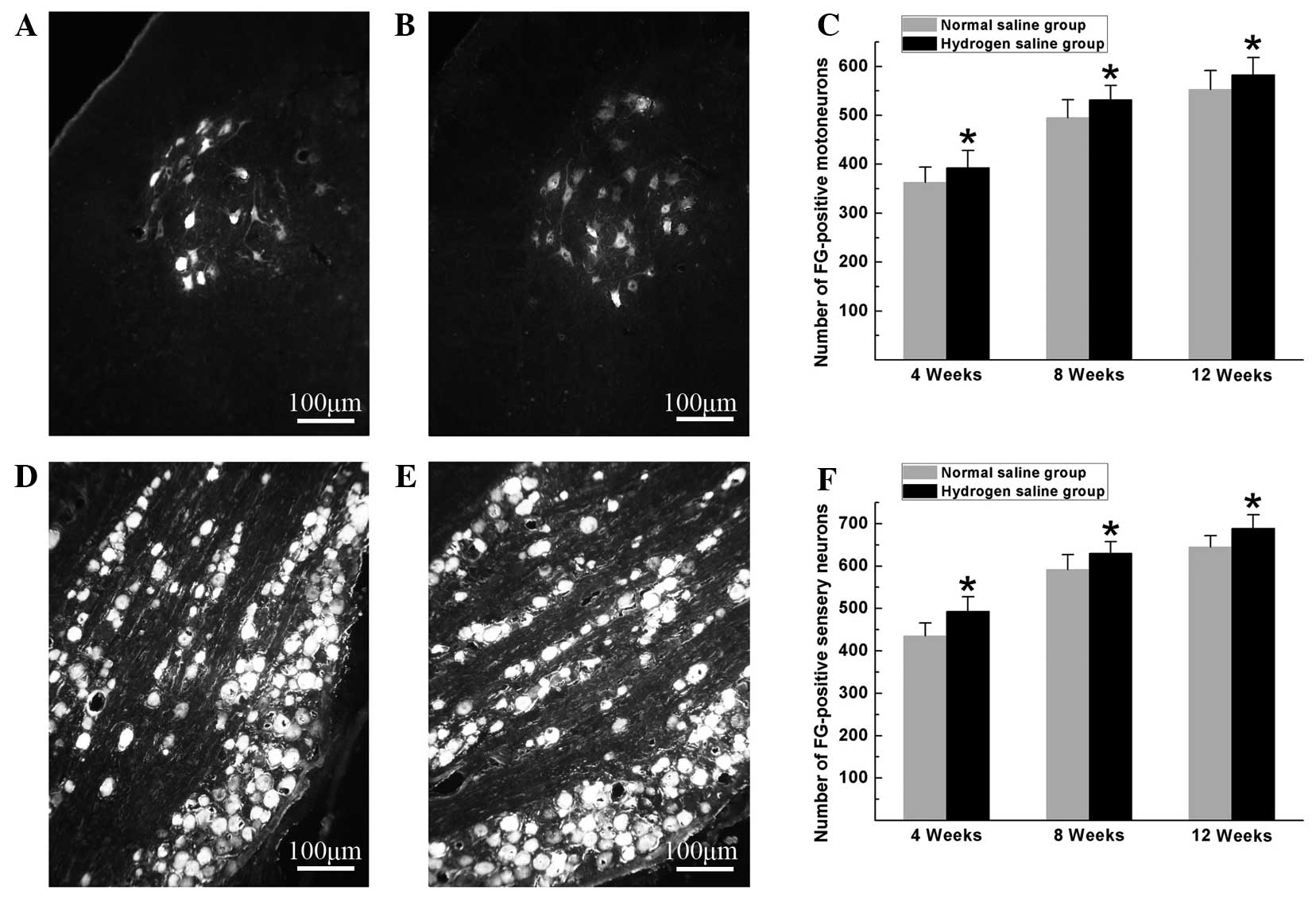
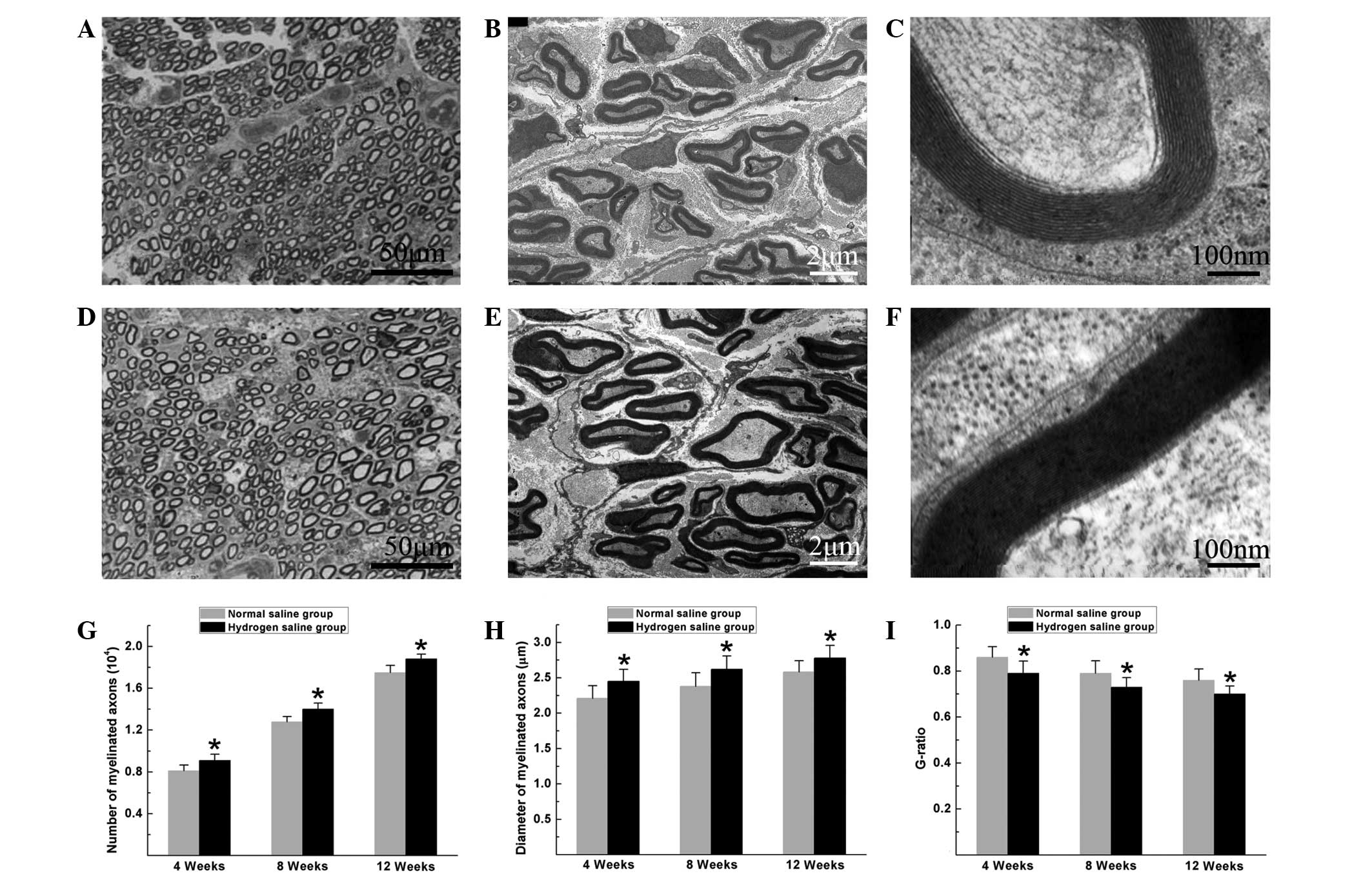
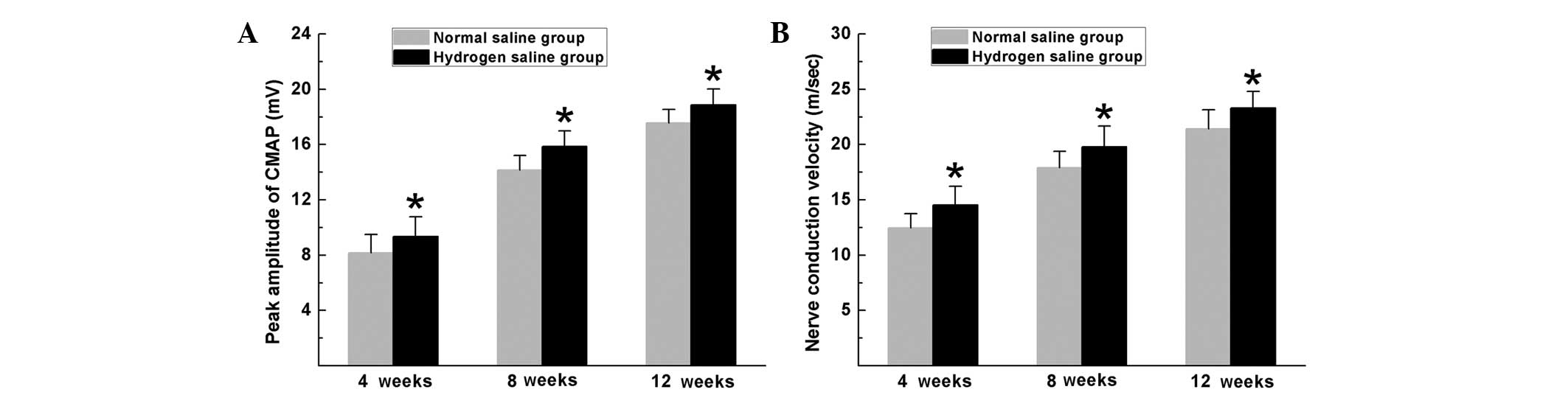
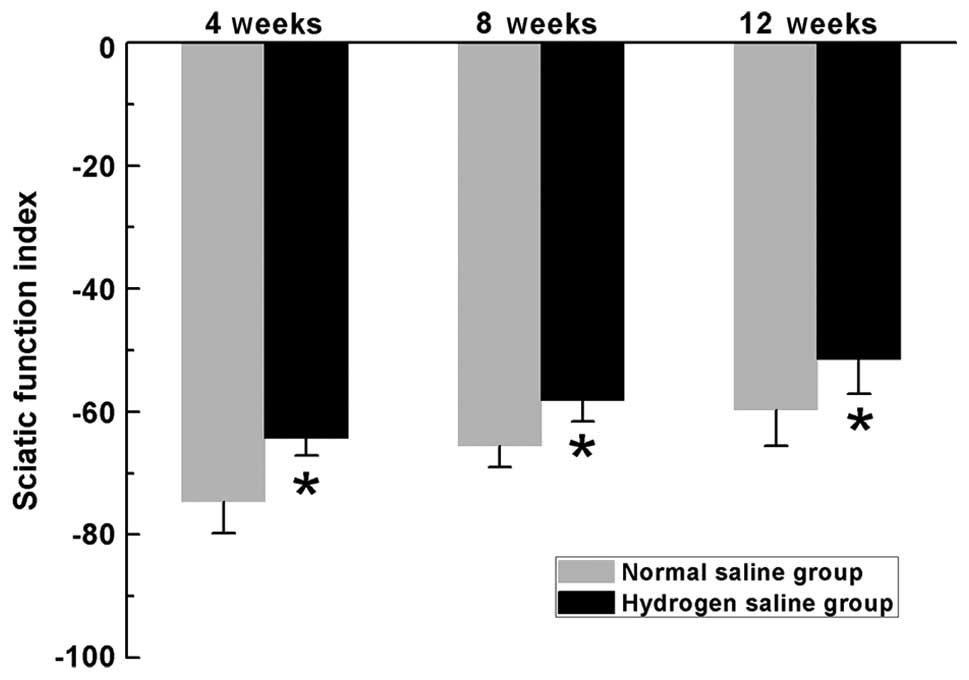
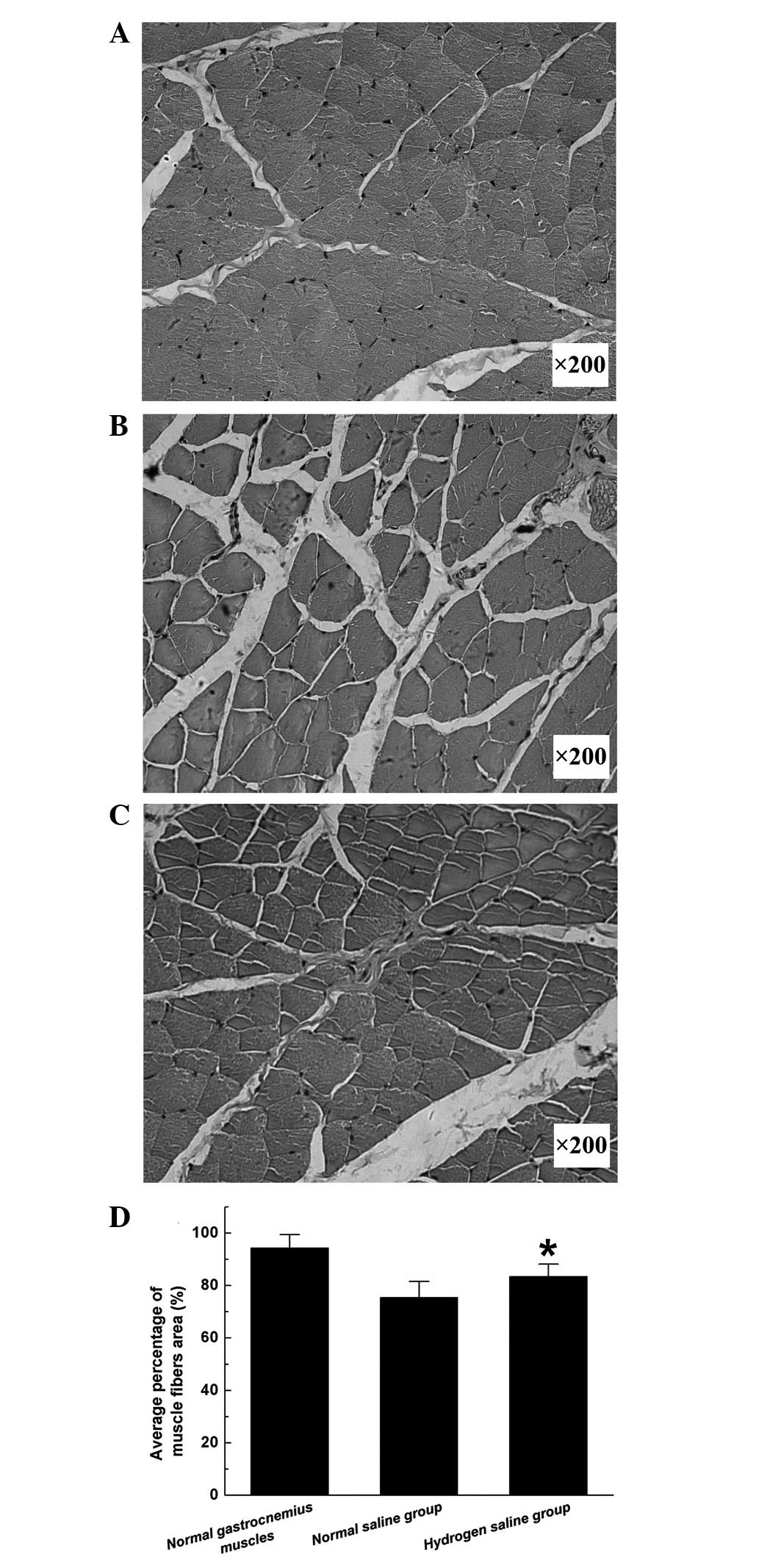
|
1
|
Alluin O, Wittmann C, Marqueste T, et al:
Functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury and implantation
of a collagen guide. Biomaterials. 30:363–373. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kehoe S, Zhang XF and Boyd D: FDA approved
guidance conduits and wraps for peripheral nerve injury: A review
of materials and efficacy. Injury. 43:553–572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tang X, Xue C, Wang Y, Ding F, Yang Y and
