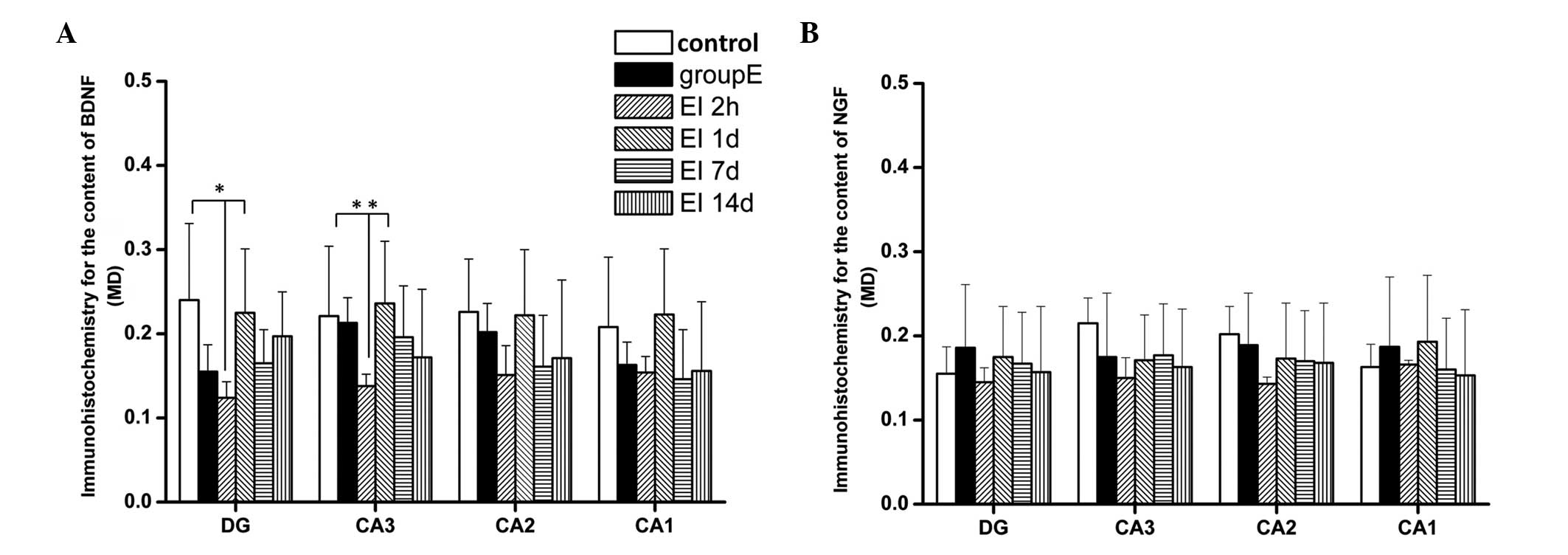
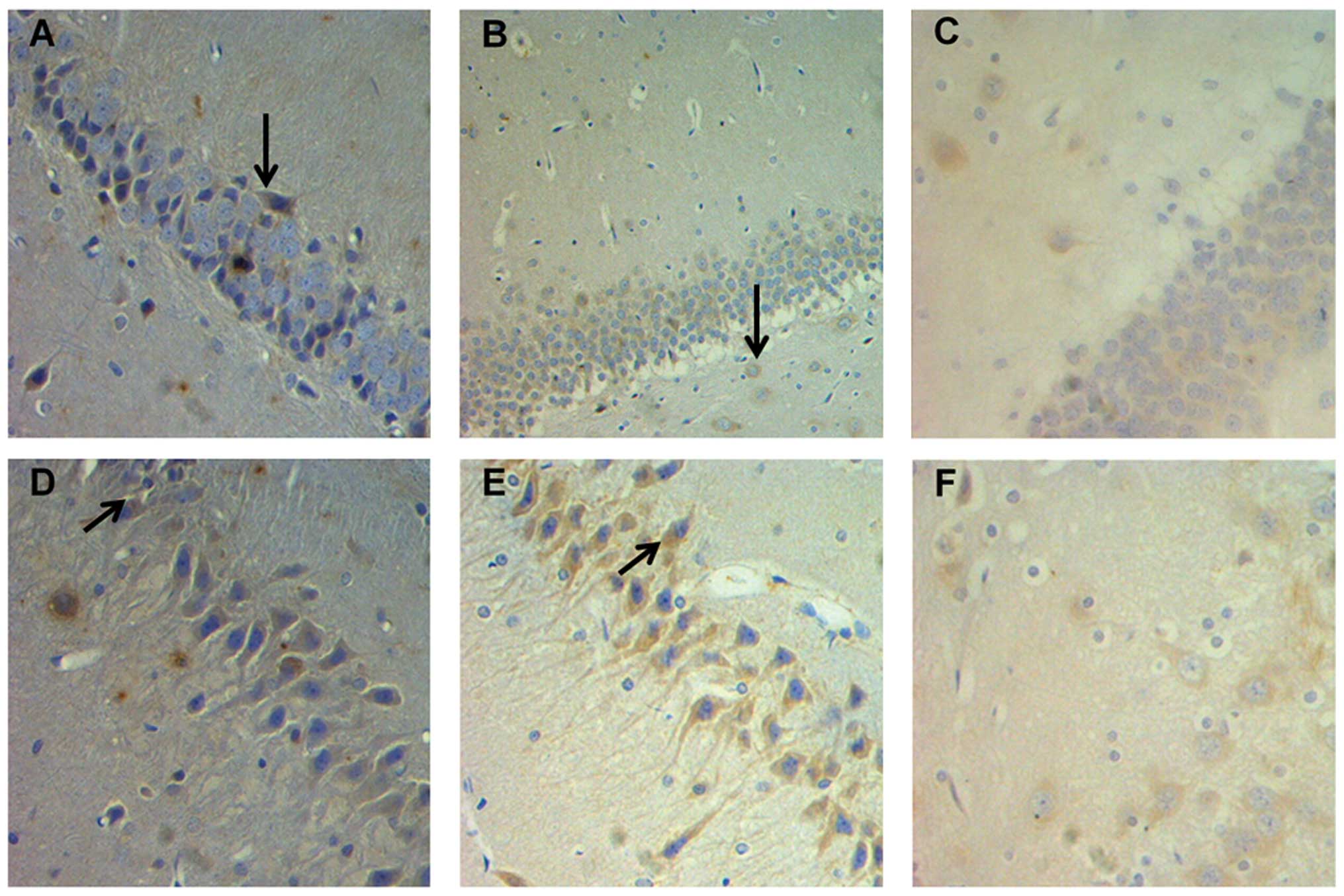
|
1
|
Li X, Wen DX, Zhao YH, Hang YN and Mandell
MS: Increase of beta-amyloid and C-reactive protein in liver
transplant recipients with postoperative cognitive dysfunction.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 12:370–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rudolph JL and Marcantonio ER: Review
articles: postoperative delirium: acute change with long-term
implications. Anesth Analg. 112:1202–1211. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rudolph JL, Marcantonio ER, Culley DJ, et
al: Delirium is associated with early postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Anesthesia. 63:941–947. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Steinmetz J, Christensen KB, Lund T, Lohse
N and Rasmussen LS; ISPOCD Group. Long term consequences of
postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology. 110:548–555.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liang G, Ward C, Peng J, Zhao Y, Huang B
and Wei H: Isoflurane causes greater neurodegeneration than an
equivalent exposure of sevoflurane in the developing brain of
neonatal mice. Anesthesiology. 112:1325–1334. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Braunecker S and Hinkelbein J: Isoflurane
is not necessarily the only cause of cognitive deficits. Eur J
Anaesthesiol. 30:432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Callaway Jk, Jones NC and Royse CF:
Isoflurane induces cognitive deficits in the Morris water maze task
in rats. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 29:239–245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin D and Zuo Z: Isoflurane induces
hippocampal cell injury and cognitive impairments in adult rats.
Neuropharmacology. 61:1354–1359. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu ZY, Luo NF and Liu J: The protective
effects of emulsified isoflurane on myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury in rats. Can J Anaesth. 56:115–125. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lucchinetti E, Schaub MC and Zaugg M:
Emulsified intravenous versus evaporated inhaled isoflurane for
heart protection: old wine in a new bottle or true innovation?
