|
1
|
McLain RF, Kapural L and Mekhail NA:
Epidural steroids for back and leg pain: Mechanism of action and
efficacy. Cleve Clin J Med. 71:961–970. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Geiss A, Larsson K, Rydevik B, Takahashi I
and Olmarker K: Autoimmune properties of nucleus pulposus: An
experimental study in pigs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:168–173.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hirsch C and Schajowicz F: Studies on
structural changes in the lumbar annulus fibrosus. Acta Orthop
Scand. 22:184–231. 1952. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kanerva A, Kommonen B, Grönblad M, et al:
Inflammatory cells in experimental intervertebral disc injury.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:2711–2715. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Olmarker K, Nordborg C, Larsson K and
Rydevik B: Ultrastructural changes in spinal nerve roots induced by
autologous nucleus pulposus. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:411–414.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
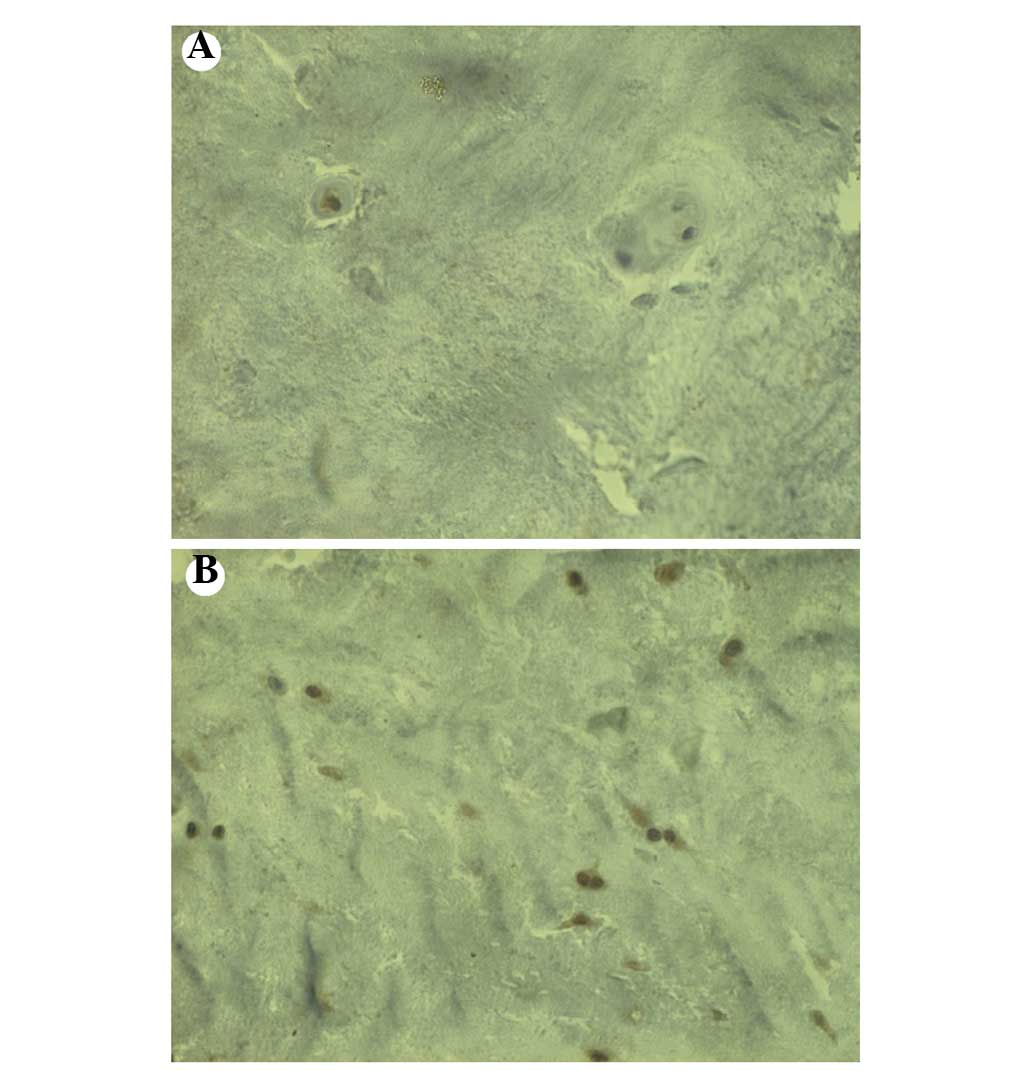
|
6
|
Olmarker K, Iwabuchi M, Larsson K and
Rydevik B: Walking analysis of rats subjected to experimental disc
herniation. Eur Spine J. 7:394–399. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
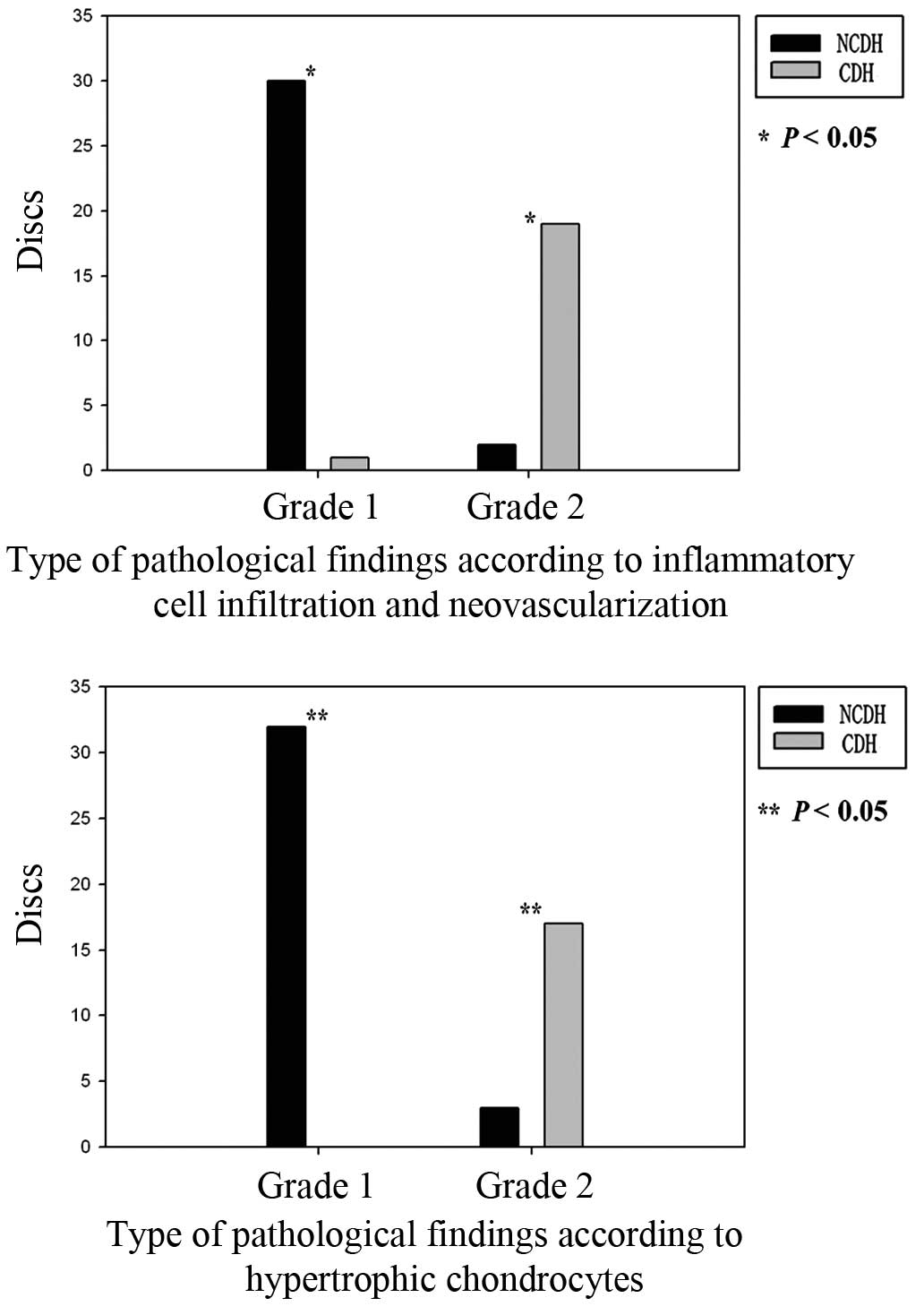
|
7
|
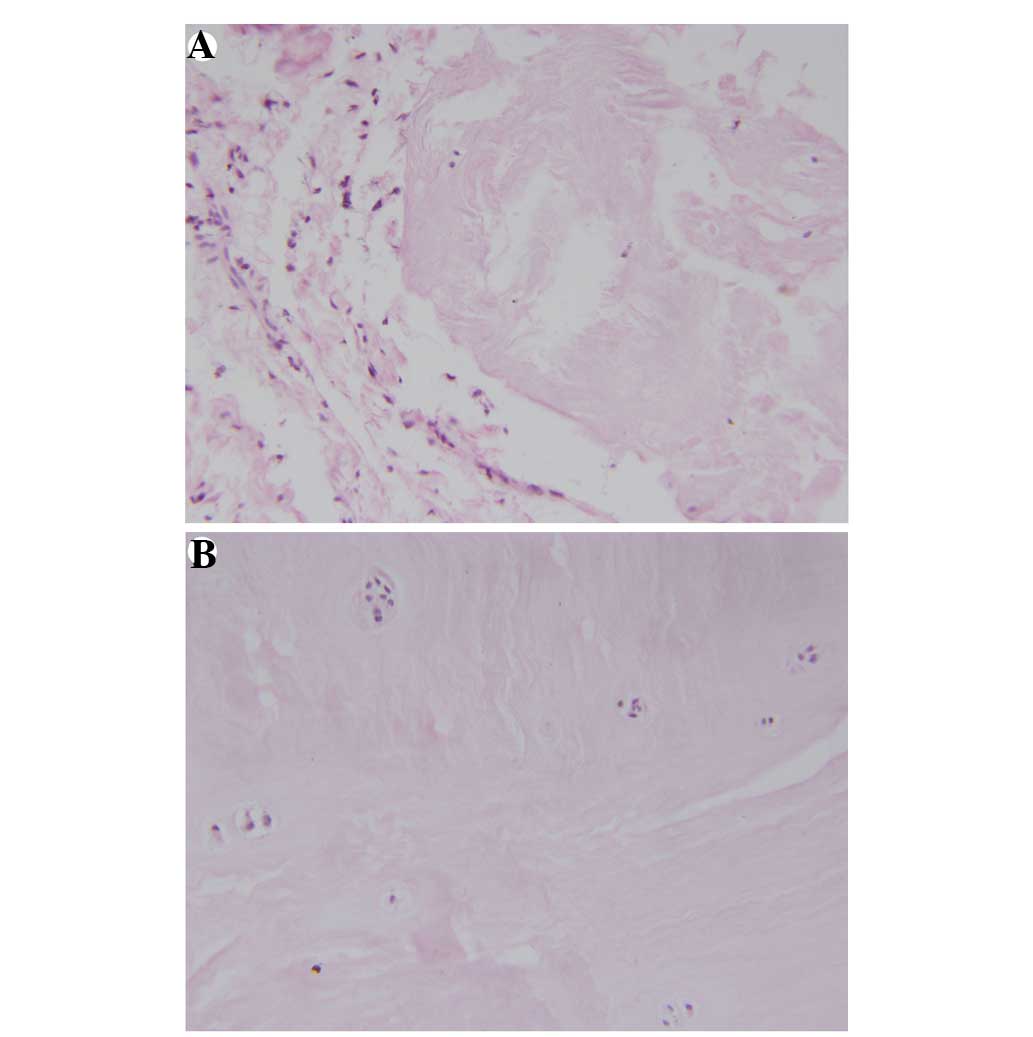
Otani K, Arai I, Mao GP, et al: Nucleus
pulposus-induced nerve root injury: Relationship between blood flow
and motor nerve conduction velocity. Neurosurgery. 45:614–620.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