Gu X: Bridging peripheral nerve defects with a tissue engineered
nerve graft composed of an in vitro cultured nerve equivalent and a
silk fibroin-based scaffold. Biomaterials. 33:3860–3867. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cui Q, Zhang J, Zhang L, Li R and Liu H:
Angelica injection improves functional recovery and motoneuron
maintenance with increased expression of brain derived neurotrophic
factor and nerve growth factor. Curr Neurovasc Res. 6:117–123.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nie X, Zhang YJ, Tian WD, et al:
Improvement of peripheral nerve regeneration by a tissue-engineered
nerve filled with ectomesenchymal stem cells. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Surg. 36:32–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hart AM, Terenghi G and Wiberg M: Neuronal
death after peripheral nerve injury and experimental strategies for
neuroprotection. Neurol Res. 30:999–1011. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al:
Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing
cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 13:688–694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fukuda K, Asoh S, Ishikawa M, Yamamoto Y,
Ohsawa I and Ohta S: Inhalation of hydrogen gas suppresses hepatic
injury caused by ischemia/reperfusion through reducing oxidative
stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 361:670–674. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sato Y, Kajiyama S, Amano A, et al:
Hydrogen-rich pure water prevents superoxide formation in brain
slices of vitamin C-depleted SMP30/GNL knockout mice. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 375:346–350. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cai J, Kang Z, Liu WW, et al: Hydrogen
therapy reduces apoptosis in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia rat model.
