|
1
|
Richardson MW, Allen GA and Monahan PE:
Thrombosis in children: Current perspective and distinct
challenges. Thromb Haemost. 88:900–911. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gurgey A and Aslan D: Outcome of
noncatheter-related thrombosis in children: Influence of underlying
or coexisting factors. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 23:159–164. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Becarevic M, Ignjatovic S and Majkic-Singh
N: Deterioration of thromboses in primary antiphospholipid
syndrome: TNF-alpha and anti-annexin A5 antibodies. Clin Lab.
58:1079–1084. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schafer A, Schulz C, Eigenthaler M, et al:
Novel role of the membrane-bound chemokine fractalkine in platelet
activation and adhesion. Blood. 103:407–412. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raab M, Daxecker H, Markovic S, Karimi A,
Griesmacher A and Mueller MM: Variation of adhesion molecule
expression on human umbilical vein endothelial cells upon multiple
cytokine application. Clin Chim Acta. 321:11–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Clemetson KJ, Clemetson JM, Proudfoot AE,
Power CA, Baggiolini M and Wells TN: Functional expression of CCR1,
CCR3, CCR4 and CXCR4 chemokine receptors on human platelets. Blood.
96:4046–4054. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bevilacqua MP, Pober JS, Majeau GR, Cotran
RS and Gimbrone MJ: Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and
cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular
endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 160:618–623. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Conway EM, Bach R, Rosenberg RD and
Konigsberg WH: Tumor necrosis factor enhances expression of tissue
factor mRNA in endothelial cells. Thromb Res. 53:231–241. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parry GC and Mackman N: Transcriptional
regulation of tissue factor expression in human endothelial cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 15:612–621. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Joseph L, Fink LM and Hauer-Jensen M:
Cytokines in coagulation and thrombosis: A preclinical and clinical
review. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 13:105–116. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Vecchi A, Introna
M and Allavena P: Cytokine activation of endothelial cells: New
molecules for an old paradigm. Thromb Haemost. 78:406–414.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Esmon CT: Inflammation and thrombosis. J
Thromb Haemost. 1:1343–1348. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tapper H and Herwald H: Modulation of
hemostatic mechanisms in bacterial infectious diseases. Blood.
96:2329–2337. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bernardo A, Ball C, Nolasco L, Moake JF
and Dong JF: Effects of inflammatory cytokines on the release and
cleavage of the endothelial cell-derived ultralarge von Willebrand
factor multimers under flow. Blood. 104:100–106. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Smadja D, Gaussem P, Roncal C, Fischer AM,
Emmerich J and Darnige L: Arterial and venous thrombosis is
associated with different angiogenic cytokine patterns in patients
with antiphospholipid syndrome. Lupus. 19:837–843. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kowalska MA, Rauova L and Poncz M: Role of
the platelet chemokine platelet factor 4 (PF4) in hemostasis and
thrombosis. Thromb Res. 125:292–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han Q, Song J, Qiao C, Wong L and Xu H:
Preparative isolation of hydrolysable tannins chebulagic acid and
chebulinic acid from Terminalia chebula by high-speed
counter-current chromatography. J Sep Sci. 29:1653–1657. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin LT, Chen TY, Chung CY, et al:
Hydrolyzable tannins (chebulagic acid and punicalagin) target viral
glycoprotein-glycosaminoglycan interactions to inhibit herpes
simplex virus 1 entry and cell-to-cell spread. J Virol.
85:4386–4398. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gyorkey F, Melnick JL, Guinn GA, Gyorkey P
and DeBakey ME: Herpesviridae in the endothelial and smooth muscle
cells of the proximal aorta in arteriosclerotic patients. Exp Mol
Pathol. 40:328–339. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Melnick JL, Petrie BL, Dreesman GR, Burek
J, McCollum CH and DeBakey ME: Cytomegalovirus antigen within human
arterial smooth muscle cells. Lancet. 2:644–647. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hajjar DP, Pomerantz KB, Falcone DJ,
Weksler BB and Grant AJ: Herpes simplex virus infection in human
arterial cells. Implications in arteriosclerosis. J Clin Invest.
