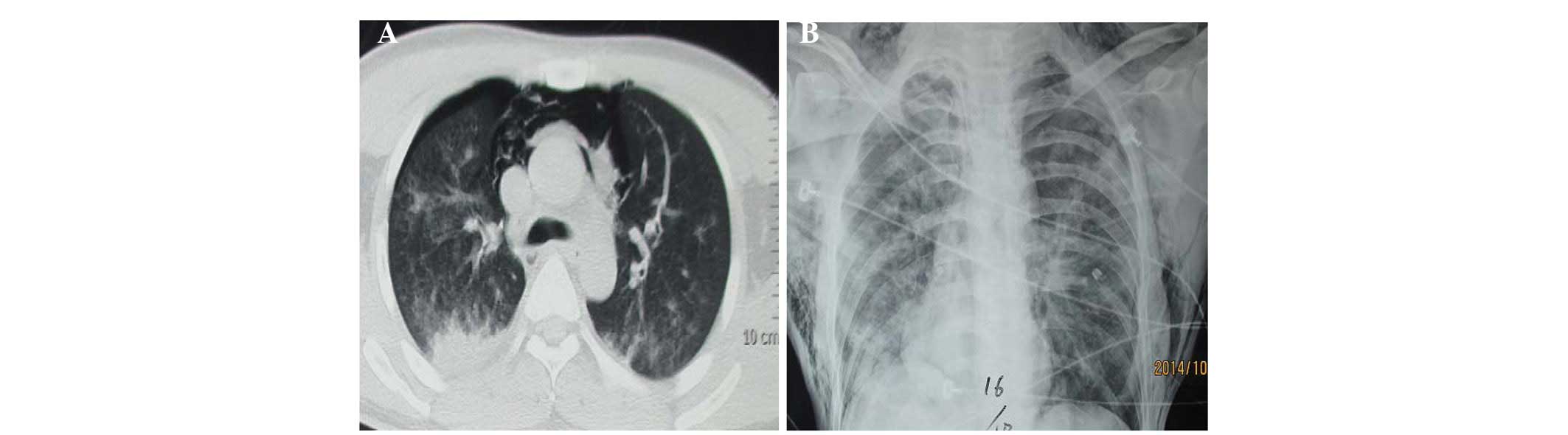
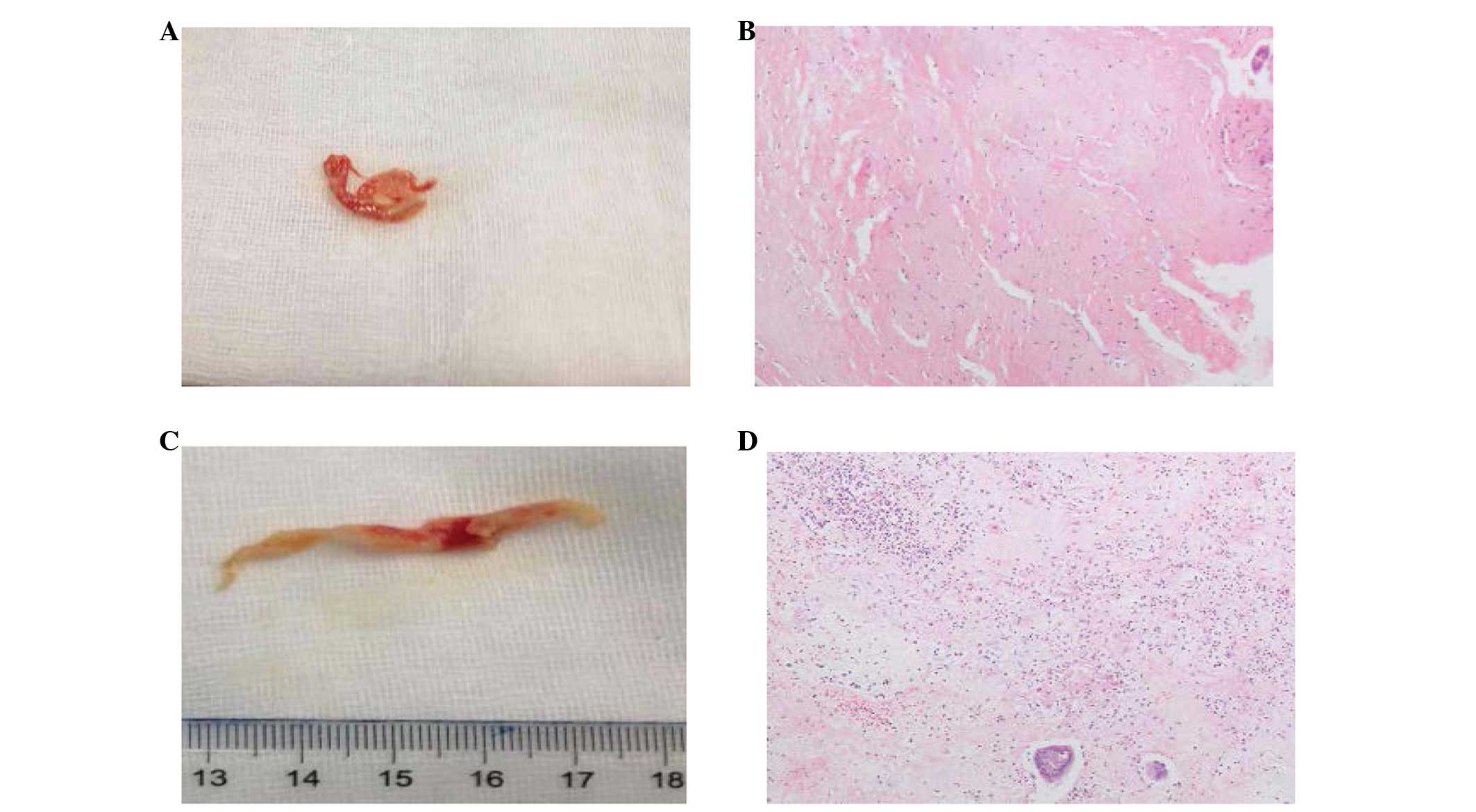
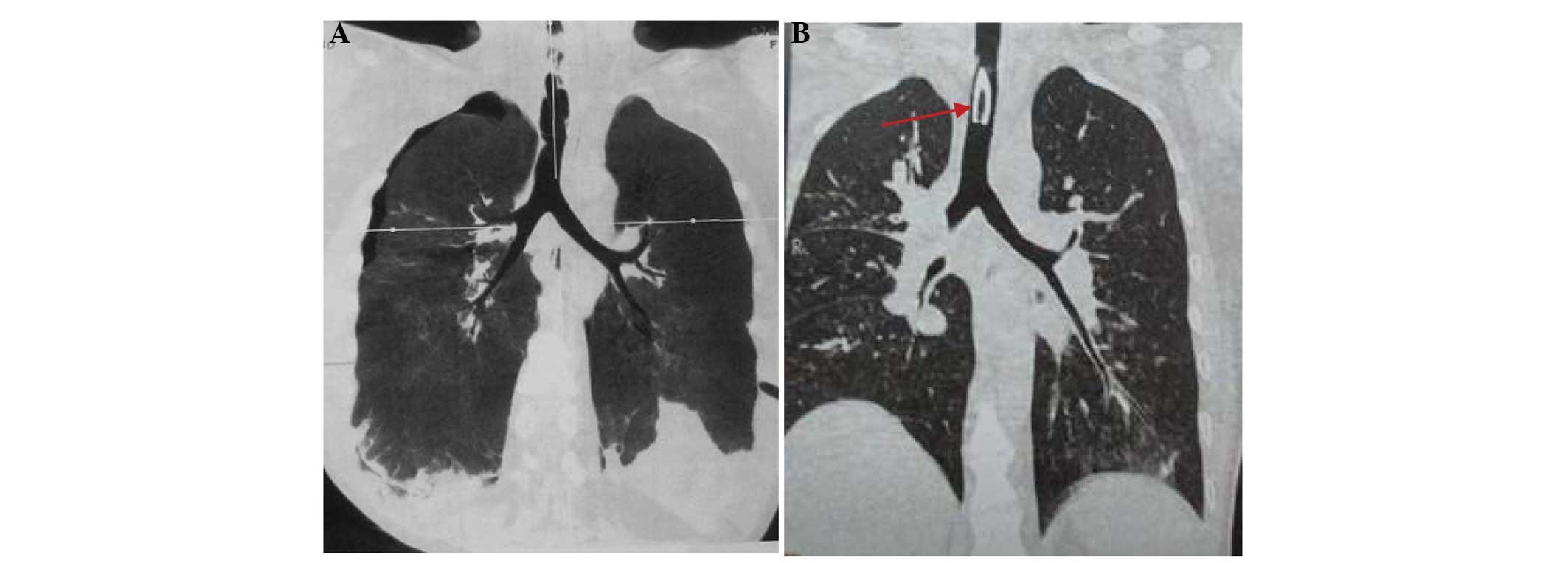
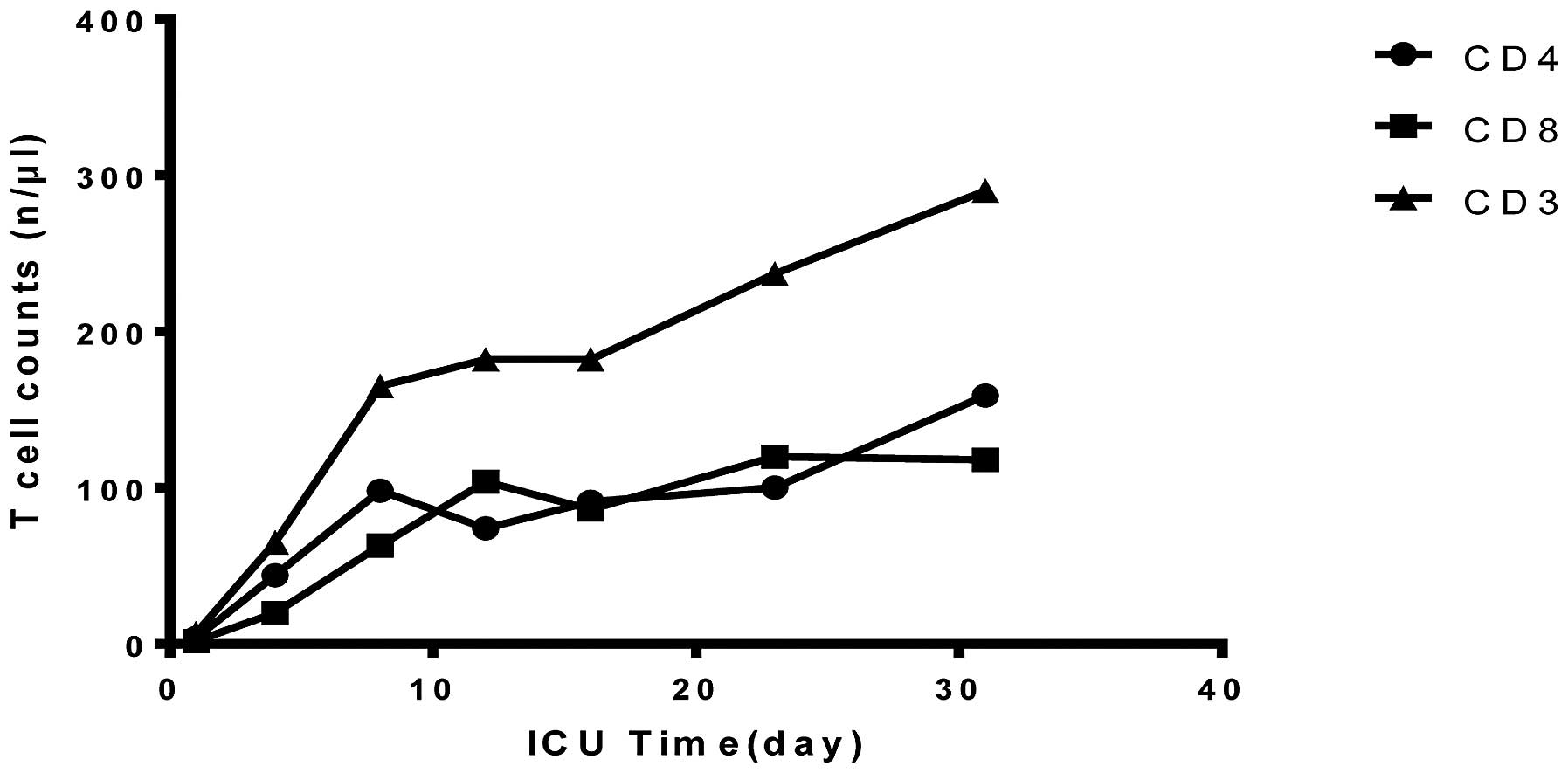
|
1
|
Ma HJ, Zhao G, Shi F and Wang YX: Eruptive
cherry angiomas associated with vitiligo: Provoked by topical
nitrogen mustard? J Dermatol. 33:877–879. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Abel EA, Sendagorta E and Hoppe RT:
Cutaneous malignancies and metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
following topical therapies for mycosis fungoides. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 14:1029–1038. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu LL, Zheng S, Wei H, Hong YX, Zhang L,
Zhang L, Chen HD and Gao XH: Multiple cutaneous malignancies and
cherry hemangiomas in a vitiligo patient treated with topical
nitrogen mustard. Dermatol Ther. 27:52–54. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weinberger B, Laskin JD, Sunil VR, Sinko
PJ, Heck DE and Laskin DL: Sulfur mustard-induced pulmonary injury:
Therapeutic approaches to mitigating toxicity. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
24:92–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Malaviya R, Sunil VR, Cervelli J, Anderson
DR, Holmes WW, Conti ML, Gordon RE, Laskin JD and Laskin DL:
