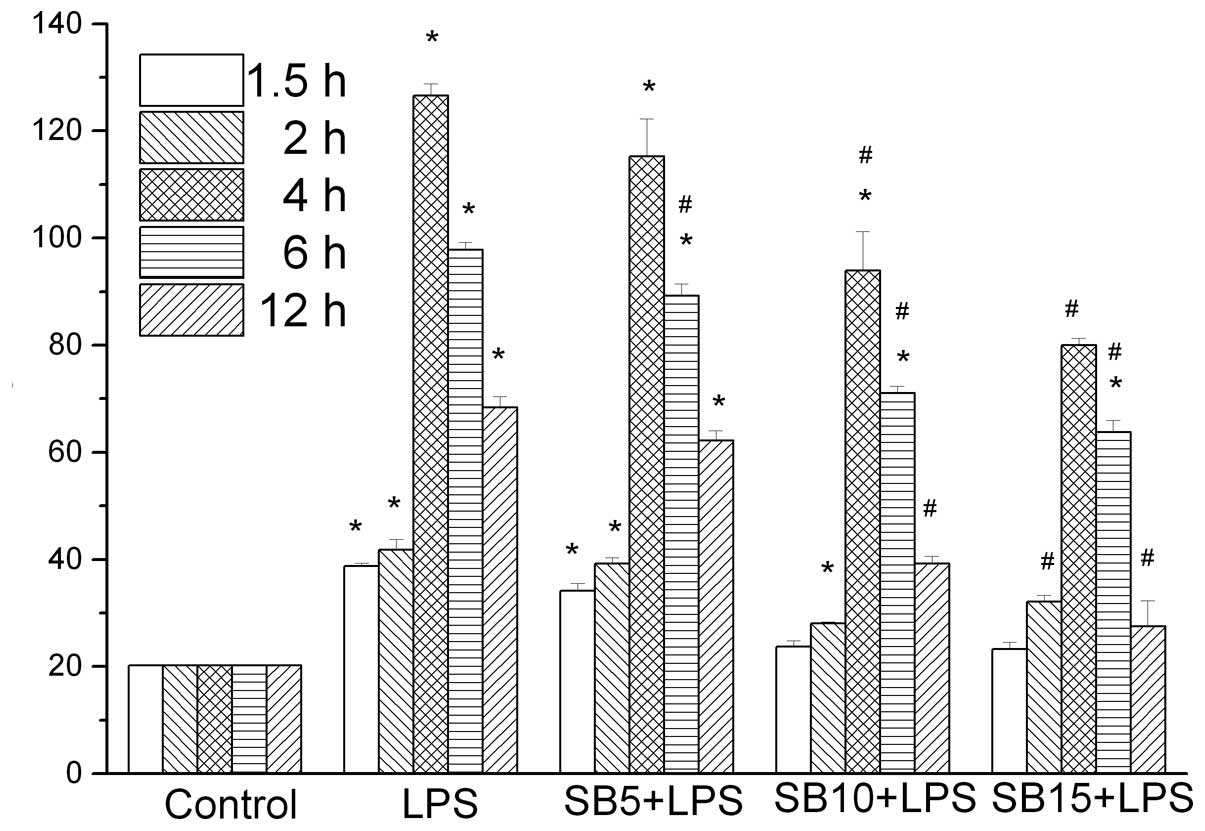
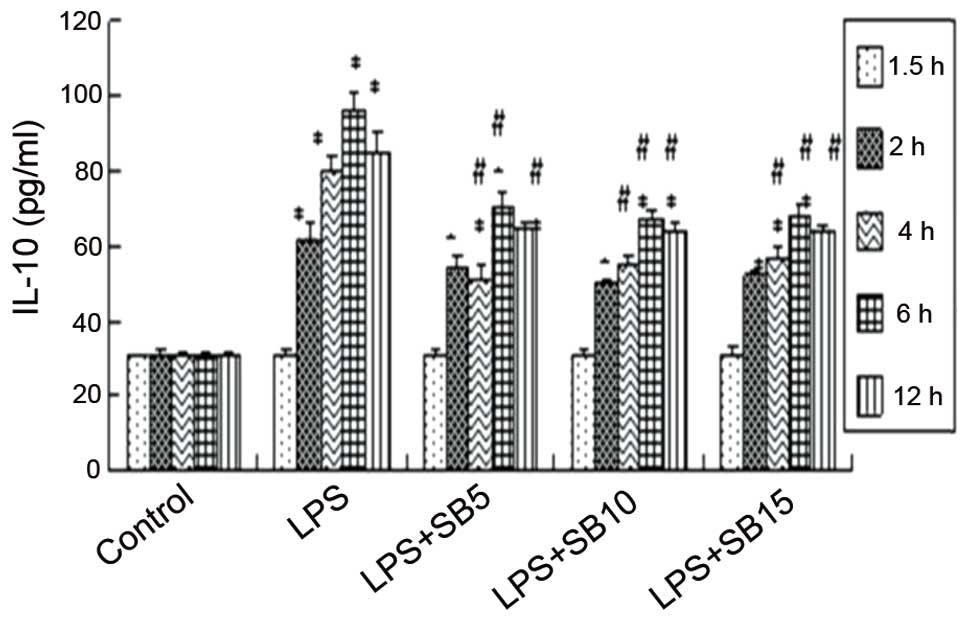
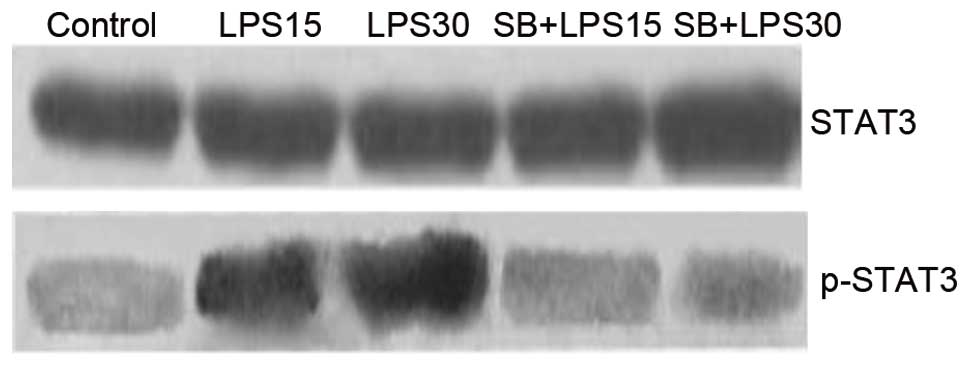
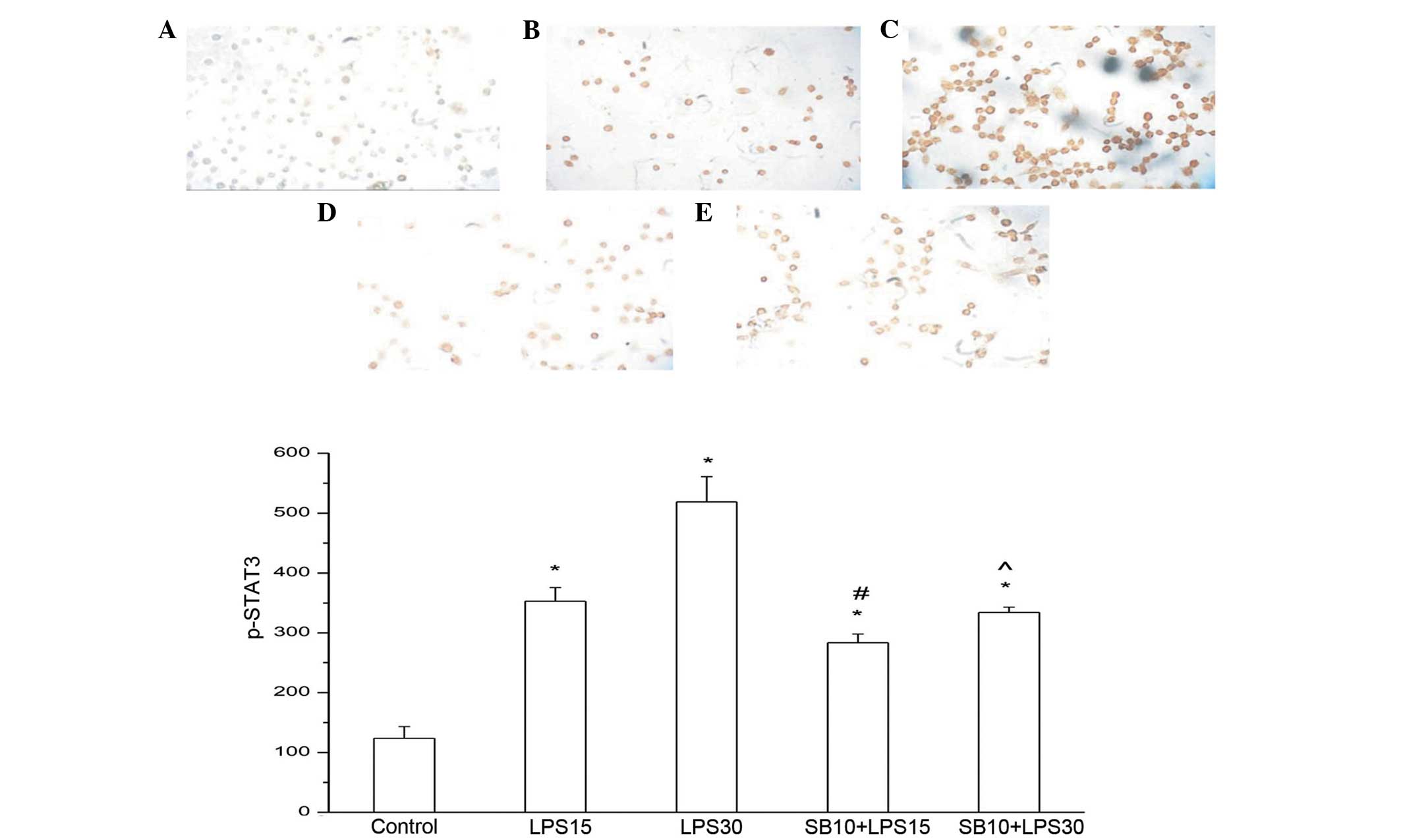
|
1
|
Todd NW, Luzina IG and Atamas SP:
Molecular and cellular mechanisms of pulmonary fibrosis.
Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 5:112012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Barnes PJ: Alveolar macrophages as
orchestrators of COPD. COPD. 1:59–70. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gao H and Ward PA: STAT3 and suppressor of
cytokine signaling 3: potential targets in lung inflammatory
responses. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 11:869–880. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jansson AH, Eriksson C and Wang X: Lung
inflammatory responses and hyperinflation induced by an
intratracheal exposure to lipopolysaccharide in rats. Lung.
182:163–171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kemp MW, Kannan PS, Saito M, et al:
Selective exposure of the fetal lung and skin/amnion (but not
gastro-intestinal tract) to LPS elicits acute systemic inflammation
in fetal sheep. PLoS One. 8:e633552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li X, Li Z, Zheng Z, Liu Y and Ma X:
Unfractionated heparin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung
inflammation by downregulating nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway.