80:1317–1321. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Visser MR, Tracy PB, Vercellotti GM,
Goodman JL, White JG and Jacob HS: Enhanced thrombin generation and
platelet binding on herpes simplex virus-infected endothelium. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 85:8227–8230. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu Y, Ricciotti E, Scalia R, et al:
Vascular COX-2 modulates blood pressure and thrombosis in mice. Sci
Transl Med. 4:132r–154r. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Armstrong PC, Kirkby NS, Zain ZN, Emerson
M, Mitchell JA and Warner TD: Thrombosis is reduced by inhibition
of COX-1, but unaffected by inhibition of COX-2, in an acute model
of platelet activation in the mouse. PLoS One. 6:e200622011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
de Gaetano G, Donati MB and Cerletti C:
Prevention of thrombosis and vascular inflammation: Benefits and
limitations of selective or combined COX-1, COX-2 and 5-LOX
inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 24:245–252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Umar A, Boisseau M, Yusup A, Upur H,
Begaud B and Moore N: Interactions between aspirin and COX-2
inhibitors or NSAIDs in a rat thrombosis model. Fundam Clin
Pharmacol. 18:559–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
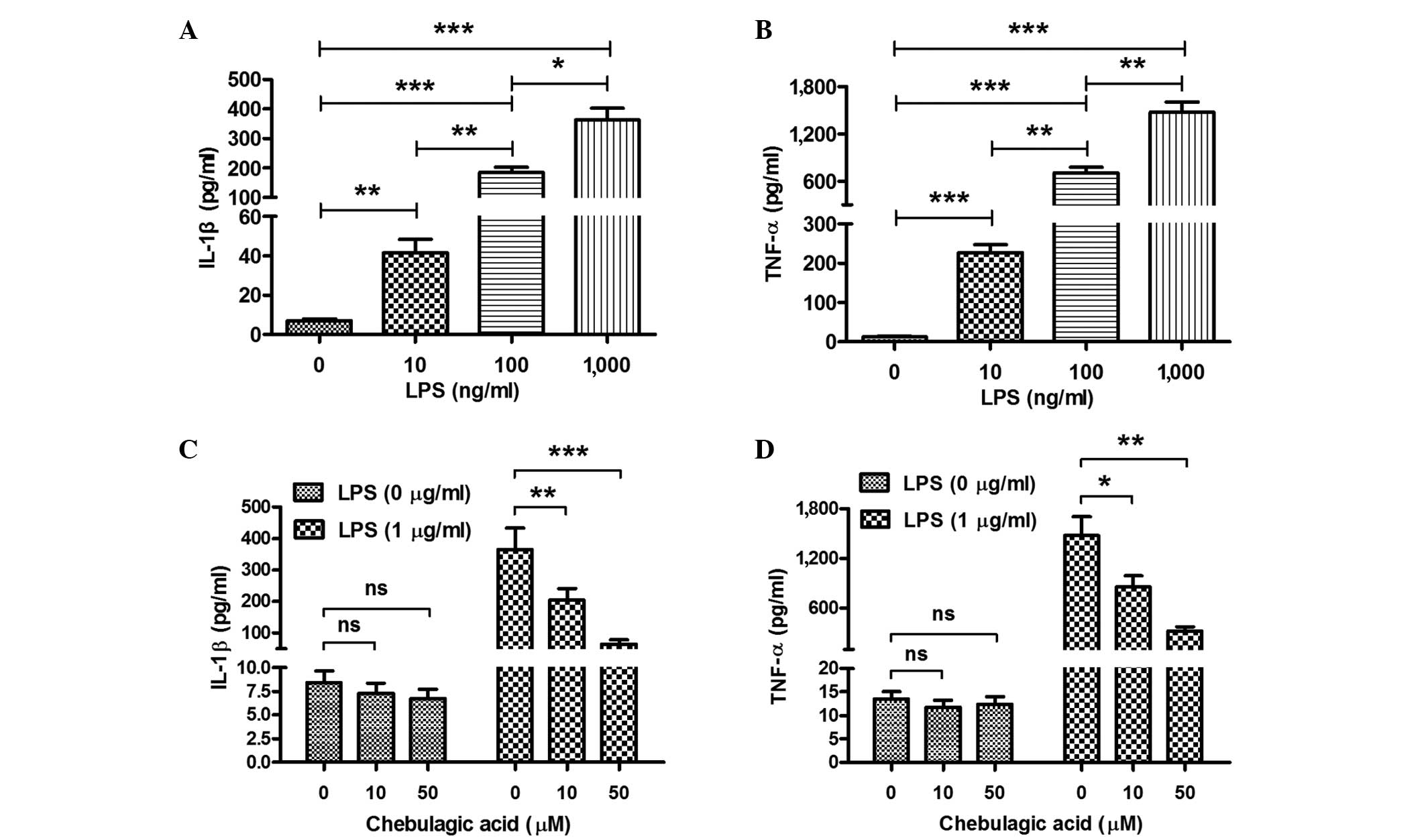
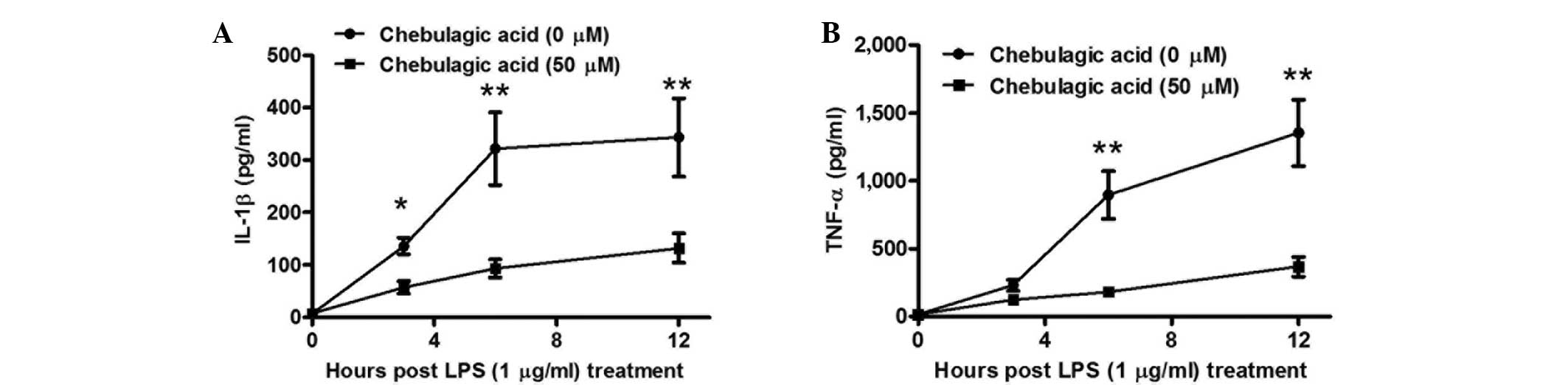
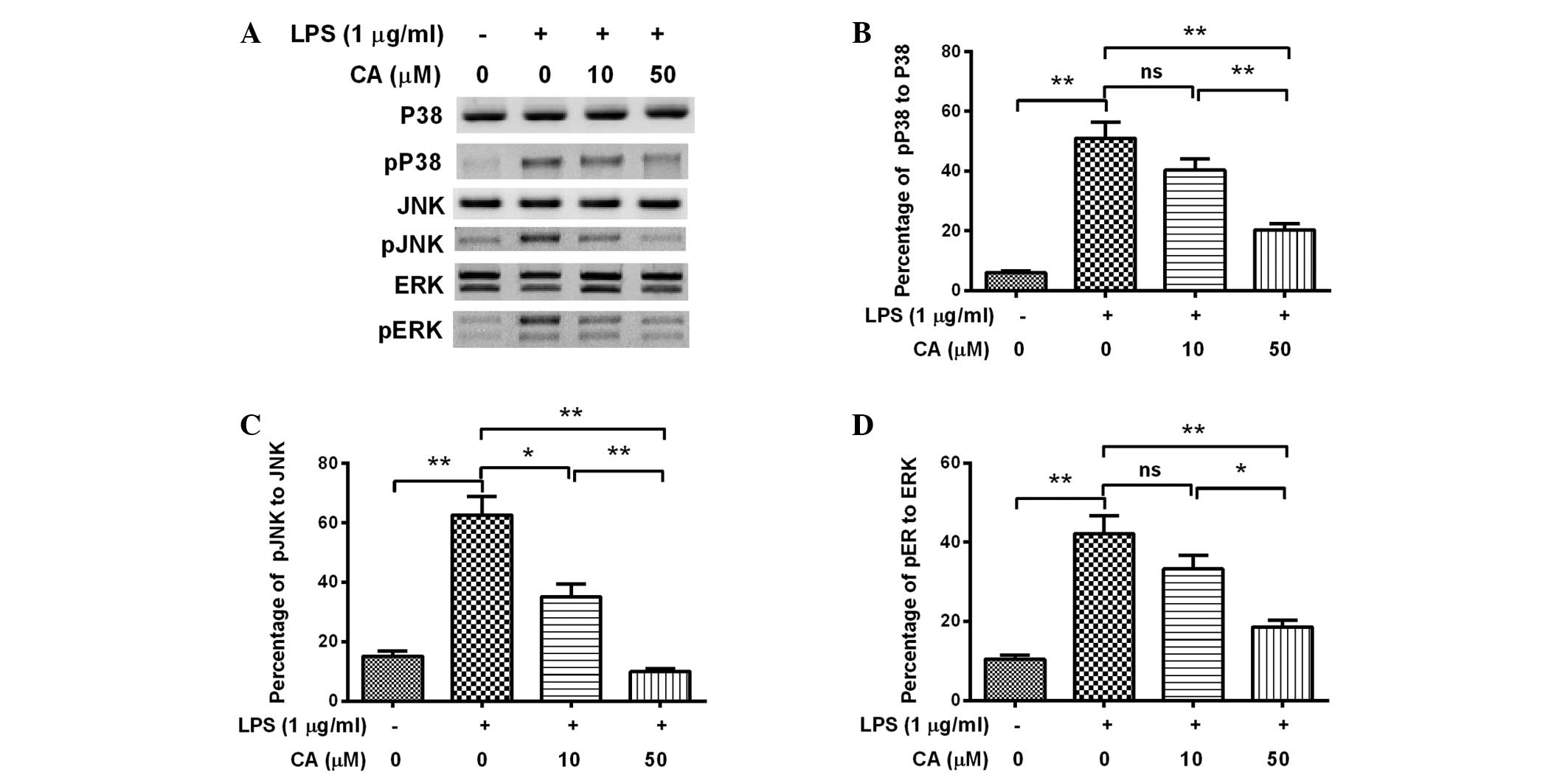
Reddy DB and Reddanna P: Chebulagic acid
(CA) attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing NF-kappaB
and MAPK activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 381:112–117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kirchner S, Boldt S, Kolch W, et al: LPS
resistance in monocytic cells caused by reverse signaling through
transmembrane TNF (mTNF) is mediated by the MAPK/ERK pathway. J
Leukoc Biol. 75:324–331. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang JS, Kim HM, Choi IY, et al: DBM1285
