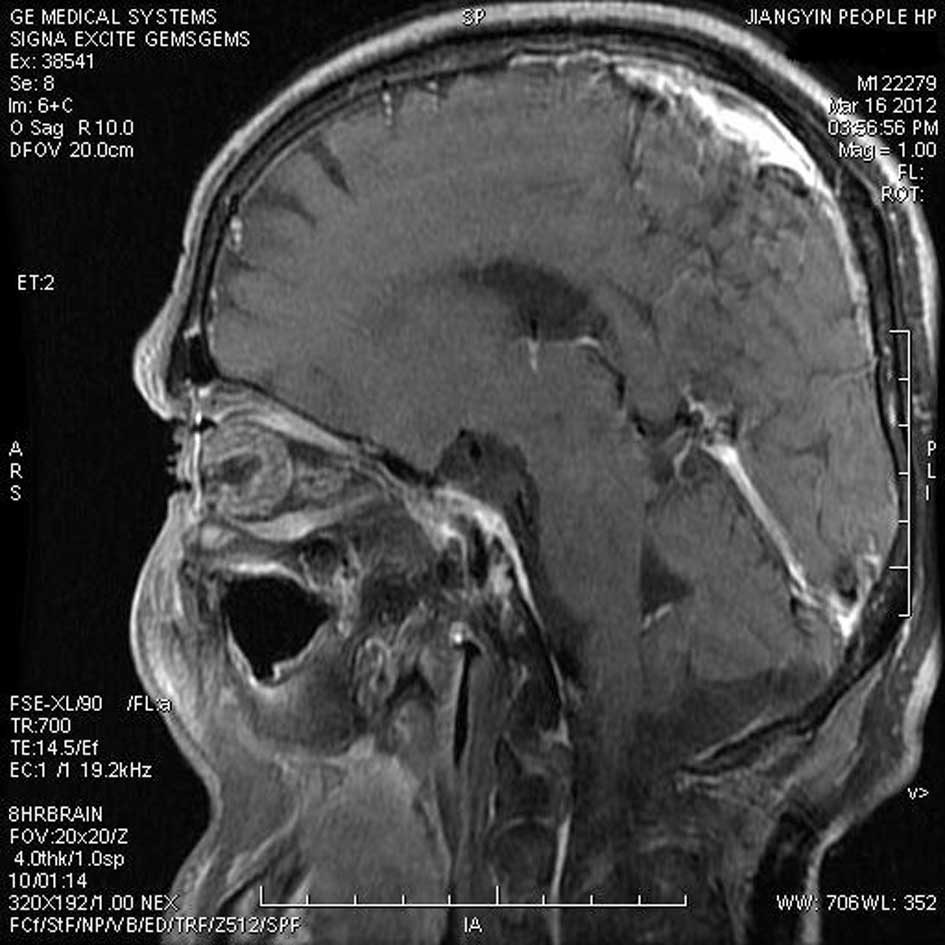
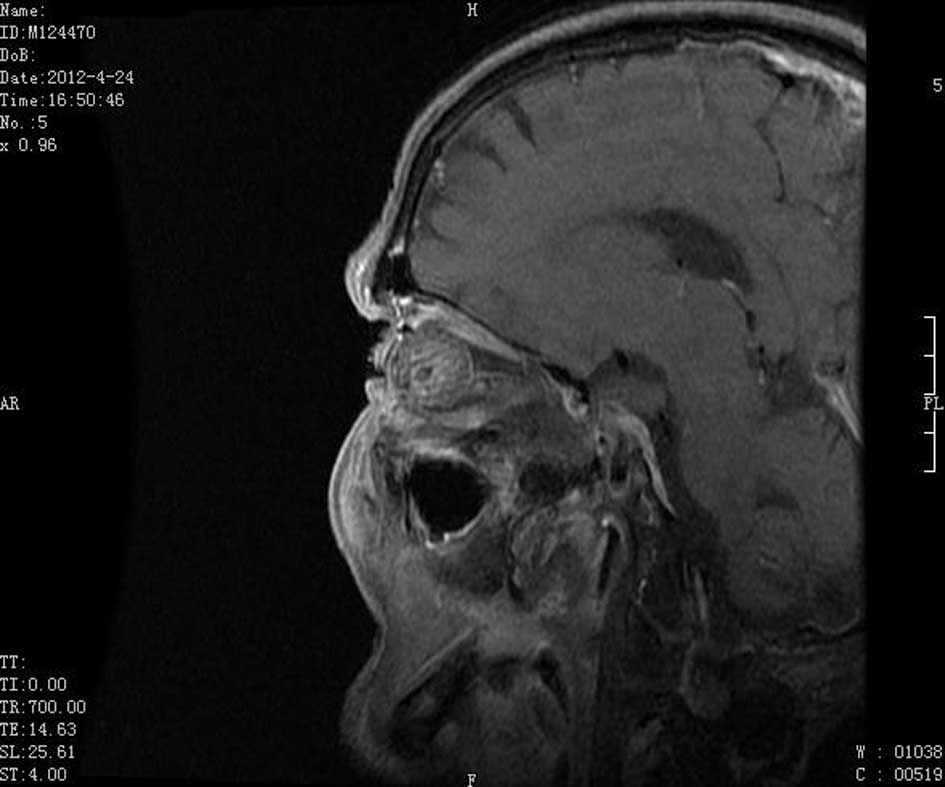
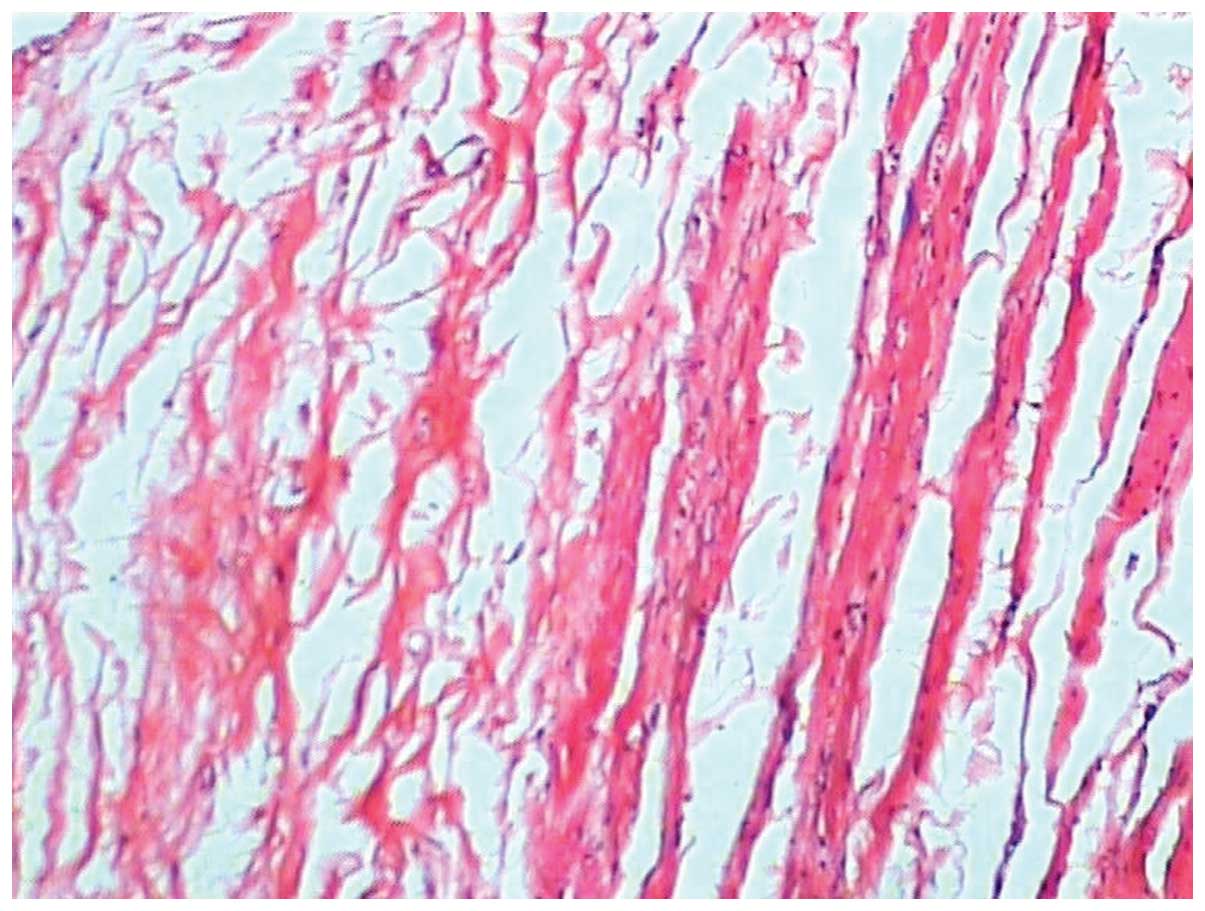
|
1
|
Tambe K, Pushpoth S, Mudhar HS and
Sandramouli S: A histopathologic study of orbital implant
vascularization. Orbit. 28:50–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buettner H and Bartley GB: Tissue
breakdown and exposure associated with orbital hydroxyapatite
implants. Am J Ophthalmol. 113:669–673. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kuzmanović Elabjer B, Petrinović-Doresić
J, Busić M and Henc-Petrinović L: Our approach in the treatment of
exposed hydroxyapatite orbital implant. Acta Med Croatica.
