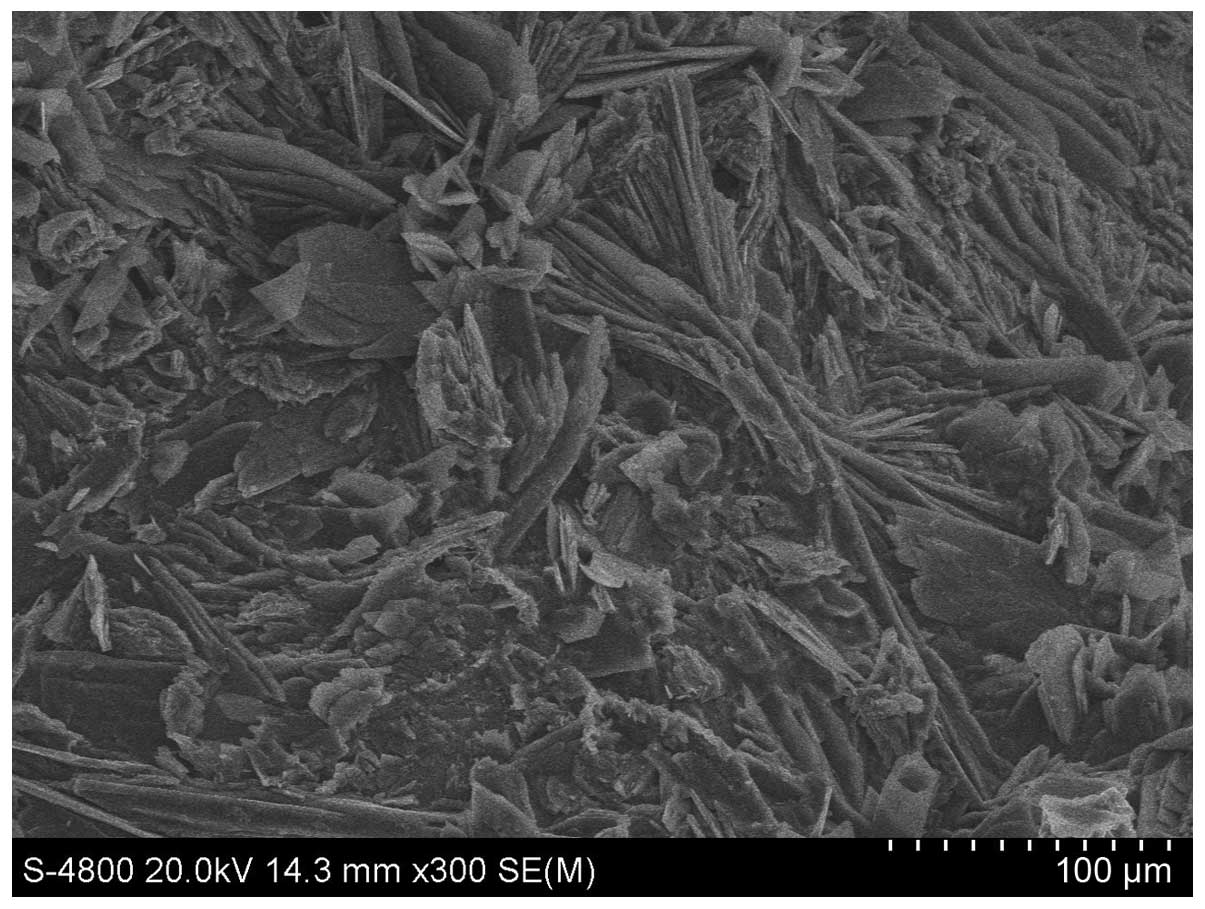
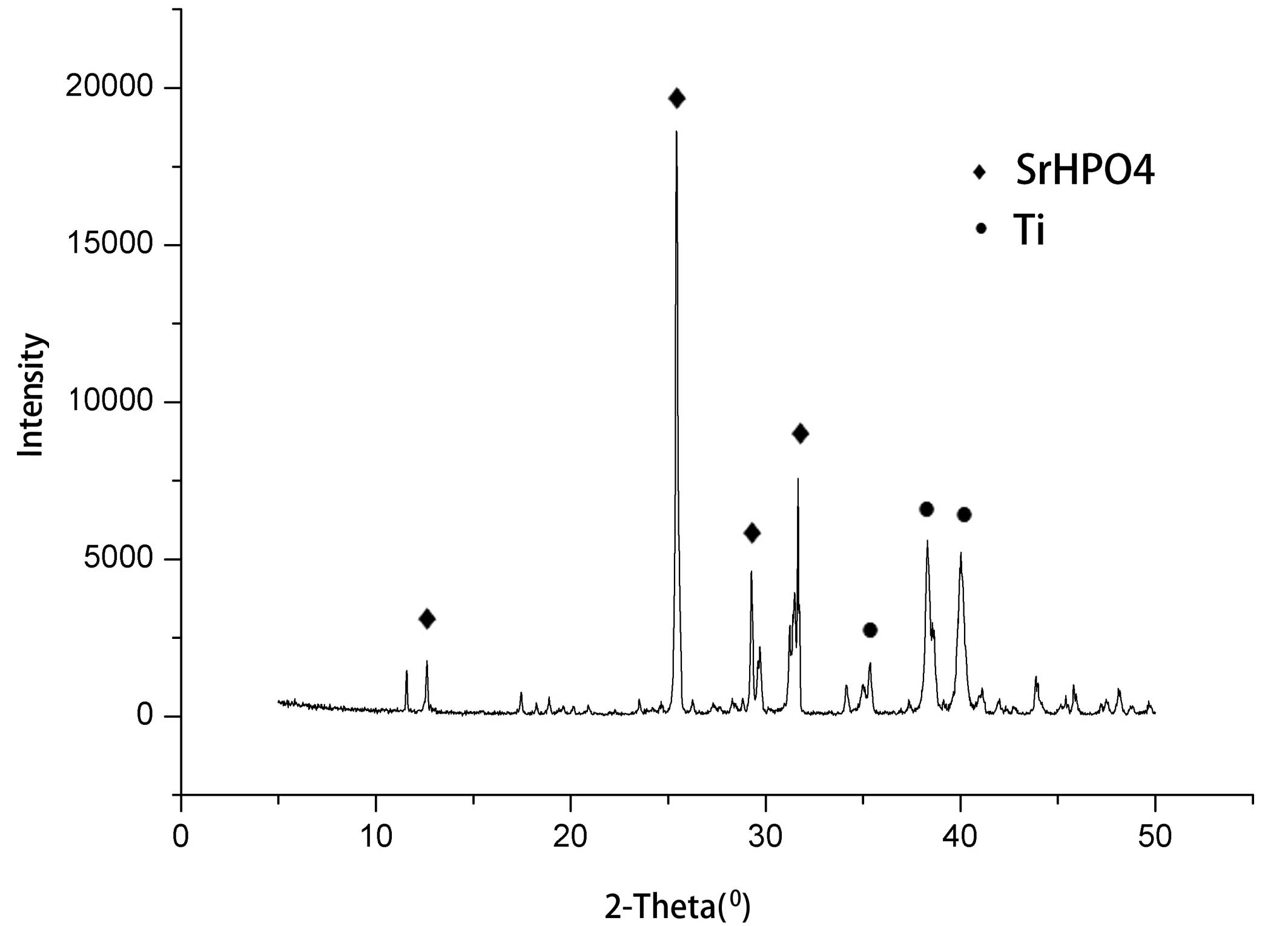
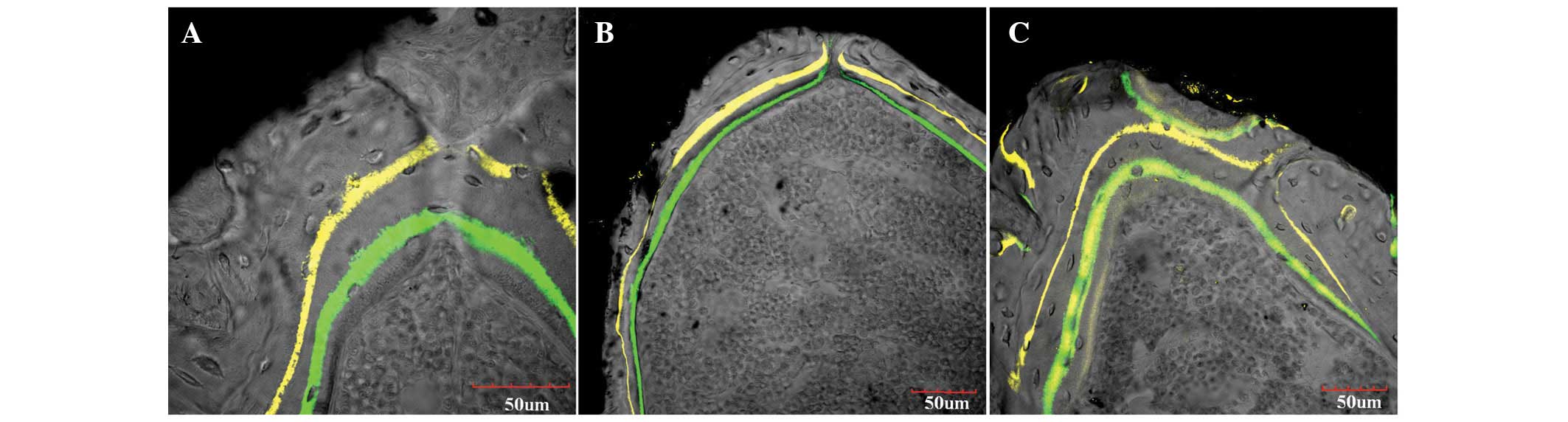
|
1
|
Akca K, Sarac E, Baysal U, Fanuscu M,
Chang TL and Cehreli M: Micro-morphologic changes around
biophysically-stimulated titanium implants in ovariectomized rats.
