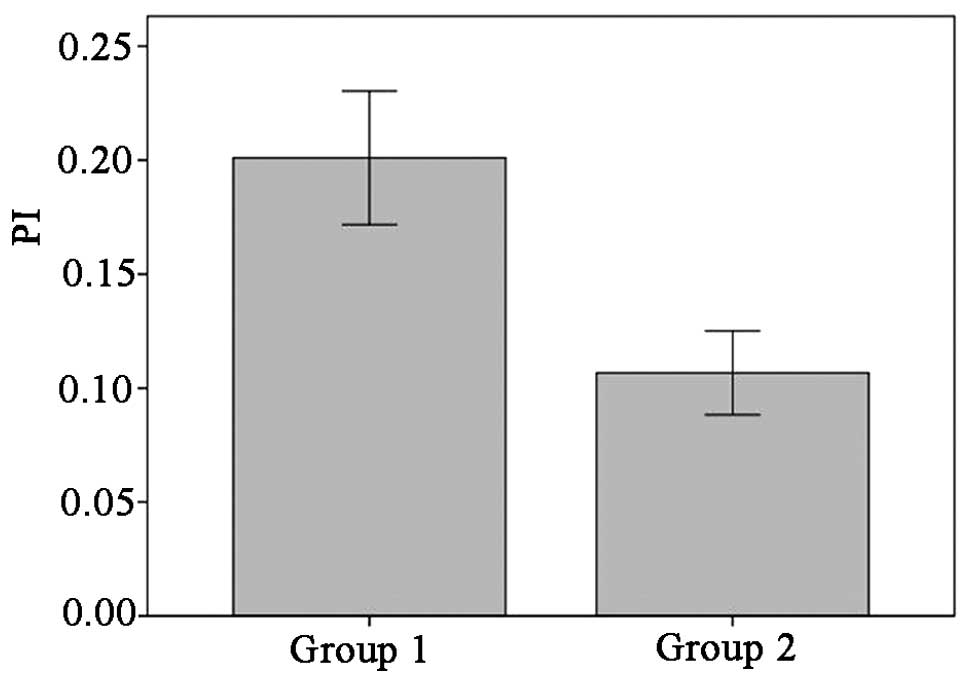
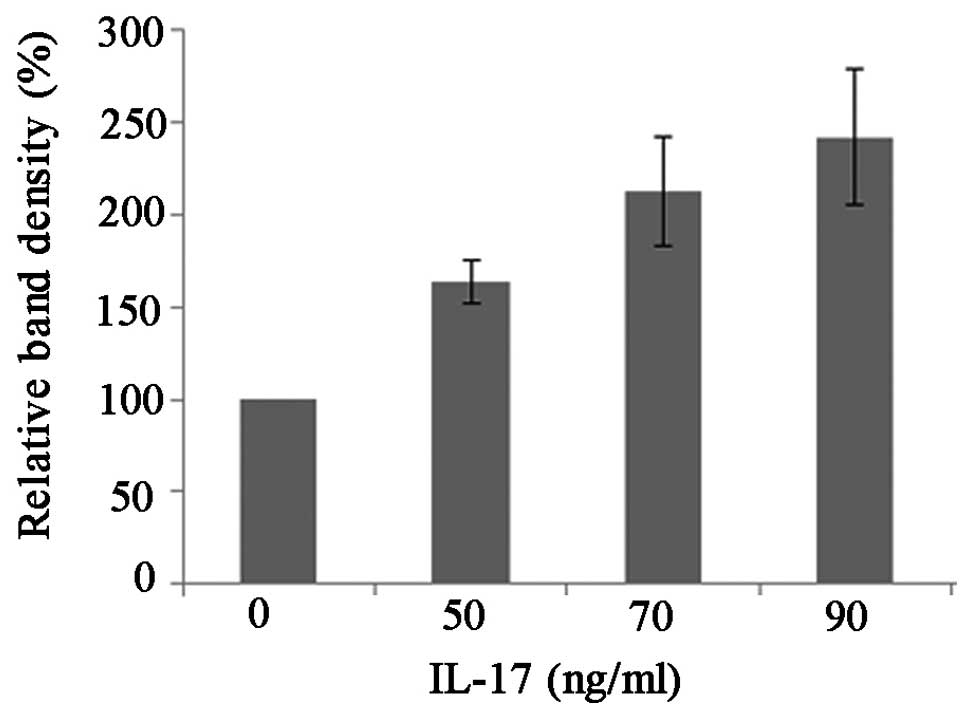
|
1
|
Ariza ME, Williams MV and Wong HK:
Targeting IL-17 in psoriasis: From cutaneous immunobiology to
clinical application. Clin Immunol. 146:131–139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bowcock AM and Krueger JG: Getting under
the skin: The immunogenetics of psoriasis. Nat Rev Immunol.
