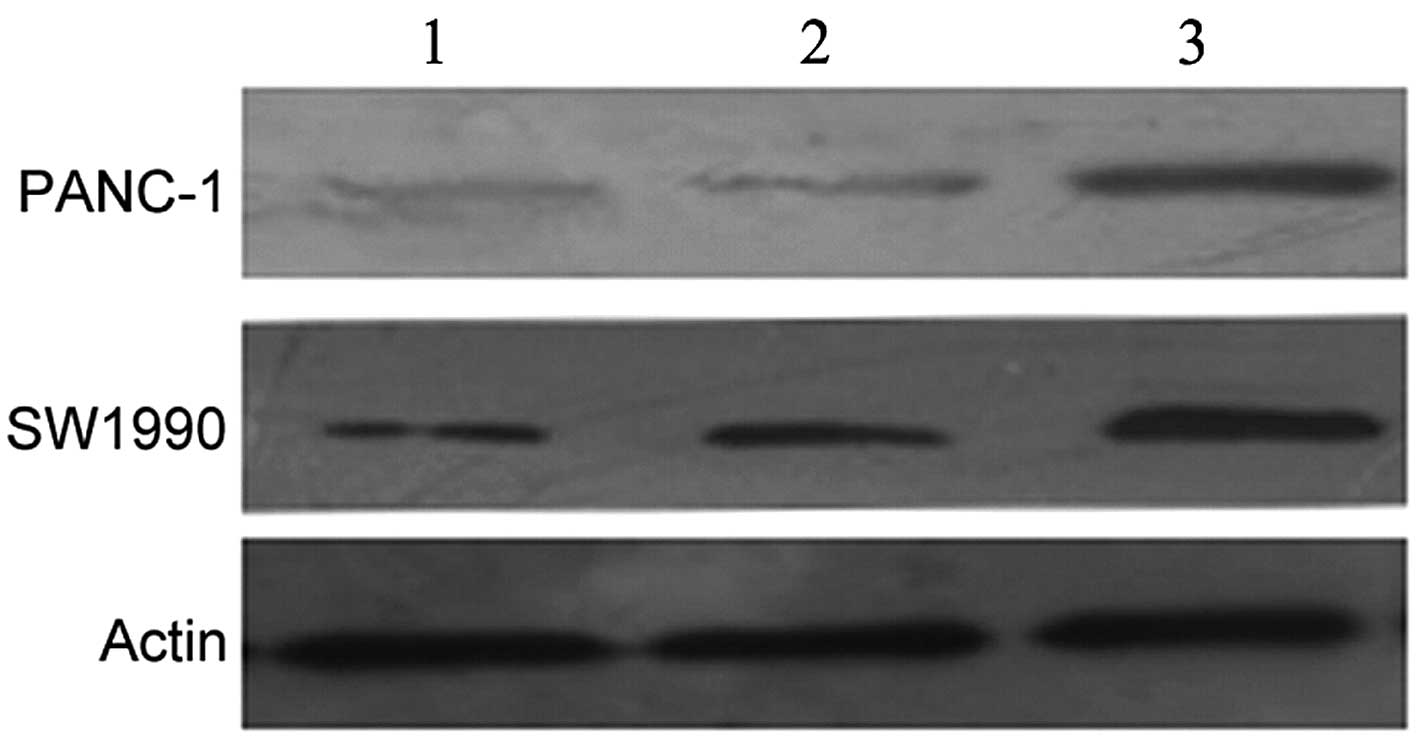
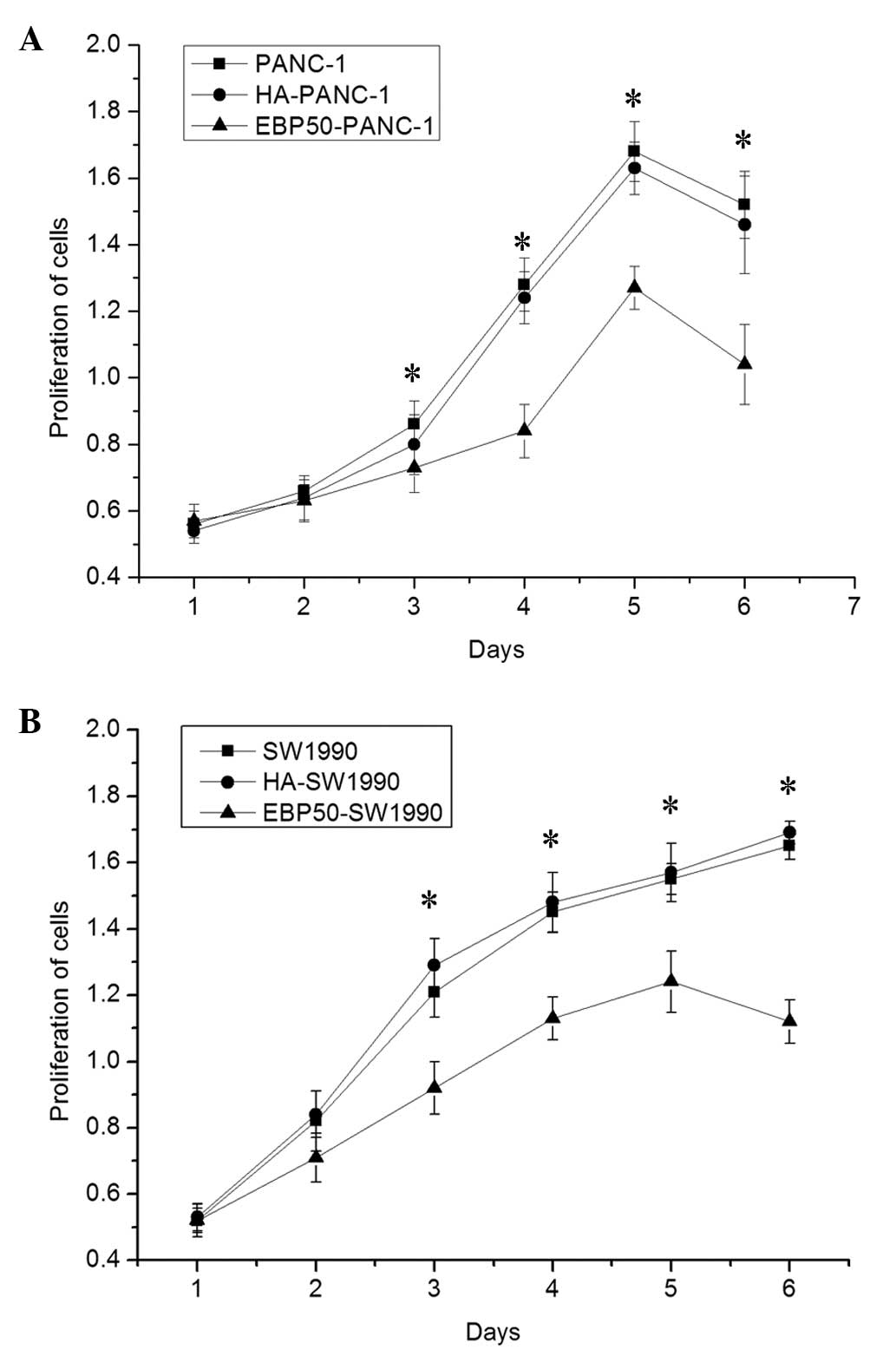
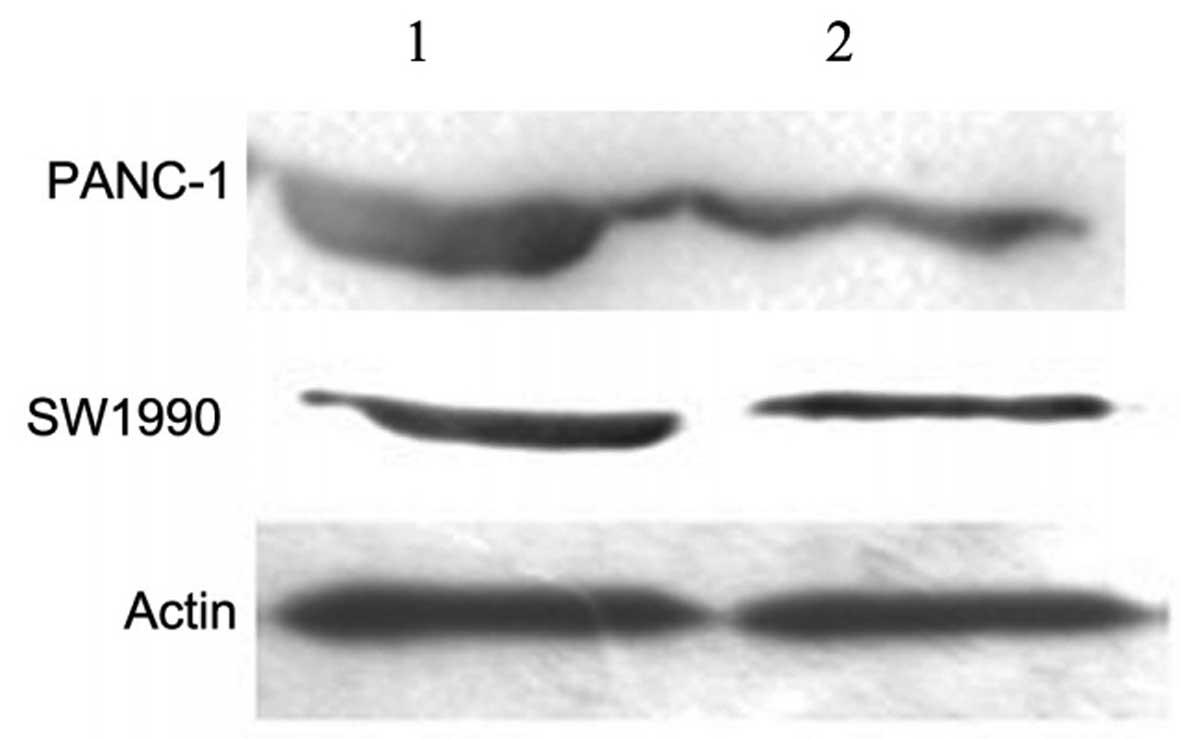
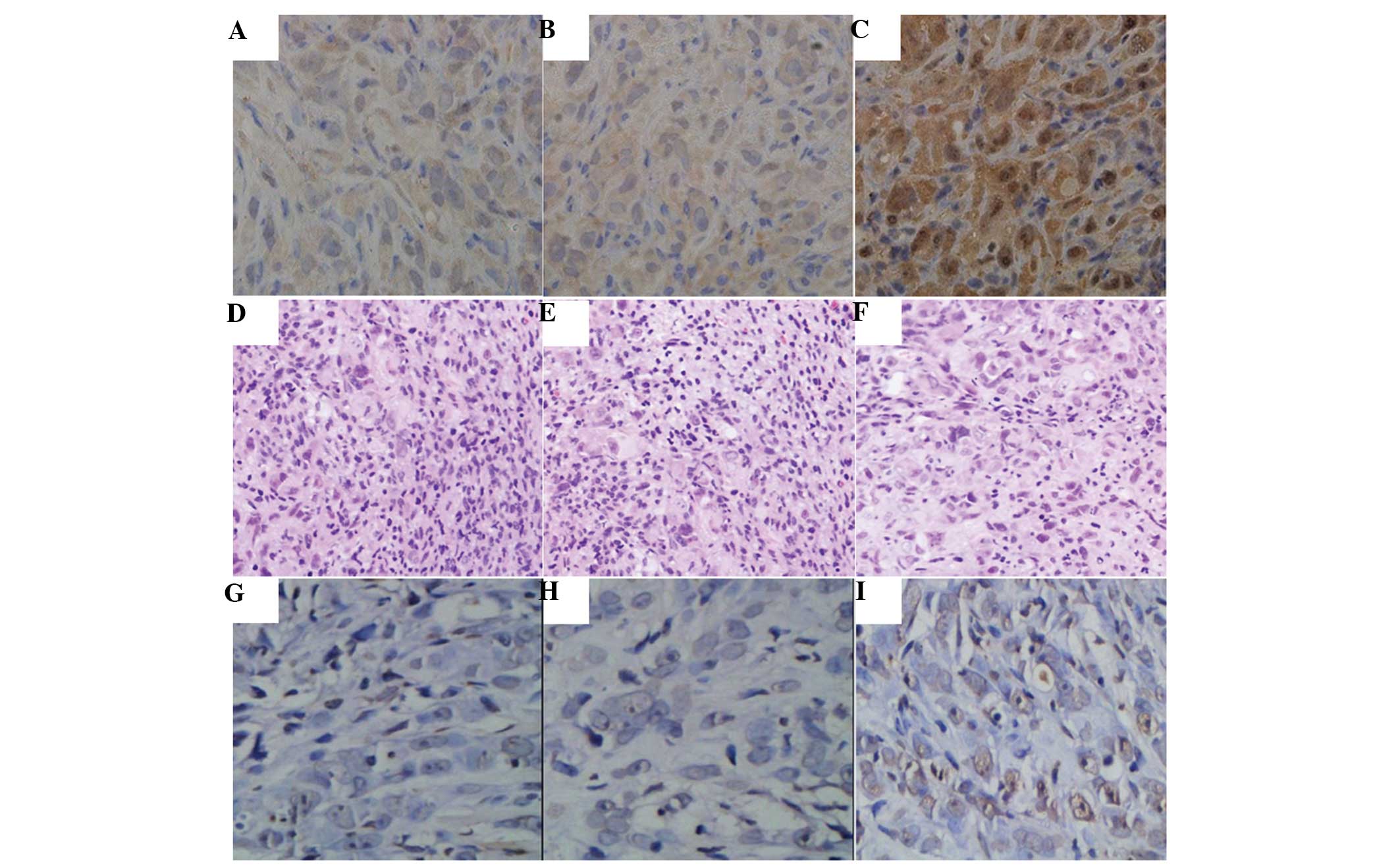
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mackenzie GG, Huang L, Alston N, et al:
Targeting mitochondrial STAT3 with the novel phospho-valproic acid
(MDC-1112) inhibits pancreatic cancer growth in mice. PLoS One.
8:e615322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Georgescu MM, Morales FC, Molina JR and