Inflammatory effects of inhaled sulfur mustard in rat lung. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 248:89–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shakarjian MP, Heck DE, Gray JP, Sinko PJ,
Gordon MK, Casillas RP, Heindel ND, Gerecke DR, Laskin DL and
Laskin JD: Mechanisms mediating the vesicant actions of sulfur
mustard after cutaneous exposure. Toxicol Sci. 114:5–19. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang GQ and Xia ZF: Tissue injury by hot
fluid containing nitrogen mustard. Burns. 33:923–926. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sunil VR, Vayas KN, Cervelli JA, Malaviya
R, Hall L, Massa CB, Gow AJ, Laskin JD and Laskin DL:
Pentoxifylline attenuates nitrogen mustard-induced acute lung
injury, oxidative stress and inflammation. Exp Mol Pathol.
97:89–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Macit E, Yaren H, Aydin I, Kunak ZI, Yaman
H, Onguru O, Uysal B, Korkmaz A, Turel S and Kenar L: The
protective effect of melatonin and S-methylisothiourea treatments
in nitrogen mustard induced lung toxicity in rats. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:1283–1290. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sunil VR, Patel KJ, Shen J, Reimer D, Gow
AJ, Laskin JD and Laskin DL: Functional and inflammatory
alterations in the lung following exposure of rats to nitrogen
