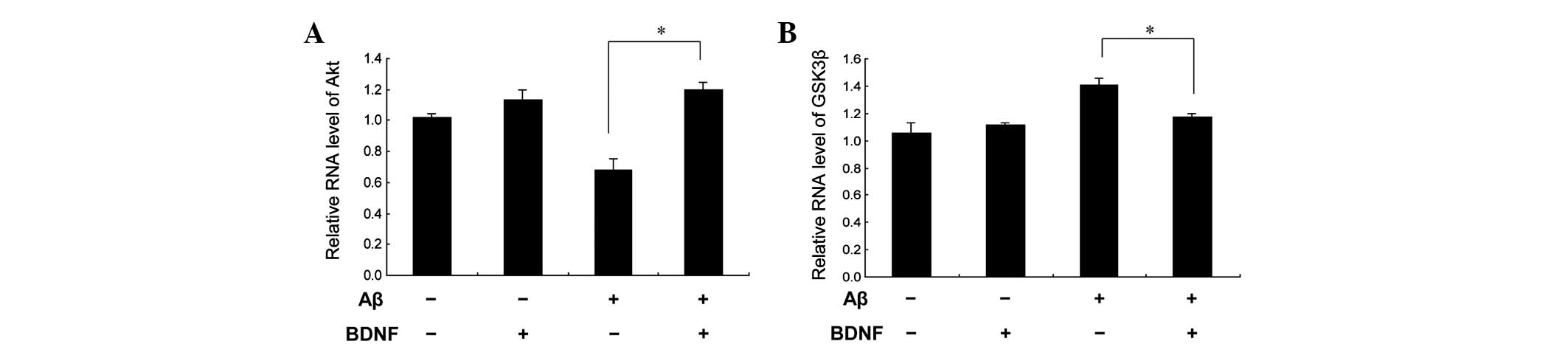
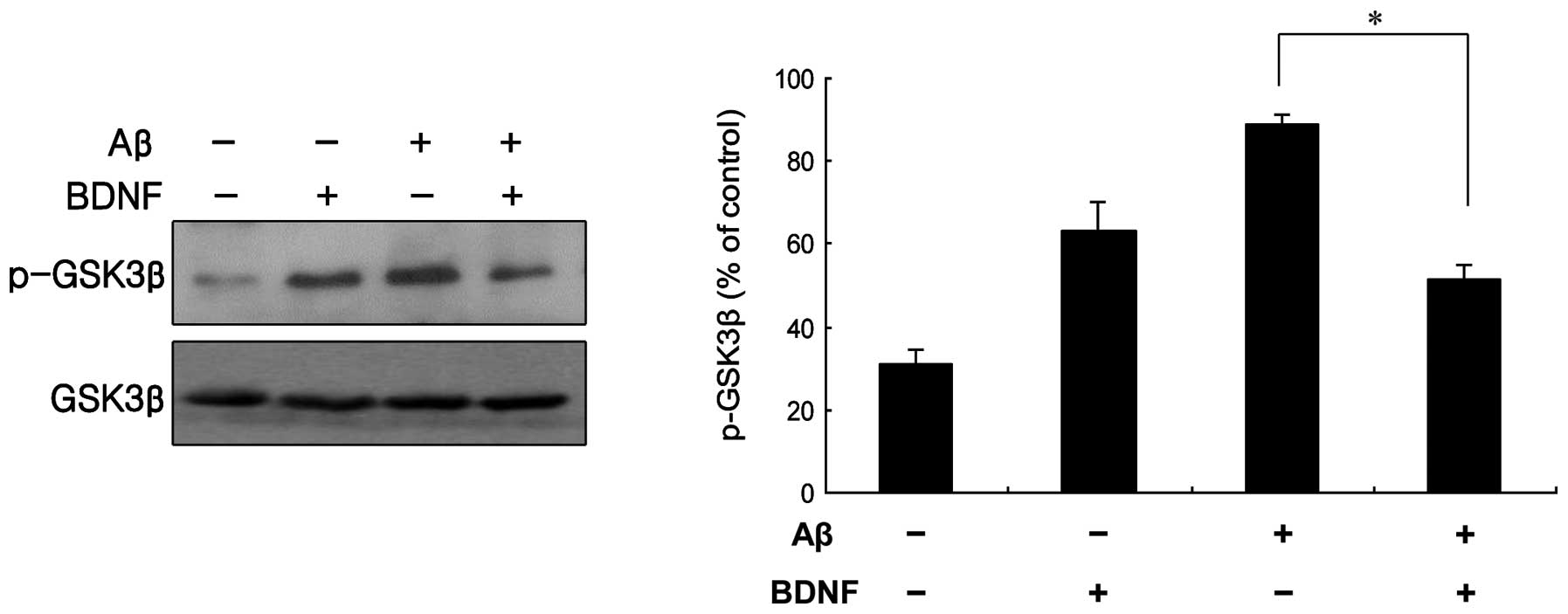
|
1
|
Mesulam MM: Neuroplasticity failure in
Alzheimer’s disease: bridging the gap between plaques and tangles.
