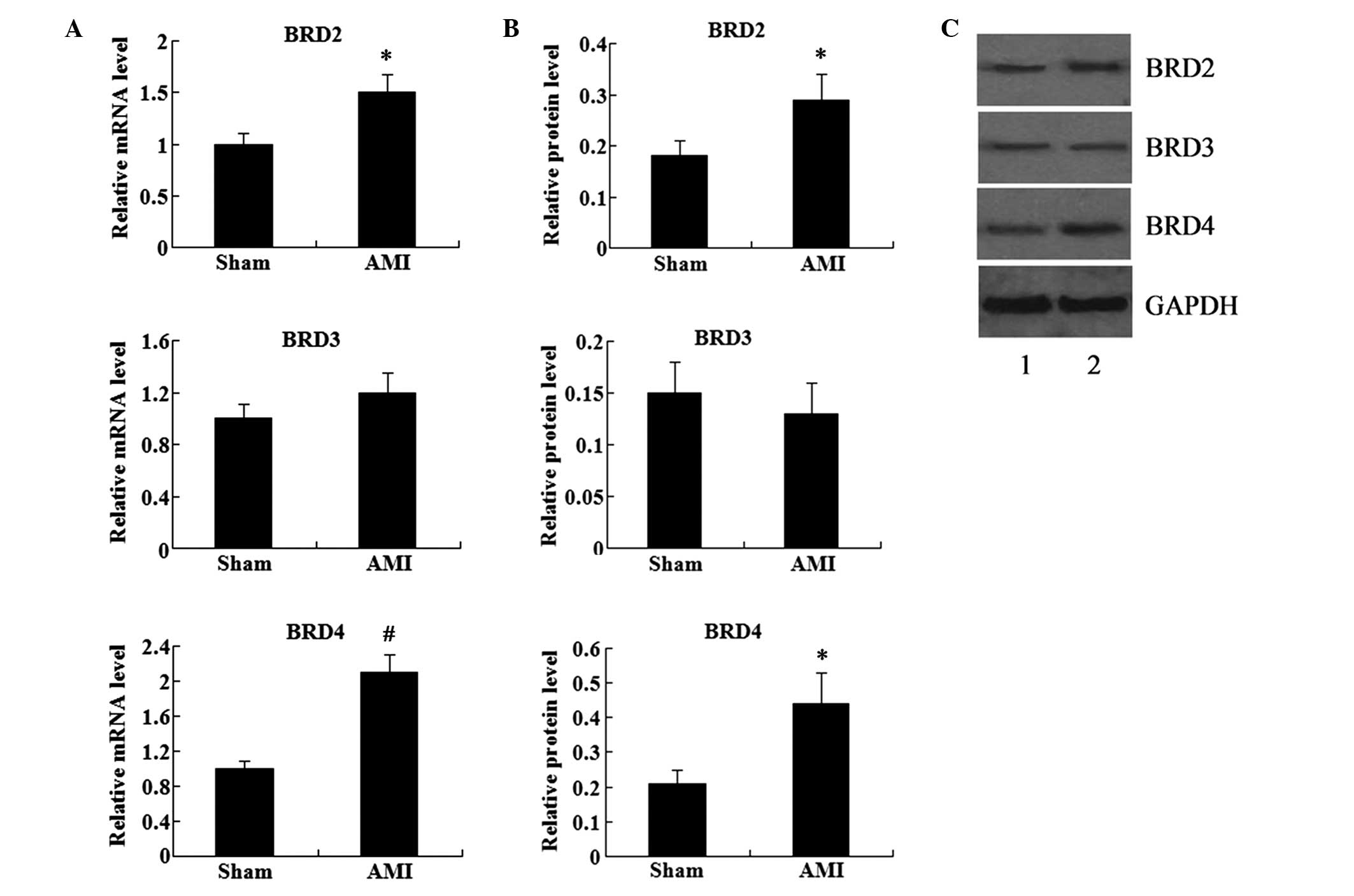
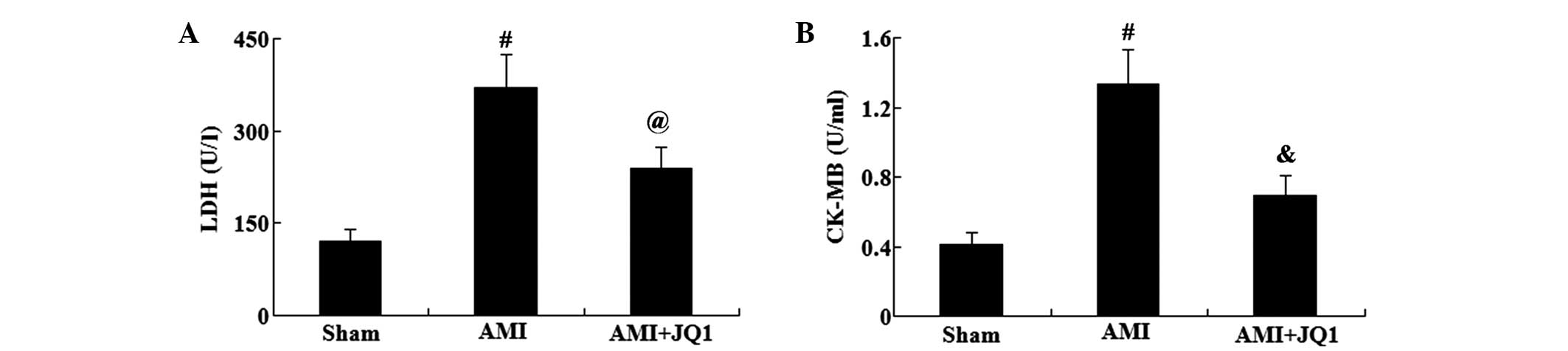
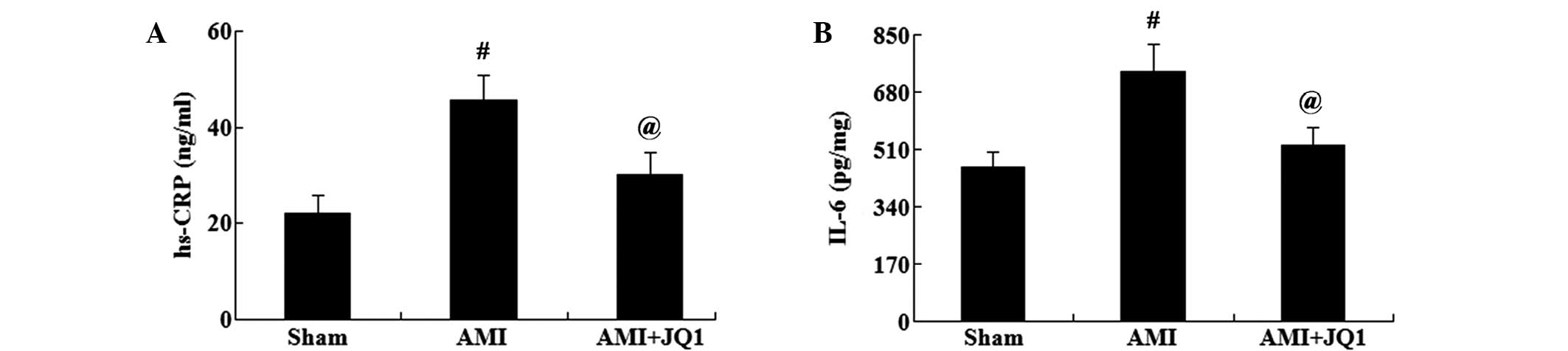
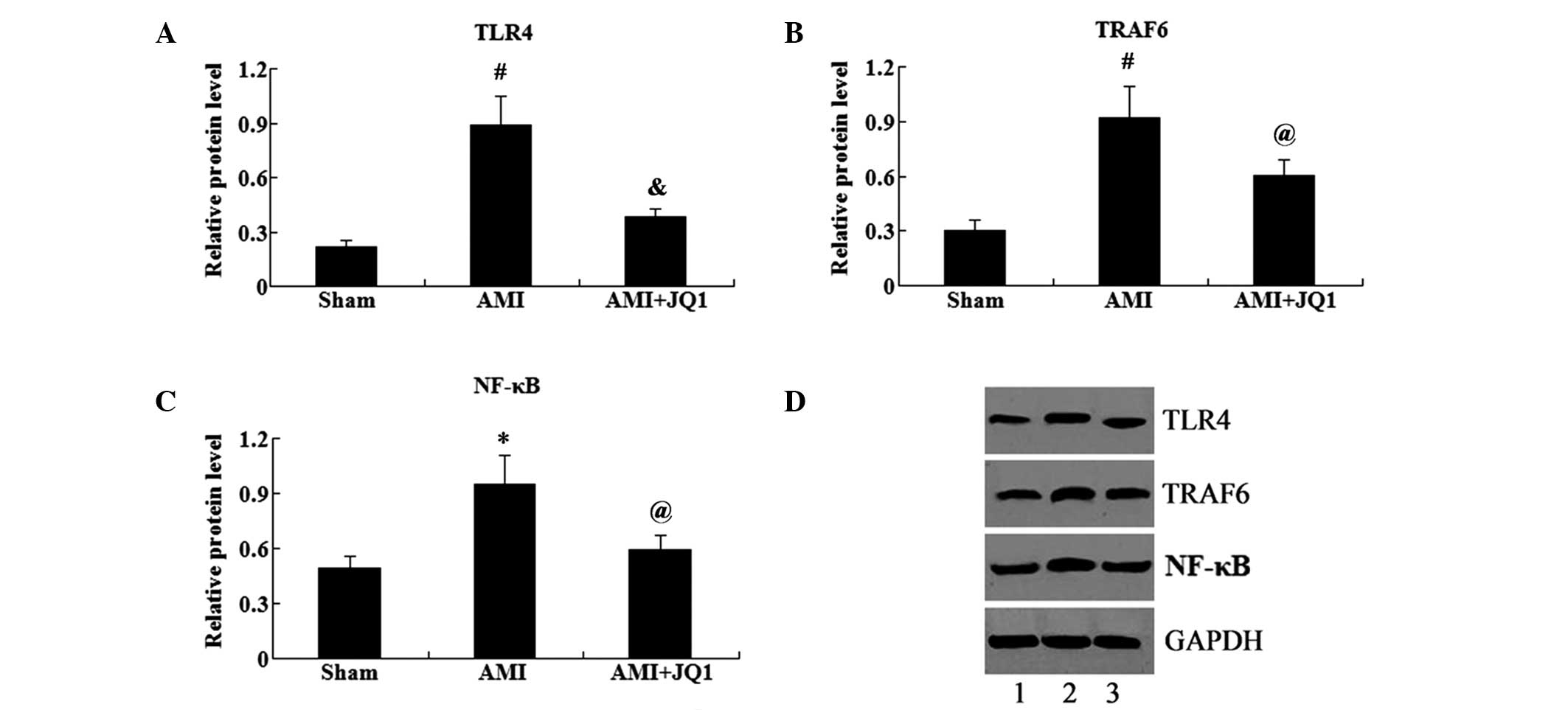
|
1
|
Ozaki K, Sato H, Inoue K, Tsunoda T,
Sakata Y, Mizuno H, Lin TH, Miyamoto Y, Aoki A, Onouchi Y, et al:
SNPs in BRAP associated with risk of myocardial infarction in Asian
populations. Nat Genet. 41:329–333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Task Force on the management of ST-segment
elevation acute myocardial infarction of the European Society of
Cardiology (ESC). Steg PG, James SK, Atar D, Badano LP,
Blömstrom-Lundqvist C, Borger MA, Di Mario C, Dickstein K, Ducrocq
G, Fernandez-Aviles F, et al: ESC Guidelines for the management of
acute myocardial infarction in patients presenting with ST-segment
elevation. Eur Heart J. 33:2569–2619. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
White HD and Chew DP: Acute myocardial
infarction. Lancet. 372:570–584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Florence B and Faller DV: You bet-cha: A
novel family of transcriptional regulators. Front Biosci.