60:141–144. 2006.(In Croatian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu L, Shi W, Luo M, Sun Y and Fan X:
Repair of exposed hydroxyapatite orbital implants by
subconjunctival tissue flaps. J Craniofac Surg. 22:1452–1456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
el-Shahed FS, Sherif MM and Ali AT:
Management of tissue breakdown and exposure associated with orbital
hydroxyapatite implants. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 11:91–94.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim HK and La TY: Treatment of intractable
orbital implant exposure with a large conjunctival defect by
secondary insertion of the implant after preceding dermis fat
graft. Int J Ophthalmol. 6:193–197. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee BJ, Lewis CD and Perry JD: Exposed
porous orbital implants treated with simultaneous secondary implant
and dermis fat graft. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg. 26:273–276.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jung SK, Paik JS, Sonn UH and Yang SW:
Surgical outcomes of acellular human dermal grafts for large
conjunctiva defects in orbital implant insertion. Graefes Arch Clin
Exp Ophthalmol. 251:1849–1854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaynak P, Karabulut GO, Ozturker C,
Perente I, Gökyiǧit B, Demirok A and Yilmaz OF: Remove, rotate and
reimplant: A novel technique for the management of exposed porous
anophthalmic implants in eviscerated patients. Eye (Lond).
28:546–552. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoon KC, Yang Y, Jeong IY and Kook MS:
Buccal mucosal graft for hydroxyapatite orbital implant exposure.
Jpn J Ophthalmol. 55:318–320. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu AY, Vagefi MR, Georgescu D, Burroughs
JR and Anderson RL: Enduragen patch grafts for exposed orbital
implants. Orbit. 30:92–95. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu L, Shi W, Luo M, Sun Y and Fan X:
Repair of exposed hydroxyapatite orbital implants by
subconjunctival tissue flaps. J Craniofac Surg. 22:1452–1456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie RL: Fresh amnion transplantation for
ocular prosthesis exposure. Zhonghua Yan Wai Shang Zhi Ye Bing Za
Zhi. 33:305–307. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
da Guarda MG, Paraguassú GM, Cerqueira NS,
Cury PR, Farias JG and Ramalho LM: Laser GaAlAs (λ 860 nm)
photobiomodulation for the treatment of bisphosphonate-induced
osteonecrosis of the jaw. Photomed Laser Surg. 30:293–297. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sato K, Moy OJ, Peimer CA, Nakamura T,
Howard C, Ko SH, Lee TC and Nishiwaki Y: An experimental study on
costal osteochondral graft. Osteoarthr Cartilage. 20:172–183. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lan CC, Wu CS, Chiou MH, Hsieh PC and Yu
HS: Low-energy helium-neon laser induces locomotion of the immature
melanoblasts and promotes melanogenesis of the more differentiated
melanoblasts: Recapitulation of vitiligo repigmentation in vitro. J
Invest Dermatol. 126:2119–2126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Klebanov GI, Teselkin YO, Babenkova IV,
Bashkueva TY, Chiehuk TV and Vladimirov YA: Low power laser
irradiation induces leukocyte priming. Gen Physiol Biophys.
17:365–376. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peccin MS, Renno AC, de Oliveira F, Giusti
PR and Ribeiro DA: Helium-neon laser improves skin repair in
rabbits. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 14:286–289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peccin MS, de Oliveira F, Muniz Renno AC,
Pacheco de Jesus GP, Pozzi R, Gomes de Moura CF, Giusti PR and
Ribeiro DA: Helium-neon laser improves bone repair in rabbits:
Comparison at two anatomic sites. Lasers Med Sci. 28:1125–1130.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Custer PL and Trinkaus KM: Porous implant
exposure: Incidence, management and morbidity. Ophthal Plast
Reconstr Surg. 23:1–7. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rong L, Fang Q and Ren DY: Hydroxyapatite
ocular prosthesis implantation under double cap sclera after the
modified enucleation. Yan Ke Xin Jin Zhan. 26:592006.(In
Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Kazem Shakouri S, Soleimanpour J,
Salekzamani Y and Oskuie MR: Effect of low-level laser therapy on
the fracture healing process. Lasers Med Sci. 25:73–77. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu X, Lyon R, Meier HT, Thometz J and
Haworth ST: Effect of lower-level laser therapy on rabbit tibial
fracture. Photomed Laser Surg. 25:487–494. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garavello I, Baranauskas V and da
Cruz-Höfling MA: The effects of low laser irradiation on
angiogenesis in injured rat tibiae. Histol Histopathol. 19:43–48.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Calin MA and Parasca SV: In vivo study of
age-related changes in the optical properties of the skin. Lasers
Med Sci. 25:269–274. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li GZ: Physical therapy for skin
diseasesClinical Dermatology in China. Zhao B: 3rd. Jiangsu Science
and Technology Press; Nanjing: pp. 231–301. 2001
|