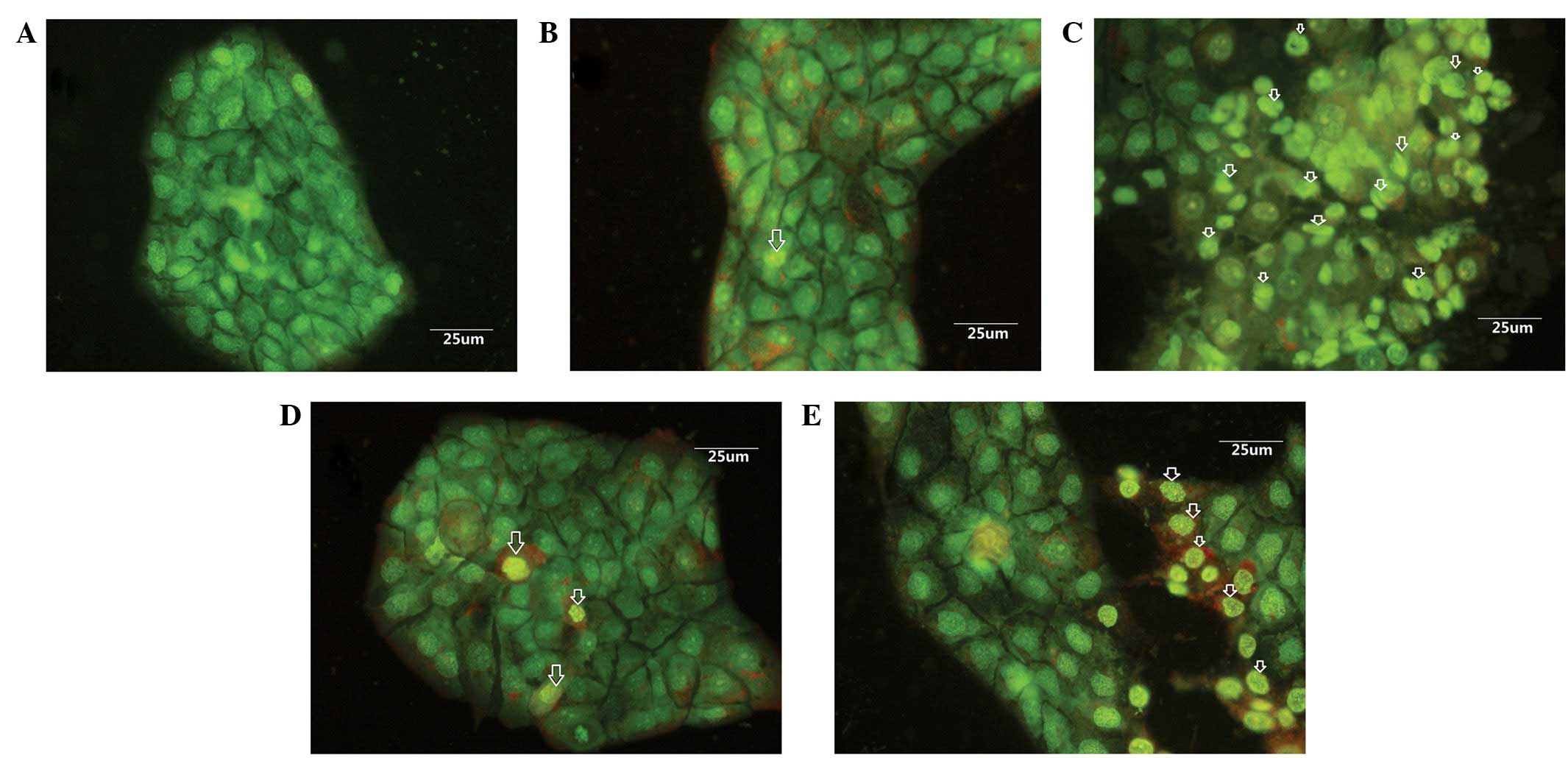
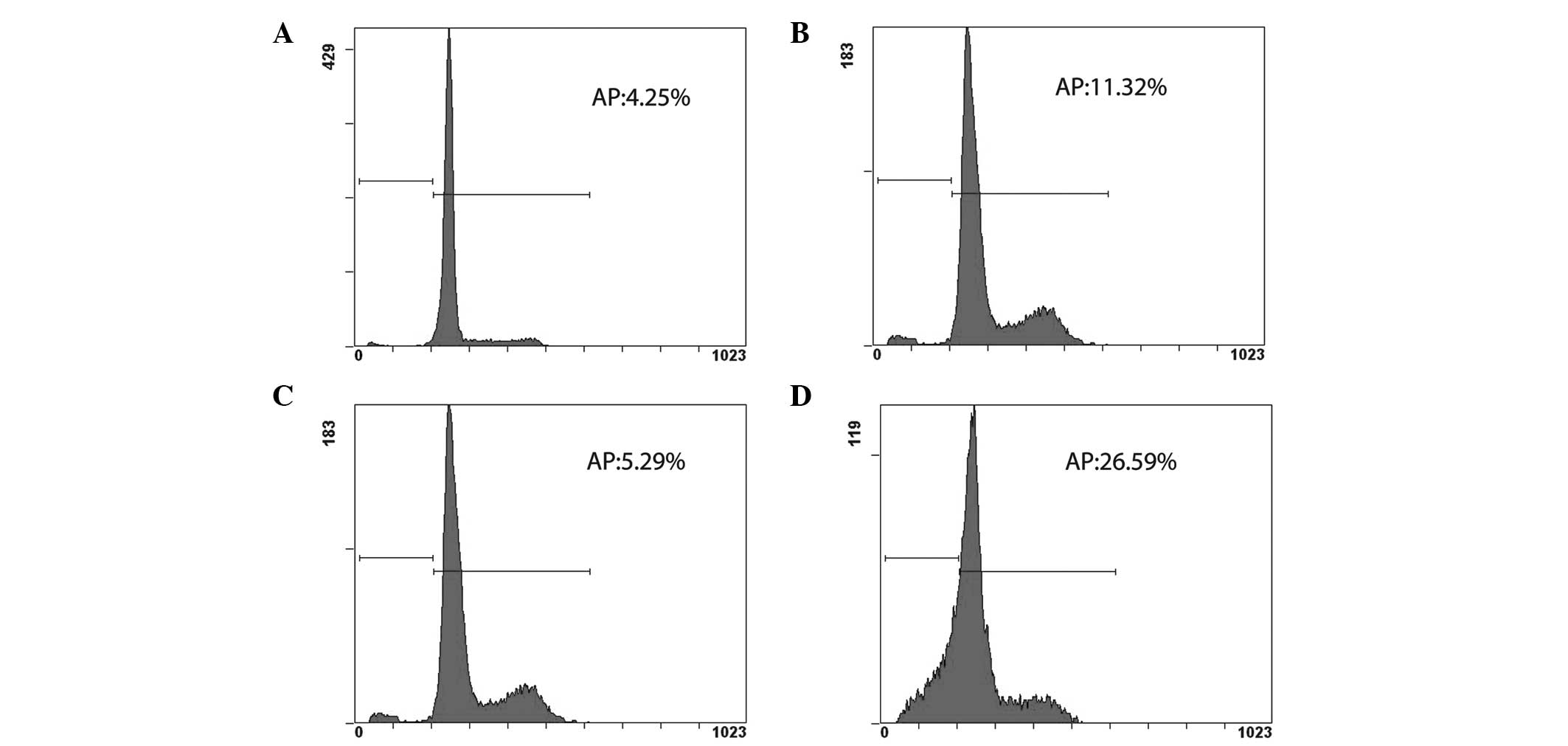