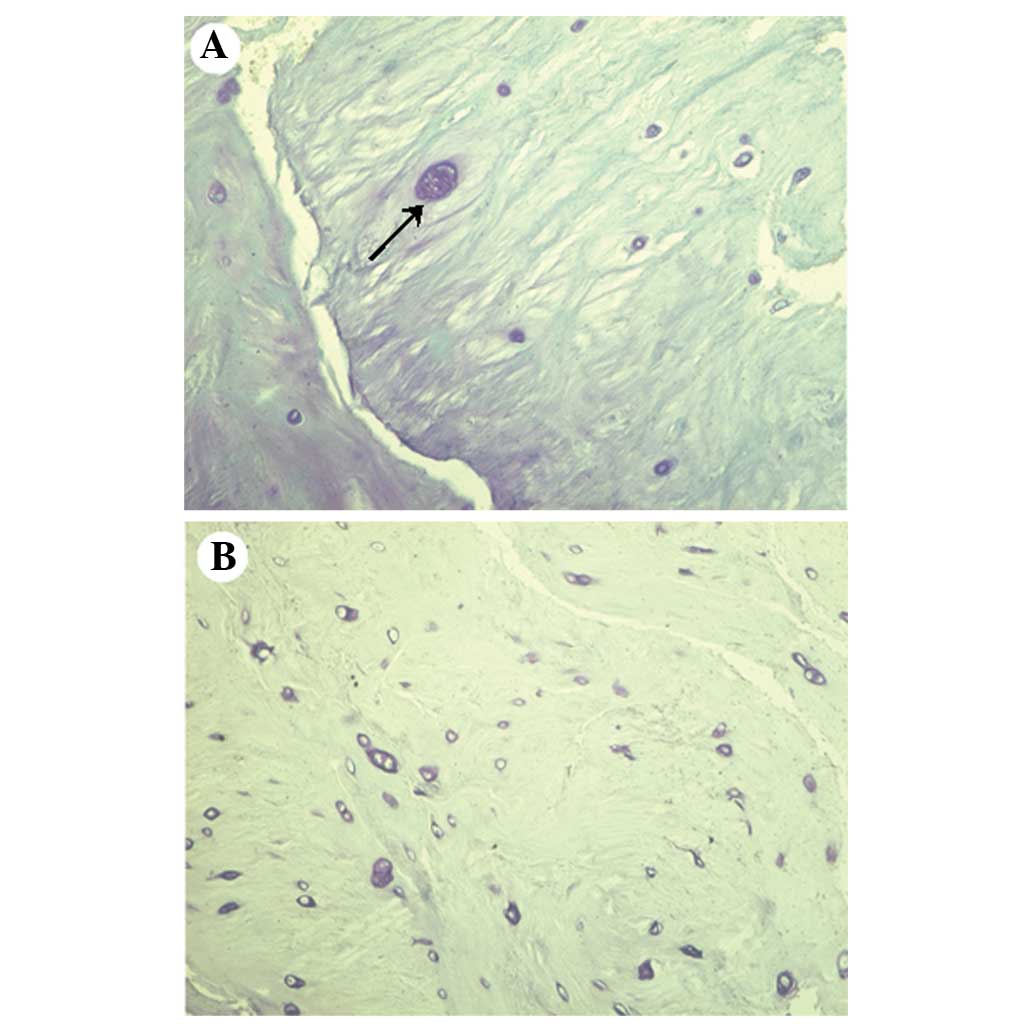
|
8
|
Igarashi T, Kikuchi S, Shubayev V and
Myers RR: 2000 Volvo Award winner in basic science studies:
Exogenous tumor necrosis factor-alpha mimics nucleus
pulposus-induced neuropathology. Molecular, histologic, and
behavioral comparisons in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
25:2975–2980. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Olmarker K, Størkson R and Berge OG:
Pathogenesis of sciatic pain: A study of spontaneous behavior in
rats exposed to experimental disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 27:1312–1317. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kallakuri S, Takebayashi T, Ozaktay AC, et
al: The effects of epidural application of allografted nucleus
pulposus in rats on cytokine expression, limb withdrawal and nerve
root discharge. Eur Spine J. 14:956–964. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murata Y, Nannmark U, Rydevik B, et al:
Nucleus pulposus-induced apoptosis in dorsal root ganglion
following experimental disc herniation in rats. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 31:382–390. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shamji MF, Allen KD, So S, et al: Gait
abnormalities and inflammatory cytokines in an autologous nucleus
pulposus model of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:648–654.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Saal JS, Franson RC, Dobrow R, et al: High
levels of inflammatory phospholipase A2 activity in lumbar disc
herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 15:674–678. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goupille P, Jayson MI, Valat JP and
