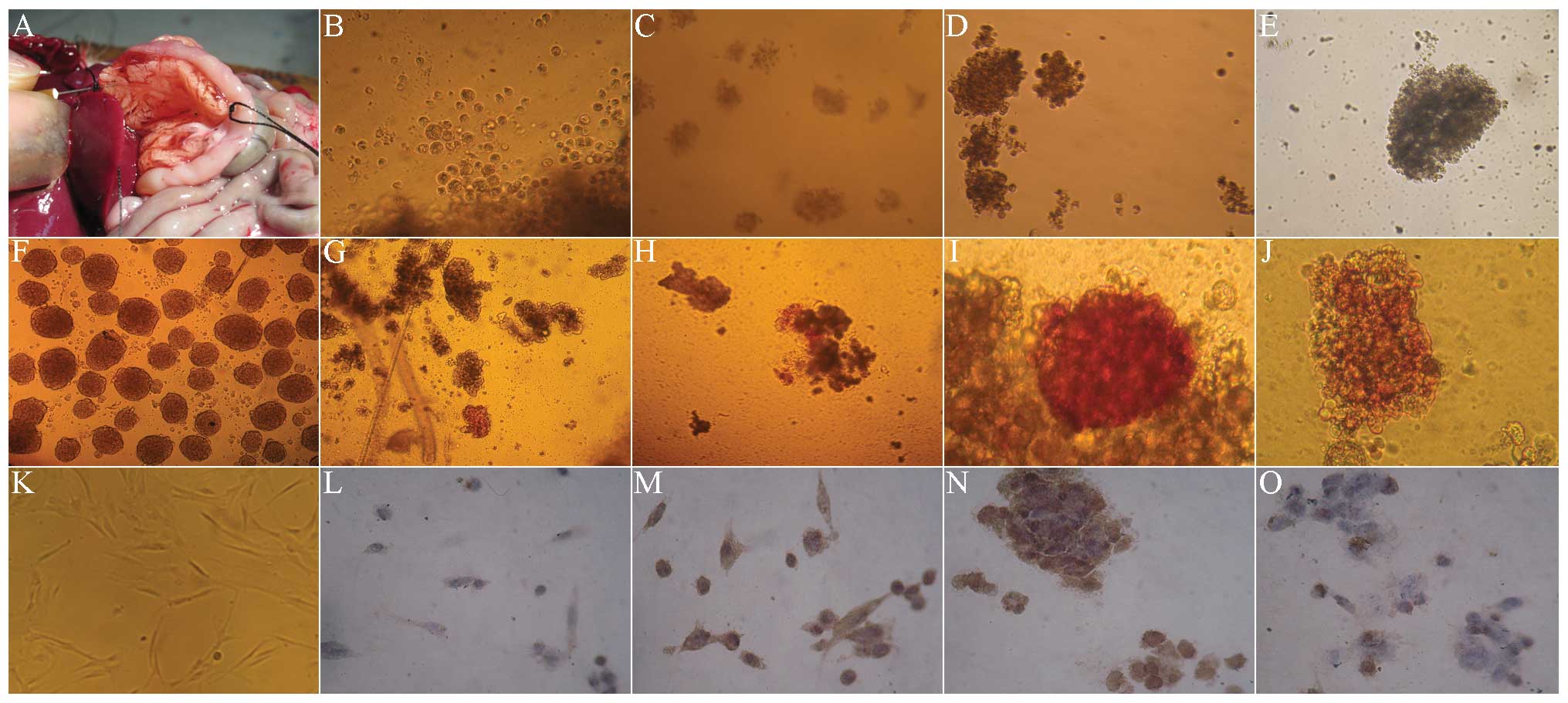
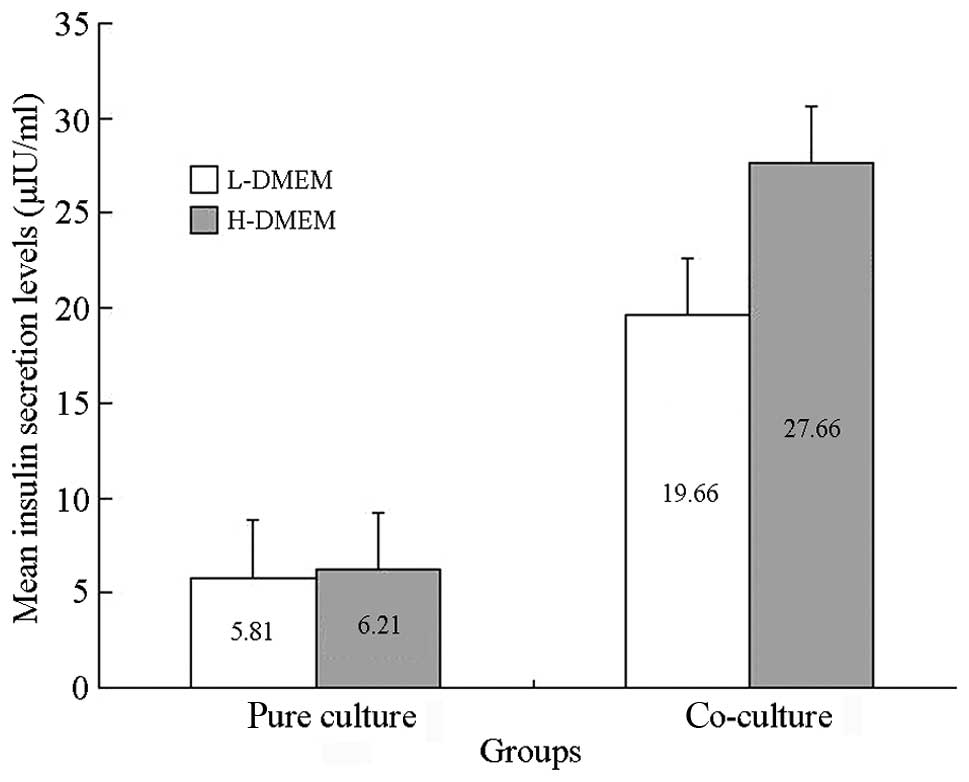
Spandidos Publications style
Wang G, Li Y, Wang Y, Dong Y, Wang FS, Ding Y, Kang Y and Xu X: Roles of the co‑culture of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly‑derived mesenchymal stem cells with rat pancreatic cells in the treatment of rats with diabetes mellitus. Exp Ther Med 8: 1389-1396, 2014.
APA
Wang, G., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, Y., Wang, F., Ding, Y. ... Xu, X. (2014). Roles of the co‑culture of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly‑derived mesenchymal stem cells with rat pancreatic cells in the treatment of rats with diabetes mellitus. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine, 8, 1389-1396. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1985
MLA
Wang, G., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, Y., Wang, F., Ding, Y., Kang, Y., Xu, X."Roles of the co‑culture of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly‑derived mesenchymal stem cells with rat pancreatic cells in the treatment of rats with diabetes mellitus". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 8.5 (2014): 1389-1396.
Chicago
Wang, G., Li, Y., Wang, Y., Dong, Y., Wang, F., Ding, Y., Kang, Y., Xu, X."Roles of the co‑culture of human umbilical cord Wharton's jelly‑derived mesenchymal stem cells with rat pancreatic cells in the treatment of rats with diabetes mellitus". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 8, no. 5 (2014): 1389-1396. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2014.1985