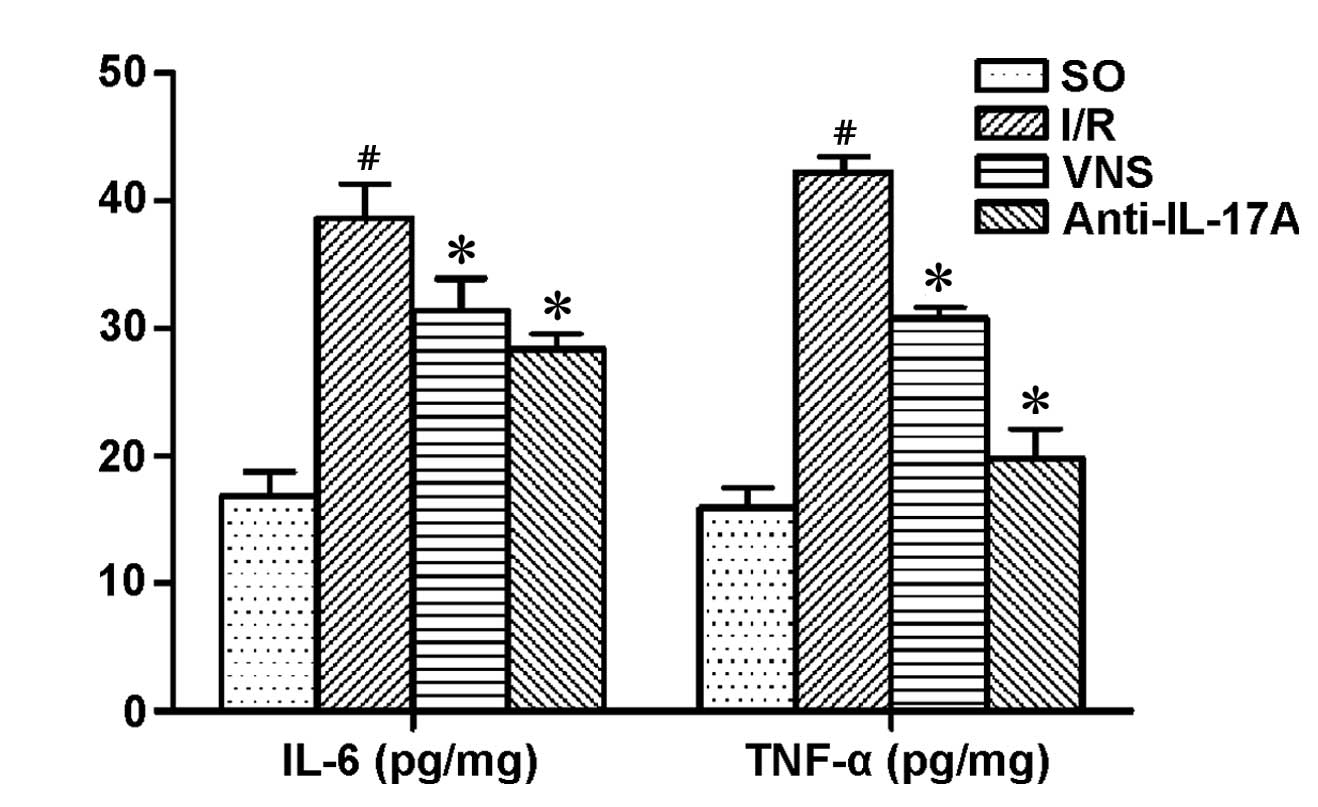
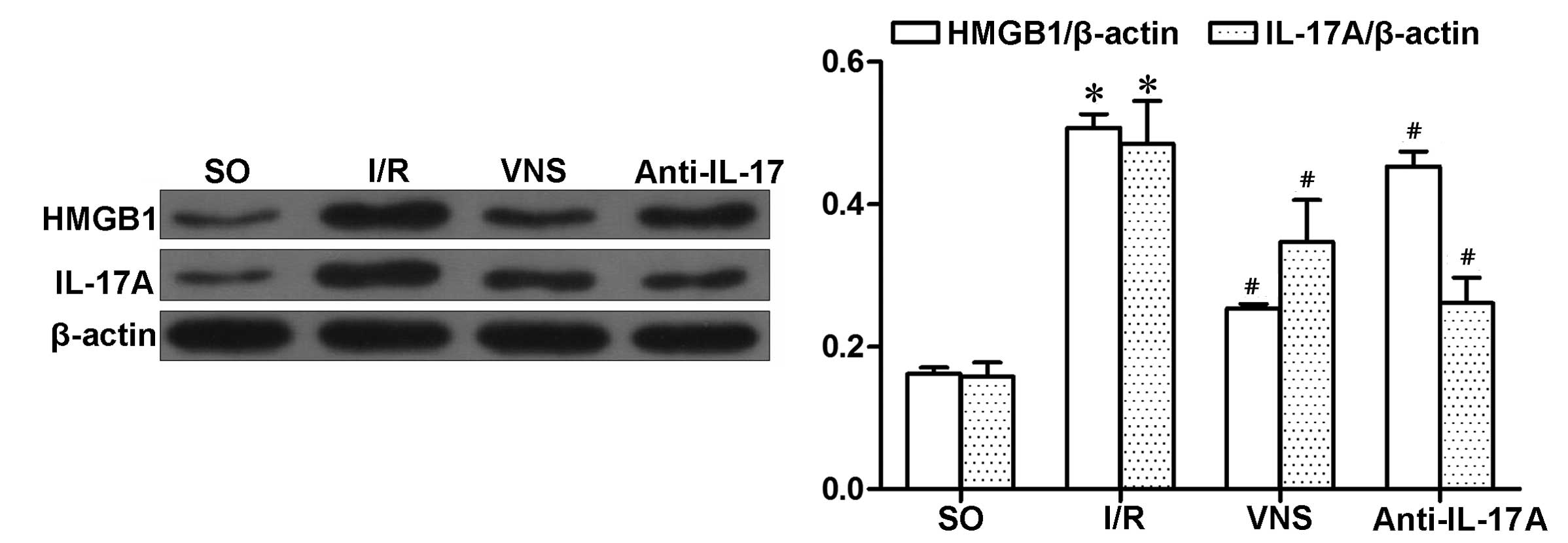
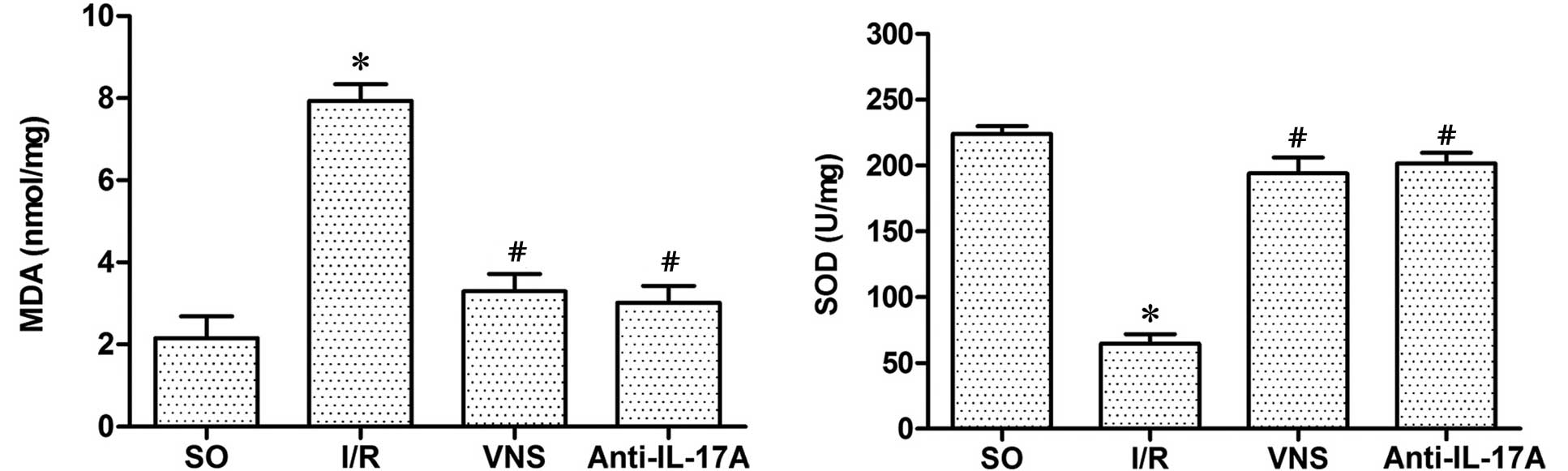
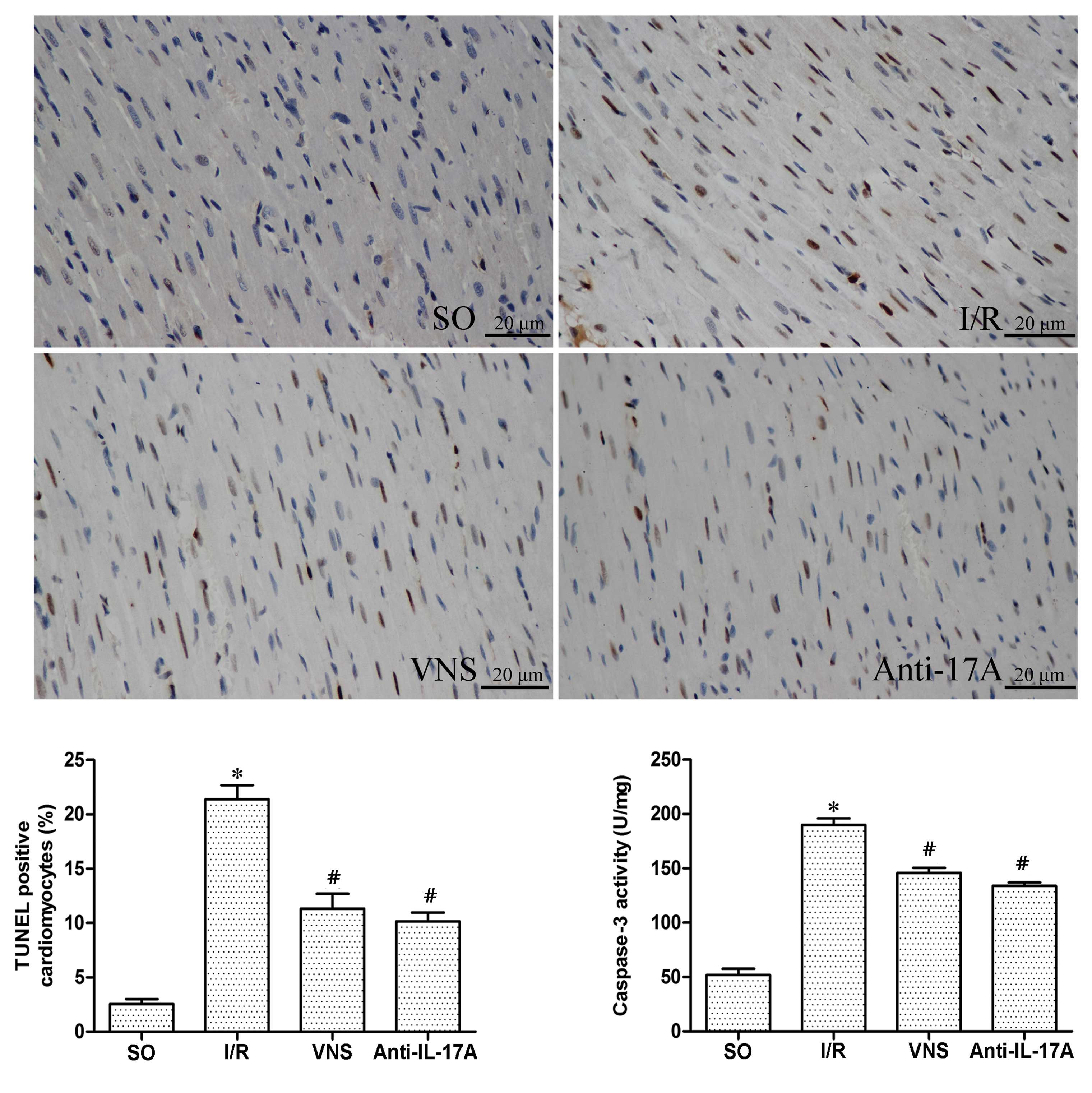
|
1
|
Yellon DM and Hausenloy DJ: Myocardial
reperfusion injury. N Engl J Med. 357:1121–1135. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Iwakura Y, Nakae S, Saijo S and Ishigame
H: The roles of IL-17A in inflammatory immune responses and host
defense against pathogens. Immunol Rev. 226:57–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ni J, Hu G, Xiong J, Shen J, Shen J, Yang
L, Tang M, Zhao Y, Ying G, Yu G, et al: Involvement of
interleukin-17A in pancreatic damage in rat experimental acute
necrotizing pancreatitis. Inflammation. 36:53–65. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang X, Sun R, Wei H and Tian Z:
High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)-Toll-like receptor