Anesth Analg. 106:1346–1349. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
National Institutes of Health. Guide for
the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition. Bethesda, MD,
USA: 2011
|
|
12
|
Miller RD, Zeng YM and Deng XM: Miller’s
Anesthesia. Inhaled anesthesia. 6th edition. Peking University
Medical Press; Beijing: pp. 109–110. 2006, (In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Lv X, Wang ZM, Huang SD, Song SH, Wu FX
and Yu WF: Emulsified isoflurane preconditioning reduces lung
injury induced by hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Int J Med
Sci. 8:353–361. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang XL, Ma HX, Yang ZB, et al: Comparison
of minimum alveolar concentration between intravenous isoflurane
lipid emulsion and inhaled isoflurane in dogs. Anesthesiology.
104:482–487. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Clausen F, Lewén A, Marklund N, Olsson Y,
McAuthor DL and Hillered L: Correlation of hippocampal
morphological changes and Morris water maze performance after
cortical contusion injury in rats. Neurosurgery. 57:154–163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Morris R: Developments of a water-maze
procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci
Methods. 11:47–60. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Abelson KS, Adem B, Royo F, Carlsson HE
and Hau J: High plasma corticosterone levels persist during
frequent automatic blood sampling in rats. In Vivo. 19:815–819.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kashyap M, Kawamorita N, Tyaqi V, et al:
Down-regulation of nerve growth factor expression in the bladder by
antisense oligonucleotides as new treatment for overactive bladder.
J Urol. 190:757–764. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Q, DU X, Xu Y, Dang L, Xiang L and
Zhang J: The effects of Gouqi extracts on Morris maze learning in
the APP/PS1 double transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.
Exp Ther Med. 5:1528–1530. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y and Song W: Morris
water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer’s
disease model mice. J Vis Exp. 53:e29202011.
|
|
21
|
Vorhees CV and Williams TM: Morris water
maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of
learning and memory. Nat Protoc. 1:848–858. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Butterfield NN, Graf P, Ries CR and
MacLeod BA: The effect of repeated isoflurane anesthesia on spatial
and psychomotor performance in young and aged mice. Anesth Analg.
98:1305–1311. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Crosby C, Culley DJ, Baxter MG, Yukhananov
R and Crosby G: Spatial memory performance 2 weeks after general
anesthesia in adult rats. Anesth Analg. 101:1389–1392. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee S, Park SH and Zuo Z: Effects of
isoflurane on learning and memory functions of wild-type and
glutamate transporter type 3 knockout mice. J Pharm Pharmacol.
64:302–307. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lin D, Cao L, Wang Z, Li J, Washington JM
and Zuo Z: Lidocaine attenuates cognitive impairment after
isoflurane anesthesia in old rats. Behav Brain Res. 228:319–327.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yau JL, Noble J and Seckl JR:
11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 1 deficiency prevents
memory deficits with aging by switching from glucocorticoid
receptor to mineralocorticoid receptor-mediated cognitive control.
J Neurosci. 31:4188–4193. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Choy KH, de Visser Y, Nichols NR and van
den Buuse M: Combined neonatal stress and young-adult
glucocorticoid stimulation in rats reduce BDNF expression in
hippocampus: effects on learning and memory. Hippocampus.
18:655–67. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Numakawa T, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Yagasaki
Y, Izumi A and Kunuqi H: Glucocorticoid receptor interaction with
TrkB promotes BDNF-triggered PLC-gamma signaling for glutamate
release via a glutamate transporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:647–652. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Henriksson BG, Söderström S, Gower AJ,
Ebendal T, Winblad B and Mohammed AH: Hippocampal nerve growth
factor levels are related to spatial learning ability in aged rats.
Behav Brain Res. 48:15–20. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Conner JM, Franks KM, Titterness AK, et
al: NGF is essential for hippocampal plasticity and learning. J
Neurosci. 29:10883–10889. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li B, Arime Y, Hall FS, Uhi GR and Sora I:
Impaired spatial working memory and decreased frontal cortex BDNF
protein level in dopamine transporter knockout mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 628:104–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|