5:699–711. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gudjonsson JE, Johnston A, Sigmundsdottir
H and Valdimarsson H: Immunopathogenic mechanisms in psoriasis.
Clin Exp Immunol. 135:1–8. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Valdimarsson H, Bake BS, Jónsdótdr I and
Fry L: Psoriasis: A disease of abnormal Keratinocyte proliferation
induced by T lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 7:256–259. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ghoreschi K, Weigert C and Röcken M:
Immunopathogenesis and role of T cells in psoriasis. Clin Dermatol.
25:574–580. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P and Nestle FO:
The IL-23/Th17 axis in the immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. J
Invest Dermatol. 129:1339–1350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Blauvelt A: T-helper 17 cells in psoriatic
plaques and additional genetic links between IL-23 and psoriasis. J
Invest Dermatol. 128:1064–1067. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chiu HY, Cheng YP and Tsai TF: T helper
type 17 in psoriasis: From basic immunology to clinical practice.
Dermatol Sin. 30:136–141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Meylan E and Tschopp J: The RIP kinases:
Crucial integrators of cellular stress. Trends Biochem Sci.
30:151–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McKay IA and Leigh IM: Altered
keratinocyte growth and differentiation in psoriasis. Clin
Dermatol. 13:105–114. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tschachler E: Psoriasis: The epidermal
component. Clin Dermatol. 25:589–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lowes MA, Kikuchi T, Fuentes-Duculan J, et
al: Psoriasis vulgaris lesions contain discrete populations of Th1
and Th17 T cells. J Invest Dermatol. 128:1207–1211. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang L, Yang XQ, Cheng J, et al:
Increased Th17 cells are accompanied by FoxP3(+) Treg cell
accumulation and correlated with psoriasis disease severity. Clin
Immunol. 135:108–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krueger JG, Fretzin S, Suárez-Fariñas M,
et al: IL-17A is essential for cell activation and inflammatory
gene circuits in subjects with psoriasis. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
130:145–154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Leonardi C, Matheson R, Zachariae C, et
al: Anti-interleukin-17 monoclonal antibody ixekizumab in chronic
plaque psoriasis. New Engl J Med. 366:1190–1199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Papp KA, Leonardi C, Menter A, et al:
Brodalumab, an anti-interleukin-17-receptor antibody for psoriasis.
New Engl J Med. 366:1181–1189. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Meylan E, Martinon F, Thome M, et al: RIP4
(DIK/PKK), a novel member of the RIP kinase family, activates
NF-kappa B and is processed during apoptosis. EMBO Rep.
3:1201–1208. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Holland PM, Willis CR, Kanaly S, et al:
RIP4 is an ankyrin repeat-containing kinase essential for
keratinocyte differentiation. Curr Biol. 12:1424–1428. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rountree RB, Willis CR, Dinh H, et al:
RIP4 regulates epidermal differentiation and cutaneous
inflammation. J Invest Dermatol. 130:102–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adams S and Munz B: RIP4 is a target of
multiple signal transduction pathways in keratinocytes:
Implications for epidermal differentiation and cutaneous wound
repair. Exp Cell Res. 316:126–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Adams S, Pankow S, Werner S and Munz B:
Regulation of NF-kappaB activity and keratinocyte differentiation
by the RIP4 protein: Implications for cutaneous wound repair. J
Invest Dermatol. 127:538–544. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bell S, Degitz K, Quirling M, et al:
Involvement of NF-kappaB signalling in skin physiology and disease.
Cell Signal. 15:1–7. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lizzul PF, Aphale A, Malaviya R, et al:
Differential expression of phosphorylated NF-kappaB/RelA in normal
and psoriatic epidermis and downregulation of NF-kappaB in response
to treatment with etanercept. J Invest Dermatol. 124:1275–1283.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gazel A, Banno T, Walsh R and Blumenberg
M: Inhibition of JNK promotes differentiation of epidermal
keratinocytes. J Biol Chem. 281:20530–20541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim HR, Cho ML, Kim KW, et al:
Up-regulation of IL-23p19 expression in rheumatoid arthritis
synovial fibroblasts by IL-17 through PI3-kinase-, NF-kappaB- and
p38 MAPK-dependent signalling pathways. Rheumatology (Oxford).
46:57–64. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Awane M, Andres PG, Li DJ and Reinecker
HC: NF-kappa B-inducing kinase is a common mediator of IL-17-,
TNF-alpha-, and IL-1 beta-induced chemokine promoter activation in
intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol. 162:5337–5344.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong C: Diversification of T-helper-cell
lineages: Finding the family root of IL-17-producing cells. Nat Rev
Immunol. 6:329–333. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|