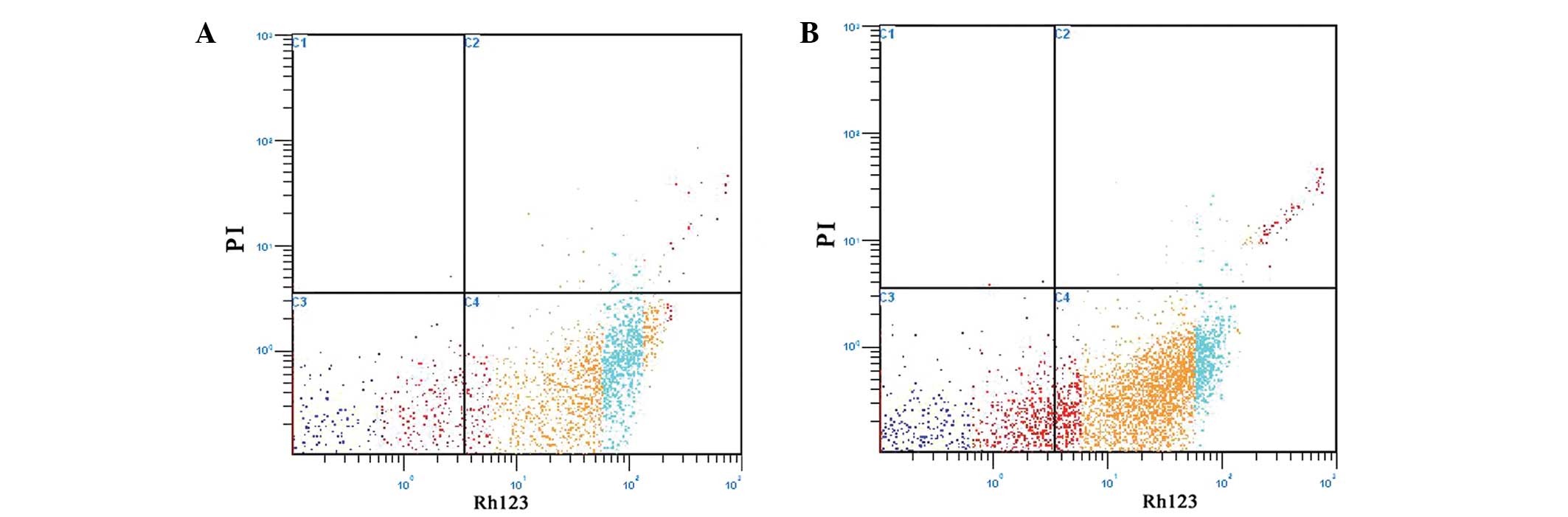
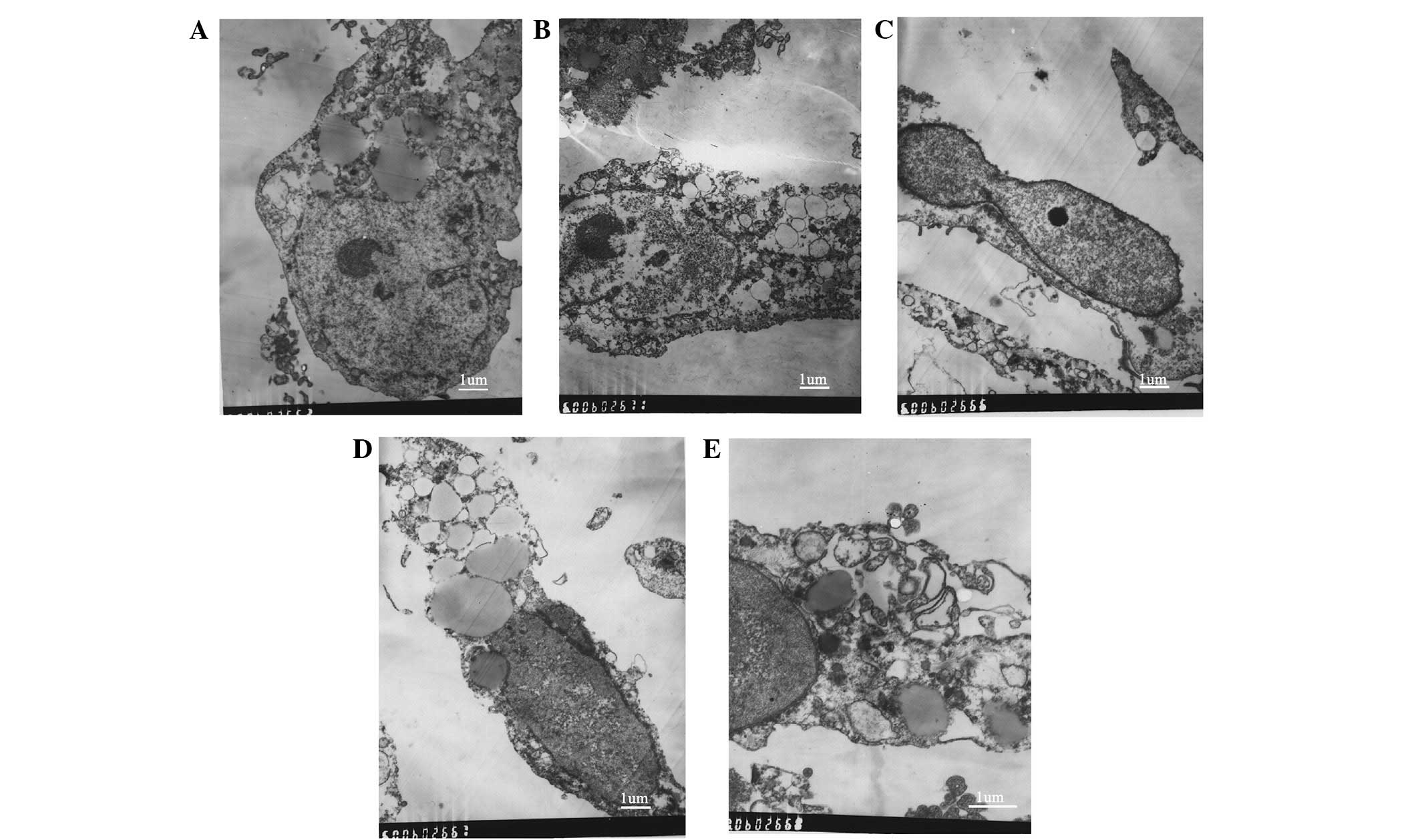
|
1
|
Tan W, Lu J, Huang M, et al: Anti-cancer
natural products isolated from chinese medicinal herbs. Chin Med.
