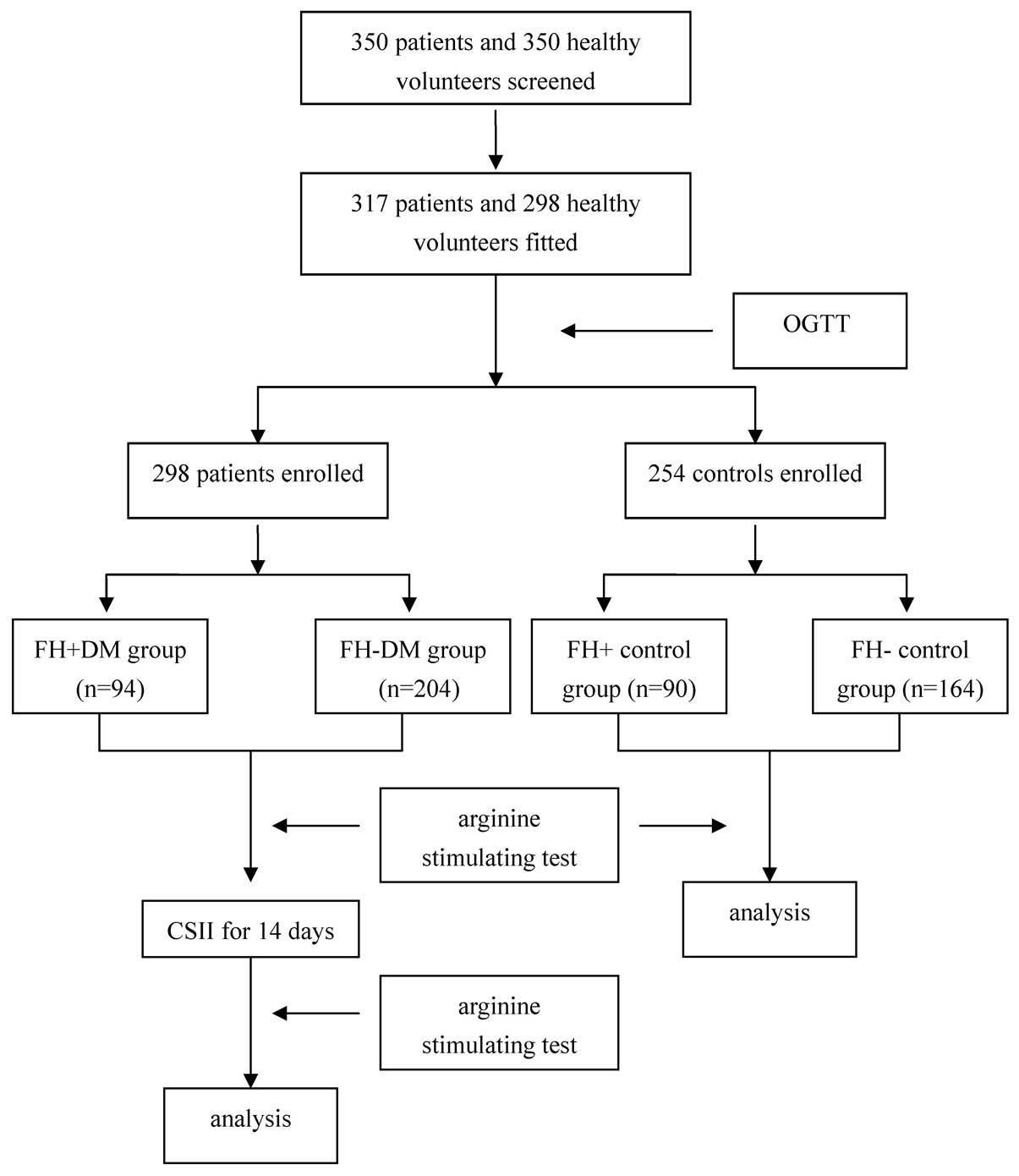
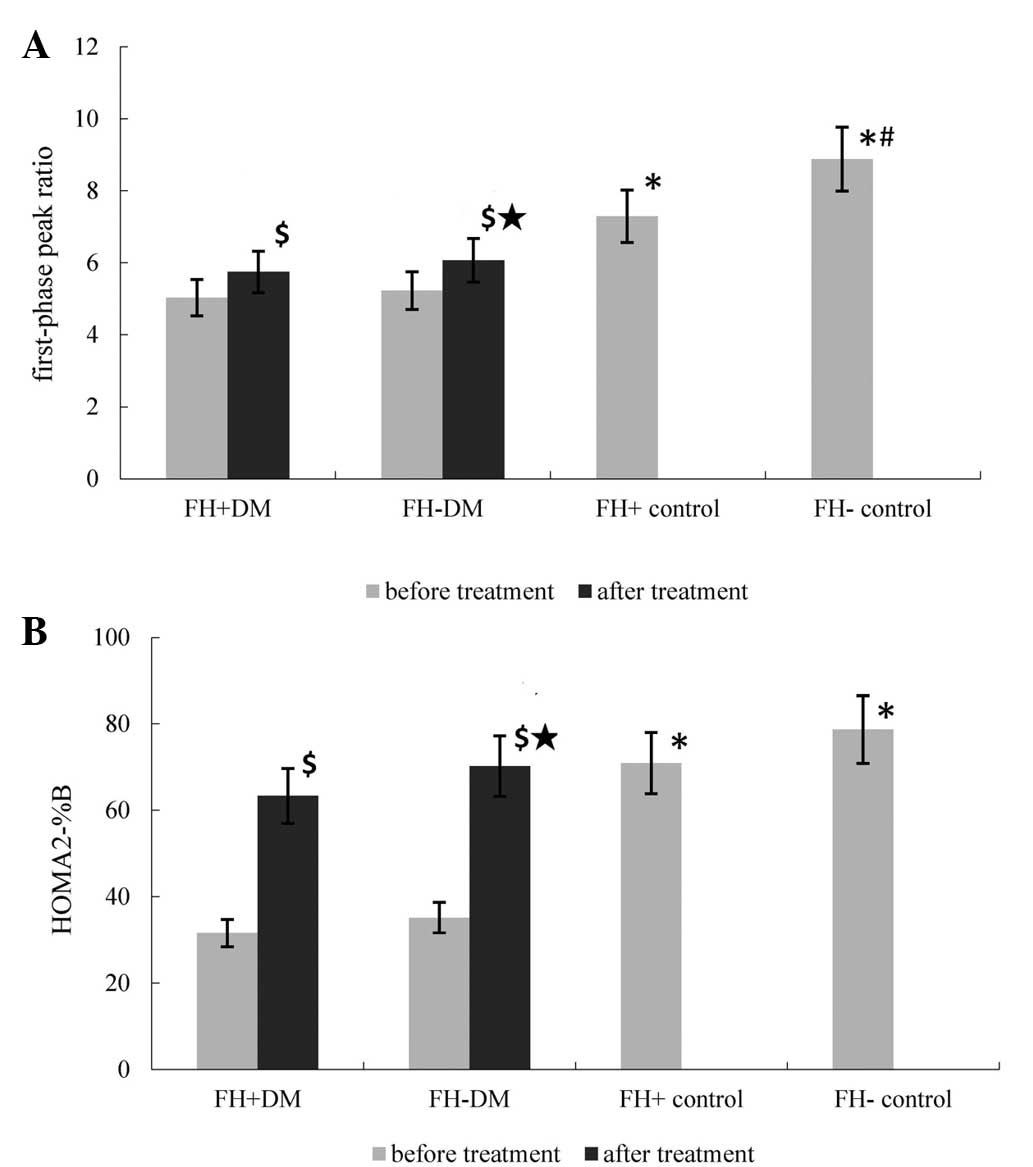
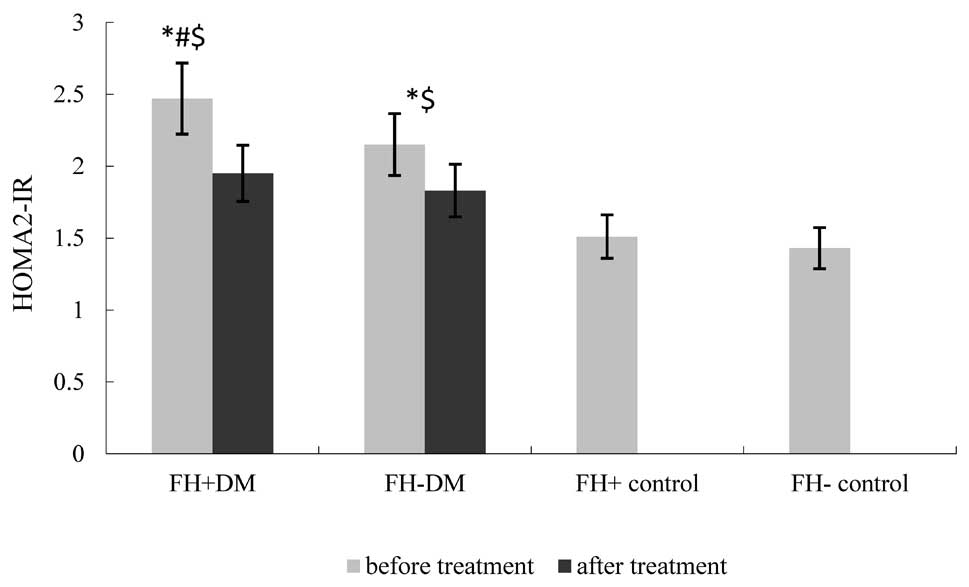
|
1
|
Polonsky KS, Sturis J and Bell GI:
Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston.
