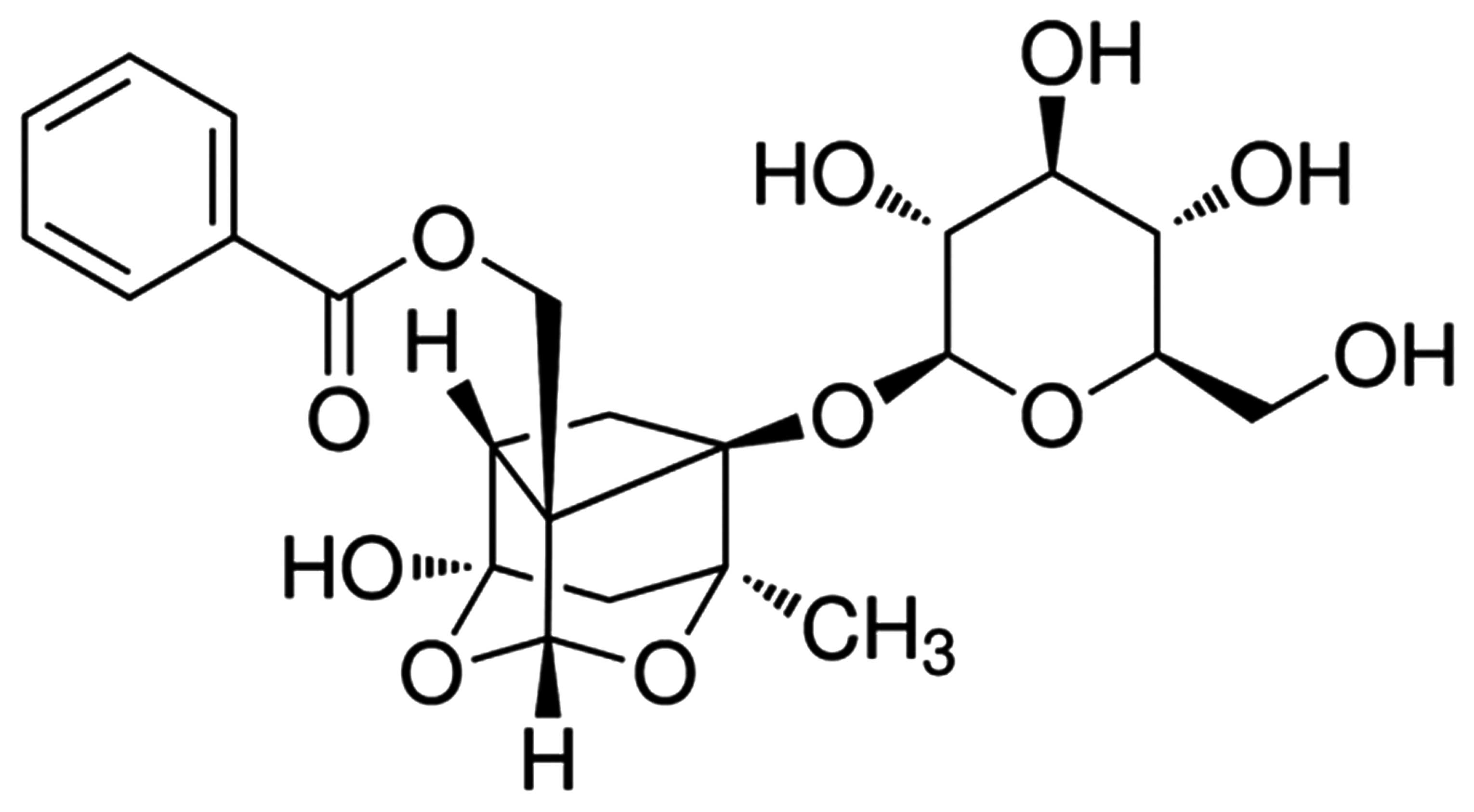
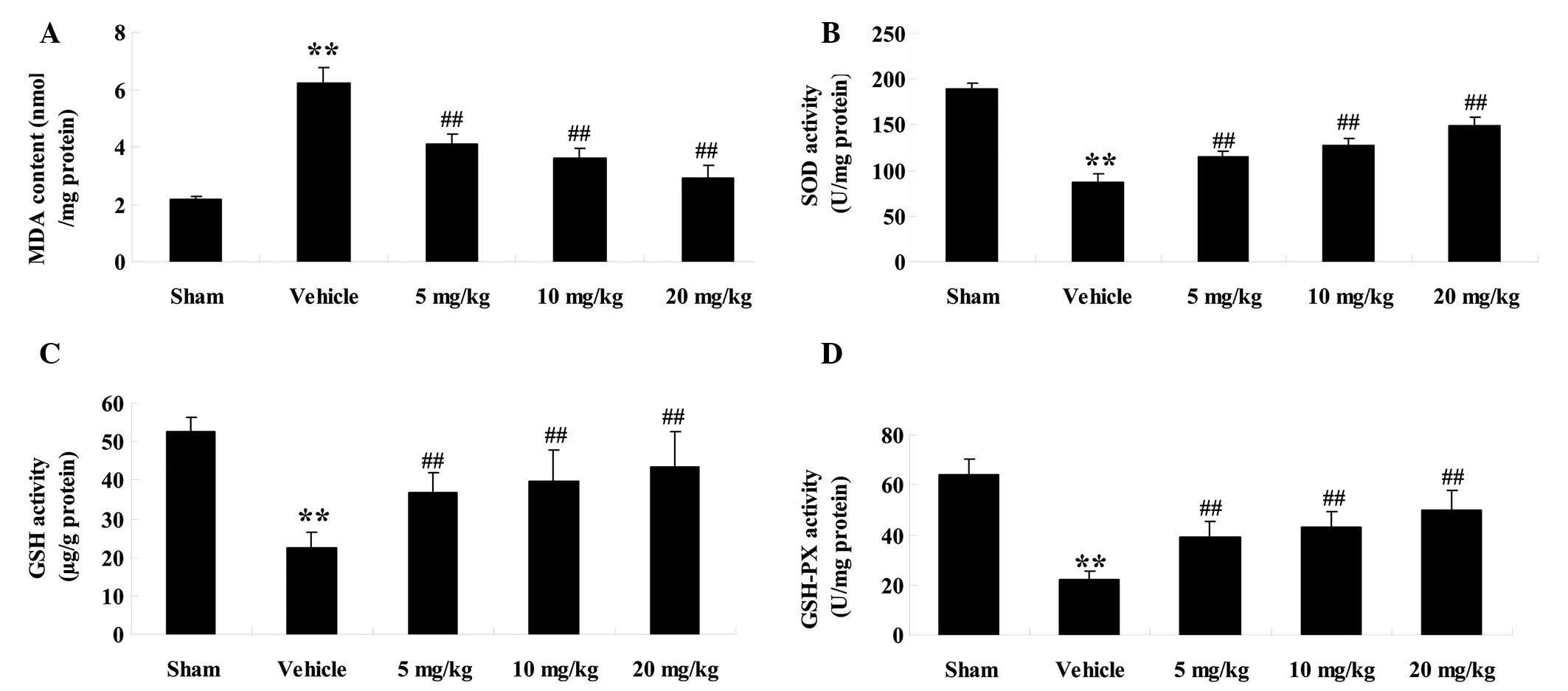
|
1
|
Grossini E, Pollesello P, Bellofatto K,
Sigaudo L, Farruggio S, Origlia V, Mombello C, Mary DA, Valente G
and Vacca G: Protective effects elicited by levosimendan against
liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in anesthetized rats. Liver
Transpl. 20:361–375. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Çekın AH, Gür G, Türkoğlu S, Aldemır D,
Yilmaz U, Gürsoy M, Taşkoparan M and Boyacioğlu S: The protective
effect of L-carnitine on hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in
rats. Turk J Gastroenterol. 24:51–56. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suzuki M, Takeuchi H, Kakita T, Unno M,
Katayose Y and Matsuno S: The involvement of the intracellular
superoxide production system in hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
injury. In vivo and in vitro experiments using transgenic mice
manifesting excessive CuZn-SOD activity. Free Radic Biol Med.