mustard. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 250:10–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malaviya R, Venosa A, Hall L, Gow AJ,
Sinko PJ, Laskin JD and Laskin DL: Attenuation of acute nitrogen
mustard-induced lung injury, inflammation and fibrogenesis by a
nitric oxide synthase inhibitor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
265:279–291. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Osterlund C, Lilliehöök B,
Ekstrand-Hammarström B, Sandström T and Bucht A: The nitrogen
mustard melphalan activates mitogen-activated phosphorylated
kinases (MAPK), nuclear factor-kappaB and inflammatory response in
lung epithelial cells. J Appl Toxicol. 25:328–337. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ucar M, Korkmaz A, Reiter RJ, Yaren H,
Oter S, Kurt B and Topal T: Melatonin alleviates lung damage
induced by the chemical warfare agent nitrogen mustard. Toxicol
Lett. 173:124–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ramsay DL, Meller JA and Zackheim HS:
Topical treatment of early cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Hematol Oncol
Clin North Am. 9:1031–1056. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xie J, Shults K, Flye L, Jiang F, Head DR
and Briggs RC: Overexpression of GSTA2 protects against cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis induced by the DNA inter-strand crosslinking
nitrogen mustard, mechlorethamine. J Cell Biochem. 95:339–351.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Inturi S, TewariSingh N, Agarwal C, White
CW and Agarwal R: Activation of DNA damage repair pathways in
response to nitrogen mustard-induced DNA damage and toxicity in
skin keratinocytes. Mutat Res 763–764. 53–63. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
DeAlencar TA, Leitão AC and Lage C:
Nitrogen mustard- and half-mustard-induced damage in Escherichia
coli requires different DNA repair pathways. Mutat Res.
582:105–115. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eldad A, Weinberg A, Breiterman S, Chaouat
M, Palanker D and Ben-Bassat H: Early nonsurgical removal of
chemically injured tissue enhances wound healing in partial
thickness burns. Burns. 24:166–172. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rappeneau S, BaezaSquiban A, Jeulin C and
Marano F: Protection from cytotoxic effects induced by the nitrogen
mustard mechlorethamine on human bronchial epithelial cells in
vitro. Toxicol Sci. 54:212–221. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hugel B, Weltin D, Holl V, Marchal J,
Dufour P, Freyssinet JM and Bischoff PL: Assessment of apoptosis
occurring in spleen cells from nitrogen mustard-treated or
gamma-irradiated mice. Anticancer Res. 18:3289–3294.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|