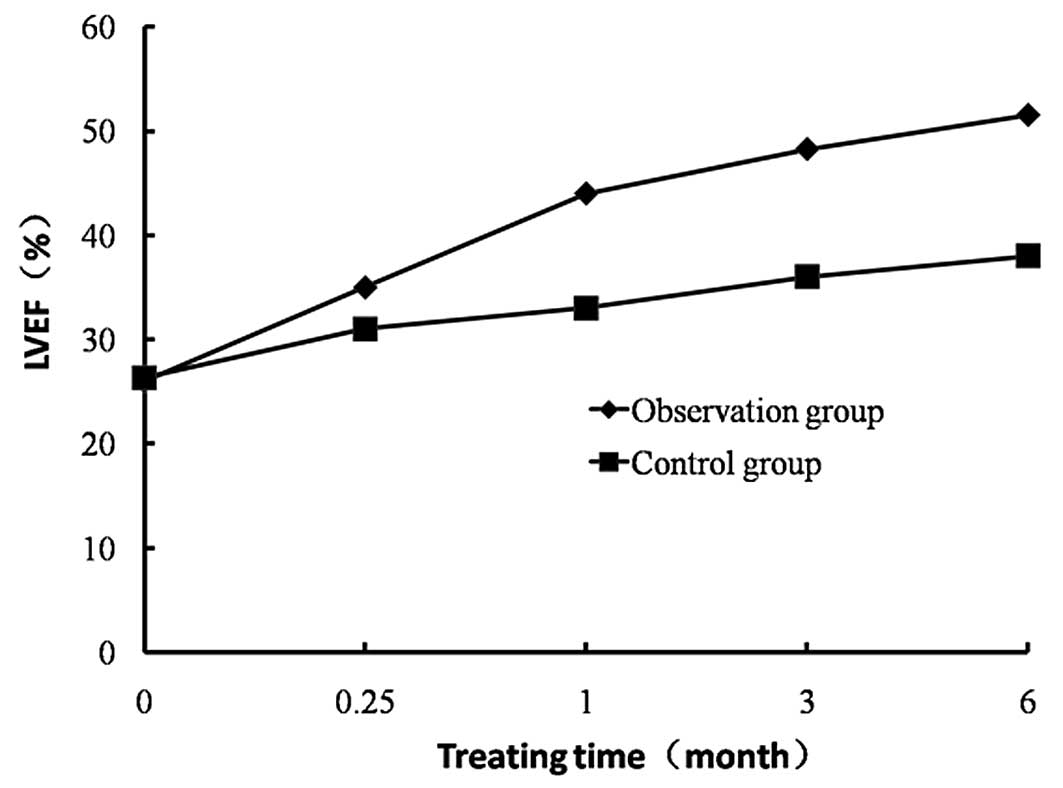
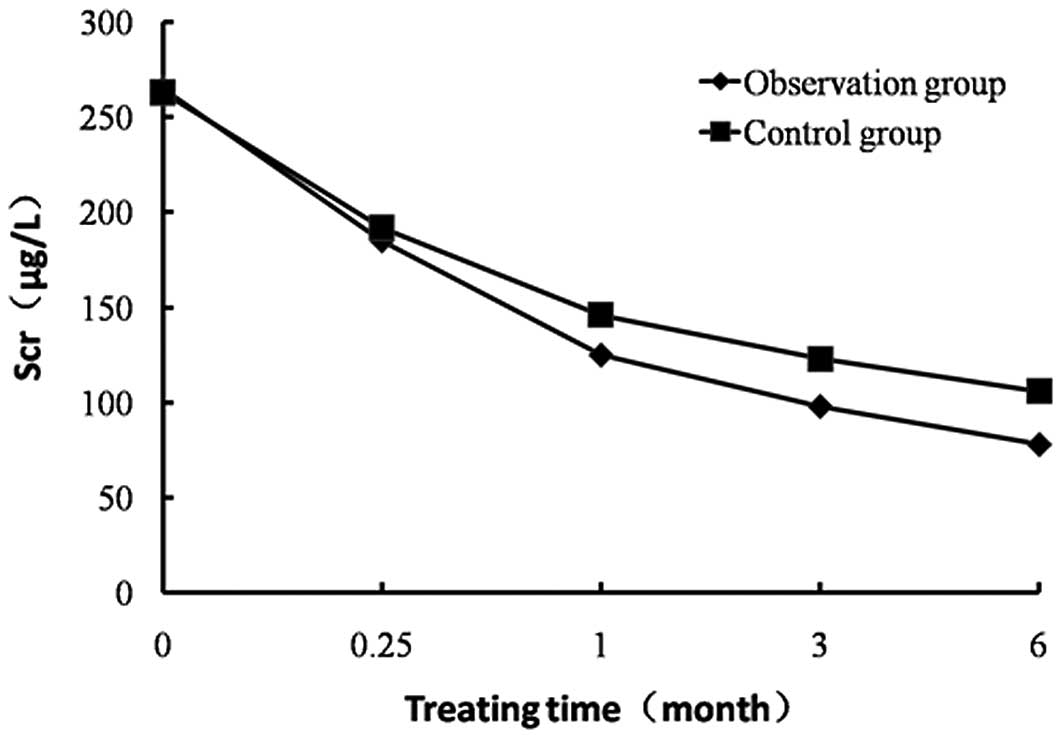
|
1
|
Orth-Gomér K: Psychosocial and behavioral
aspects of cardiovascular disease prevention in men and women. Curr
Opin Psychiatry. 20:147–151. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berezin AE, Kremzer AA, Samura TA and
Martovitskaya YV: Circulating endothelial-derived apoptotic
microparticles in the patients with ischemic symptomatic chronic
heart failure: Relevance of pro-inflammatory activation and
outcomes. Int Cardiovasc Res J. 8:116–123. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maughan D and Toth M: Discerning primary
and secondary factors responsible for clinical fatigue in
multisystem diseases. Biology (Basel). 3:606–622. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lang NN, Wong CM, Dalzell JR, Jansz S,
Leslie SJ and Gardner RS: The ease of use and reproducibility of
the Alere™ Heart Check System: A comparison of patient and
healthcare professional measurement of BNP. Biomark Med. 8:791–796.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Armstrong C: ACCF and AHA release
guidelines on the management of heart failure. Am Fam Physician.
90:186–189. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nativi-Nicolau J, Ryan JJ and Fang JC:
Current therapeutic approach in heart failure with preserved
ejection fraction. Heart Fail Clin. 10:525–538. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Imamura T, Kinugawa K, Ohtani T, Sakata Y,
Higo T, Kinugawa S, Tsutsui H, Sunagawa K and Komuro I: Assessment
of quality of life during long-term treatment of tolvaptan in
refractory heart failure: Design and rationale of the AQUA-TLV
study. Int Heart J. 55:264–267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rad EM and Assadi F: Management of
hypertension in children with cardiovascular disease and heart
failure. Int J Prev Med. 5(Suppl 1): S10–S16. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cocco G and Jerie P: Comparison between
ivabradine and low-dose digoxin in the therapy of diastolic heart
failure with preserved left ventricular systolic function. Clin
Pract. 3:e292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pitt B, Pfeffer MA, Assmann SF, Boineau R,
Anand IS, Claggett B, Clausell N, Desai AS, Diaz R, Fleg JL, et al:
Spironolactone for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
N Engl J Med. 370:1383–1392. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
De Vecchis R, Esposito C and Ariano C:
Efficacy and safety assessment of isolated ultrafiltration compared
to intravenous diuretics for acutely decompensated heart failure: A
systematic review with meta-analysis. Minerva Cardioangiol.