29:756–763. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng P, Wang F, Chen K, Shen M, Dai W, Xu
L, Zhang Y, Wang C, Li J, Yang J, et al: Hydrogen sulfide
ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatitis by inhibiting
apoptosis and autophagy pathways. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:9352512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ramachandran S, Liaw JM, Jia J, Glasgow
SC, Liu W, Csontos K, Upadhya GA, Mohanakumar T and Chapman WC:
Ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat steatotic liver is dependent on
NFkappaB P65 activation. Transpl Immunol. 26:201–206. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kamo N, Ke B, Ghaffari AA, Shen XD,
Busuttil RW, Cheng G and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: ASC/caspase-1/IL-1β
signaling triggers inflammatory responses by promoting HMGB1
induction in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Hepatology.
58:351–362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhu Y, Dang S and Hua Z: Advanced
achievements about neuroprotective mechanisms of paeoniflorin.
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 35:1490–1493. 2010.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ding MP, Feng F and Hu HT: Effects of
puerarin on expression of nuclear factor kappaB after cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi.
32:2515–2518. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu W, Zhang Q, Yang X, Wang Y and Sun L:
Puerarin inhibits adhesion molecule expression in
tnf-alpha-stimulated human endothelial cells via modulation of the
nuclear factor kappaB pathway. Pharmacology. 85:27–35. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hino H, Takahashi H, Suzuki Y, Tanaka J,
Ishii E and Fukuda M: Anticonvulsive effect of paeoniflorin on
experimental febrile seizures in immature rats: Possible
application for febrile seizures in children. PLoS One.
7:e429202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guo RB, Wang GF, Zhao AP, Gu J, Sun XL and
Hu G: Paeoniflorin protects against ischemia-induced brain damages
in rats via inhibiting MAPKs/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory responses.
PLoS One. 7:e497012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu DZ, Zhao FL, Liu J, Ji XQ, Ye Y and
Zhu XZ: Potentiation of adenosine A1 receptor agonist CPA-induced
antinociception by paeoniflorin in mice. Biol Pharm Bull.
29:1630–1633. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shen XD, Ke B, Zhai Y, Gao F, Anselmo D,
Lassman CR, Busuttil RW and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: Stat4 and Stat6
signaling in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice: HO-1
dependence of Stat4 disruption-mediated cytoprotection. Hepatology.
37:296–303. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uchida Y, Ke B, Freitas MC, Ji H, Zhao D,
Benjamin ER, Najafian N, Yagita H, Akiba H, Busuttil RW and
Kupiec-Weglinski JW: The emerging role of T-cell immunoglobulin
mucin-1 in the mechanism of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury
in the mouse. Hepatology. 51:1363–1372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao C, He X, Wang W, Zhang L, Lin H and Du
L: Kinetic distribution of paeoniflorin in cortex of normal and
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats after intravenous administration
of Paeoniae Radix extract. Biomed Chromatogr. 20:1283–1288. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Uchida Y, Freitas MC, Zhao D, Busuttil RW
and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: The protective function of neutrophil
elastase inhibitor in liver ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Transplantation. 89:1050–1056. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun R, Yi YP, Lv LL, Zhang ZP, Sun H and
Liu GQ: Effects of paeoniflorin on pathological changes in global
brain ischemia model rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 32:2518–2522.
2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu J, Zhu X, Qi X, Che J and Cao B:
Paeoniflorin protects human EA.hy926 endothelial cells against
gamma-radiation induced oxidative injury by activating the
NF-E2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Toxicol Lett.
