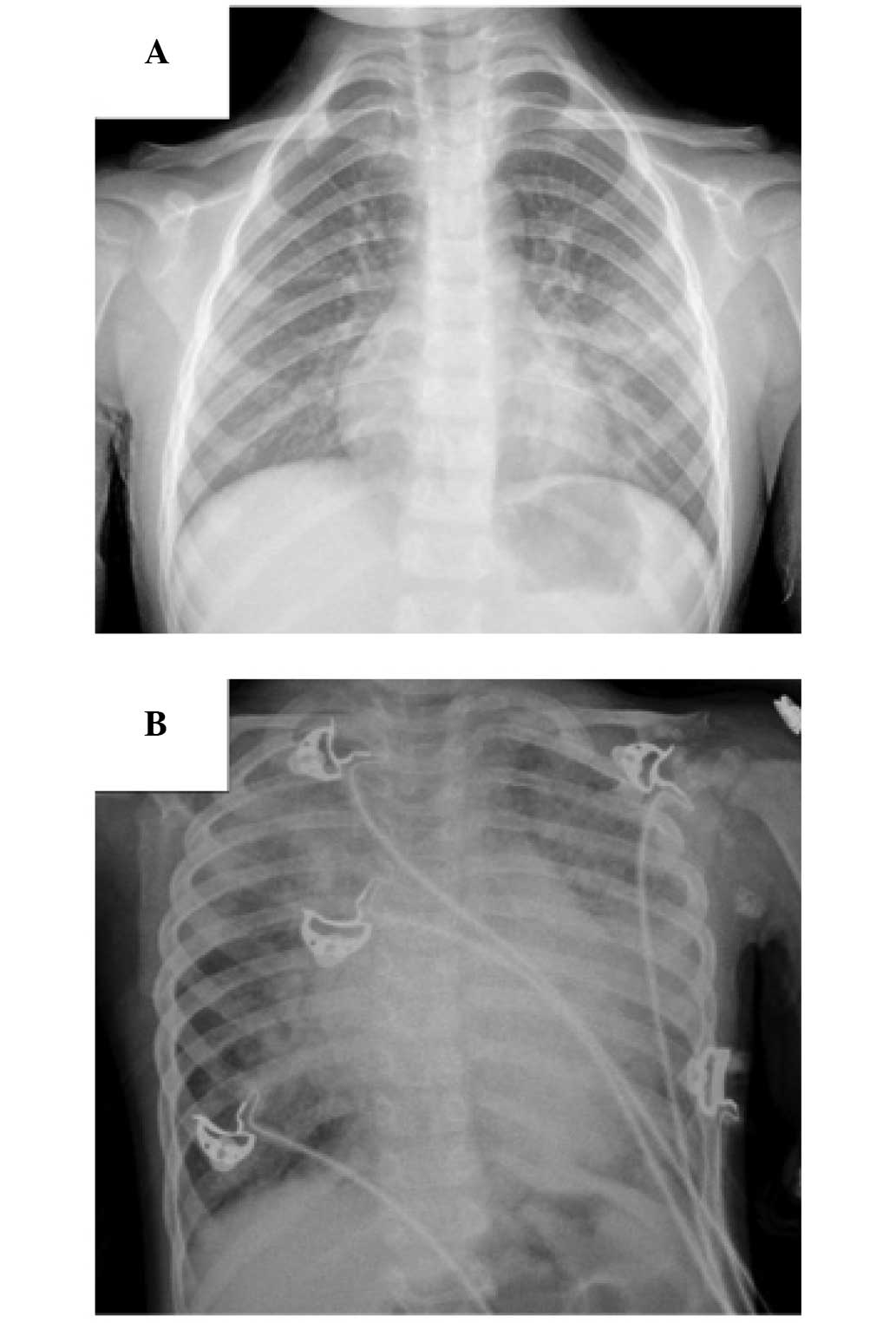
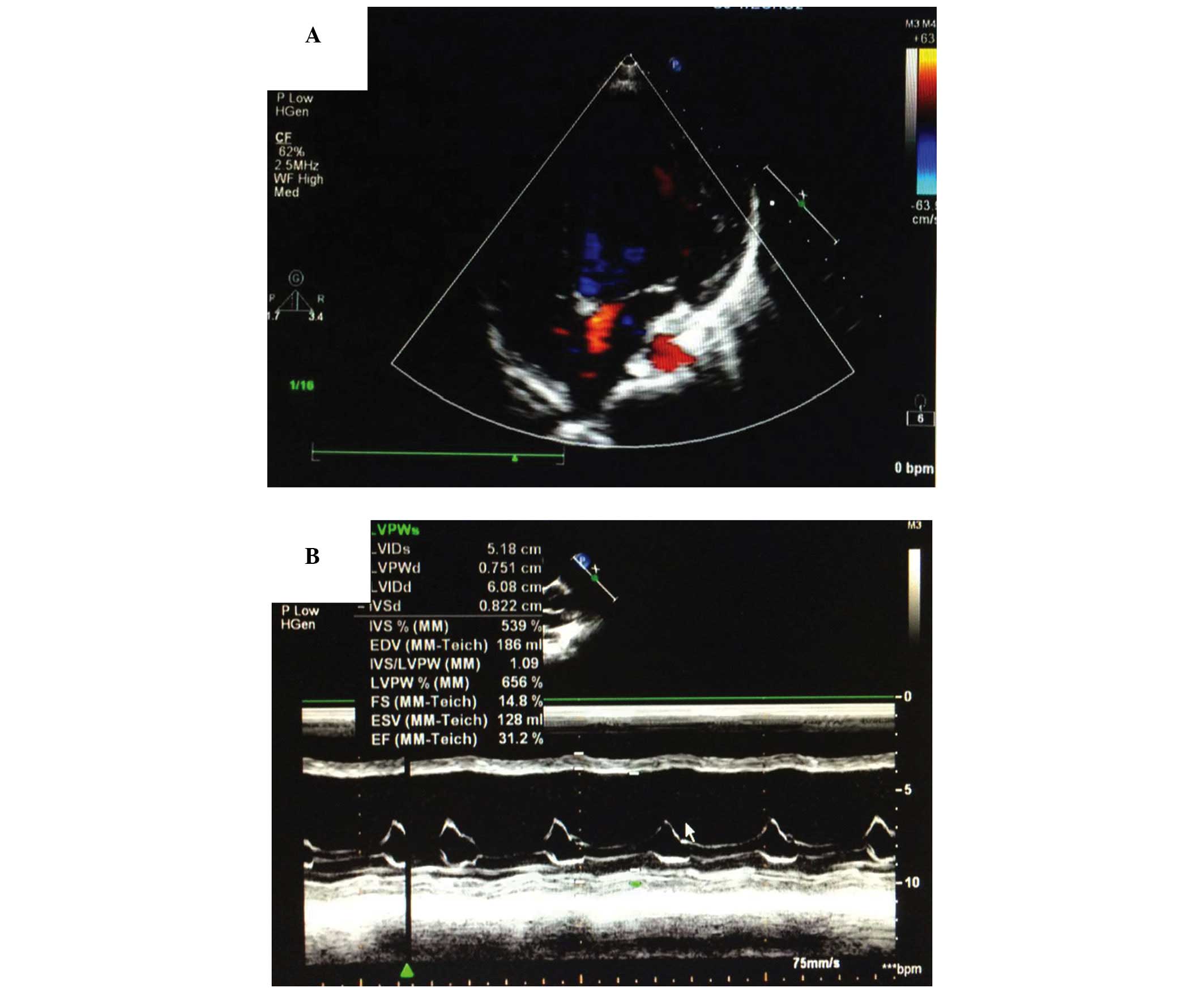
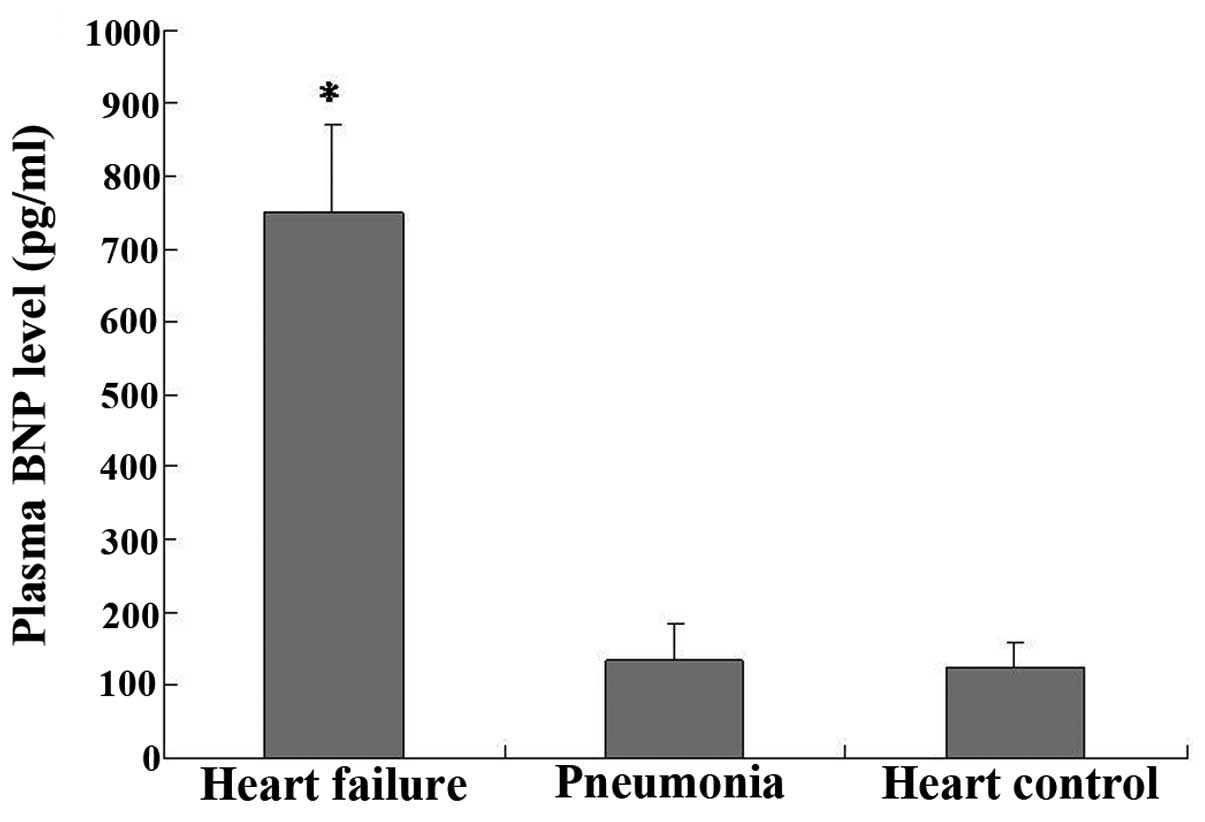
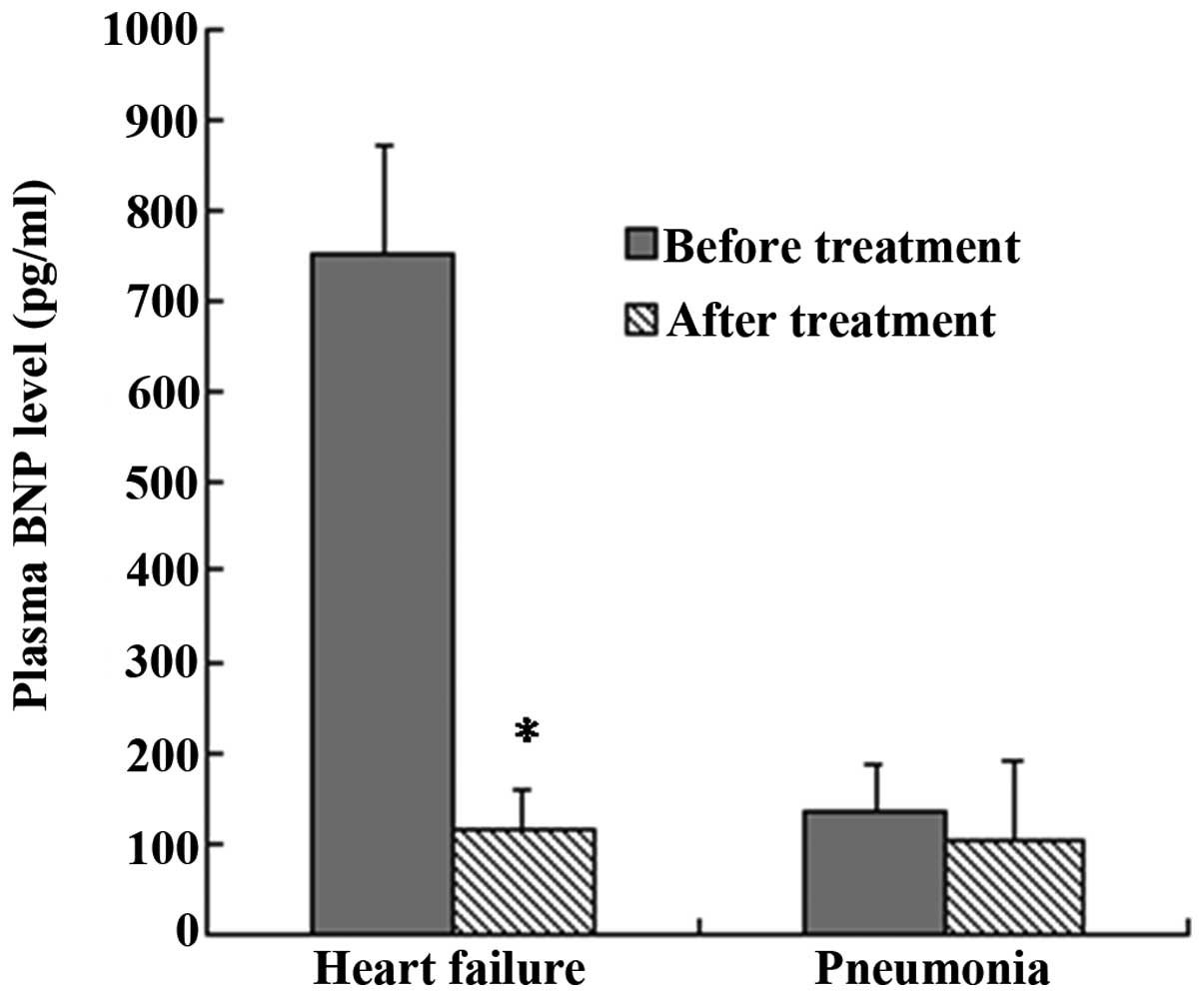
|
1
|
Clerico A, Giannoni A, Vittorini S, et al:
Thirty years of the heart as an endocrine organ: Physiological role
and clinical utility of cardiac natriuretic hormones. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H12–H20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cantinotti M, Giovannini S, Murzi B and
Clerico A: Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic relevance of
B-type natriuretic hormone and related peptides in children with
congenital heart diseases. Clin Chem Lab Med. 49:567–580. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hunt PJ, Richards AM, Nicholls MG, et al:
Immunoreactive amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide
(NT-PROBNP): A new marker of cardiac impairment. Clin Endocrinol
(Oxf). 47:287–296. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mair J, Friedl W, Thomas S and Puschendorf
B: Natriuretic peptides in assessment of left-ventricular
dysfunction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 230:132–142. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
McKelvie RS, Moe GW, Ezekowitz JA, et al:
The 2012 Canadian Cardiovascular Society heart failure management
guidelines update: Focus on acute and chronic heart failure. Can J
Cardiol. 29:168–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McMurray JJ, Adamopoulos S, Anker SD, et
al: ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines: ESC Guidelines for the
diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: 2012
The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic
Heart Failure 2012 of the European Society of Cardiology. Developed
in collaboration with the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the
ESC. Eur Heart J. 33:1787–1847. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Metra M, Ponikowski P, Dickstein K, et al:
Advanced chronic heart failure: A position statement from the Study
Group On Advanced Heart Failure of the Heart Failure Association of
the European Society of Cardiology. Eur J Heart Fail. 9:684–694.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heart Failure Society of America.
