|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nordenstedt H, White DL and El-Serag HB:
The changing pattern of epidemiology in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Dig Liver Dis. 42 Suppl 3:S206–S214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gao J, Xie L, Yang WS, et al: Risk factors
of hepatocellular carcinoma-current status and perspectives. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:743–752. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Flejter WL, McDaniel LD, Johns D,
Friedberg EC and Schultz RA: Correction of xeroderma pigmentosum
complementation group D mutant cell phenotypes by chromosome and
gene transfer: Involvement of the human ERCC2 DNA repair gene. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:261–265. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shen MR, Jones IM and Mohrenweiser H:
Nonconservative amino acid substitution variants exist at
polymorphic frequency in DNA repair genes in healthy humans. Cancer
Res. 58:604–608. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seker H, Butkiewicz D, Bowman ED, et al:
Functional significance of XPD polymorphic variants: Attenuated
apoptosis in human lymphoblastoid cells with the XPD 312 Asp/Asp
genotype. Cancer Res. 61:7430–7434. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pabalan N, Francisco-Pabalan O, Sung L,
Jarjanazi H and Ozcelik H: Meta-analysis of two ERCC2 (XPD)
polymorphisms, Asp312Asn and Lys751Gln, in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 124:531–541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yin QH, Liu C, Hu JB, Meng RR, Li L and
Wang YJ: XPD Lys751Gln and Asp312Asn polymorphisms and gastric
cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis of case-control studies.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:231–236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
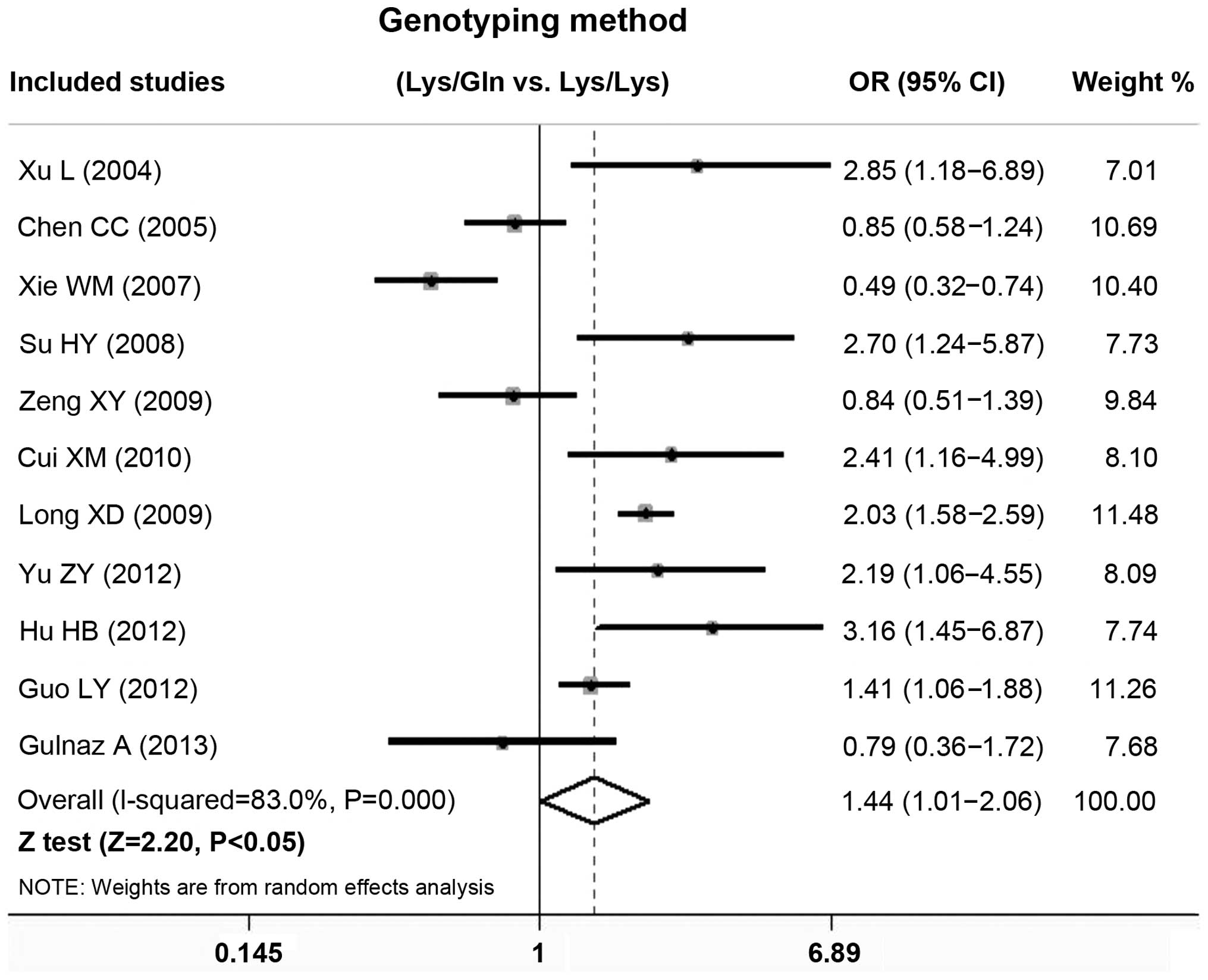
Xu L, Wu YQ, Jing Y, et al: A case-control
study on polymorphism of DNA repair gene XPD and susceptibility to
hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor. 24:5265292004.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Chen CC, Yang SY, Liu CJ, et al:
Association of cytokine and DNA repair gene polymorphisms with
hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Epidemiol.
34:1310–1318. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xie WM: Association between the nucleotide
excision repair (NER) genes polymorphisms and genetic
susceptibility and clinical phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma.