Hayashi Y: Roles of NHERF1/EBP50 in cancer. Curr Mol Med.
8:459–468. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ghaneh P, Costello E and Neoptolemos JP:
Biology and management of pancreatic cancer. Postgrad Med J.
84:478–497. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Clapéron A, Guedj N, Mergey M, et al: Loss
of EBP50 stimulates EGFR activity to induce EMT phenotypic features
in biliary cancer cells. Oncogene. 31:1376–1388. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun C, Zheng J, Cheng S, Feng D and He J:
EBP50 phosphorylation by Cdc2/Cyclin B kinase affects actin
cytoskeleton reorganization and regulates functions of human breast
cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. Mol Cells. 36:47–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kreimann EL, Morales FC, de Orbeta-Cruz J,
et al: Cortical stabilization of beta-catenin contributes to
NHERF1/EBP50 tumor suppressor function. Oncogene. 26:5290–5299.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shibata T, Chuma M, Kokubu A, Sakamoto M
and Hirohashi S: EBP50, a beta-catenin-associating protein,
enhances Wnt signaling and is over-expressed in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 38:178–186. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee YJ, Choi IK, Sheen YY, Park SN and
Kwon HJ: Identification of EBP50 as a specific biomarker for
carcinogens via the analysis of mouse lymphoma cellular proteome.