Lindenfeld J, Albert NM, Boehmer JP, et al: HFSA 2010 comprehensive
heart failure practice guideline. J Card Fail. 16:e1–e194. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Felker GM, Adams KF Jr, Konstam MA, et al:
The problem of decompensated heart failure: Nomenclature,
classification and risk stratification. Am Heart J. 145(Suppl 2):
18–25. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Arnold LM, Crouch MA, Carroll NV and
Oinonen MJ: Outcomes associated with vasoactive therapy in patients
with acute decompensated heart failure. Pharmacotherapy.
26:1078–1085. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kliegman RM, Stanton BMD, St. Geme J,
Schor N and Behrman RE: Part XIX, Respiratory System. Nelson
Textbook of Pediatrics (19th). (Philadephia, PA). Saunders
(Elsevier). 2015.
|
|
12
|
Maisel A, Krishnaswamy P, Nowak RM, et al:
Rapid measurement of B-type natriuretic peptide in the emergency
diagnosis of heart failure. N Engl J Med. 347:161–167. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morrison LK, Harrison A, Krishnaswamy P,
et al: Utility of a rapid B-natriuretic peptide assay in
differentiating congestive heart failure from lung disease in
patients presenting with dyspnea. J Am Coll Cardiol. 39:202–209.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mair J, Hammerer-Lercher A and Puschendorf
B: The impact of cardiac natriuretic peptide determination on the
diagnosis and management of heart failure. Clin Chem Lab Med.
39:571–588. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
de Bold AJ, Borenstein HB, Veress AT, et
al: A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous
injection of atrial myocardial extracts in rats. Life Sci.
28:89–94. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saito Y, Nakao K, Itoh H, et al: Brain
natriuretic peptide is a novel cardiac hormone. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 158:360–368. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Burnett JC, Kao PC, Hu DC, et al: Atrial
natriuretic peptide elevation in congestive heart failure in human.
Science. 231:1145–1147. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Frankenstein L, Nelles M, Slavutsky M, et
al: Beta-blockers influence the short-term and long-term prognostic
information of natriuretic peptides and catecholamines in chronic
heart failure independent from specific agents. J Heart Lung
Transplant. 26:1033–1039. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Di Angelantonio E, Chowdhury R, Sarwar N,
et al: B-type natriuretic peptides and cardiovascular risk:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of 40 prospective studies.
Circulation. 120:2177–2187. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Doust JA, Pietrzak E, Dobson A and
Glasziou P: How well does B-type natriuretic peptide predict death
and cardiac events in patients with heart failure: systematic
review. BMJ. 330:6252005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vesbianu D, Vesbianu C, Bernstein P, et
al: Plasma brain natriuretic peptide-an independent predictor of
mortality and rehospitalization in congestive heart failure-a
meta-analysis. World Heart J. 1:349–354. 2008.
|
|
22
|
Oremus M, Raina PS, Santaguida P, et al: A
systematic review of BNP as a predictor of prognosis in persons
with coronary artery disease. Clin Biochem. 41:260–265. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|