Inflammation. 36:1201–1208. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jarrar D, Kuebler JF, Rue LW 3rd, et al:
Alveolar macrophage activation after trauma-hemorrhage and sepsis
is dependent on NF-kappaB and MAPK/ERK mechanisms. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 283:L799–L805. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang H, Yan C, Cao J, et al: An essential
role for Stat3 in regulating IgG immune complex-induced pulmonary
inflammation. FASEB J. 25:4292–4300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ling YL, Meng AH, Zhao XY, et al: Effect
of cholecystokinin on cytokines during endotoxic shock in rats.
World J Gastroenterol. 7:667–671. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meng AH, Ling YL, Zhang XP and Zhang JL:
Anti-inflammatory effect of cholecystokinin and its signal
transduction mechanism in endotoxic shock rat. World J
Gastroenterol. 8:712–717. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meng AH, Ling YL, Zhang XP, Zhao XY and
Zhang JL: CCK-8 inhibits expression of TNF-α in the spleen of
endotoxic shock rats and signal transduction mechanism of p38 MAPK.
World J Gastroenterol. 8:139–143. 2002.
|
|
12
|
Song KS, Yoon JH, Kim KS and Ahn DW:
c-Ets1 inhibits the interaction of NF-κB and CREB, and
downregulates IL-1β-induced MUC5AC overproductionduring airway
inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 5:207–215. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wijagkanalan W, Kawakami S, Higuchi Y, et
al: Intratracheally instilled mannosylated cationic liposome/NFκB
decoy complexes for effective prevention of LPS-induced lung
inflammation. J Control Release. 149:42–50. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lomas-Neira J, Chung CS, Perl M, et al:
Role of alveolar macrophage and migrating neutrophils in
hemorrhage-induced priming for ALI subsequent to septic challenge.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 290:L51–L58. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schnyder-Candrian S, Quesniaux VF, Di
Padova F, et al: Dual effects of p38 MAPK on TNF-dependent
bronchoconstriction and TNF-independent neutrophil recruitment in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome. J
Immunol. 175:262–269. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nishiki S, Hato F, Kamata N, et al:
Selective activation of STAT3 in human monocytes stimulated by
G-CSF: implication in inhibition of LPS-induced TNF-alpha
production. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 286:C1302–C1311. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang YJ, Chen J, Otsuka M, et al:
Macrophage deletion of p38alpha partially impairs
lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular activation. J Immunol.