Neuron. 24:521–529. 1999.
|
|
2
|
Dickson DW: Neuropathology of Alzheimer’s
disease and other dementias. Clin Geriatr Med. 17:209–228.
2001.
|
|
3
|
Song B, Davis K, Liu XS, Lee HG, Smith M
and Liu X: Inhibition of Polo-like kinase 1 reduces
beta-amyloid-induced neuronal cell death in Alzheimer’s disease.
Aging (Albany NY). 3:846–851. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Selkoe DJ: Alzheimer’s disease is a
synaptic failure. Science. 298:789–791. 2002.
|
|
5
|
Yankner BA: Mechanisms of neuronal
degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron. 16:921–932. 1996.
|
|
6
|
Götz J and Ittner LM: Animal models of
Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia. Nat Rev Neurosci.
9:532–544. 2008.
|
|
7
|
Poo MM: Neurotrophins as synaptic
modulators. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2:24–32. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lindvall O, Kokaia Z, Bengzon J, Elmér E
and Kokaia M: Neurotrophins and brain insults. Trends Neurosci.
17:490–496. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lewin GR and Barde YA: Physiology of the
neurotrophins. Annu Rev Neurosci. 19:289–317. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich
M and Hemmings BA: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by
insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature. 378:785–789. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun L, Guo C, Liu D and Zhao Y, Zhang Y,
Song Z, Han H, Chen D and Zhao Y: Protective effects of bone
morphogenetic protein 7 against amyloid-beta induced neurotoxicity
in PC12 cells. Neuroscience. 184:151–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abràmoff MD, Magalhães PJ and Ram SJ:
Image processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics International. 11:36–42.
2004.
|
|
13
|
Zhao R, Zhang Z, Song Y, Wang D, Qi J and
Wen S: Implication of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt/glycogen
synthase kinase-3β pathway in ginsenoside Rb1’s attenuation of
beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity and tau phosphorylation. J
Ethnopharmacol. 133:1109–1116. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Amtul Z, Uhrig M and Beyreuther K:
Additive effects of fatty acid mixtures on the levels and ratio of
amyloid β40/42 peptides differ from the effects of individual fatty
acids. J Neurosci Res. 89:1795–1801. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hongpaisan J, Sun MK and Alkon DL: PKC ɛ
activation prevents synaptic loss, Aβ elevation, and cognitive
deficits in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. J Neurosci.
31:630–643. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Kaminsky YG, Marlatt MW, Smith MA and
Kosenko EA: Subcellular and metabolic examination of amyloid-beta
peptides in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis: evidence for
Abeta(25–35). Exp Neurol. 221:26–37. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng S, Wuu J, Mufson EJ and Fahnestock M:
Precursor form of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mature
brain-derived neurotrophic factor are decreased in the pre-clinical
stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 93:1412–1421.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Laske C, Stransky E, Leyhe T, Eschweiler
GW, Maetzler W, Wittorf A, Soekadar S, Richartz E, Koehler N,
Bartels M, Buchkremer G and Schott K: BDNF serum and CSF
concentrations in Alzheimer’s disease, normal pressure
hydrocephalus and healthy controls. J Psychiatr Res. 41:387–394.
2007.
|
|
19
|
Murer MG, Boissiere F, Yan Q, Hunot S,
Villares J, Faucheux B, Agid Y, Hirsch E and Raisman-Vozari R: An
immunohistochemical study of the distribution of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor in the adult human brain, with particular
reference to Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience. 88:1015–1032.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Koide H, Asai T, Furuya K, Tsuzuku T, Kato
H, Dewa T, Nango M, Maeda N and Oku N: Inhibition of Akt (ser473)
phosphorylation and rapamycin-resistant cell growth by knockdown of
mammalian target of rapamycin with small interfering RNA in
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1-targeting vector.
Biol Pharm Bull. 34:602–608. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mannoury la Cour C, Salles MJ, Pasteau V
and Millan MJ: Signaling pathways leading to phosphorylation of Akt
and GSK-3β by activation of cloned human and rat cerebral
D2 and D3 receptors. Mol Pharmacol.
79:91–105. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Sánchez-Blázquez P, Rodríguez-Muñoz M and
Garzón J: Mu-opioid receptors transiently activate the Akt-nNOS
pathway to produce sustained potentiation of PKC-mediated
NMDAR-CaMKII signaling. PLoS One. 5:e112782010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Soriano FX, Papadia S, Hofmann F,
Hardingham NR, Bading H and Hardingham GE: Preconditioning doses of
NMDA promote neuroprotection by enhancing neuronal excitability. J
Neurosci. 26:4509–4518. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grimes CA and Jope RS: The multifaceted
roles of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta in cellular signaling. Prog
Neurobiol. 65:391–426. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Beaulieu JM, Gainetdinov RR and Caron MG:
Akt/GSK3 signaling in the action of psychotropic drugs. Annu Rev
Pharmacol Toxicol. 49:327–347. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|