6:272011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Monks NR, Li B, Gunjan S, et al: Natural
products genomics: A novel approach for the discovery of
anti-cancer therapeutics. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 64:217–225.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Nobel WT, Matthijs HCP, Elert von Elert
E and Mur LR: Comparison of the light-limited growth of the
nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria AnabaenaAphanizomenon.
New Phytologist. 138:579–587. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Reynolds CS, Huszar V, Kruk C, et al:
Towards a functional classification of the freshwater
phytoplankton. J Plankton Res. 24:417–428. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Chen W, Li D, et al: First report
of aphantoxins in China - waterblooms of toxigenic Aphanizomenon
flos-aquae in lake Dianchi. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 65:84–92.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Klock J, Wieland A, Seifert R and
Michaelis W: Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) from
cyanobacterial mats: Characterisation and isolation method
optimisation. Marine Biol. 152:1077–1085. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mooberry SL, Leal RM, Tinley TL, et al:
The molecular pharmacology of symplostatin 1: A new antimitotic
dolastatin 10 analog. Int J Cancer. 104:512–521. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Singh RK, Tiwari SP, Rai AK and Mohapatra
TM: Cyanobacteria: An emerging source for drug discovery. J
Antibiot (Tokyo). 64:401–412. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Park HK, Kim IH, Kim J and Nam TJ:
Induction of apoptosis by laminarin, regulating the insulin-like
growth factor-IR signaling pathways in HT-29 human colon cells. Int
J Mol Med. 30:734–738. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xue M, Ge Y, Zhang J, et al: Anticancer
properties and mechanisms of fucoidan on mouse breast cancer in
vitroin vivo. PLoS One. 7:e434832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ou Y, Xu S, Zhu D, et al: Molecular
mechanisms of exopolysaccharide from Aphanothece halaphytica
(EPSAH) induced apoptosis in HeLa cells. PLoS One. 9:e872232014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hou R, Zhou QL, Wang BX, et al: Diosgenin
induces apoptosis in HeLa cells via activation of caspase pathway.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:1077–1082. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang D, Hu C, Wang G, Li D, Li G and Liu
Y: Zebrafish neurotoxicity from aphantoxins - cyanobacterial
paralytic shellfish poisons (PSPs) from Aphanizomenon
flos-aquae DC-1. Environ Toxicol. 28:239–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yap TA and Workman P: Exploiting the
cancer genome: Strategies for the discovery and clinical
development of targeted molecular therapeutics. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 52:549–573. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang L, Wang P, Wang H, et al: Fucoidan
derived from Undaria pinnatifida induces apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma SMMC-7721 cells via the ROS-mediated
mitochondrial pathway. Mar Drugs. 11:1961–1976. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alarifi S, Ali D, Alakhtani S, et al:
Reactive oxygen species-mediated DNA damage and apoptosis in human
skin epidermal cells after exposure to nickel nanoparticles. Biol
Trace Elem Res. 157:84–93. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Chen W, Guillermo R, et al:
Alpha-santalol, a chemopreventive agent against skin cancer, causes
G2/M cell cycle arrest in both p53-mutated human epidermoid
carcinoma A431 cells and p53 wild-type human melanoma UACC-62
cells. BMC Res Notes. 3:2202010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ma S, Shan LQ, Xiao YH, et al: The
cytotoxicity of methacryloxylethyl cetyl ammonium chloride, a
cationic antibacterial monomer, is related to oxidative stress and
the intrinsic mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res.
44:1125–1133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lemasters JJ, Nieminen AL, Qian T, Trost
LC, Elmore SP, Nishimura Y, Crowe RA, Cascio WE, Bradham CA,
Brenner DA and Herman B: The mitochondrial permeability transition
in cell death: A common mechanism in necrosis, apoptosis and
autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1366:177–196. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu F, Zhang SH, Shao RG and Zhen YS:
Anticancer activity of sodium caffeate and its mechanism. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 26:1248–1252. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Galfano A, Novara G, Iafrate M, et al:
Improvement of seminal parameters and pregnancy rates after
antegrade sclerotherapy of internal spermatic veins. Fertil Steril.
91:1085–1089. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zou T, Liu X, Ding S and Xing J:
Evaluation of sperm mitochondrial function using rh123/PI dual
fluorescent staining in asthenospermia and oligoasthenozoospermia.
J Biomed Res. 24:404–410. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|