|
1
|
Diez-Padrisa N, Bassat Q, Machevo S, et
al: Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein for invasive bacterial
pneumonia diagnosis among children in Mozambique, a malaria-endemic
area. PLoS One. 5:e132262010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Banstola A and Banstola A: The
epidemiology of hospitalization for pneumonia in children under
five in the rural western region of Nepal: a descriptive study.
PLoS One. 8:e713112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Seif El Dien HM and Abd ElLatif DAK: The
value of bedside Lung Ultrasonography in diagnosis of neonatal
pneumonia. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 44:339–347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zaidi AKM, Ganatra HA, Syed S, et al:
Effect of case management on neonatal mortality due to sepsis and
pneumonia. BMC Public Health. 11 (Suppl 3):132011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Falade AG and Ayede AI: Epidemiology,
aetiology and management of childhood acute community-acquired
pneumonia in developing countries - a review. Afr J Med Med Sci.
40:293–308. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nissen MD: Congenital and neonatal
pneumonia. Paediatr Respir Rev. 8:195–203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bang AT, Bang RA, Morankar VP, Sontakke PG
and Solanki JM: Pneumonia in neonates: can it be managed in the
community? Arch Dis Child. 68:550–556. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hansen AB, Verder H and Staun-Olsen P:
Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule and C-reactive protein as
early markers of infection in newborns. J Perinat Med. 28:97–103.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Swede H, Hajduk AM, Sharma J, et al:
Baseline serum C-reactive protein and death from colorectal cancer
in the NHANES III cohort. Int J Cancer. 134:1862–1870. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McDade TW, Rutherford J, Adair L and
Kuzawa CW: Early origins of inflammation: microbial exposures in
infancy predict lower levels of C-reactive protein in adulthood.
Proc Biol Sci. 277:1129–1137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jordan KK, Christensen IJ, Heilmann C,
Sengelov H and Muller KG: Pretransplant C-reactive protein as a
prognostic marker in allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Scand J
Immunol. 79:206–213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mukerji R, Mirza S, Roche AM, et al:
Pneumococcal surface protein A inhibits complement deposition on
the pneumococcal surface by competing with the binding of
C-reactive protein to cell-surface phosphocholine. J Immunol.
189:5327–5335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu J, Marjon KD, Marnell LL, et al:
Recognition and functional activation of the human IgA receptor
(FcalphaRI) by C-reactive protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:4974–4979. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martins OM, Fonseca VF, Borges I, Martins
V, Portal VL and Pellanda LC: C-Reactive protein predicts acute
myocardial infarction during high-risk noncardiac and vascular
surgery. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 66:773–776. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jones G, Sebba A, Gu J, et al: Comparison
of tocilizumab monotherapy versus methotrexate monotherapy in
patients with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: the AMBITION
study. Ann Rheum Dis. 69:88–96. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Beisswenger PJ, Brown WV, Ceriello A, et
al: Meal-induced increases in C-reactive protein, interleukin-6 and
tumour necrosis factor α are attenuated by prandial + basal insulin
in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med. 28:1088–1095. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van Wijk DF, Boekholdt SM, Wareham NJ, et
al: C-reactive protein, fatal and nonfatal coronary artery disease,
stroke and peripheral artery disease in the prospective
EPIC-Norfolk cohort study. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
33:2888–2894. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration, .
Kaptoge S, Di Angelantonio E, Lowe G, et al: C-reactive protein
concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke and
mortality: an individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet.
375:132–140. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang X, Zhang J, Liu J, et al: C-reactive
protein promotes adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells via
NADPH oxidase-mediated oxidative stress. J Cell Biochem.
113:857–867. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mogelvang R, Pedersen SH, Flyvbjerg A, et
al: Comparison of osteoprotegerin to traditional atherosclerotic
risk factors and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein for diagnosis
of atherosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 109:515–520. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Vugt SF, Broekhuizen BD, Lammens C, et
al: Grace consortium: Use of serum C reactive protein and
procalcitonin concentrations in addition to symptoms and signs to
predict pneumonia in patients presenting to primary care with acute
cough: diagnostic study. BMJ. 346:F24502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hillas G, Vassilakopoulos T, Plantza P, et
al: C-reactive protein and procalcitonin as predictors of survival
and septic shock in ventilator-associated pneumonia. Eur Respir J.
