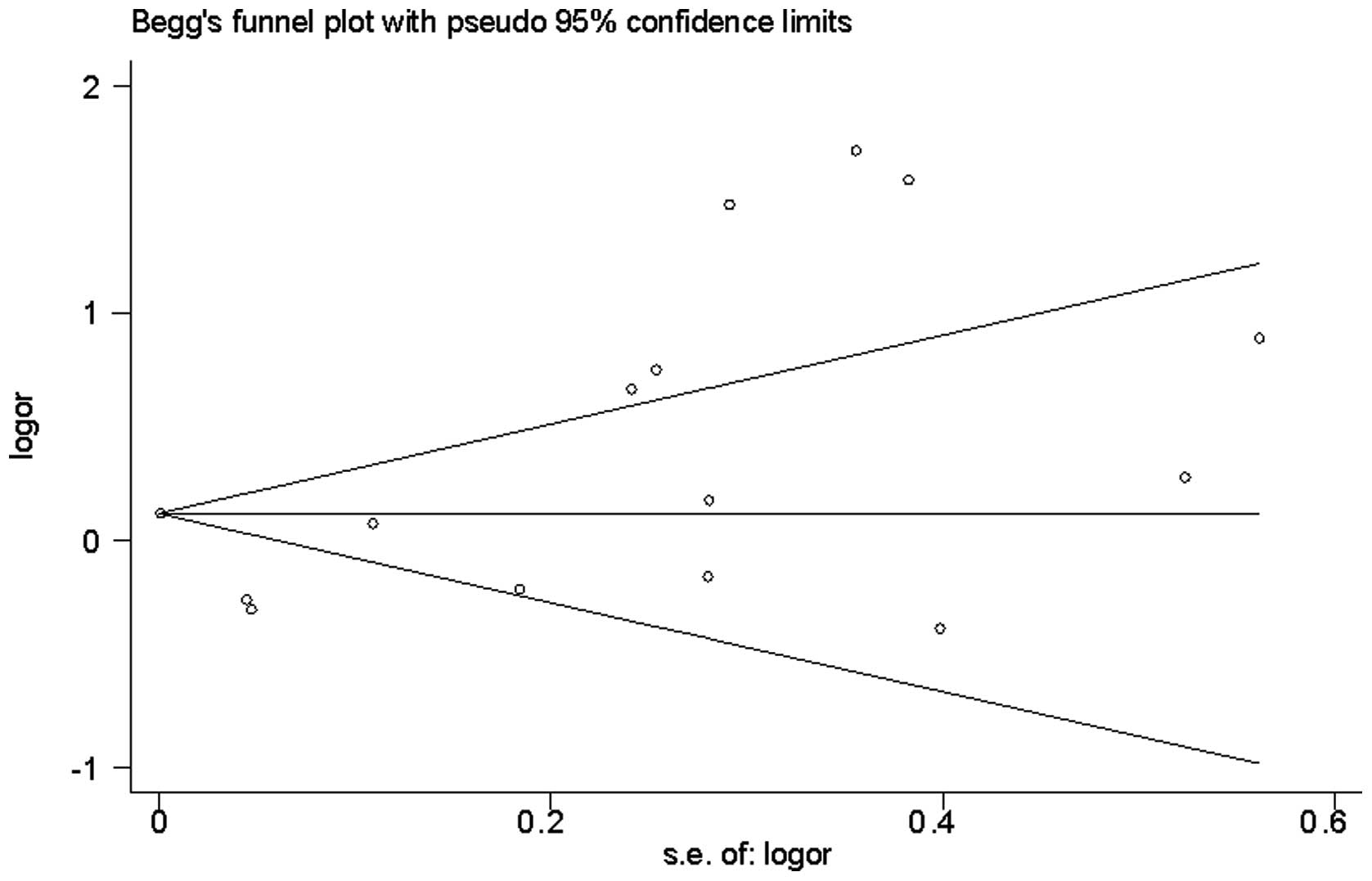
|
1
|
Shaw JE, Sicree RA and Zimmet PZ: Global
estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 87:4–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee JY, Jeon I, Lee JM, et al: Diabetes
mellitus as an independent risk factor for lung cancer: A
meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Cancer. 49:2411–2423.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J and Wiersma
ST: Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: New
estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity.
Vaccine. 30:2212–2219. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Keyvani H, Agah S, Kabir A and Alavian SM:
Prevalence and risk factors of isolated anti-HBc antibody and
occult hepatitis B infection in hemodialysis patients: A nationwide
study. Ann Hepatol. 12:213–219. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schillie SF, Xing J, Murphy TV and Hu DJ:
Prevalence of hepatitis B virus infection among persons with
diagnosed diabetes mellitus in the United States, 1999–2010. J
Viral Hepat. 19:674–676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li-Ng M, Tropp S, Danoff A and Bini EJ:
Association between chronic hepatitis B virus infection and
diabetes among Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders. Dig Liver
Dis. 39:549–556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang SQ, Chen HS, Jiang D, et al:
Relationship between chronic hepatitis C and type II diabetes
mellitus. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi.
