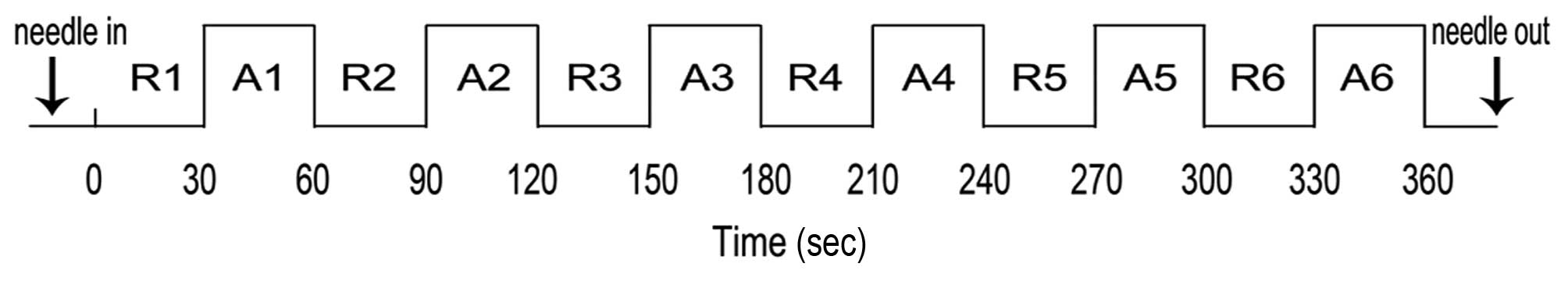
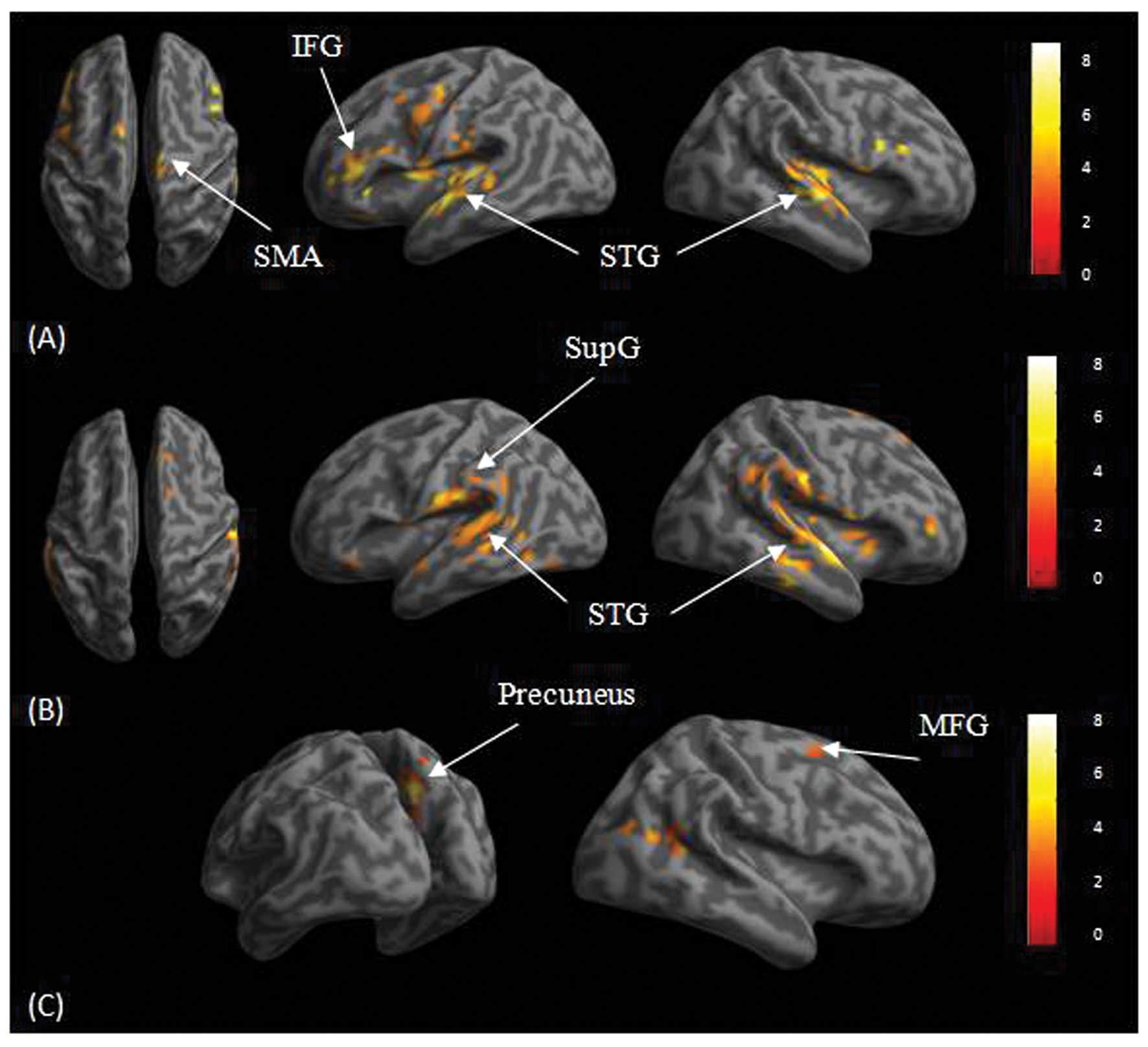
|
1
|
Diehl DL, Kaplan G, Coulter I, Glik D and
Hurwitz EL: Use of acupuncture by American physicians. J Altern
Complement Med. 3:119–126. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
No authors listed. NIH Consensus
Conference. Acupuncture. JAMA. 280:1518–1524. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
World Health Organization. Acupuncture:
Review and Analysis of Reports on Controlled Clinical Trials. WHO
Western Pacific Region; Geneva, Switzerland: 2003
|
|
4
|
Mayer DJ: Acupuncture: an evidence-based
review of the clinical literature. Annu Rev Med. 51:49–63. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li L, Liu H, Li YZ, et al: The human brain
response to acupuncture on same-meridian acupoints: evidence from
an fMRI study. J Altern Complement Med. 14:673–678. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chang S: Physiological rhythms, dynamical
diseases and acupuncture. Chin J Physiol. 53:77–90. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee MS, Lee YH, Shin BC, et al: Is there
any energy transfer during acupuncture? Am J Chin Med. 33:507–512.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Slopek A and Feng HT: Qi, time and
acupuncture. J Acupunct Tuina Sci. 7:75–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li YM: Effect of warming-needle
acupuncture at different time of the day on superoxide dismutase
and T-cell subsets of old people. Zhong Yi Za Zhi. 22:1840–1842.
2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Xie GG, Zhao CJ, Lu XQ, et al: Effects of
acupuncture at different Shichen (traditional twelve two-hour
periods) on serum SOD and MDA in guinea pigs. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.
27:757–760. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Wu F, Huang R and Xiong KR: Effect of
electroacupuncture intervention at different time-points in a day
on expression of c-fos and neuronal nitric oxide synthase in medial
prefrontal cortex in ketamine addiction rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu.
38:386–392. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhong XY, Su XX, Liu J and Zhu GQ:
Clinical effects of acupuncture combined with nimodipine for
treatment of vascular dementia in 30 cases. J Tradit Chin Med.
29:174–176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang H, Wang M, Guo J and Li Z: The
midnight-noon ebb-flow point selection for 30 cases of acute
ischemic cerebrovascular diseases. J Tradit Chin Med. 28:193–197.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhen JP, Liu C, He JZ, Wang GB, et al: The
research of brain fMRI in acupuncture of KI in different time.
Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Ying Xiang Xue Za Zhi. 6:325–331.
2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Stux G and Hammerschlag R: Clinical
Acupuncture: Scientific Basis. Springer; New York, NY: 2001,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huang W, Pach D, Napadow V, et al:
Characterizing acupuncture stimuli using brain imaging with FMRI -
a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. PLoS One.
