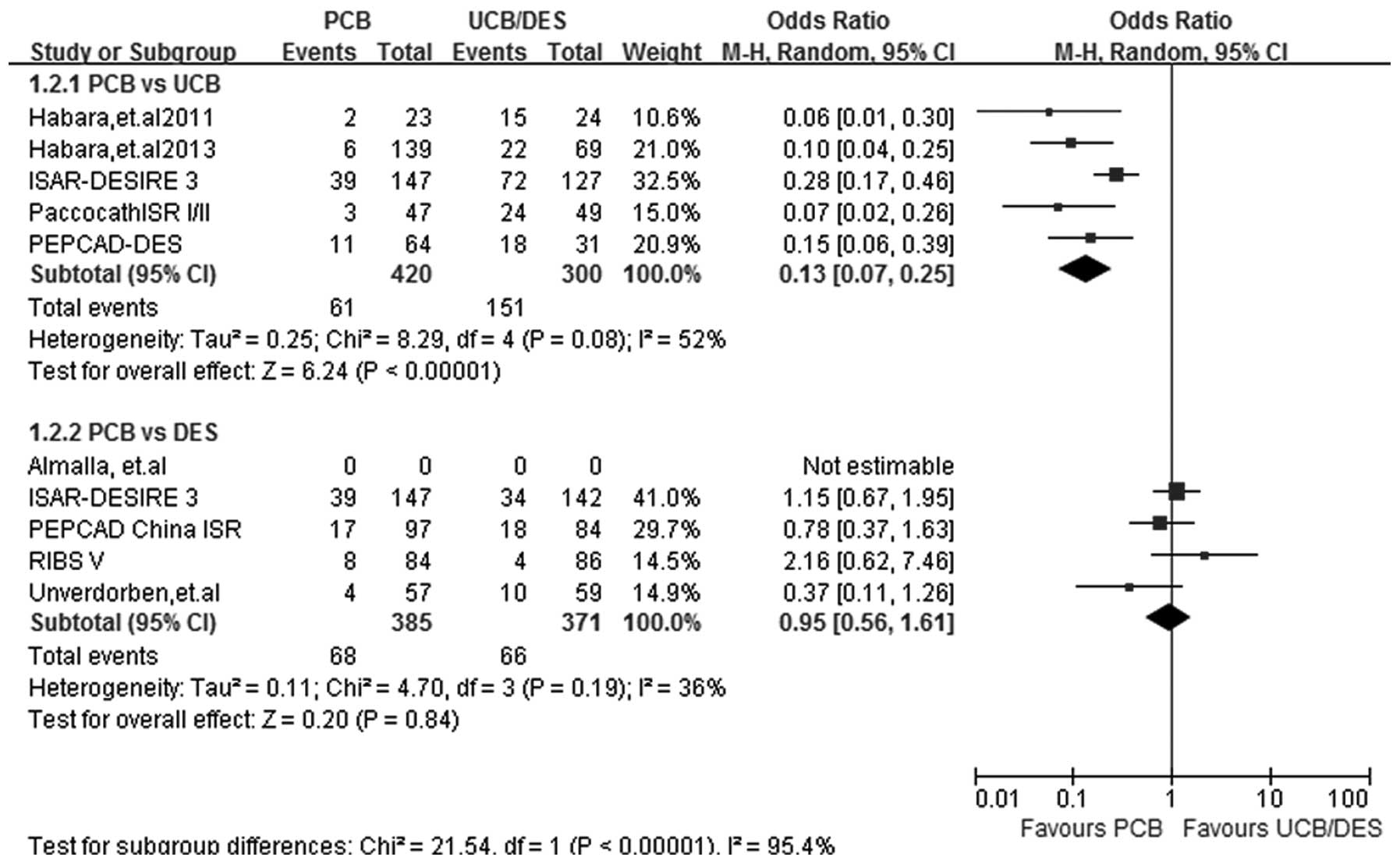
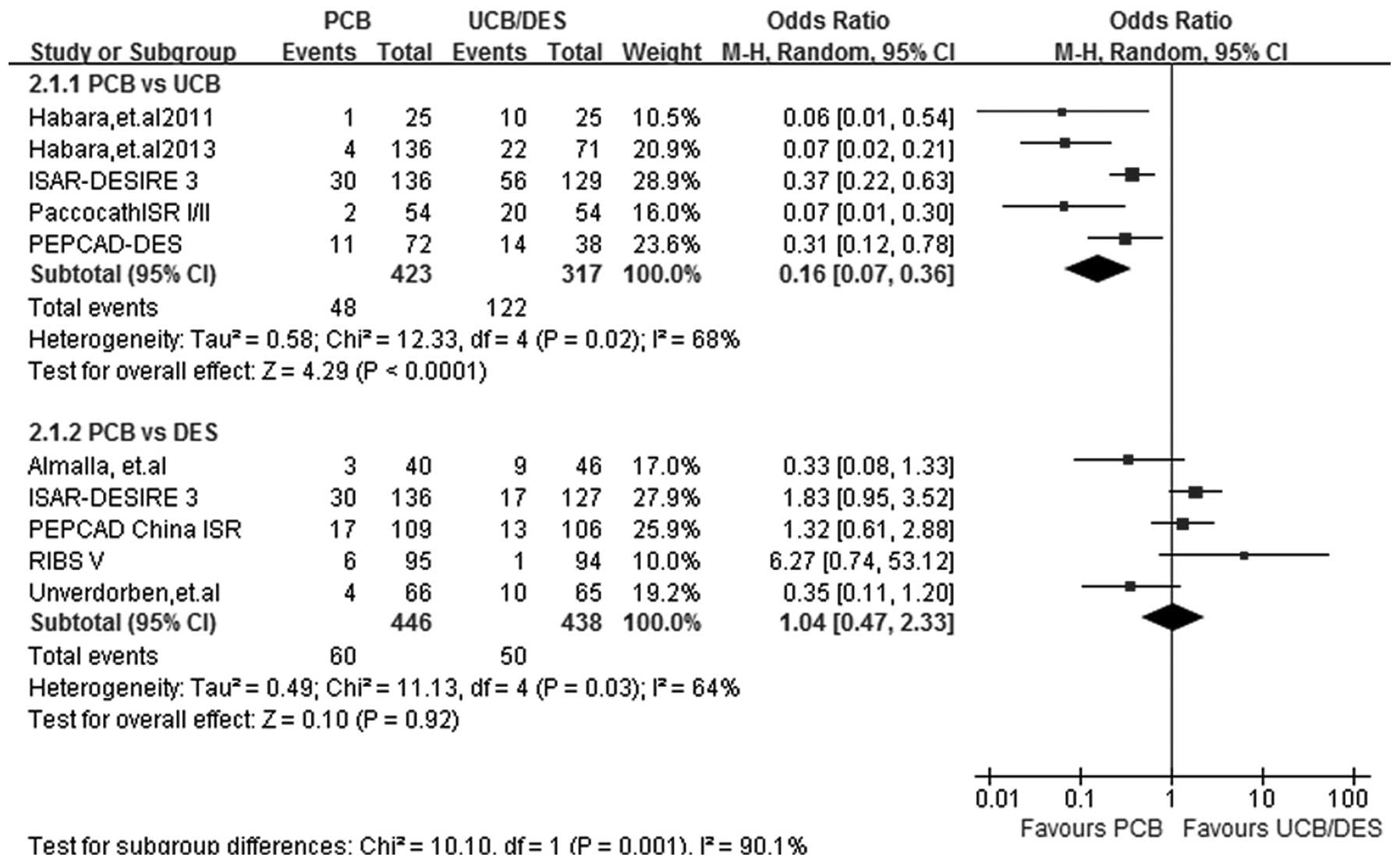
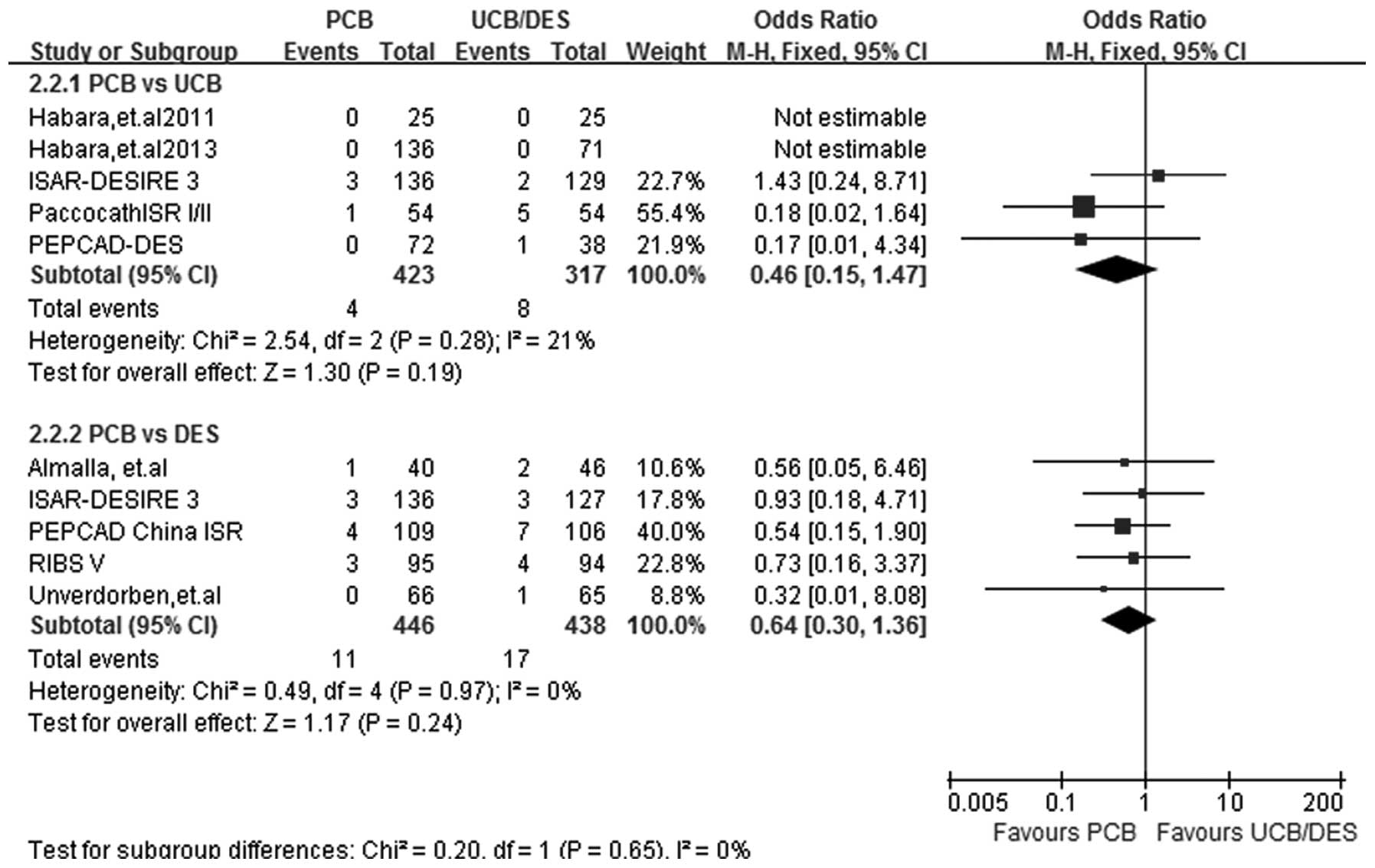
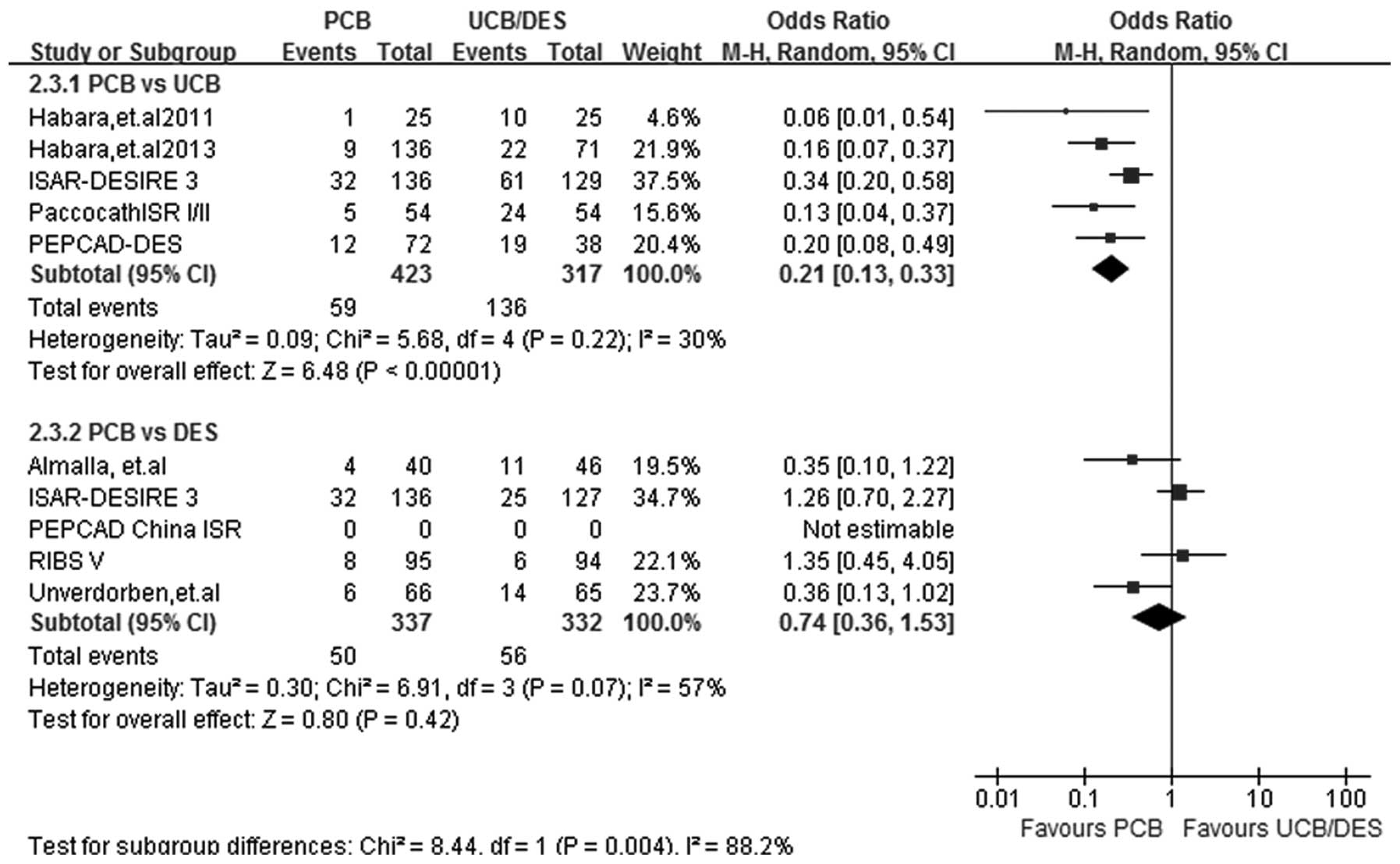
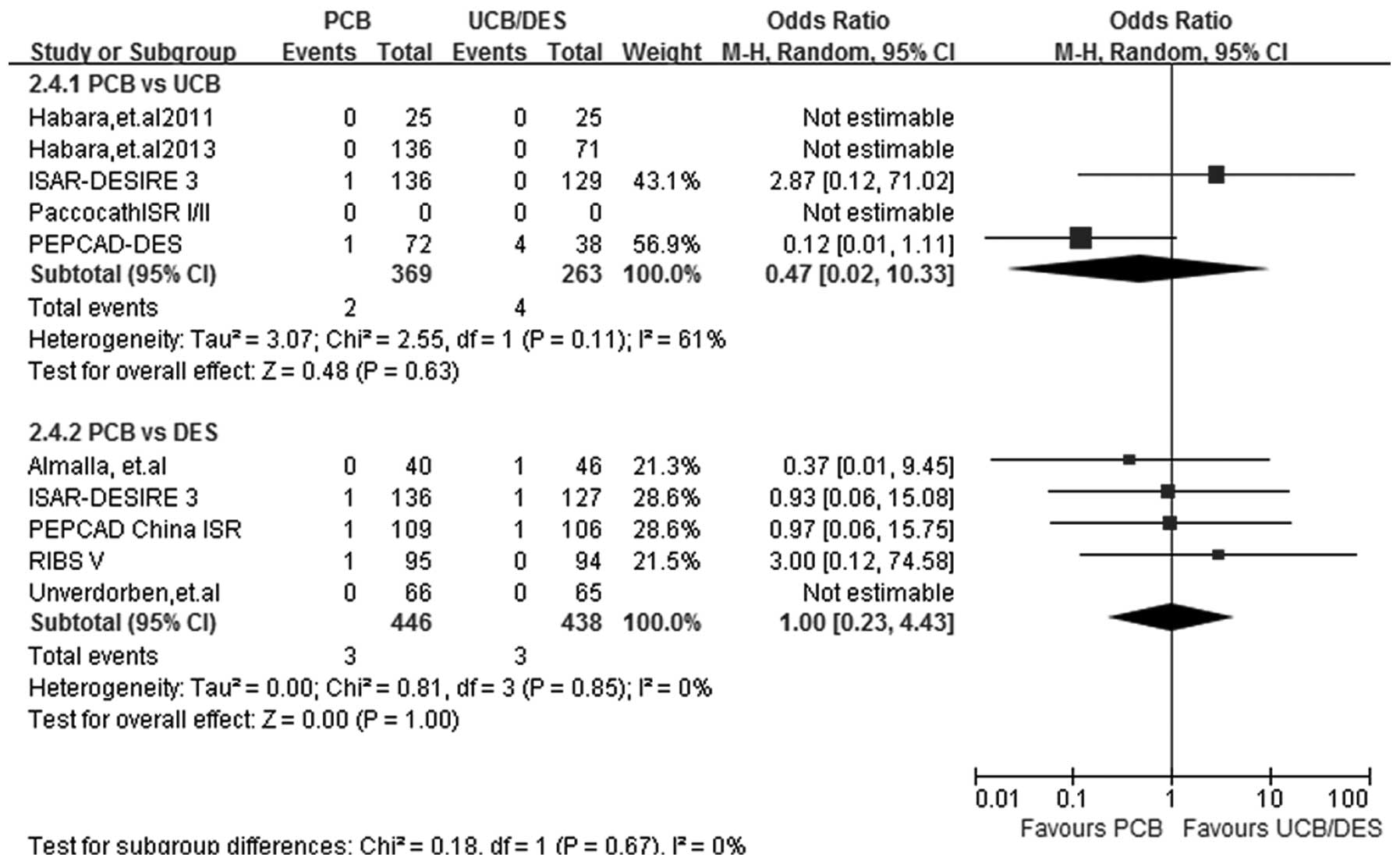
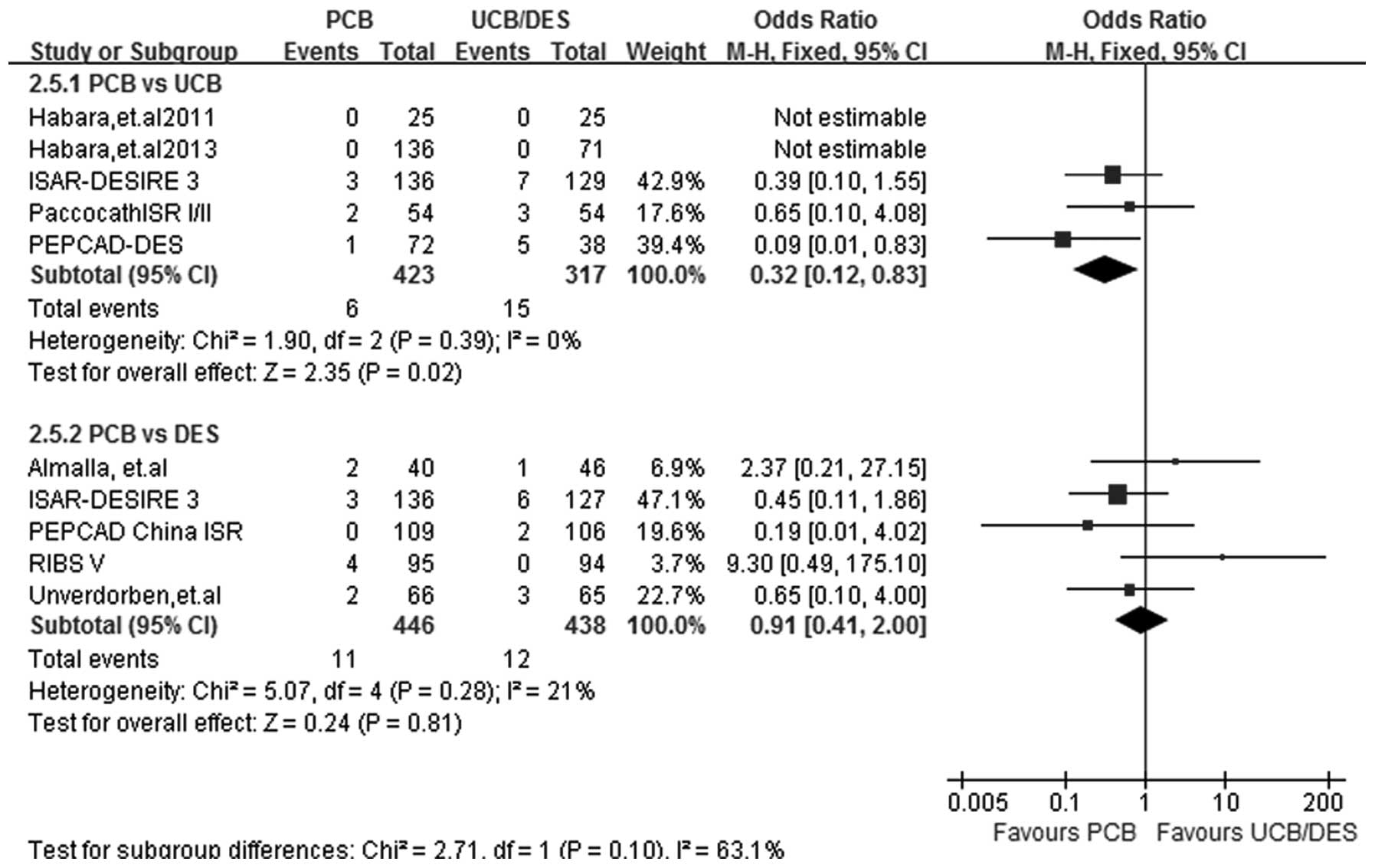
|
1
|
Moses JW, Leon MB, Popma JJ, et al: SIRIUS
Investigators: Sirolimus-eluting stents versus standard stents in
patients with stenosis in a native coronary artery. N Engl J Med.