Freemont AJ: The role of inflammation in disk herniation-associated
radiculopathy. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 28:60–71. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tolonen J, Grönblad M, Vanharanta H, et
al: Growth factor expression in degenerated intervertebral disc
tissue. An immunohistochemical analysis of transforming growth
factor beta, fibroblast growth factor and platelet-derived growth
factor. Eur Spine J. 15:588–596. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nagano T, Yonenobu K, Miyamoto S, et al:
Distribution of the basic fibroblast growth factor and its receptor
gene expression in normal and degenerated rat intervertebral discs.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:1972–1978. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tolonen J, Grönblad M, Virri J, et al:
Basic fibroblast growth factor immunoreactivity in blood vessels
and cells of disc herniations. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 20:271–276.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kang JD, Stefanovic-Racic M, McIntyre LA,
et al: Toward a biochemical understanding of human intervertebral
disc degeneration and herniation. Contributions of nitric oxide,
interleukins, prostaglandin E2, and matrix metalloproteinases.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 22:1065–1073. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang JD, Georgescu HI, McIntyre-Larkin L,
et al: Herniated lumbar intervertebral discs spontaneously produce
matrix metalloproteinases, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, and
prostaglandin E2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:271–277. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brisby H, Byröd G, Olmarker K, et al:
Nitric oxide as a mediator of nucleus pulposus-induced effects on
spinal nerve roots. J Orthop Res. 18:815–820. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Richardson SM, Doyle P, Minogue BM, et al:
Increased expression of matrix metalloproteinase-10, nerve growth
factor and substance P in the painful degenerate intervertebral
disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:R1262009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takahashi H, Suguro T, Okazima Y, et al:
Inflammatory cytokines in the herniated disc of the lumbar spine.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 21:218–224. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ozaktay AC, Cavanaugh JM, Asik I, et al:
Dorsal root sensitivity to interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6 and
tumor necrosis factor in rats. Eur Spine J. 11:467–475. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hoyland JA, Le Maitre C and Freemont AJ:
Investigation of the role of IL-1 and TNF in matrix degradation in
the intervertebral disc. Rheumatology (Oxford). 47:809–814. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Geiss A, Larsson K, Junevik K, et al:
Autologous nucleus pulposus primes T cells to develop into
interleukin-4-producing effector cells: An experimental study on
the autoimmune properties of nucleus pulposus. J Orthop Res.
27:97–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rand N, Reichert F, Floman Y and
Rotshenker S: Murine nucleus pulposus-derived cells secrete
interleukins-1-beta, −6, and −10 and granulocyte-macrophage
colony-stimulating factor in cell culture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
22:2598–2602. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Burke JG, Watson RW, McCormack D, et al:
Intervertebral discs which cause low back pain secrete high levels
of proinflammatory mediators. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 84:196–201.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang K-Y, Lin R-M, Chen W-Y, et al: IL-20
may contribute to the pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc
herniation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:2034–2040. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
O'Donnell JL and O'Donnell AL:
Prostaglandin E2 content in herniated lumbar disc disease. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 21:1653–1656. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Olmarker K and Larsson K: Tumor necrosis
factor alpha and nucleus-pulposus-induced nerve root injury. Spine
(Phila Pa 1976). 23:2538–2544. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoshida T, Park JS, Yokosuka K, et al:
Effect of a nonprotein bioactive agent on the reduction of
cyclooxygenase-2 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human
intervertebral disc cells in vitro. J Neurosurg Spine. 9:411–418.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Iwabuchi S, Ito M, Chikanishi T, et al:
Role of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha, cyclooxygenase-2,
prostaglandin E2, and effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in
an in vitro herniated disc resorption model. J Orthop Res.