62:131–146. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mpe MT, Klug EQ, Silwa KS, Hitzeroth J and
Smith DA: Heart failure society of South Africa (HeFSSA)
perspective on the European society of cardiology (ESC) 2012
chronic heart failure guideline. S Afr Med J. 103(9 Suppl 2):
660–667. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Verbrugge FH, Nijst P, Dupont M, Reynders
C, Penders J, Tang WH and Mullens W: Prognostic value of glomerular
filtration changes versus natriuretic response in decompensated
heart failure with reduced ejection. J Card Fail. 20:817–824. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Seronde MF, Laribi S, Collins SP, Deye N,
Logeart D, Plaisance P, Cohen-Solal A and Mebazaa A: Heart failure
diagnosis in acute conditions has high agreement with inpatient
diagnosis. Eur J Emerg Med. Feb 23–2015.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miller-Davis C, Marden S and Leidy NK: The
New York Heart Association Classes and functional status: What are
we really measuring? Heart Lung. 35:217–224. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Uemura O, Ushijima K, Nagai T, Yamada T,
Hayakawa H, Nabeta Y, Shinkai Y, Koike K and Kuwabara M: Reference
serum cystatin C levels in Japanese children. Clin Exp Nephrol.
14:453–456. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang X, Xu G, Li H, Liu Y and Wang F:
Reference intervals for serum creatinine with enzymatic assay and
evaluation of four equations to estimate glomerular filtration rate
in a healthy Chinese adult population. Clin Chim Acta.
412:1793–1797. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Moukarbel GV and Solomon SD: Treatment of
asymptomatic left ventricular dysfuntion. Curr Treat Options
Cardiovasc Med. 10:476–485. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rami K: Aggressive salt and water
restriction in acutely decompensated heart failure: is it worth its
weight in salt? Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 11:1125–1128. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee KK, Shilane D, Hlatky MA, Yang J,
Steimle AE and Go AS: Effectiveness and safety of spironolactone
for systolic heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 112:1427–1432. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hasenfuß G, Edelmann F and Wachter R:
Recommendations for the treatment of heart failure: What's new?
Internist (Berl). 54:1141–1151. 2013.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ferreira JP, Santos M, Almeida S, Marques
I, Bettencourt P and Carvalho H: Tailoring diuretic therapy in
acute heart failure: Insight into early diuretic response
predictors. Clin Res Cardiol. 102:745–753. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vaduganathan M, Marti CN, Georgiopoulou
VV, Kalogeropoulos AP and Butler J: Classification of patients
hospitalized for heart failure. Heart Fail Clin. 9:277–283. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Frankenstein L, Katus HA, Grundtvig M,
Hole T, de Blois J, Schellberg D, Atar D, Zugck C and Agewall S:
Norwegian Heart Failure Registry steering committee: Association
between spironolactone added to beta-blockers and ACE inhibition
and survival in heart failure patients with reduced ejection
fraction: A propensity score-matched cohort study. Eur J Clin
Pharmacol. 69:1747–1755. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ng TM, Hshieh S, Chan CY and Elkayam U:
Clinical experience with low-dose continuous infusion of furosemide
in acute heart failure: Assessment of efficacy and safety. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 17:373–381. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parry HM, Doney AS, Palmer CN and Lang CC:
State of play of pharmacogenetics and personalized medicine in
heart failure. Cardiovasc Ther. 31:315–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
O'Dell KM, Kalus JS, Kucukarslan S and
Czerska B: Nesiritide for secondary pulmonary hypertension in
patients with end-stage heart failure. Am J Health Syst Pharm.
62:606–609. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen HH, Martin FL, Gibbons RJ, Schirger
JA, Wright RS, Schears RM, Redfield MM, Simari RD, Lerman A,
Cataliotti A and Burnett JC Jr: Low-dose nesiritide in human
anterior myocardial infarction suppresses aldosterone and preserves
ventricular function and structure: A proof of concept study.
Heart. 95:1315–1319. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|