349:1315–1323. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dangas GD, Claessen BE, Caixeta A, Sanidas
EA, Mintz GS and Mehran R: In-stent restenosis in the drug-eluting
stent era. J Am Coll Cardiol. 56:1897–1907. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim YH, Lee BK, Park DW, et al: Comparison
with conventional therapies of repeated sirolimus-eluting stent
implantation for the treatment of drug-eluting coronary stent
restenosis. Am J Cardiol. 98:1451–1454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mishkel GJ, Moore AL, Markwell S, Shelton
MC and Shelton ME: Long-term outcomes after management of
restenosis or thrombosis of drug-eluting stents. J Am Coll Cardiol.
49:181–184. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stone GW, Ellis SG, O'Shaughnessy CD, et
al: TAXUS V ISR Investigators: Paclitaxel-eluting stents vs
vascular brachytherapy for in-stent restenosis within bare-metal
stents: The TAXUS V ISR randomized trial. JAMA. 295:1253–1263.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhatt DL: Intensifying platelet inhibition
- navigating between Scylla and Charybdis. N Engl J Med.
357:2078–2081. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Loh JP and Waksman R: Paclitaxel
drug-coated balloons: A review of current status and emerging
applications in native coronary artery de novo lesions. JACC
Cardiovasc Interv. 5:1001–1012. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gray WA and Granada JF: Drug-coated
balloons for the prevention of vascular restenosis. Circulation.
121:2672–2680. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cutlip DE, Windecker S, Mehran R, et al:
Academic Research Consortium: Clinical end points in coronary stent
trials: A case for standardized definitions. Circulation.
115:2344–2351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rittger H, Brachmann J, Sinha AM, et al: A
randomized, multicenter, single-blinded trial comparing
paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty with plain balloon
angioplasty in drug-eluting stent restenosis: The PEPCAD-DES study.