6:D1008–D1018. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Florence BL and Faller DV: Drosophila
female sterile (1) homeotic is a multifunctional transcriptional
regulator that is modulated by Ras signaling. Dev Dyn. 237:554–564.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matzuk MM, McKeown MR, Filippakopoulos P,
Li Q, Ma L, Agno JE, Lemieux ME, Picaud S, Yu RN, Qi J, et al:
Small-molecule inhibition of BRDT for male contraception. Cell.
150:673–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Banerjee C, Archin N, Michaels D, Belkina
AC, Denis GV, Bradner J, Sebastiani P, Margolis DM and Montano M:
BET bromodomain inhibition as a novel strategy for reactivation of
HIV-1. J Leukoc Biol. 92:1147–1154. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nicodeme E, Jeffrey KL, Schaefer U, Beinke
S, Dewell S, Chung CW, Chandwani R, Marazzi I, Wilson P, Coste H,
et al: Suppression of inflammation by a synthetic histone mimic.
Nature. 468:1119–1123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB,
Shi J, Jacobs HM, Kastritis E, Gilpatrick T, Paranal RM, Qi J, et
al: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target
c-Myc. Cell. 146:904–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Filippakopoulos P, Qi J, Picaud S, Shen Y,
Smith WB, Fedorov O, Morse EM, Keates T, Hickman TT, Felletar I, et
al: Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature.
468:1067–1073. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anand P, Brown JD, Lin CY, Qi J, Zhang R,
Artero PC, Alaiti MA, Bullard J, Alazem K, Margulies KB, et al: BET
bromodomains mediate transcriptional pause release in heart
failure. Cell. 154:569–582. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Haldar SM and McKinsey TA: BET-ting on
chromatin-based therapeutics for heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
74:98–102. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Delmore JE, Issa GC, Lemieux ME, Rahl PB,
Shi J, Jacobs HM, Kastritis E, Gilpatrick T, Paranal RM, Qi J, et
al: BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target
c-Myc. Cell. 146:904–917. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang X, Peng R, Ren Y, Apparsundaram S,
Deguzman J, Bauer CM, Hoffman AE, Hamilton S, Liang Z, Zeng H, et
al: BET bromodomain proteins mediate downstream signaling events
following growth factor stimulation in human lung fibroblasts and
are involved in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Mol
Pharmacol. 83:283–293. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Spiltoir J, Stratton MS, Cavasin MA,
Demos-Davies K, Reid BG, Qi J, Bradner JE and McKinsey TA: BET
acetyl-lysine binding proteins control pathological cardiac
hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 63:175–179. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eckle T, Grenz A, Köhler D, Redel A, Falk
M, Rolauffs B, Osswald H, Kehl F and Eltzschig HK: Systematic
evaluation of a novel model for cardiac ischemic preconditioning in
mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291:H2533–H2540. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marushige K: Activation of chromatin by
acetylation of histone side chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
73:3937–3941. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dhalluin C, Carlson JE, Zeng L, He C,
Aggarwal AK and Zhou MM: Structure and ligand of a histone
acetyltransferase bromodomain. Nature. 399:491–496. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jacobson RH, Ladurner AG, King DS and
Tjian R: Structure and function of a human TAFII250 double
bromodomain module. Science. 288:1422–1425. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Owen DJ, Ornaghi P, Yang JC, Lowe N, Evans
PR, Ballario P, Neuhaus D, Filetici P and Travers AA: The
structural basis for the recognition of acetylated histone H4 by
the bromodomain of histone acetyltransferase gcn5p. EMBO J.