suppresses tumor necrosis factor alpha production by blocking p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase/mitogen-activated protein
kinase-activated protein kinase 2 signaling pathway. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 334:657–664. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Medvedev AE, Lentschat A, Wahl LM,
Golenbock DT and Vogel SN: Dysregulation of LPS-induced Toll-like
receptor 4-MyD88 complex formation and IL-1 receptor-associated
kinase 1 activation in endotoxin-tolerant cells. J Immunol.
169:5209–5216. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Levy O: Innate immunity of the human
newborn: Distinct cytokine responses to LPS and other toll-like
receptor agonists. J Endotoxin Res. 11:113–116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schouten M, Wiersinga WJ, Levi M and van
der Poll T: Inflammation, endothelium and coagulation in sepsis. J
Leukoc Biol. 83:536–545. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hartge MM, Unger T and Kintscher U: The
endothelium and vascular inflammation in diabetes. Diab Vasc Dis
Res. 4:84–88. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Maseri A:
Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 105:1135–1143. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Rojas E, Rodriguez-Molina D, Bolli P, et
al: The role of adiponectin in endothelial dysfunction and
hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 16:4632014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hirahashi J, Hishikawa K, Kaname S, et al:
Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18) links inflammation and thrombosis after
glomerular injury. Circulation. 120:1255–1265. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Contreras JL, Eckstein C, Smyth CA, et al:
Activated protein C preserves functional islet mass after
intraportal transplantation: A novel link between endothelial cell
