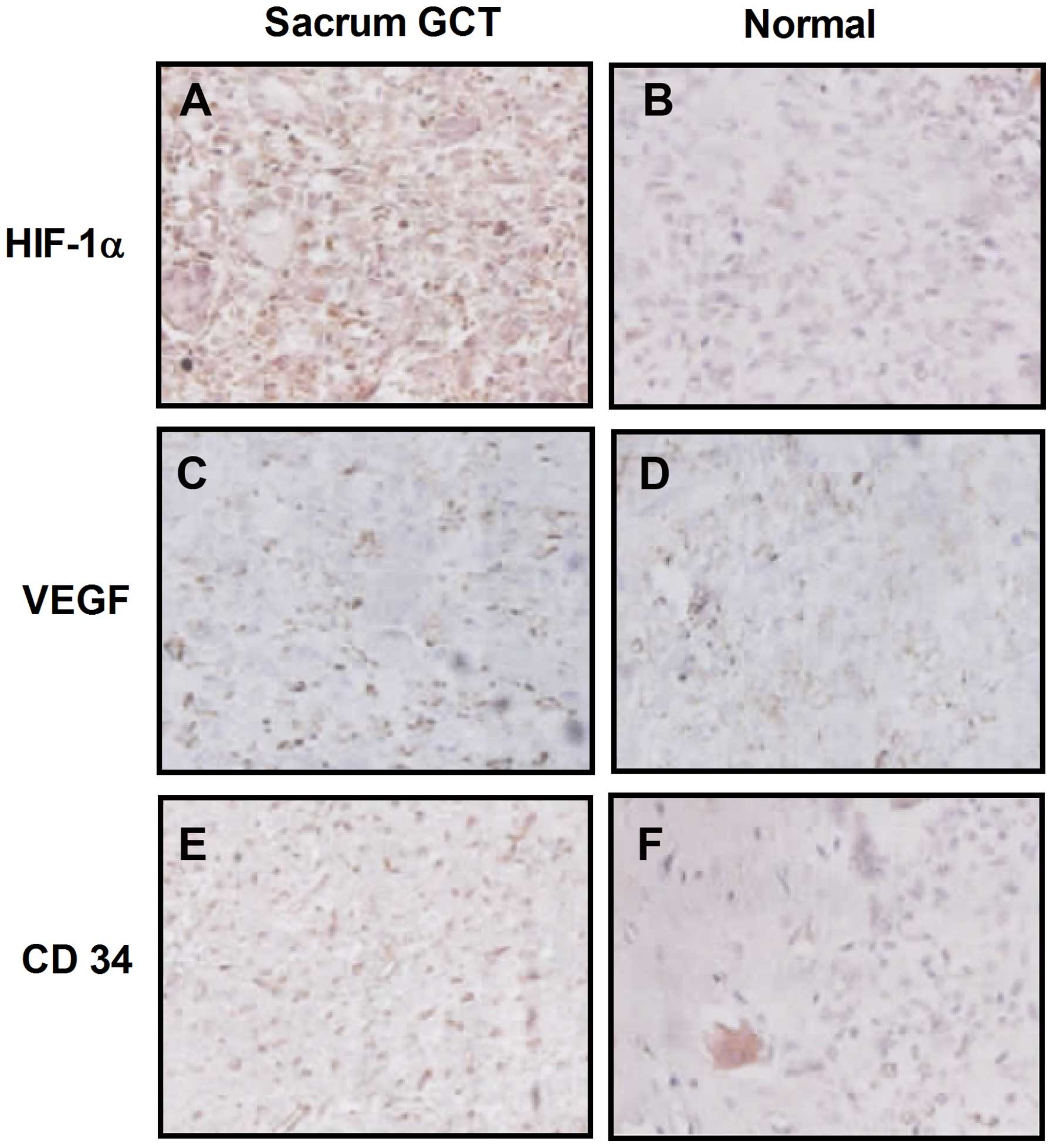
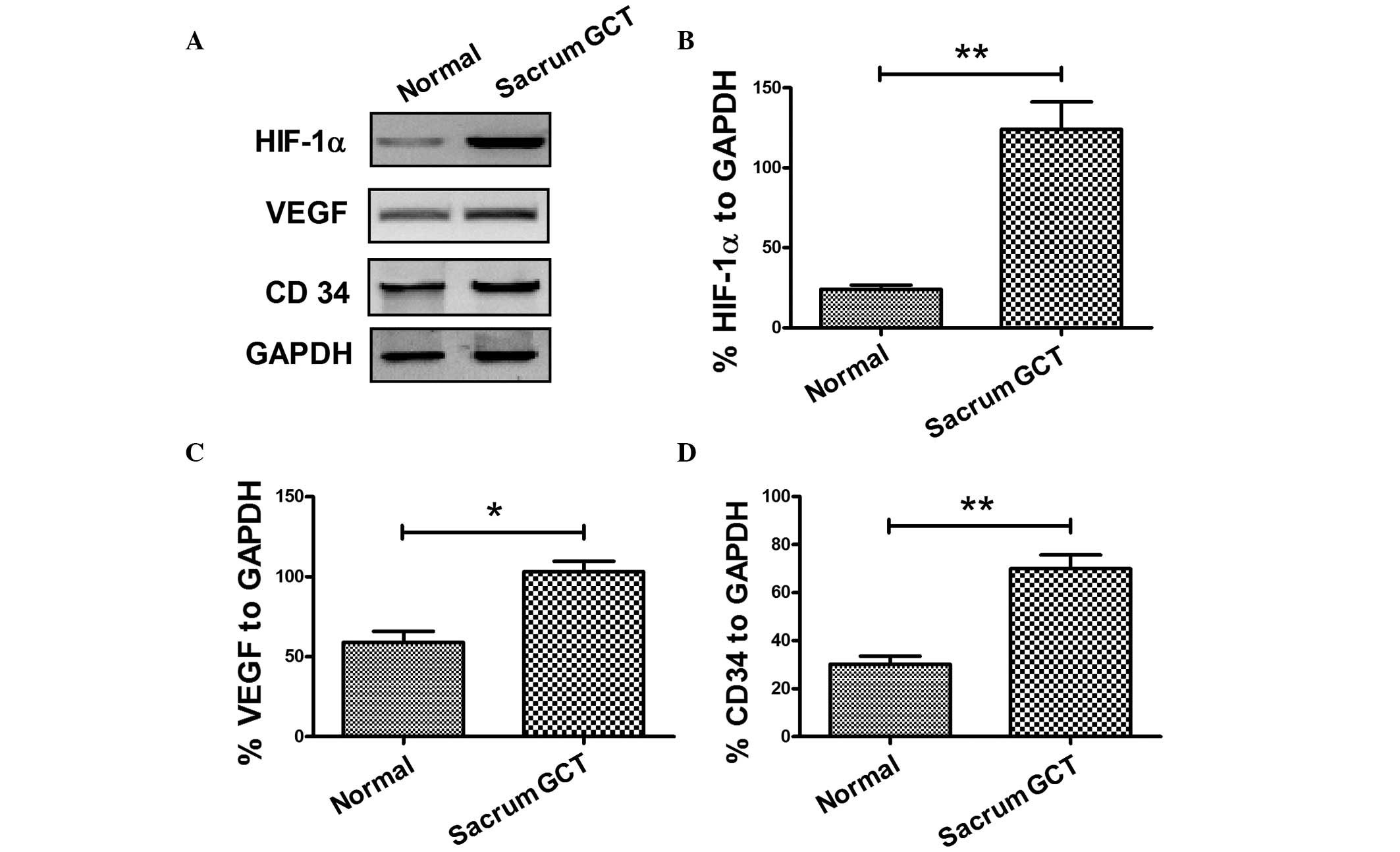
|
1
|
Anract P, De Pinieux G, Cottias P,
Pouillart P, Forest M and Tomeno B: Malignant giant-cell tumours of
bone. Clinico-pathological types and prognosis: a review of 29
cases. Int Orthop. 22:19–26. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gamberi G, Serra M, Ragazzini P, et al:
Identification of markers of possible prognostic value in 57 giant
cell tumors of bone. Oncol Rep. 10:351–356. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miszczyk L, Wydmański J and Spindel J:
Efficacy of radiotherapy for giant cell tumor of bone: given either
postoperatively or as sole treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
49:1239–1242. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Turcotte RE, Sim FH and Unni KK: Giant
cell tumor of the sacrum. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 291:215–221.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Turcotte RE: Giant cell tumor of bone.
Orthop Clin North Am. 37:35–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sung HW, Shu WP, Wang HM, Yuai SY and Tsai
YB: Surgical treatment of primary tumors of the sacrum. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 215:91–98. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo W, Ji T, Tang X and Yang Y: Outcome of
conservative surgery for giant cell tumor of the sacrum. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 34:1025–1031. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McDonald DJ, Sim FH, McLeod RA and Dahlin
DC: Giant-cell tumor of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 68:235–242.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Campanacci M, Baldini N, Boriani S and
Sudanese A: Giant-cell tumor of bone. J Bone Joint Surg Am.
69:106–114. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olivera P, Perez E, Ortega A, et al:
Estrogen receptor expression in giant cell tumors of the bone. Hum
Pathol. 33:165–169. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Morgan T, Atkins GJ, Trivett MK, et al:
Molecular profiling of giant cell tumor of bone and the
osteoclastic localization of ligand for receptor activator of
nuclear factor kappaB. Am J Pathol. 167:117–128. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Skubitz KM, Cheng EY, Clohisy DR, Thompson
RC and Skubitz AP: Gene expression in giant-cell tumors. J Lab Clin
Med. 144:193–200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Atkins GJ, Haynes DR, Graves SE, et al:
Expression of osteoclast differentiation signals by stromal
elements of giant cell tumors. J Bone Miner Res. 15:640–649. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cummins EP and Taylor CT:
Hypoxia-responsive transcription factors. Pflugers Arch.