7:e329602012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Cho SY, Kim M, Sun JJ, et al: A comparison
of brain activity between healthy subjects and stroke patients on
fMRI by acupuncture stimulation. Chin J Integr Med. 19:269–276.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li G, Jack CR Jr and Yang ES: An fMRI
study of somatosensory-implicated acupuncture points in stable
somatosensory stroke patients. J Magn Reson Imaging. 24:1018–1024.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xue X, You Y, Tao J, et al:
Electro-acupuncture at points of Zusanli and Quchi exerts
anti-apoptotic effect through the modulation of PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway. Neurosci Lett. 558:14–19. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tao J, Chen B, Gao Y, et al:
Electroacupuncture enhances hippocampal NSCs proliferation in
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats via activation of notch
signaling pathway. Int J Neurosci. 124:204–212. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu P, Zhou G, Zhang Y, et al: The hybrid
GLM–ICA investigation on the neural mechanism of acupoint ST36: an
fMRI study. Neurosci Lett. 479:267–271. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cho SY, Jahng GH, Park SU, Jung WS, Moon
SK and Park JM: fMRI study of effect on brain activity according to
stimulation method at LI11, ST36: painful pressure and acupuncture
stimulation of same acupoints. J Altern Complement Med. 16:489–495.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fang J, Jin Z, Wang Y, et al: The salient
characteristics of the central effects of acupuncture needling:
limbic-paralimbic-neocortical network modulation. Hum Brain Mapp.
30:1196–1206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hui KK, Liu J, Marina O, et al: The
integrated response of the human cerebro-cerebellar and limbic
systems to acupuncture stimulation at ST 36 as evidenced by fMRI.
Neuroimage. 27:479–496. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bai L, Qin W, Tian J, et al: Time-varied
characteristics of acupuncture effects in fMRI studies. Hum Brain
Mapp. 30:3445–3460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Claunch JD, Chan ST, Nixon EE, et al:
Commonality and specificity of acupuncture action at three
acupoints as evidenced by FMRI. Am J Chin Med. 40:695–712. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang WT, Jin Z, Luo F, Zhang L, Zeng YW
and Han JS: Evidence from brain imaging with fMRI supporting
functional specificity of acupoints in humans. Neurosci Lett.
354:50–53. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bai L, Tian J, Zhong C, et al: Acupuncture
modulates temporal neural responses in wide brain networks:
evidence from fMRI study. Mol Pain. 6:732010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang XY, Shi GX, Li QQ, Zhang ZH, Xu Q and
Liu CZ: Characterization of deqi sensation and acupuncture effect.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013:3197342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li K, Shan B, Xu J, et al: Changes in FMRI
in the human brain related to different durations of manual
acupuncture needling. J Altern Complement Med. 12:615–623. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yan B, Li K, Xu J, et al:
Acupoint-specific fMRI patterns in human brain. Neurosci Lett.
383:236–240. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, et al:
Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear
approach. Hum Brain Mapp. 2:189–210. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Poldrack RA: Imaging brain plasticity:
conceptual and methodological issues - a theoretical review.
Neuroimage. 12:1–13. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Poldrack RA and Gabrieli JD:
Characterizing the neural mechanisms of skill learning and
repetition priming: evidence from mirror reading. Brain. 124:67–82.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Holmes AP and Friston KJ:
Generalisability, random effects and population inference.
Neuroimage. 7:S7541998.
|
|
36
|
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B,
Papathanassiou D, et al: Automated anatomical labeling of
activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of
the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage. 15:273–289. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Napadow V, Makris N, Liu J, et al: Effects
of electroacupuncture versus manual acupuncture on the human brain
as measured by fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp. 24:193–205. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hui KK, Liu J, Makris N, et al:
Acupuncture modulates the limbic system and subcortical gray
structures of the human brain: evidence from fMRI studies in normal
subjects. Hum Brain Mapp. 9:13–25. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hui KK, Marina O, Claunch JD, et al:
Acupuncture mobilizes the brain’s default mode and its
anti-correlated network in healthy subjects. Brain Res.
1287:84–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Morgane PJ, Galler JR and Mokler DJ: A
review of systems and networks of the limbic forebrain/limbic
midbrain. Prog Neurobiol. 75:143–160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang W, Qi JP, Xia YL, et al: The response
of human motor cortex to acupuncture of S36 and G34 as revealed by
functional MRI. Zhong Hua Wu li Yi Xue Yu Kang Fu Za Zhi.
26:472–475. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
42
|
Schmahmann JD: The cerebrocerebellar
system: anatomic substrates of the cerebellar contribution to
cognition and emotion. Int Rev Psychiatry. 13:247–260. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Beissner F and Henke C: Methodological
problems in FMRI studies on acupuncture: a critical review with
special emphasis on visual and auditory cortex activations. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011:6076372011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Kong J, Gollub RL, Webb JM, et al:
Test-retest study of fMRI signal change evoked by
electroacupuncture stimulation. Neuroimage. 34:1171–1181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|