218:224–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang Z, Chen W, Yan X, Bi L, Guo S and
Zhan Z: Paeoniflorin protects cells from GalN/TNF-α-induced
apoptosis via ER stress and mitochondria-dependent pathways in
human L02 hepatocytes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
46:357–367. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kong P, Chi R, Zhang L, Wang N and Lu Y:
Effects of paeoniflorin on tumor necrosis factor-α-induced insulin
resistance and changes of adipokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.
Fitoterapia. 91:44–50. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng YQ, Wei W, Zhu L and Liu JX: Effects
and mechanisms of Paeoniflorin, a bioactive glucoside from paeony
root, on adjuvant arthritis in rats. Inflamm Res. 56:182–188. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He SQ, Zhang YH, Venugopal SK, Dicus CW,
Perez RV, Ramsamooj R, Nantz MH, Zern MA and Wu J: Delivery of
antioxidative enzyme genes protects against
ischemia/reperfusion-induced liver injury in mice. Liver Transpl.
12:1869–1879. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim J, Kim HY and Lee SM: Protective
effects of geniposide and genipin against hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Biomol Ther (Seoul).
21:132–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Underhill DM, Rossnagle E, Lowell CA and
Simmons RM: Dectin-1 activates Syk tyrosine kinase in a dynamic
subset of macrophages for reactive oxygen production. Blood.
106:2543–2550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yun N, Kang JW and Lee SM: Protective
effects of chlorogenic acid against ischemia/reperfusion injury in
rat liver: Molecular evidence of its antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory properties. J Nutr Biochem. 23:1249–1255. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zetzmann CP, Swamy OR, Loss GE Jr,
Bohorquez H and Cohen AJ: Improving Donor Livers by Inhibiting
TNF-α Production. Ochsner J. 10:250–255. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Teoh N, Leclercq I, Pena AD and Farrell G:
Low-dose TNF-alpha protects against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion
injury in mice: Implications for preconditioning. Hepatology.
37:118–128. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pan S, Liu L, Pan H, Ma Y, Wang D, Kang K,
Wang J, Sun B, Sun X and Jiang H: Protective effects of
hydroxytyrosol on liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 57:1218–1227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lan Z, Chen L, Fu Q, Ji W, Wang S, Liang
Z, Qu R, Kong L and Ma S: Paeoniflorin attenuates amyloid-beta
peptide-induced neurotoxicity by ameliorating oxidative stress and
regulating the NGF-mediated signaling in rats. Brain Res.
1498:9–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen T, Guo ZP, Jiao XY, Jia RZ, Zhang YH,
Li JY, Huang XL and Liu HJ: Peoniflorin suppresses tumor necrosis
factor-α induced chemokine production in human dermal microvascular
endothelial cells by blocking nuclear factor-κB and ERK pathway.
Arch Dermatol Res. 303:351–360. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen T, Guo ZP, Wang L, Qin S, Cao N, Li
MM, Jia RZ and Wang TT: Paeoniflorin suppresses vascular damage and
the expression of E-selectin and ICAM-1 in a mouse model of
cutaneous Arthus reaction. Exp Dermatol. 22:453–457. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rao ML, Tang M, He JY and Dong Z: Effects
of paeoniflorin on cerebral blood flow and the balance of PGI2/TXA2
of rats with focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Yao Xue
Xue Bao. 49:55–60. 2014.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gündüz E, Dursun R, Zengin Y, İçer M,
Durgun HM, Kanıcı A, Kaplan İ, Alabalık U, Gürbüz H and Güloğlu C:
Lycium barbarum extract provides effective protection against
paracetamol-induced acute hepatotoxicity in rats. Int J Clin Exp
Med. 8:7898–7905. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu J, Zhu X, Qi X, Che J and Cao B:
Paeoniflorin protects human EA.hy926 endothelial cells against
gamma-radiation induced oxidative injury by activating the
NF-E2-related factor 2/heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Toxicol Lett.
218:224–234. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim HY and Lee SM: Ferulic acid attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion-induced hepatocyte apoptosis via inhibition of
JNK activation. Eur J Pharm Sci. 45:708–715. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|