180:5075–5082. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Campbell J, Ciesielski CJ, Hunt AE, et al:
A novel mechanism for TNF-alpha regulation by p38 MAPK: involvement
of NF-kappa B with implications for therapy in rheumatoid
arthritis. J Immunol. 173:6928–6937. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu FQ, Liu Y, Lui VC, Lamb JR, Tam PK and
Chen Y: Hypoxia modulates lipopolysaccharide induced TNF-alpha
expression in murine macrophages. Exp Cell Res. 314:1327–1336.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao Q, Shepherd EG, Manson ME, et al: The
role of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in the
response of alveolar macrophages to lipopolysaccharide: attenuation
of proinflammatory cytokine biosynthesis via feedback control of
p38. J Biol Chem. 280:8101–8108. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ehlting C, Lai WS, Schaper F, et al:
Regulation of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) mRNA
stability by TNF-alpha involves activation of the MKK6/p38MAPK/MK2
cascade. J Immunol. 178:2813–2826. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li W, Huang H, Zhang Y, Fan T, Liu X, Xing
W and Niu X: Anti-inflammatory effect of tetrahydrocoptisine from
Corydalis impatiens is a function of possible inhibition of TNF-α,
IL-6 and NO production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peritoneal
macrophages through inhibiting NF-κB activation and MAPK pathway.
Eur J Pharmacol. 715:62–71. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Soromou LW, Chu X, Jiang L, Wei M, Huo M,
Chen N, Guan S, Yang X, Chen C, Feng H and Deng X: In vitro and in
vivo protection provided by pinocembrin against
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses. Int
Immunopharmacol. 14:66–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Geiser T: Inflammatory cytokines and
chemokines in acute inflammatory disease. Schweiz Med Wochenschr.
129:540–546. 1999.(In German).
|
|
25
|
Sumita N, Bito T, Nakajima K and Nishigori
C: Stat3 activation is required for cell proliferation and
tumorigenesis but not for cell viability in cutaneous squamouscell
carcinoma cell lines. Exp Dermatol. 15:291–299. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Severgnini M, Takahashi S, Rozo LM, et al:
Activation of the STAT pathway in acute lung injury. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 286:L1282–L1292. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
El Kasmi KC, Holst J, Coffre M, et al:
General nature of the STAT3-activated anti-inflammatory response. J
Immunol. 177:7880–7888. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Prêle CM, Keith-Magee AL, Murcha M and
Hart PH: Activated signal transducer and activator of
transcription-3 (STAT3) is a poor regulator of tumour necrosis
factor-alpha production by human monocytes. Clin Exp Immunol.
147:564–572. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsukawa A, Kudo S, Maeda T, Numata K,
Watanabe H, Takeda K, Akira S and Ito T: Stat3 in resident
macrophages as a repressor protein of inflammatory response. J
Immunol. 175:3354–3359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gao H, Guo RF, Speyer CL, et al: STAT3
activation in acute lung injury. J Immunol. 172:7703–7712. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chappell VL, Le LX, LaGrone L and Mileski
WJ: Stat proteins play a role in tumor necrosis factor alpha gene
expression. Shock. 14:400–403. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abreu MT, Arnold ET, Thomas LS, et al:
TLR4 and MD-2 expression is regulated by immune-mediated signals in
human intestinal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 277:20431–20437.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Jong PR, Schadenberg AW, van den Broek
T, et al: STAT3 regulates monocyte TNF-alpha production in systemic
inflammation caused by cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass.
PLoS One. 7:e350702012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qin H, Roberts KL, Niyongere SA, Cong Y,
Elson CO and Benveniste EN: Molecular mechanism of
lipopolysaccharide-induced SOCS-3 gene expression in macrophages
and microglia. J Immunol. 179:5966–5976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Park SY, Baik YH, Cho JH, Kim S, Lee KS
and Han JS: Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide
synthesis by nicotine through S6K1-p42/44 MAPK pathwayand STAT3
(Ser 727) phosphorylation in Raw 264.7 cells. Cytokine. 44:126–134.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ipaktchi K, Mattar A, Niederbichler AD, et
al: Attenuating burn wound inflammatory signaling reduces systemic
inflammation and acute lung injury. J Immunol. 177:8065–8071. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen Y, Kam CS, Liu FQ, et al: LPS-induced
up-regulation of TGF-beta receptor 1 is associated with TNF-alpha
expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. J Leukoc Biol.
83:1165–1173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|