University of Guangxi Medical; 2007, (In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Su HY: A case-control study on the
association between single nucleotide polymorphism of DNA injury
repair gene XPD, XRCC1 and hepatocellular carcinoma. University of
China Medical; 2008, (In Chinese).
|
|
13
|
Zeng XY, Qiu XQ, Ji L and Yu HP: Study on
the relationship between hepatocellular carcinoma and the
interaction between polymorphisms in DNA repair gene XPD and
environmental factors. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi.
30:7027052009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cui ZM and Su HY: A case-control study on
the polymorphism of gene XPD and the susceptibility of primary
hepatic carcinoma. Med J Chin People Health. 22:9129142010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Long XD, Ma Y, Zhou YF, et al: XPD codon
312 and 751 polymorphisms, and AFB1 exposure, and hepatocellular
carcinoma risk. BMC Cancer. 9:4002009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu HB: A study on relationship between
familial clustering of hepatocellular carcinoma and such factors as
polymorphism of XPD genes, etc. in Guangxi popution. University of
Guangxi Medical; 2012, (In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Guo LY, Jin XP, Niu W, Li XF, Liu BH and
Wang YL: Association of XPD and XRCC1 genetic polymorphisms with
hepatocellular carcinoma risk. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:4423–4426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gulnaz A, Sayyed AH, Amin F, et al:
Association of XRCC1, XRCC3, and XPD genetic polymorphism with an
increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma because of the hepatitis
B and C virus. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:166–179. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li J, Li Z, Feng L, Guo W and Zhang S:
Polymorphisms of DNA repair gene XRCC1 and hepatocellular carcinoma
risk among East Asians: A meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 34:261–269.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang SX, Wu FX, Luo M, et al: The
glutathione S-Transferase P1 341C>T polymorphism and cancer
risk: A meta-analysis of 28 case-control studies. PLoS One.
8:e567222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al: Global
Cancer Statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:86–108. 2015.
|
|
24
|
Llovet JM and Bruix J: Novel advancements
in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma in 2008. J Hepatol.
48 Suppl 1:S20–S37. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiao L, Hassan MM, Bondy ML, Abbruzzese
JL, Evans DB and Li D: The XPD Asp312Asn and Lys751Gln
polymorphisms, corresponding haplotype, and pancreatic cancer risk.
Cancer Lett. 245:61–68. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Au WW, Navasumrit P and Ruchirawat M: Use
of biomarkers to characterize functions of polymorphic DNA repair
genotypes. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 207:301–313. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cleaver JE: Common pathways for
ultraviolet skin carcinogenesis in the repair and replication
defective groups of xeroderma pigmentosum. J Dermatol Sci. 23:1–11.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Benhamou S and Sarasin A: ERCC2/XPD gene
polymorphisms and cancer risk. Mutagenesis. 17:463–469. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Manuguerra M, Saletta F, Karagas MR, et
al: XRCC3 and XPD/ERCC2 single nucleotide polymorphisms and the
risk of cancer: A HuGE review. Am J Epidemiol. 164:297–302. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lavender NA, Komolafe OO, Benford M, et
al: No association between variant DNA repair genes and prostate
cancer risk among men of African descent. Prostate. 70:113–119.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu H, Cao S, Liu Y, Ding X, Wu Q and Ma
H: Genetic polymorphisms of xeroderma pigmentosum group D and
prostate cancer risk: A meta-analysis. J Cancer Res Ther.
9:187–192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu S, Zhang H, Tang Y and Wang J:
Polymorphisms in XPD and hOGG1 and prostate cancer risk: A
meta-analysis. Urol Int. 89:233–240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feng Z, Ni Y, Dong W, Shen H and Du J:
Association of ERCC2/XPD polymorphisms and interaction with tobacco
smoking in lung cancer susceptibility: A systemic review and
meta-analysis. Mol Biol Rep. 39:57–69. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mei CR, Luo M, Li HM, Deng WJ and Zhou QH:
DNA Repair Gene Polymorphisms in the Nucleotide Excision Repair
Pathway and Lung Cancer Risk: A Meta-analysis. Chin J Cancer Res.
23:79–91. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhan P, Wang Q, Wei SZ, et al: ERCC2/XPD
Lys751Gln and Asp312Asn gene polymorphism and lung cancer risk: A
meta-analysis involving 22 case-control studies. J Thorac Oncol.
5:1337–1345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xue H, Lu Y, Lin B, Chen J, Tang F and
Huang G: The effect of XPD/ERCC2 polymorphisms on gastric cancer
risk among different ethnicities: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 7:e434312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang Z, Li C, Xu Y, Cai S and Wang X:
Associations between XPD polymorphisms and risk of breast cancer: A
meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 123:203–212. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Qiu LX, Yao L, Zhang J, et al: XPD
Lys751Gln polymorphism and breast cancer susceptibility: A
meta-analysis involving 28,709 subjects. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
124:229–235. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hu YY, Yuan H, Jiang GB, et al:
Associations between XPD Asp312Asn polymorphism and risk of head
and neck cancer: A meta-analysis based on 7,122 subjects. PLoS One.
7:e352202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yuan H, Niu YM, Wang RX, Li HZ and Chen N:
Association between XPD Lys751Gln polymorphism and risk of head and
neck cancer: A meta-analysis. Genet Mol Res. 10:3356–3364. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duan XL, Gong H, Zeng XT, et al:
Association between XPD Asp312Asn polymorphism and esophageal
cancer susceptibility: A meta-analysis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:3299–3303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu XB, Dai LP, Wang YP, Wang KJ and Zhang
JY: DNA repair gene xeroderma pigmentosum group D 751 polymorphism
and the risk on esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. Zhonghua Liu
Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 30:2812852009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|