Head Face Med. 3:282007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Goldhahn J, Seebeck J, Frei R, Frenz B,
Antoniadis I and Schneider E: New implant designs for fracture
fixation in osteoporotic bone. Osteoporos Int. 16(Suppl 2):
S112–S119. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Marco F, Milena F, Gianluca G and Vittoria
O: Peri-implant osteogenesis in health and osteoporosis. Micron.
36:630–644. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Soen S, Fukunaga M, Sugimoto T, et al:
Japanese Society for Bone and Mineral Research and Japan
Osteoporosis Society Joint Review Committee for the Revision of the
Diagnostic Criteria for Primary Osteoporosis: Diagnostic criteria
for primary osteoporosis: year 2012 revision. J Bone Miner Metab.
31:247–257. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Viera-Negrón YE, Ruan WH, Winger JN, Hou
X, Sharawy MM and Borke JL: Effect of ovariectomy and alendronate
on implant osseointegration in rat maxillary bone. J Oral
Implantol. 34:76–82. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Du Z, Chen J, Yan F and Xiao Y: Effects of
Simvastatin on bone healing around titanium implants in
osteoporotic rats. Clin Oral Implants Res. 20:145–150. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ohkawa Y, Tokunaga K and Endo N:
Intermittent administration of human parathyroid hormone (1–34)
increases new bone formation on the interface of hydroxyapatite
coated titanium rods implanted into ovariectomized rat femora. J
Orthop Sci. 3:533–542. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Brennan TC, Rybchyn MS, Green W, Atwa S,
Conigrave AD and Mason RS: Osteoblasts play key roles in the
mechanisms of action of strontium ranelate. Br J Pharmacol.
157:1291–1300. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fonseca JE: Rebalancing bone turnover in
favour of formation with strontium ranelate: implications for bone
strength. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47(Suppl 4): iv17–iv19. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Le Nihouannen D, Hacking SA, Gbureck U,
Komarova SV and Barralet JE: The use of RANKL-coated brushite
cement to stimulate bone remodelling. Biomaterials. 29:3253–3259.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qi MC, Zhou XQ, Hu J, et al: Oestrogen
replacement therapy promotes bone healing around dental implants in
osteoporotic rats. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 33:279–285. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qi M, Hu J, Li J, et al: Effect of
zoledronate acid treatment on osseointegration and fixation of
implants in autologous iliac bone grafts in ovariectomized rabbits.
Bone. 50:119–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Herrmann I, Lekholm U, Holm S and Kultje
C: Evaluation of patient and implant characteristics as potential
prognostic factors for oral implant failures. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Implants. 20:220–230. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Motohashi M, Shirota T, Tokugawa Y, Ohno
K, Michi K and Yamaguchi A: Bone reactions around
hydroxyapatite-coated implants in ovariectomized rats. Oral Surg
Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 87:145–152. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mori H, Manabe M, Kurachi Y and Nagumo M:
Osseointegration of dental implants in rabbit bone with low mineral
density. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 55:351–362. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujimoto T, Niimi A, Sawai T and Ueda M:
Effects of steroid-induced osteoporosis on osseointegration of
titanium implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 13:183–189.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang S, Lee SJ, Ahn SJ, Heo MS and Kim TW:
Bone thickness of the palate for orthodontic mini-implant anchorage
in adults. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 131(4 Suppl): S74–S81.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ohmae M, Saito S, Morohashi T, et al: A
clinical and histological evaluation of titanium mini-implants as
anchors for orthodontic intrusion in the beagle dog. Am J Orthod
Dentofacial Orthop. 119:489–497. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ozawa S, Ogawa T, Iida K, et al:
Ovariectomy hinders the early stage of bone-implant integration:
histomorphometric, biomechanical, and molecular analyses. Bone.
30:137–143. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bonnelye E, Chabadel A, Saltel F and
Jurdic P: Dual effect of strontium ranelate: stimulation of
osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation
and resorption in vitro. Bone. 42:129–138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ni GX, Yao ZP, Huang GT, Liu WG and Lu WW:
The effect of strontium incorporation in hydroxyapatite on
osteoblasts in vitro. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 22:961–967. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Choudhary S, Halbout P, Alander C, Raisz L
and Pilbeam C: Strontium ranelate promotes osteoblastic
differentiation and mineralization of murine bone marrow stromal
cells: involvement of prostaglandins. J Bone Miner Res.
22:1002–1010. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Capuccini C, Torricelli P, Sima F, et al:
Strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite coatings synthesized by
pulsed-laser deposition: in vitro osteoblast and osteoclast
response. Acta Biomater. 4:1885–1893. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Caverzasio J and Thouverey C: Activation
of FGF receptors is a new mechanism by which strontium ranelate
induces osteoblastic cell growth. Cell Physiol Biochem. 27:243–250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Baier M, Staudt P, Klein R, et al:
Strontium enhances osseointegration of calcium phosphate cement: a
histomorphometric pilot study in ovariectomized rats. J Orthop Surg
Res. 8:162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pan HB, Zhao XL, Zhang X, et al: Strontium
borate glass: potential biomaterial for bone regeneration. J R Soc
Interface. 7:1025–1031. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|