35:805–811. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Diez-Padrisa N, Bassat Q, Morais L, et al:
Procalcitonin and C-reactive protein as predictors of blood culture
positivity among hospitalised children with severe pneumonia in
Mozambique. Trop Med Int Health. 17:1100–1107. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Koster MJ, Broekhuizen BD, Minnaard MC, et
al: Diagnostic properties of C-reactive protein for detecting
pneumonia in children. Respir Med. 107:1087–1093. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
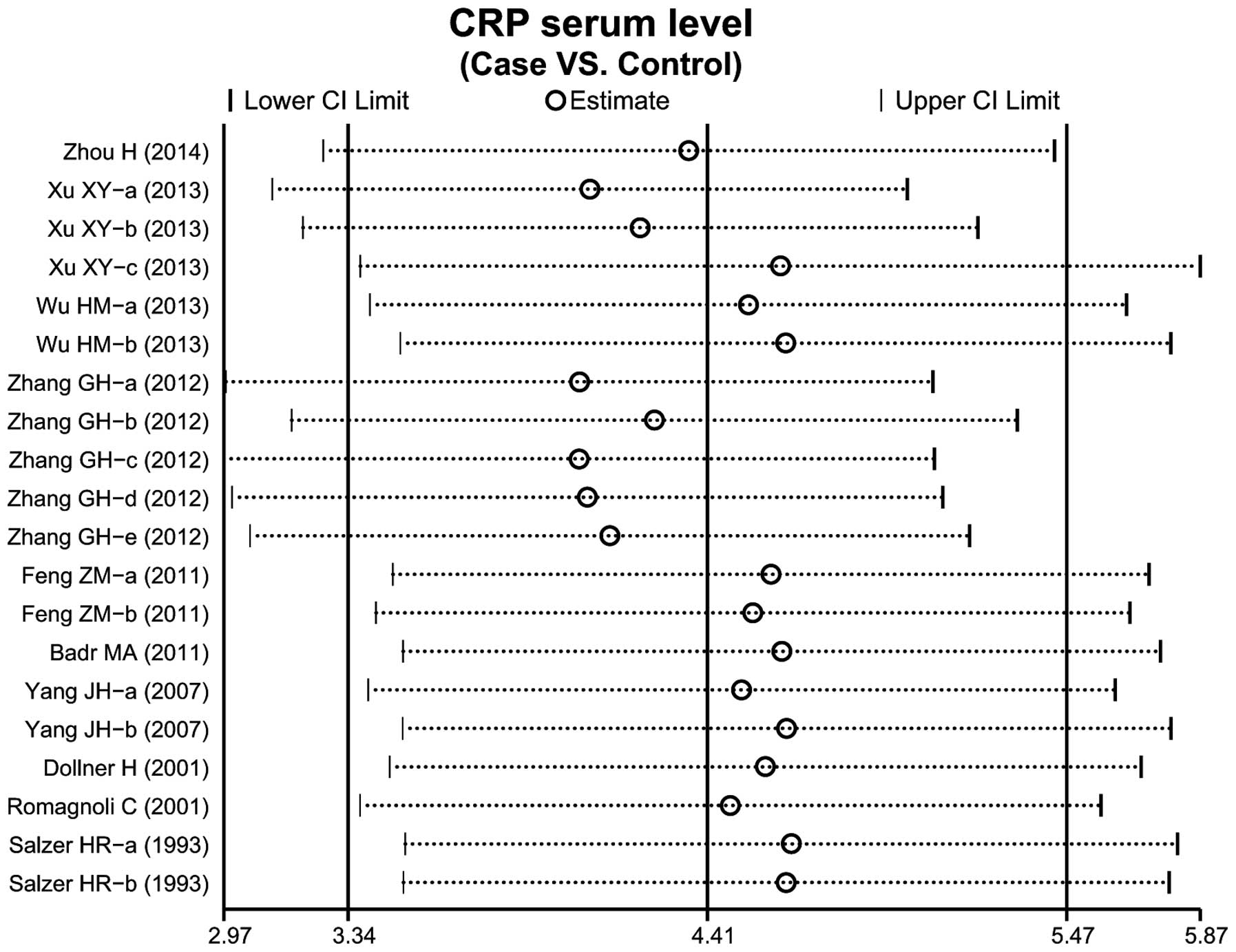
Xu XY and Li ZF: Value of detection of
procalcitonin and C-reactive protein in diagnosis of infectious
pneumonia in neonates. Zhonghua Yi Yuan Gan Ran Xue Za Zhi.