(TLR)4-interleukin (IL)-23-IL-17A axis in drug-induced
damage-associated lethal hepatitis: Interaction of γδ T cells with
macrophages. Hepatology. 57:373–384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu X, Xu W and Jiang H: HMGB1/IL-17A axis:
An important mechanism for myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Int J Cardiol. 174:447–448. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liao YH, Xia N, Zhou SF, Tang TT, Yan XX,
Lv BJ, Nie SF, Wang J, Iwakura Y, Xiao H, et al: Interleukin-17A
contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and neutrophil infiltration. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 59:420–429. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao M, Sun L, Liu JJ, Wang H, Miao Y and
Zang WJ: Vagal nerve modulation: A promising new therapeutic
approach for cardiovascular diseases. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
39:701–705. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
De Ferrari GM and Schwartz PJ: Vagus nerve
stimulation: from pre-clinical to clinical application: challenges
and future directions. Heart Fail Rev. 16:195–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Q, Cheng Y, Xue FS, Yuan YJ, Xiong J,
Li RP, Liao X and Liu JH: Postconditioning with vagal stimulation
attenuates local and systemic inflammatory responses to myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Inflamm Res. 61:1273–1282.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Park J, Kang JW and Lee SM: Activation of
the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway by nicotine attenuates
hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via heme oxygenase-1 induction.