Neurosci Lett. 441:167–172. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen C, Chen Q, Mao Y, et al:
Hydrogen-rich saline protects against spinal cord injury in rats.
Neurochem Res. 35:1111–1118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yonamine R, Satoh Y, Kodama M, Araki Y and
Kazama T: Coadministration of hydrogen gas as part of the carrier
gas mixture suppresses neuronal apoptosis and subsequent behavioral
deficits caused by neonatal exposure to sevoflurane in mice.
Anesthesiology. 118:105–113. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Q, Kang Z, Cai J, et al: Hydrogen-rich
saline protects myocardium against ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 234:1212–1219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
de Medinaceli L, Freed WJ and Wyatt RJ: An
index of the functional condition of rat sciatic nerve based on
measurements made from walking tracks. Exp Neurol. 77:634–643.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hare GM, Evans PJ, Mackinnon SE, et al:
Walking track analysis: A long-term assessment of peripheral nerve
recovery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 89:251–258. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki Y, Tanihara M, Ohnishi K, Suzuki K,
Endo K and Nishimura Y: Cat peripheral nerve regeneration across 50
mm gap repaired with a novel nerve guide composed of freeze-dried
alginate gel. Neurosci Lett. 259:75–78. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang J, Lu L, Hu X, et al: Electrical
stimulation accelerates motor functional recovery in the rat model
of 15-mm sciatic nerve gap bridged by scaffolds with longitudinally
oriented microchannels. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 24:736–745.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Novikova L, Novikov L and Kellerth JO:
Persistent neuronal labeling by retrograde fluorescent tracers: A
comparison between Fast Blue, Fluoro-Gold and various dextran
conjugates. J Neurosci Methods. 74:9–15. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu SY and Gordon T: The cellular and
molecular basis of peripheral nerve regeneration. Mol Neurobiol.
14:67–116. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA: Caspases:
Killer proteases. Trends Biochem Sci. 22:299–306. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vukosavic S, Dubois-Dauphin M, Romero N
and Przedborski S: Bax and Bcl-2 interaction in a transgenic mouse
model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem.
73:2460–2468. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Naik AK, Tandan SK, Dudhgaonkar SP, et al:
Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of peripheral
neuropathy and modulation by N-acetyl-L-cysteine in rats. Eur J
Pain. 10:573–579. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Senoglu M, Nacitarhan V, Kurutas EB,
Senoglu N, Altun I, Atli Y and Ozbag D: Intraperitoneal
alpha-lipoic acid to prevent neural damage after crush injury to
the rat sciatic nerve. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj.
4:222009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Formichi P, Battisti C, Radi E, Di Maio G
and Federico A: Apoptosis, oxidative stress and neurological
disease. J Siena Acad Sci. 1:40–45. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bromberg MB: Quantitative
ElectromyographyElectrodiagnosis in Clinical Neurology. Aminoff MJ:
4th. Churchill Livingstone; New York, NY: pp. 257–263. 1999
|
|
26
|
Rosen JM, Pham HN and Hentz VR: Fascicular
tubulization: A comparison of experimental nerve repair techniques
in the cat. Ann Plast Surg. 22:467–478. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matsumoto K, Ohnishi K, Kiyotani T, et al:
Peripheral nerve regeneration across an 80-mm gap bridged by a
polyglycolic acid (PGA)-collagen tube filled with laminin-coated
collagen fibers: A histological and electrophysiological evaluation
of regenerated nerves. Brain Res. 868:315–328. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sherman DL and Brophy PJ: Mechanisms of
axon ensheathment and myelin growth. Nat Rev Neurosci. 6:683–690.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|