23:2515–2517. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Zhang GH, Chen CX and He JQ: Study on the
correction between the serum SIL-2R, CRP, myocardial enzyme and
neonatal pneumonia. Zhongguo Yi Yao Dao Bao. 9:75–76. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Badr MA, Ali YF, Albanna EA, Beshir MR and
Amr GE: Ventilator associated pneumonia in critically-ill neonates
admitted to neonatal intensive care unit, Zagazig University
Hospitals. Iran J Pediatr. 21:418–424. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Salzer HR, Pollak A, Herkner K, Weninger M
and Schemper W: Value of measurement of neutrophil elastase-alpha 1
proteinase inhibitor levels in the early diagnosis of neonatal
infection. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 12:553–556. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ben Shimol S, Dagan R, Givon-Lavi N, et
al: Evaluation of the World Health Organization criteria for chest
radiographs for pneumonia diagnosis in children. Eur J Pediatr.
171:369–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jackson D, White IR and Riley RD:
Quantifying the impact of between-study heterogeneity in
multivariate meta-analyses. Stat Med. 31:3805–3820. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
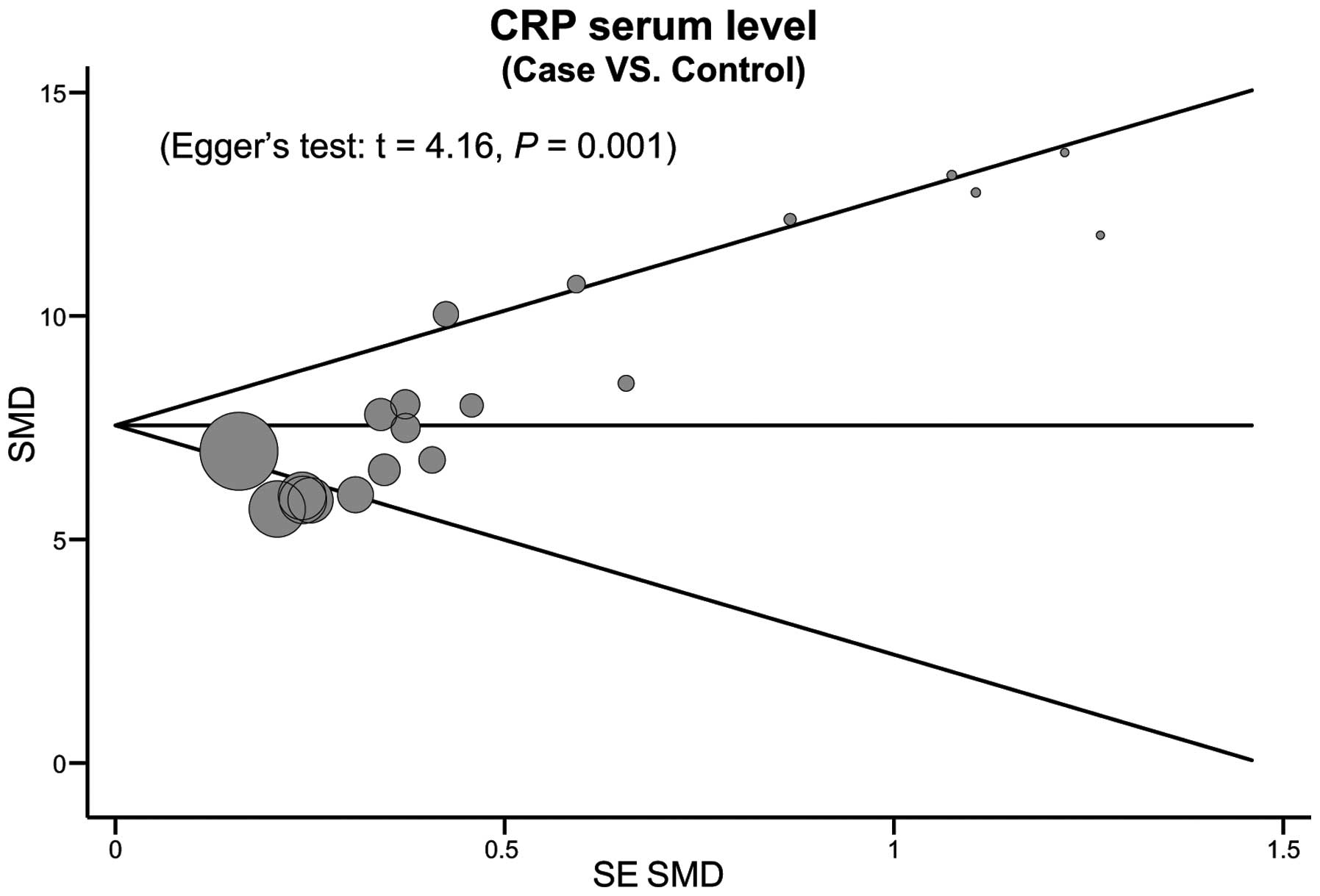
Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR
and Rushton L: Comparison of two methods to detect publication bias
in meta-analysis. JAMA. 295:676–680. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zintzaras E and Ioannidis JP: HEGESMA:
genome search meta-analysis and heterogeneity testing.
Bioinformatics. 21:3672–3673. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng ZM, Li X and Yang RG: Analysis on
detection results of blood lactic acid and C-reactive protein in
pneumonic neonates. Zhongguo Yi Yao Dao Bao. 8:85–86. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
35
|
Wu HM: Value of detection of PCT, hs-CRP
and WBC in diagnosis of early neonatal pneumonia. Haixia Yufang
Yixue Zazhi. 19:83–84. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Yang JH, Wei XS and Liao B: Significance