Eur J Pharmacol. 707:61–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tang Q, Li J, Zhu H, Li P, Zou Z and Xiao
Y: Hmgb1-IL-23-IL-17-IL-6-Stat3 axis promotes tumor growth in
murine models of melanoma. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:7138592013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Calvillo L, Vanoli E, Andreoli E, Besana
A, Omodeo E, Gnecchi M, Zerbi P, Vago G, Busca G and Schwartz PJ:
Vagal stimulation, through its nicotinic action, limits infarct
size and the inflammatory response to myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 58:500–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
National Research Council; Guide for the
Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Washington (DC): National
Academies Press (US). 1996.
|
|
14
|
Hu X, Zhou X, He B, Xu C, Wu L, Cui B, Wen
H, Lu Z and Jiang H: Minocycline protects against myocardial
ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting high mobility group
box 1 protein in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 638:84–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thayer JF and Lane RD: The role of vagal
function in the risk for cardiovascular disease and mortality. Biol
Psychol. 74:224–242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shinlapawittayatorn K, Chinda K, Palee S,
Surinkaew S, Thunsiri K, Weerateerangkul P, Chattipakorn S,
KenKnight BH and Chattipakorn N: Low-amplitude, left vagus nerve
stimulation significantly attenuates ventricular dysfunction and
infarct size through prevention of mitochondrial dysfunction during
acute ischemia-reperfusion injury. Heart Rhythm. 10:1700–1707.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Katare RG, Ando M, Kakinuma Y, Arikawa M,
Handa T, Yamasaki F and Sato T: Vagal nerve stimulation prevents
reperfusion injury through inhibition of opening of mitochondrial
permeability transition pore independent of the bradycardiac
effect. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 137:223–231. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun L, Zhao M, Yu XJ, Wang H, He X, Liu JK
and Zang WJ: Cardioprotection by acetylcholine: A novel mechanism
via mitochondrial biogenesis and function involving the PGC-1α
pathway. J Cell Physiol. 228:1238–1248. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion - from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu X, Fu W and Jiang H: HMGB1: A potential
therapeutic target for myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury.
Int J Cardiol. 155:4892012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Marrero MB and Bencherif M: Convergence of
alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-activated pathways for
anti-apoptosis and anti-inflammation: Central role for JAK2
activation of STAT3 and NF-kappaB. Brain Res. 1256:1–7. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu H, Li J, Wang S, Liu K, Wang L and
Huang L: Hmgb1-TLR4-IL-23-IL-17A axis promote ischemia-reperfusion
injury in a cardiac transplantation model. Transplantation.
95:1448–1454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ekici F, Karson A, Dillioglugil MO, Gurol
G, Kir HM and Ates N: The effects of vagal nerve stimulation in
focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion model. Turk Neurosurg.
23:451–457. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsutsumi T, Ide T, Yamato M, Kudou W,
Andou M, Hirooka Y, Utsumi H, Tsutsui H and Sunagawa K: Modulation
of the myocardial redox state by vagal nerve stimulation after
experimental myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 77:713–721.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong SS, Liu JJ, Yu XJ, Lu Y and Zang WJ:
Protection against ischemia-induced oxidative stress conferred by
vagal stimulation in the rat heart: Involvement of the AMPK-PKC
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 13:14311–14325. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pinart M, Zhang M, Li F, Hussain F, Zhu J,
Wiegman C, Ryffel B and Chung KF: IL-17A modulates oxidant
stress-induced airway hyperresponsiveness but not emphysema. PLoS
One. 8:e584522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|