activation, thrombosis, inflammation and islet cell death.
Diabetes. 53:2804–2814. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Suzuki E, Takahashi M, Oba S and
Nishimatsu H: Oncogene- and oxidative stress-induced cellular
senescence shows distinct expression patterns of proinflammatory
cytokines in vascular endothelial cells. Scientific World Journal.
2013:7547352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mishra M, Kumar H, Bajpai S, Singh RK and
Tripathi K: Level of serum IL-12 and its correlation with
endothelial dysfunction, insulin resistance, proinflammatory
cytokines and lipid profile in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 94:255–261. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Brigotti M, Carnicelli D, Ravanelli E, et
al: Molecular damage and induction of proinflammatory cytokines in
human endothelial cells exposed to Shiga toxin 1, Shiga toxin 2 and
alpha-sarcin. Infect Immun. 75:2201–2207. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bensaude E, Turner JL, Wakeley PR, et al:
Classical swine fever virus induces proinflammatory cytokines and
tissue factor expression and inhibits apoptosis and interferon
synthesis during the establishment of long-term infection of
porcine vascular endothelial cells. J Gen Virol. 85:1029–1037.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pontillo A, Girardelli M, Agostinis C,
Masat E, Bulla R and Crovella S: Bacterial LPS differently
modulates inflammasome gene expression and IL-1beta secretion in
trophoblast cells, decidual stromal cells and decidual endothelial
cells. Reprod Sci. 20:563–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu Y, Chen X, Duan H, Hu Y and Mu X:
Pulsatilla decoction and its active ingredients inhibit secretion
of NO, ET-1, TNF-alpha and IL-1 alpha in LPS-induced rat intestinal
microvascular endothelial cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 27:284–288.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|