of the detection of PCT, hs-CRP and IL-6 in diagnosis of neonatal
pneumonia. Chongqing Yixue. 36:1194–1195. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
37
|
Zhou H: Significance of joint detection
serum cystatin cand CRP in neonatal pneumonia. Chengde Yixueyuan
Xuebao. 31:31–32. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
38
|
Døllner H, Vatten L and Austgulen R: Early
diagnostic markers for neonatal sepsis: comparing C-reactive
protein, interleukin-6, soluble tumour necrosis factor receptors
and soluble adhesion molecules. J Clin Epidemiol. 54:1251–1257.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Romagnoli C, Frezza S, Cingolani A, et al:
Plasma levels of interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in preterm
neonates evaluated for sepsis. Eur J Pediatr. 160:345–350. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Volanakis JE: Human C-reactive protein:
expression, structure and function. Mol Immunol. 38:189–197. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Arinzon Z, Peisakh A, Schrire S and Berner
Y: C-reactive protein (CRP): an important diagnostic and prognostic
tool in nursing-home-associated pneumonia. Arch Gerontol Geriatr.
53:364–369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moreno MS, Nietmann H, Matias CM and Lobo
SM: C-reactive protein: a tool in the follow-up of nosocomial
pneumonia. J Infect. 61:205–211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Marnell L, Mold C and Du Clos TW:
C-reactive protein: ligands, receptors and role in inflammation.
Clin Immunol. 117:104–111. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rudan I, Boschi-Pinto C, Biloglav Z,
Mulholland K and Campbell H: Epidemiology and etiology of childhood
pneumonia. Bull World Health Organ. 86:408–416. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mintegi S, Benito J, Pijoan JI, et al:
Occult pneumonia in infants with high fever without source: a
prospective multicenter study. Pediatr Emerg Care. 26:470–474.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|