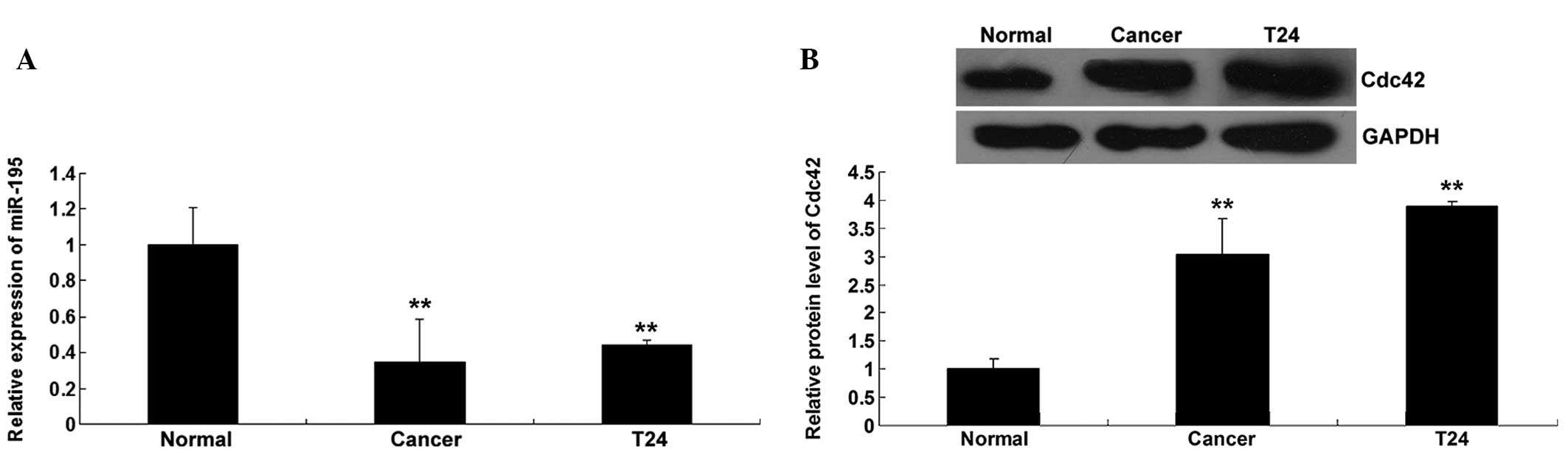
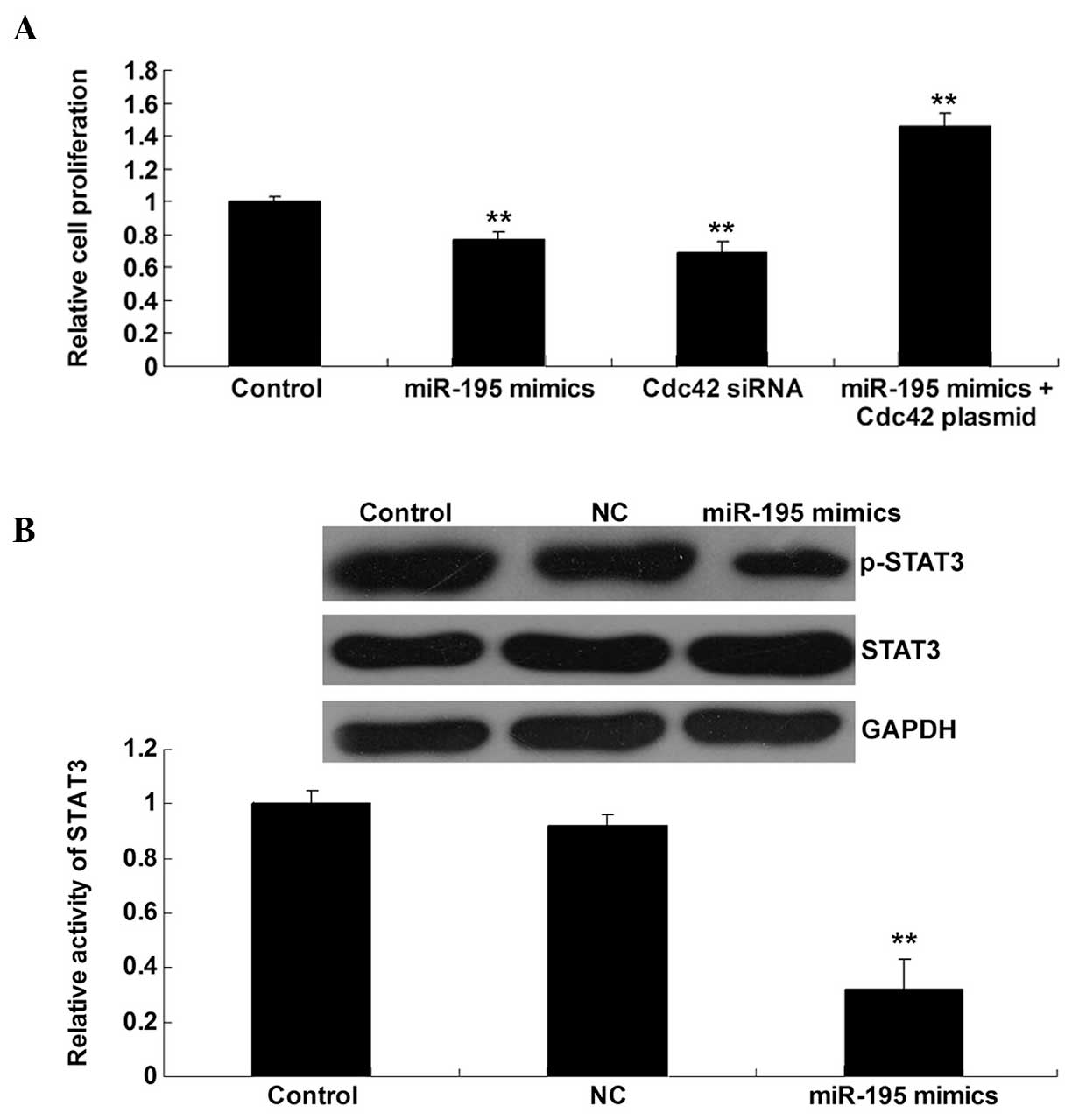
|
1
|
Skeldon SC and Larry Goldenberg S: Bladder
cancer: A portal into men's health. Urol Oncol. 33:40–44. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Nekoohesh L and
Motevaseli E: Bladder cancer biomarkers: review and update. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2395–2403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang X, Liang M, Dittmar R and Wang L:
Extracellular microRNAs in urologic malignancies: chances and
challenges. Int J Mol Sci. 14:14785–14799. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ichimi T, Enokida H, Okuno Y, et al:
Identification of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA
signatures in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:345–352. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoshino H, Seki N, Itesako T, Chiyomaru T,
Nakagawa M and Enokida H: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in
bladder cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 10:396–404. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chabre O, Libé R, Assie G, et al: Serum
miR-483-5p and miR-195 are predictive of recurrence risk in
adrenocortical cancer patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 20:579–594.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yongchun Z, Linwei T, Xicai W, et al:
MicroRNA-195 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell
proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting MYB. Cancer
Lett. 347:65–74. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tahiri A, Leivonen SK, Lüders T, et al:
Deregulation of cancer-related miRNAs is a common event in both
benign and malignant human breast tumors. Carcinogenesis. 35:76–85.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang G, Wu D, Zhu J, et al: Upregulation
of miR-195 increases the sensitivity of breast cancer cells to
Adriamycin treatment through inhibition of Raf-1. Oncol Rep.
30:877–889. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fei X, Qi M, Wu B, Song Y, Wang Y and Li
T: MicroRNA-195-5p suppresses glucose uptake and proliferation of
human bladder cancer T24 cells by regulating GLUT3 expression. FEBS
Lett. 586:392–397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin Y, Wu J, Chen H, et al:
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 is a novel target in micoRNA-195-mediated
cell cycle arrest in bladder cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 586:442–447.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dogini DB, Pascoal VD, Avansini SH, Vieira
AS, Pereira TC and Lopes-Cendes I: The new world of RNAs. Genet Mol