J Am Coll Cardiol. 59:1377–1382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Scheller B, Hehrlein C, Bocksch W, et al:
Two year follow-up after treatment of coronary in-stent restenosis
with a paclitaxel-coated balloon catheter. Clin Res Cardiol.
97:773–781. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Habara S, Mitsudo K, Kadota K, et al:
Effectiveness of paclitaxel-eluting balloon catheter in patients
with sirolimus-eluting stent restenosis. JACC Cardiovasc Interv.
4:149–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu B, Gao R, Wang J, et al: PEPCAD China
ISR Trial Investigators: A prospective, multicenter, randomized
trial of paclitaxel-coated balloon versus paclitaxel-eluting stent
for the treatment of drug-eluting stent in-stent restenosis:
Results from the PEPCAD China ISR trial. JACC Cardiovasc Interv.
7:204–211. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Unverdorben M, Vallbracht C, Cremers B, et
al: Paclitaxel-coated balloon catheter versus paclitaxel-coated
stent for the treatment of coronary in-stent restenosis.
Circulation. 119:2986–2994. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Byrne RA, Neumann FJ, Mehilli J, et al:
ISAR-DESIRE 3 investigators: Paclitaxel-eluting balloons,
paclitaxel-eluting stents, and balloon angioplasty in patients with
restenosis after implantation of a drug-eluting stent (ISAR-DESIRE
3): A randomised, open-label trial. Lancet. 381:461–467. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Habara S, Iwabuchi M, Inoue N, et al: A
multicenter randomized comparison of paclitaxel-coated balloon
catheter with conventional balloon angioplasty in patients with
bare-metal stent restenosis and drug-eluting stent restenosis. Am
Heart J. 166:527–533. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Alfonso F, Perez-Vizcayno MJ, Cardenas A,
et al: RIBS V Study Investigators, under the auspices of the
Working Group on Interventional Cardiology of the Spanish Society
of Cardiology: A randomized comparison of drug-eluting balloon
versus everolimus-eluting stent in patients with bare-metal
stent-in-stent restenosis: The RIBS V Clinical Trial (Restenosis
Intra-stent of Bare Metal Stents: Paclitaxel-eluting balloon vs
everolimus-eluting stent). J Am Coll Cardiol. 63:1378–1386. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Almalla M, Schroder J, Pross V, Marx N and
Hoffmann R: Paclitaxel-eluting balloon versus everolimus-eluting
stent for treatment of drug-eluting stent restenosis. Catheter
Cardiovasc Interv. 83:881–887. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kastrati A, Mehilli J, von Beckerath N, et
al: ISAR-DESIRE Study Investigators: Sirolimus-eluting stent or
paclitaxel-eluting stent vs balloon angioplasty for prevention of
recurrences in patients with coronary in-stent restenosis: A
randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 293:165–171. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Scheller B, Hehrlein C, Bocksch W, et al:
Treatment of coronary in-stent restenosis with a paclitaxel-coated
balloon catheter. N Engl J Med. 355:2113–2124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu CM, Kwong JS and Sanderson JE:
Drug-eluting balloons for coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis
of randomized controlled trials. Int J Cardiol. 168:197–206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Navarese EP, Austin D, Gurbel PA, et al:
Drug-coated balloons in treatment of in-stent restenosis: A
meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clin Res Cardiol.
102:279–287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Steinberg DH, Gaglia MA Jr, Pinto Slottow
TL, et al: Outcome differences with the use of drug-eluting stents
for the treatment of in-stent restenosis of bare-metal stents
versus drug-eluting stents. Am J Cardiol. 103:491–495. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Byrne RA, Cassese S, Windisch T, et al:
Differential relative efficacy between drug-eluting stents in
patients with bare metal and drug-eluting stent restenosis;
evidence in support of drug resistance: Insights from the
ISAR-DESIRE and ISAR-DESIRE 2 trials. Euro Intervention. 9:797–802.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alfonso F: Treatment of drug-eluting stent
restenosis the new pilgrimage: Quo vadis? J Am Coll Cardiol.
55:2717–2720. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wohrle J, Zadura M, Mobius-Winkler S, et
al: SeQuentPlease World Wide Registry: Clinical results of SeQuent
please paclitaxel-coated balloon angioplasty in a large-scale,
prospective registry study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 60:1733–1738.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|