Non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus - a genetically programmed
failure of the beta cell to compensate for insulin resistance. N
Engl J Med. 334:777–783. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Retnakaran R and Zinman B: Short-term
intensified insulin treatment in type 2 diabetes: long-term effects
on β-cell function. Diabetes Obes Metab. 14(Suppl 3): 161–166.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tian J, Wang J, Li Y, et al: Endothelial
function in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes receiving
early intensive insulin therapy. Am J Hypertens. 25:1242–1248.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harrison LB, Adams-Huet B, Raskin P and
Lingvay I: β-cell function preservation after 3.5 years of
intensive diabetes therapy. Diabetes Care. 35:1406–1412. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fukui T and Hirano T: High-density
lipoprotein subspecies between patients with type 1 diabetes and
type 2 diabetes without/with intensive insulin therapy. Endocr J.
59:561–569. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen A, Huang Z, Wan X, et al: Attitudes
toward diabetes affect maintenance of drug-free remission in
patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes after short-term
continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion treatment. Diabetes Care.
35:474–481. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fang D, Guan H, Liu J, et al: Early
intensive insulin therapy attenuates the p38 pathway in the renal
cortex and indices of nephropathy in diabetic rats. Endocr J.
59:81–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dailey G: Early and intensive therapy for
management of hyperglycemia and cardiovascular risk factors in
patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Ther. 33:665–678. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Holman RR, Paul SK, Bethel MA, Matthews DR
and Neil HA: 10-year follow-up of intensive glucose control in type
2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 359:1577–1589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gaede P, Lund-Andersen H, Parving HH and
Pedersen O: Effect of a multifactorial intervention on mortality in
type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 358:580–591. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu Y, Li L, Xu Y, et al: Short-term
intensive therapy in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes partially
restores both insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in subjects
with long-term remission. Diabetes Care. 34:1848–1853. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shah PK, Mudaliar S, Chang AR, et al:
Effects of intensive insulin therapy alone and in combination with
pioglitazone on body weight, composition, distribution and liver
fat content in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab.
13:505–510. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weng J, Li Y, Xu W, et al: Effect of
intensive insulin therapy on beta-cell function and glycaemic
control in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a
multicentre randomised parallel-group trial. Lancet. 371:1753–1760.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Valdez R, Yoon PW, Liu T and Khoury MJ:
Family history and prevalence of diabetes in the U.S. population:
the 6-year results from the National Health and Nutrition
Examination Survey (1999–2004). Diabetes Care. 30:2517–2522. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li P, Zhang JF, Li L, et al: The impact of
a family history of type 2 diabetes on insulin secretion and
insulin sensitivity in individuals with varying glucose tolerance.
Am J Med Sci. 345:22–27. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xia Z, Wang Z, Cai Q, et al: Prevalence
and risk factors of type 2 diabetes in the adults in Haikou city,
Hainan island, China. Iran J Public Health. 42:222–230.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Oh YJ, Nam HK, Rhie YJ, Park SH and Lee
KH: Low serum adiponectin levels in Korean children with a family
history of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Horm Res Paediatr. 77:382–387.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Das M, Pal S and Ghosh A: Family history
of type 2 diabetes and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in adult
Asian Indians. J Cardiovasc Dis Res. 3:104–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lambert M: ADA releases revisions to
recommendations for standards of medical care in diabetes. Am Fam
Physician. 85:514–515. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bhowmik B, Diep LM, Munir SB, et al:
HbA(1c) as a diagnostic tool for diabetes and pre-diabetes: the
Bangladesh experience. Diabet Med. 30:e70–e77. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Praveen EP, Sahoo J, Khurana ML, et al:
Insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in normoglycemic offspring
of individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Impact of line of
inheritance. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 16:105–111. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zengi A, Ercan G, Caglayan O, et al:
Increased oxidative DNA damage in lean normoglycemic offspring of
type 2 diabetic patients. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.
119:467–471. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Retnakaran R, Qi Y, Opsteen C, Vivero E
and Zinman B: Initial short-term intensive insulin therapy as a
strategy for evaluating the preservation of beta-cell function with
oral antidiabetic medications: a pilot study with sitagliptin.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 12:909–915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Opsteen C, Qi Y, Zinman B and Retnakaran
R: Effect of short-term intensive insulin therapy on quality of
life in type 2 diabetes. J Eval Clin Pract. 18:256–261. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chon S, Oh S, Kim SW, et al: The effect of
early insulin therapy on pancreatic β-cell function and long-term
glycemic control in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients.
Korean J Intern Med. 25:273–281. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li HQ, Wang BP, Deng XL, et al: Insulin
improves β-cell function in glucose-intolerant rat models induced
by feeding a high-fat diet. Metabolism. 60:1566–1574. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
Zengi A, Ercan G, Caglayan O, et al:
Increased oxidative DNA damage in lean normoglycemic offspring of
type 2 diabetic patients. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.
119:467–471. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|