450:363–371. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Licausi F, Weits DA, Pant BD, Scheible WR,
Geigenberger P and van Dongen JT: Hypoxia responsive gene
expression is mediated by various subsets of transcription factors
and miRNAs that are determined by the actual oxygen availability.
New Phytol. 190:442–456. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Semenza GL: Targeting HIF-1 for cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:721–732. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH,
et al: The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for
cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 452:230–233. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA and Semenza GL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS
heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 92:5510–5514. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pouysségur J, Dayan F and Mazure NM:
Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour
regression. Nature. 441:437–443. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kaelin WG Jr and Ratcliffe PJ: Oxygen
sensing by metazoans: the central role of the HIF hydroxylase
pathway. Mol Cell. 30:393–402. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Blancher C, Moore JW, Talks KL, Houlbrook
S and Harris AL: Relationship of hypoxia-inducible factor
(HIF)-1alpha and hif-2alpha expression to vascular endothelial
growth factor induction and hypoxia survival in human breast cancer
cell lines. Cancer Res. 60:7106–7113. 2000.
|
|
22
|
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, et al:
Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in common human
cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res. 59:5830–5835.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pralhad T, Madhusudan S and Rajendrakumar
K: Concept, mechanisms and therapeutics of angiogenesis in cancer
and other diseases. J Pharm Pharmacol. 55:1045–1053. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Taylor RM, Kashima TG, Knowles HJ and
Athanasou NA: VEGF, FLT3 ligand, PIGF and HGF can substitute for
M-CSF to induce human osteoclast formation: Implications for giant
cell tumour pathobiology. Lab Invest. 92:1398–1406. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Saikia B, Goel A and Gupta SK: Fine-needle
aspiration cytologic diagnosis of giant-cell tumor of the sacrum
presenting as a rectal mass: A case report. Diagn Cytopathol.
24:39–41. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hara H, Akisue T, Fujimoto T, et al:
Expression of vegf and its receptors and angiogenesis in bone and
soft tissue tumors. Anticancer Res. 26:4307–4311. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Athanasou NA, Bliss E, Gatter KC, Heryet
A, Woods CG and McGee JO: An immunohistological study of giant-cell
tumour of bone: evidence for an osteoclast origin of the giant
cells. J Pathol. 147:153–158. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bertoni F, Present D and Enneking WF:
Giant-cell tumor of bone with pulmonary metastases. J Bone Joint
Surg Am. 67:890–900. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brahimi-Horn MC and Pouysségur J:
Harnessing the hypoxia-inducible factor in cancer and ischemic
disease. Biochem Pharmacol. 73:450–457. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Knowles HJ and Athanasou NA:
Hypoxia-inducible factor is expressed in giant cell tumour of bone
and mediates paracrine effects of hypoxia on monocyte-osteoclast
differentiation via induction of VEGF. J Pathol. 215:56–66. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barleon B, Sozzani S, Zhou D, Weich HA,
Mantovani A and Marmé D: Migration of human monocytes in response
to vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is mediated via the
VEGF receptor flt-1. Blood. 87:3336–3343. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Engsig MT, Chen QJ, Vu TH, et al: Matrix
metalloproteinase 9 and vascular endothelial growth factor are
essential for osteoclast recruitment into developing long bones. J
Cell Biol. 151:879–889. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Aldridge SE, Lennard TW, Williams JR and
Birch MA: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in
osteoclast differentiation and function. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 335:793–798. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mori S, Akagi M, Kikuyama A, Yasuda Y and
Hamanishi C: Axial shortening during distraction osteogenesis leads
to enhanced bone formation in a rabbit model through the
HIF-1alpha/vascular endothelial growth factor system. J Orthop Res.
24:653–663. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zheng MH, Xu J, Robbins P, et al: Gene
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in giant cell
tumors of bone. Hum Pathol. 31:804–812. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kumta SM, Huang L, Cheng YY, Chow LT, Lee
KM and Zheng MH: Expression of VEGF and MMP-9 in giant cell tumor
of bone and other osteolytic lesions. Life Sci. 73:1427–1436. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brizel DM, Rosner GL, Prosnitz LR and
Dewhirst MW: Patterns and variability of tumor oxygenation in human
soft tissue sarcomas, cervical carcinomas, and lymph node
metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 32:1121–1125. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hill SA, Pigott KH, Saunders MI, et al:
Microregional blood flow in murine and human tumours assessed using
laser Doppler microprobes. Br J Cancer Suppl. 27:S260–S263.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cohen-Jonathan E, Evans SM, Koch CJ, et
al: The farnesyltransferase inhibitor L744,832 reduces hypoxia in
tumors expressing activated H-ras. Cancer Res. 61:2289–2293.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|