19:6141–6149. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chung CW, Coste H, White JH, Mirguet O,
Wilde J, Gosmini RL, Delves C, Magny SM, Woodward R, Hughes SA, et
al: Discovery and characterization of small molecule inhibitors of
the BET family bromodomains. J Med Chem. 54:3827–3838. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW and Entman ML:
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
53:31–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Freitas F, Brucker N, Durgante J, Bubols
G, Bulcão R, Moro A, Charão M, Baierle M, Nascimento S, Gauer B, et
al: Urinary 1-hydroxypyrene is associated with oxidative stress and
inflammatory biomarkers in acute myocardial infarction. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 11:9024–9037. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang YU, Kim MJ, Choi JS, Kim CS, Bae EH,
Ma SK, Ahn YK, Jeong MH, Kim YJ, Cho MC, et al: Other Korea Acute
Myocardial Infarction Registry Investigators: Concomitant impact of
high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and renal dysfunction in
patients with acute myocardial infarction. Yonsei Med J.
55:132–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang XH, Liu SQ, Wang YL and Jin Y:
Correlation of serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and
interleukin-6 in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Genet Mol
Res. 13:4260–4266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takeda K, Kaisho T and Akira S: Toll-like
receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 21:335–376. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beutler B: Inferences, questions and
possibilities in Toll-like receptor signalling. Nature.
430:257–263. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van
Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, et al:
Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations
in Tlr4 gene. Science. 282:2085–2088. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lee JY, Ye J, Gao Z, Liu MY, Van Huffel C,
Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M and Galanos C: Reciprocal
modulation of Toll-like receptor-4 signaling pathways involving
MyD88 and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT by saturated and
polyunsaturated fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 278:37041–37051. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arslan F, de Kleijn DP and Pasterkamp G:
Innate immune signaling in cardiac ischemia. Nat Rev Cardiol.
8:292–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Timmers L, Pasterkamp G, de Hoog VC,
Arslan F, Appelman Y and de Kleijn DP: The innate immune response
in reperfused myocardium. Cardiovasc Res. 94:276–283. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chong AJ, Shimamoto A, Hampton CR,
Takayama H, Spring DJ, Rothnie CL, Yada M, Pohlman TH and Verrier
ED: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates ischemia/reperfusion injury of
the heart. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 128:170–179. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Timmers L, Sluijter JP, van Keulen JK,
Hoefer IE, Nederhoff MG, Goumans MJ, Doevendans PA, van Echteld CJ,
Joles JA, Quax PH, et al: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates maladaptive
left ventricular remodeling and impairs cardiac function after
myocardial infarction. Circ Res. 102:257–264. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shimamoto A, Chong AJ, Yada M, Shomura S,
Takayama H, Fleisig AJ, Agnew ML, Hampton CR, Rothnie CL, Spring
DJ, et al: Inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 with eritoran
attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulation.
114(Suppl 1): S1270–S1274. 2006.
|
|
36
|
van der Pouw Kraan TC, Bernink FJ,
Yildirim C, Koolwijk P, Baggen JM, Timmers L, Beek AM, Diamant M,
Chen WJ, van Rossum AC, et al: Systemic toll-like receptor and
interleukin-18 pathway activation in patients with acute ST
elevation myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 67:94–102.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Akira S and Takeda K: Toll-like receptor
signaling. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:499–511. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Timmers L, van Keulen JK, Hoefer IE, Meijs
MF, van Middelaar B, den Ouden K, van Echteld CJ, Pasterkamp G and
de Kleijn DP: Targeted deletion of nuclear factor kappaB p50
enhances cardiac remodeling and dysfunction following myocardial
infarction. Circ Res. 104:699–706. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yin Q, Lin SC, Lamothe B, Lu M, Lo YC,
Hura G, Zheng L, Rich RL, Campos AD, Myszka DG, et al: E2
interaction and dimerization in the crystal structure of TRAF6. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 16:658–666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|