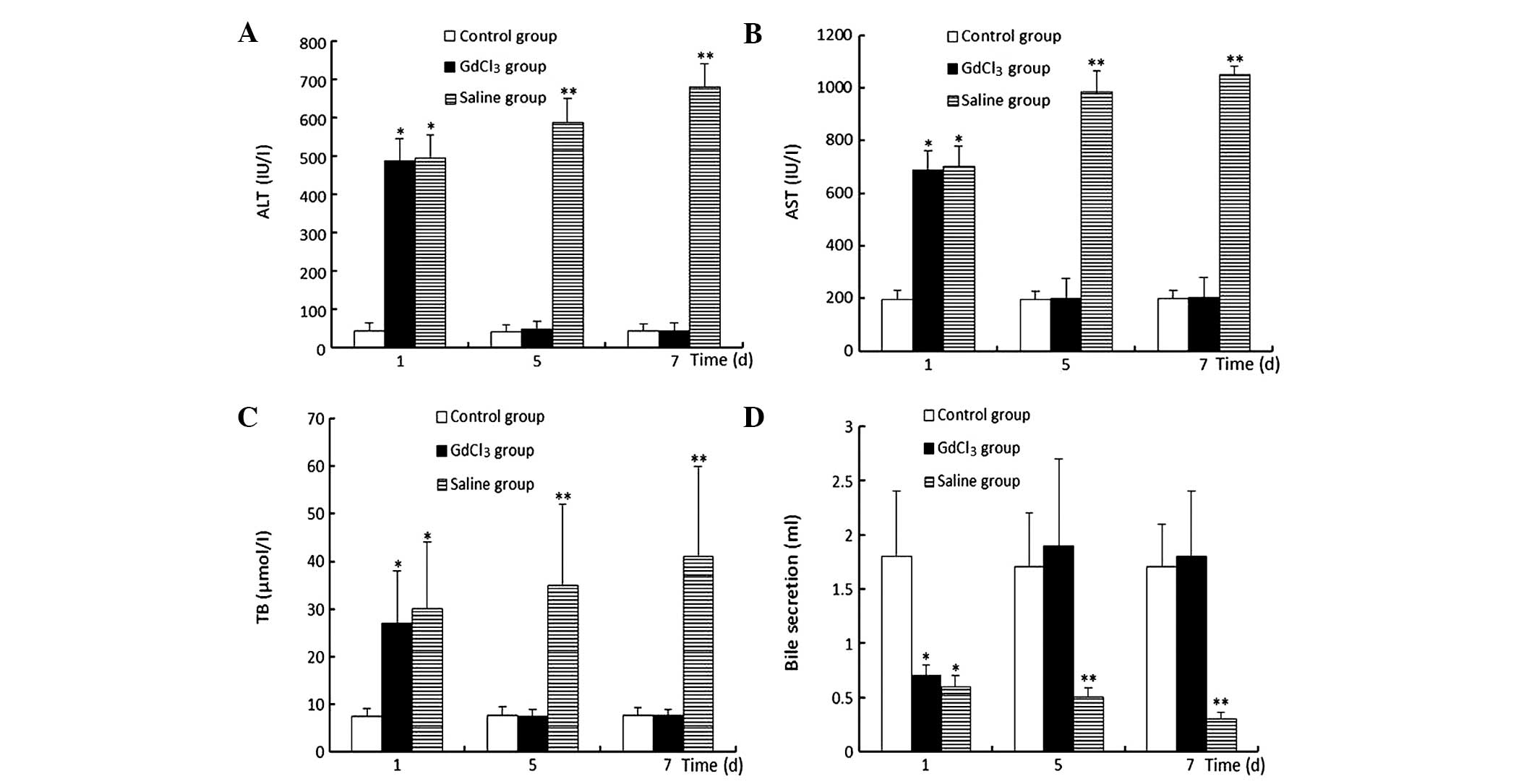
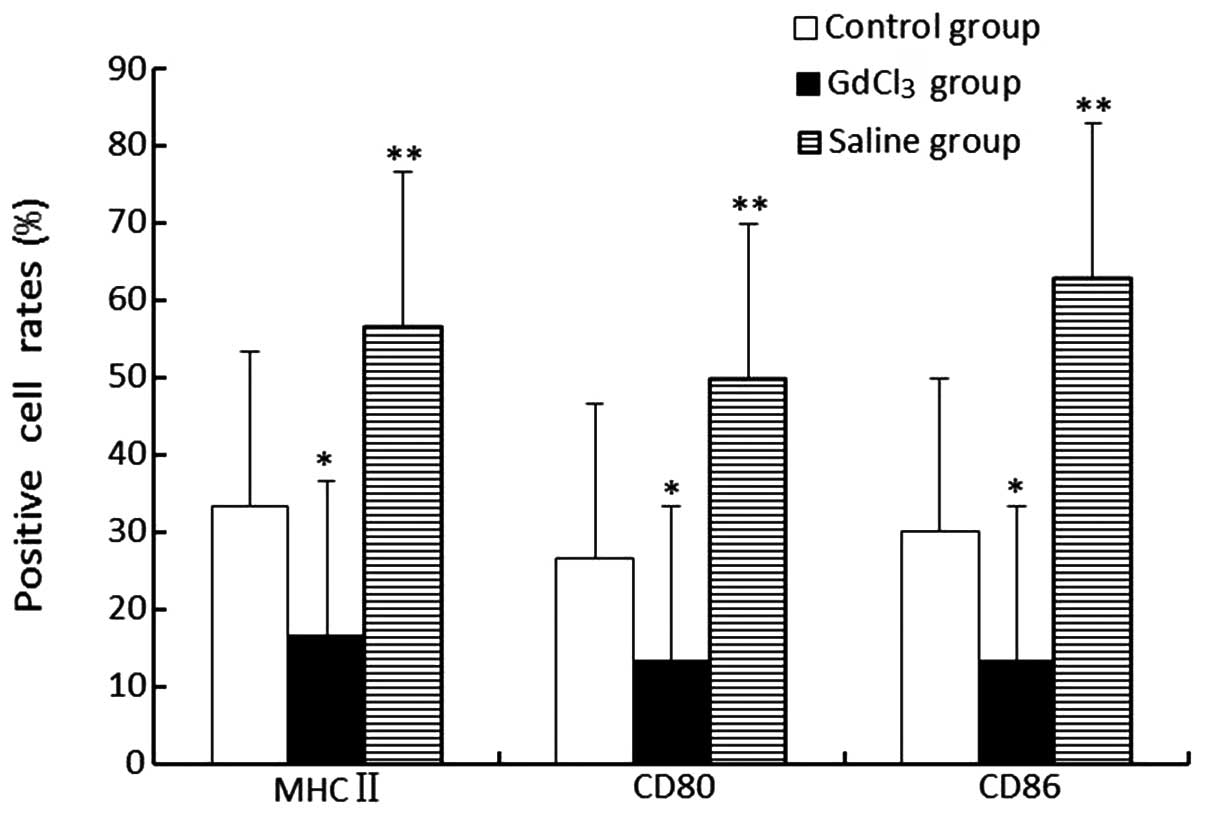
|
1
|
Rüttinger D, Vollmar B, Kempter B and
Messmer K: Failure of Kupffer cell blockade to prevent disseminated
intravascular coagulation in endotoxemic rats despite improved
survival. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 383:75–80. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vollmar B, Rüttinger D, Wanner GA, et al:
Modulation of Kupffer cell activity by gadolinium chloride in
endotoxemic rats. Shock. 6:434–441. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dimitrios G, George P, Stavros I, et al:
The protective effect of alpha-tocopherol and GdCl3
against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Surg Today.