Mol Cells. 33:309–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lv XG, Ji MY, Dong WG, et al: EBP50 gene
transfection promotes 5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in gastric
cancer cells through Bax- and Bcl-2-triggered mitochondrial
pathways. Mol Med Rep. 5:1220–1226. 2012.
|
|
11
|
Molina JR, Morales FC, Hayashi Y, Aldape
KD and Georgescu MM: Loss of PTEN binding adapter protein NHERF1
from plasma membrane in glioblastoma contributes to PTEN
inactivation. Cancer Res. 70:6697–6703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fraenzer JT, Pan H, Minimo L Jr, Smith GM,
Knauer D and Hung G: Overexpression of the NF2 gene inhibits
schwannoma cell proliferation through promoting PDGFR degradation.
Int J Oncol. 23:1493–1500. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morales FC, Takahashi Y, Kreimann EL and
Georgescu MM: Ezrin-radixin-moesin (ERM)-binding phosphoprotein 50
organizes ERM proteins at the apical membrane of polarized
epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:17705–17710. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin YY, Hsu YH, Huang HY, et al: Aberrant
nuclear localization of EBP50 promotes colorectal carcinogenesis in
xenotransplanted mice by modulating TCF-1 and β-catenin
interactions. J Clin Invest. 122:1881–1894. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morales FC, Hayashi Y, van Pelt CS and
Georgescu MM: NHERF1/EBP50 controls lactation by establishing basal
membrane polarity complexes with prolactin receptor. Cell Death
Dis. 3:e3912012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ji MY, Fan DK, Lv XG, Peng XL, Lei XF and
Dong WG: The detection of EBP50 expression using quantum dot
immunohistochemistry in pancreatic cancer tissue and down-regulated
EBP50 effect on PC-2 cells. J Mol Histol. 43:517–526. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pan Y, Wang L and Dai JL: Suppression of
breast cancer cell growth by Na+/H+ exchanger
regulatory factor 1 (NHERF1). Breast Cancer Res. 8:R632006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo J, Gao J, Li Z, et al: Adenovirus
vector-mediated Gli1 siRNA induces growth inhibition and apoptosis
in human pancreatic cancer with Smo-dependent or Smo-independent Hh
pathway activation in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Lett.
339:185–194. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu WJ and Liu HL: Induction of pancreatic
cancer cell apoptosis, invasion, migration, and enhancement of
chemotherapy sensitivity of gemcitabine, 5-FU, and oxaliplatin by
hnRNP A2/B1 siRNA. Anticancer Drugs. 24:566–576. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li X, Yan J, Wang L, et al: Beclin1
inhibition promotes autophagy and decreases gemcitabine-induced
apoptosis in Miapaca2 pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int.
13:262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boyer C, Teo J, Phillips P, et al:
Effective delivery of siRNA into cancer cells and tumors using
well-defined biodegradable cationic star polymers. Mol Pharm.
10:2435–2444. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morales FC, Takahashi Y, Momin S, Adams H,
Chen X and Georgescu MM: NHERF1/EBP50 head-to-tail intramolecular
interaction masks association with PDZ domain ligands. Mol Cell
Biol. 27:2527–2537. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hayashi Y, Molina JR, Hamilton SR and
Georgescu MM: NHERF1/EBP50 is a new marker in colorectal cancer.
Neoplasia. 12:1013–1022. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li X, Xu WM, Yin TL, Zhao QH, Peng LY and
Yang J: Temporal and spatial regulation of
ezrin-radixin-moesin-binding phosphoprotein-50-kDa (EBP50) during
embryo implantation in mouse uterus. Int J Mol Sci. 13:16418–16429.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yao W, Feng D, Bian W, et al: EBP50
inhibits EGF-induced breast cancer cell proliferation by blocking
EGFR phosphorylation. Amino Acids. 43:2027–2035. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|