17:46–49. 2003.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qureshi H, Ahsan T, Mujeeb SA, et al:
Diabetes mellitus is equally frequent in chronic HCV and HBV
infection. J Pak Med Assoc. 52:280–283. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang JH, Sun CM, Xu XB and Bao CX:
Susceptibility of diabetes in patients with positive hepatitis B
surface antigen. Zhongguo Wuzhen Xue Zazhi. 2:5642002.(In
Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Spradling PR, Simons B, Narayanan M, et
al: Incidence of diabetes mellitus in a population-based cohort of
persons with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Viral Hepat.
20:510–513. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jan CF, Chen CJ, Chiu YH, et al: A
population-based study investigating the association between
metabolic syndrome and hepatitis B/C infection (Keelung
Community-based Integrated Screening study No.10). Int J Obes
(Lond). 30:794–799. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reilly ML, Schillie SF, Smith E, et al:
Increased risk of acute hepatitis B among adults with diagnosed
diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 6:858–866. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang ZS, Huang TS, Wu TH, et al:
Asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B virus infection does not increase
the risk of diabetes mellitus: A ten-year observation. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:1420–1425. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang CS, Chang TT, Yao WJ, et al: The
impact of smoking on incident type 2 diabetes in a cohort with
hepatitis B but not hepatitis C infection. J Viral Hepat. Aug.
31–2010.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
15
|
Imazeki F, Yokosuka O, Fukai K, et al:
Prevalence of diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance in patients
with chronic hepatitis C: Comparison with hepatitis B
virus-infected and hepatitis C virus-cleared patients. Liver Int.
28:355–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao P, Wang JB and Jiao J: Investigation
on the incidence of diabetes in chronic hepatitis C patients and
their HCV genotypes. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 14:86–88.
2006.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Knobler H, Schihmanter R, Zifroni A, et
al: Increased risk of type 2 diabetes in noncirrhotic patients with
chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Mayo Clin Proc. 75:355–359.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Naing C, Mak JW, Ahmed SI and Maung M:
Relationship between hepatitis C virus infection and type 2
diabetes mellitus: Meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol.
18:1642–1651. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Picardi A, D'Avola D, Gentilucci UV, et
al: Diabetes in chronic liver disease: From old concepts to new
evidence. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 22:274–283. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harrison SA: Liver disease in patients
with diabetes mellitus. J Clin Gastroenterol. 40:68–76. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Raddatz D and Ramadori G: Carbohydrate
metabolism and the liver: Actual aspects from physiology and
disease. Z Gastroenterol. 45:51–62. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tappy L and Minehira K: New data and new
concepts on the role of the liver in glucose homeostasis. Curr Opin
Clin Nutr Metab Care. 4:273–277. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Teli T, Xanthaki D and Karalis KP:
Regulation of appetite and insulin signaling in inflammatory
states. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1083:319–328. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Postic C, Dentin R and Girard J: Role of
the liver in the control of carbohydrate and lipid homeostasis.
Diabetes Metab. 30:398–408. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Collier B, Dossett LA, May AK and Diaz JJ:
Glucose control and the inflammatory response. Nutr Clin Pract.
23:3–15. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leclercq IA, Da Silva Morais A, Schroyen
B, et al: Insulin resistance in hepatocytes and sinusoidal liver
cells: Mechanisms and consequences. J Hepatol. 47:142–156. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Majano PL, García-Monzón C, López-Cabrera
M, et al: Inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in chronic
viral hepatitis. Evidence for a virus-induced gene upregulation. J
Clin Invest. 101:1343–1352. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoffe B, Burns DK, Bhatt HS and Combes B:
Extrahepatic hepatitis B virus DNA sequences in patients with acute
hepatitis B infection. Hepatology. 12:187–192. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimoda T, Shikata T, Karasawa T, et al:
Light microscopic localization of hepatitis B virus antigens in the
human pancreas. Possibility of multiplication of hepatitis B virus
in the human pancreas. Gastroenterology. 81:998–1005.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ji D, Cheng J, Dong Z, et al: Screening
and identification of genes trans-regulated by HBV pre-S2 protein
with cDNA microarray. World Chin J Digestology. 12:1559–1563.
2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Selvin E, Parrinello CM, Sacks DB, et al:
Trends in prevalence and control of diabetes in the United States,
1988–1994 and 1999–2010. Ann Intern Med. 160:517–525. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, et
al: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and
projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 103:137–149. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|