Biol. 37 (1 Suppl):285–293. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stengel K and Zheng Y: Cdc42 in oncogenic
transformation, invasion, and tumorigenesis. Cell Signal.
23:1415–1423. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu F, Chen Y, Li Y, Ju J, Wang Z and Yan
D: RNA-interference-mediated Cdc42 silencing down-regulates
phosphorylation of STAT3 and suppresses growth in human
bladder-cancer cells. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 49:121–128. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han Y, Chen J, Zhao X, et al: MicroRNA
expression signatures of bladder cancer revealed by deep
sequencing. PLoS One. 6:e182862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Itesako T, Seki N, Yoshino H, et al: The
microRNA expression signature of bladder cancer by deep sequencing:
The functional significance of the miR-195/497 cluster. PLoS One.
9:e843112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ni S, Hu J, Duan Y, Shi S, Li R, Wu H, Qu
Y and Li Y: Down expression of LRP1B promotes cell migration via
RhoA/Cdc42 pathway and actin cytoskeleton remodeling in renal cell
cancer. Cancer Sci. 104:817–825. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma L, Deng X, Wu M, Zhang G and Huang J:
Down-regulation of miRNA-204 by LMP-1 enhances CDC42 activity and
facilitates invasion of EBV-associated nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cells. FEBS Lett. 588:1562–1570. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zins K, Lucas T, Reichl P, Abraham D and
Aharinejad S: A Rac1/Cdc42 GTPase-specific small molecule inhibitor
suppresses growth of primary human prostate cancer xenografts and
prolongs survival in mice. PLoS One. 8:e749242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Volanis D, Zaravinos A, Kadiyska T,
Delakas D, Zoumpourlis V and Spandidos DA: Expression profile of
Rho kinases in urinary bladder cancer. J BUON. 16:511–521.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Raptis L, Arulanandam R, Geletu M and
Turkson J: The R(h)oads to Stat3: Stat3 activation by the Rho
GTPases. Exp Cell Res. 317:1787–1795. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Arulanandam R, Vultur A, Cao J, et al:
Cadherin-cadherin engagement promotes cell survival via Rac1/Cdc42
and signal transducer and activator of transcription-3. Mol Cancer
Res. 7:1310–1327. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Debidda M, Wang L, Zang H, Poli V and
Zheng Y: A role of STAT3 in Rho GTPase-regulated cell migration and
proliferation. J Biol Chem. 280:17275–17285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|