36:450–456. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sindram D, Porte RJ, Hoffman MR, et al:
Synergism between platelets and leukocytes in inducing endothelial
cell apoptosis in the cold ischemic rat liver: a Kupffer
cell-mediated injury. FASEB J. 15:1230–1232. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giakoustidis DE, Iliadis S, Tsantilas D,
et al: Blockade of Kupffer cells by gadolinium chloride reduces
lipid peroxidation and protects liver from ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Hepatogastroenterology. 50:1587–1592. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jahnke C, Mehrabi A, Golling M, et al:
Evaluation of microperfusion disturbances in the transplanted liver
after Kupffer cell destruction using GdCl3: An
experimental porcine study. Transplant Proc. 38:1588–1595. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen Y, Liu Z, Liang S, et al: Role of
Kupffer cells in the induction of tolerance of orthotopic liver
transplantation in rats. Liver Transpl. 14:823–836. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen Y, Liu H, Liu Z, et al: Blockade of
inducible costimulator pathway to prevent acute rejection in rat
liver transplantation. Am J Surg. 198:244–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xie X, Ye Y, Zhou L, et al: Küpffer cells
promote acute rejection via induction of Th17 differentiation in
rat liver allografts. Transplant Proc. 42:3784–3792. 2010.
|
|
10
|
Delrivière L, Gibbs P, Kobayashi E, et al:
Technical details for safer venous and biliary anastomoses for
liver transplantation in the rat. Microsurgery. 18:12–18.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen GS and Qi HZ: Effect of Kupffer cells
on immune tolerance in liver transplantation. Asian Pac J Trop Med.
5:970–972. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tiegs G and Lohse AW: Immune tolerance:
what is unique about the liver. J Autoimmun. 34:1–6. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
You Q, Cheng L, Kedl RM and Ju C:
Mechanism of T cell tolerance induction by murine hepatic Kupffer
cells. Hepatology. 48:978–990. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jones C, Badger SA, Hoper M, et al:
Hepatic cytokine response can be modulated using the Kupffer cell
blocker gadolinium chloride in obstructive jaundice. Int J Surg.
11:46–51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lorenzo LP, Shatynski KE, Clark S, et al:
Defective thymic progenitor development and mature T-cell responses
in a mouse model for Down syndrome. Immunology. 139:447–458. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Llacuna L, Marí M, Lluis JM, et al:
Reactive oxygen species mediate liver injury through parenchymal
nuclear factor-kappaB inactivation in prolonged
ischemia/reperfusion. Am J Pathol. 174:1776–1785. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao X, Boenisch O, Yeung M, et al:
Critical role of proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 in allograft
rejection and tolerance. Am J Transplant. 12:90–101. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao J, Li P and Gao S: Effect of
TGF-beta1 on the expression of IL-12, IL-15, IL-18, IL-4 and IL-10
in heart transplantation rejection in rats. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 27:643–645. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Yan T, Shi LJ, et al: Knockdown of
interleukin-2 by shRNA-mediated RNA interference prolongs liver
allograft survival. J Surg Res. 159:582–587. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen Y, Chen J, Liu Z, et al: Relationship
between TH1/TH2 cytokines and immune tolerance in liver
transplantation in rats. Transplant Proc. 40:2691–2695. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liao W, Zeng F, Kang K, et al: Lipoxin A4
attenuates acute rejection via shifting TH1/TH2 cytokine balance in
rat liver transplantation. Transplant Proc. 45:2451–2454. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Feng JF, Chen F, Liu H, et al: Induction
of immune tolerance by pre-infusion of apoptotic lymphocytes
derived from peripheral blood of donor rats before liver
transplantation. Minerva Chir. 68:183–189. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hu A, Li Q, Shi H, et al: Donor-derived
bone marrow transfusion produces mixed chimerism and promotes a Th2
shift in Th1/Th2 balance in rat heterotopic small bowel
transplantation. Dig Liver Dis. 44:988–994. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lian ZR, Xu YF, Wang XB, et al:
Suppression of histone deacetylase 11 promotes expression of IL-10
in Kupffer cells and induces tolerance following orthotopic liver
transplantation in rats. J Surg Res. 174:359–368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|