26:1274–1278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ohtori S, Inoue G, Koshi T, et al:
Substance P-saporin down-regulates substance P receptor
immunoreactive sensory dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating the
lumbar intervertebral discs in rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
31:2987–2991. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miyamoto H, Saura R, Harada T, et al: The
role of cyclooxygenase-2 and inflammatory cytokines in pain
induction of herniated lumbar intervertebral disc. Kobe J Med Sci.
46:13–28. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Miyamoto H, Saura R, Doita M, et al: The
role of cyclooxygenase-2 in lumbar disc herniation. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 27:2477–2483. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yoshida M, Nakamura T, Kikuchi T, et al:
Expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in primary
cultures of rabbit intervertebral disc cells. J Orthop Res.
20:1298–1304. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Haro H, Kato T, Komori H, et al: Vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis in herniated
disc resorption. J Orthop Res. 20:409–415. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Caruso R, Pallone F and Monteleone G:
Emerging role of IL-23/IL-17 axis in H pylori-associated pathology.
World J Gastroenterol. 13:5547–5551. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fujino S, Andoh A, Bamba S, et al:
Increased expression of interleukin 17 in inflammatory bowel
disease. Gut. 52:65–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Loffredo S, Ayala F, Marone G, et al:
Immunopathogenesis of psoriasis and pharmacological perspectives. J
Rheumatol Suppl. 83:9–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hwang SY and Kim HY: Expression of IL-17
homologs and their receptors in the synovial cells of rheumatoid
arthritis patients. Mol Cells. 19:180–184. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou W, Kang HS and Kim BS: Th17 cells
enhance viral persistence and inhibit T cell cytotoxicity in a
model of chronic virus infection. J Exp Med. 206:313–328. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kokubu T, Haudenschild DR, Moseley TA, et
al: Immunolocalization of IL-17A, IL-17B, and their receptors in
chondrocytes during fracture healing. J Histochem Cytochem.
56:89–95. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shamji MF, Allen KD, So S, et al: Gait
abnormalities and inflammatory cytokines in an autologous nucleus
pulposus model of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:648–654.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shamji MF, Setton LA, Jarvis W, et al:
Proinflammatory cytokine expression profile in degenerated and
herniated human intervertebral disc tissues. Arthritis Rheum.
62:1974–1982. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cheng L, Fan W, Liu B, et al: Th17
lymphocyte levels are higher in patients with ruptured than
non-ruptured lumbar discs, and are correlated with pain intensity.
Injury. 44:1805–1810. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kobayashi S, Meir A, Kokubo Y, et al:
Ultrastructural analysis on lumbar disc herniation using surgical
specimens: Role of neovascularization and macrophages in hernias.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:655–662. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Naylor A: The biophysical and biochemical
aspects of intervertebral disc herniation and degeneration. Ann R
Coll Surg Engl. 31:91–114. 1962.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Doita M, Kanatani T, Ozaki T, et al:
Influence of macrophage infiltration of herniated disc tissue on
the production of matrix metalloproteinases leading to disc
resorption. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 26:1522–1527. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rätsep T, Minajeva A and Asser T:
Relationship between neovascularization and degenerative changes in
herniated lumbar intervertebral discs. Eur Spine J. 22:2474–2480.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
David G, Ciurea AV, Iencean SM and Mohan
A: Angiogenesis in the degeneration of the lumbar intervertebral
disc. J Med Life. 3:154–161. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kim KW, Lim TH, Kim JG, et al: The origin
of chondrocytes in the nucleus pulposus and histologic findings
associated with the transition of a notochordal nucleus pulposus to
a fibrocartilaginous nucleus pulposus in intact rabbit
intervertebral discs. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 28:982–990. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ha KY, Kim BG, Kim KW, et al: Apoptosis in
the sequestrated nucleus pulposus compared to the remaining nucleus
pulposus in the same patient. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 36:683–689.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|