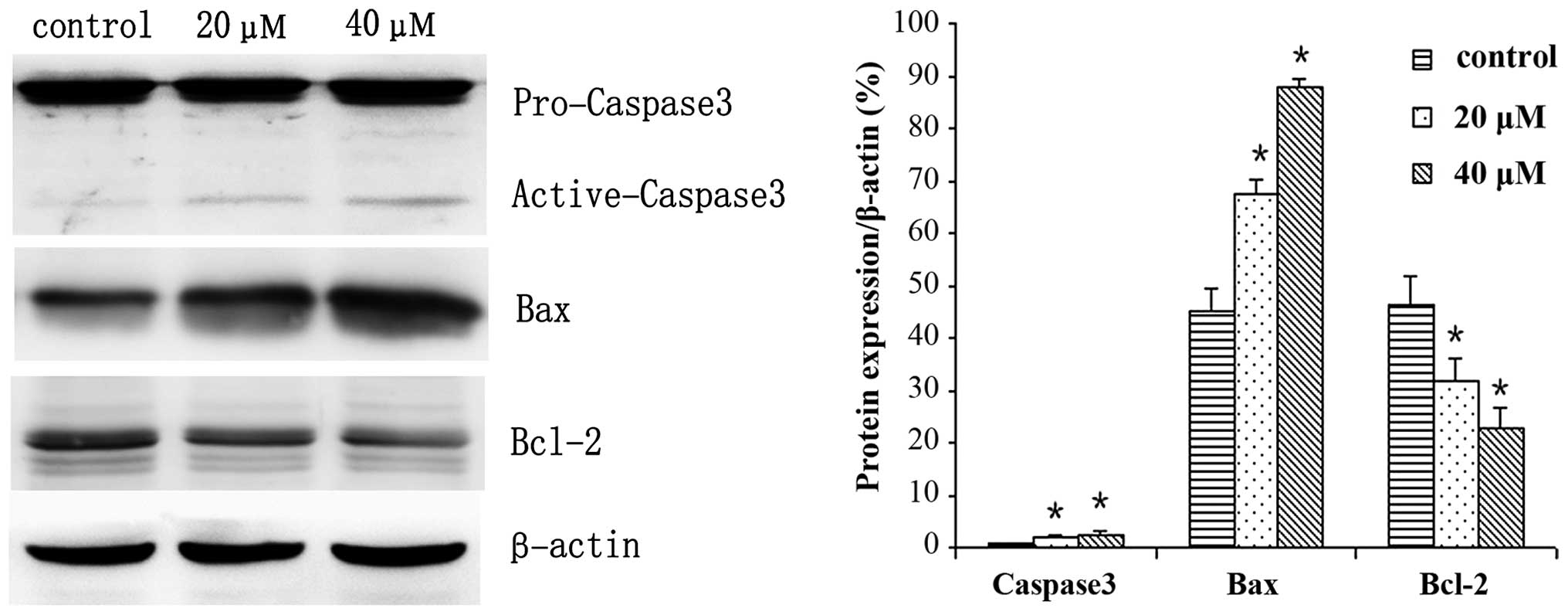
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guggenheim DE and Shah MA: Gastric cancer
epidemiology and risk factors. J Surg Oncol. 107:230–236. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cervantes A, Roda D, Tarazona N, Roselló S
and Pérez-Fidalgo JA: Current questions for the treatment of
advanced gastric cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 39:60–67. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jing H, Zhou X, Dong X, Cao J, Zhu H, Lou
J, Hu Y, He Q and Yang B: Abrogation of Akt signaling by
Isobavachalcone contributes to its anti-proliferative effects
towards human cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 294:167–177. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Akihisa T, Tokuda H, Hasegawa D, Ukiya M,
Kimura Y, Enjo F, Suzuki T and Nishino H: Chalcones and other
compounds from the exudates of Angelica keiskei and their cancer
chemopreventive effects. J Nat Prod. 69:38–42. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bhalla VX, Nayak UR and Dev S: Some new
flavonoids from Psoralea corylifolia. Tetrahedron Lett.
20:2401–2406. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Szliszka E, Jaworska D, Ksek M, Czuba ZP
and Król W: Targeting death receptor TRAIL-R2 by chalcones for
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci.
13:15343–15359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Szliszka E, Czuba ZP, Mazur B, Sedek L,
Paradysz A and Krol W: Chalcones enhance TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 11:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li W, Li S, Higai K, Sasaki T, Asada Y,
Ohshima S and Koike K: Evaluation of licorice flavonoids as protein
tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
23:5836–5839. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nishimura R, Tabata K, Arakawa M, Ito Y,
Kimura Y, Akihisa T, Nagai H, Sakuma A, Kohno H and Suzuki T:
Isobavachalcone, a chalcone constituent of Angelica keiskei,
induces apoptosis in neuroblastoma. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:1878–1883.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jin X, Zhu Z and Shi Y: Metastasis
mechanism and gene/protein expression in gastric cancer with
distant organs metastasis. Bull Cancer. 101:E1–E12. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Khan KH, Blanco-Codesido M and Molife LR:
Cancer therapeutics, Targeting the apoptotic pathway. Crit Rev
Oncol Hematol. 90:6200–219. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Westin JR: Status of PI/3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway inhibitors in lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk.
14:335–342. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Koehler BC, Jäger D and Schulze-Bergkamen
H: Targeting cell death signaling in colorectal cancer Current
strategies and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol.
20:1923–1934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aranda F, Vacchelli E, Eggermont A, Galon
J, Fridman WH, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Trial Watch,
Immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies in cancer therapy.
Oncoimmunology. 3:e272972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park JW, Choi YJ, Suh SI, Baek WK, Suh MH,
Jin IN, Min DS, Woo JH, Chang JS, Passaniti A, Lee YH and Kwon TK:
Bcl-2 overexpression attenuates resveratrol-induced apoptosis in
U937 cells by inhibition of caspase-3 activity. Carcinogenesis.
22:1633–1639. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sharawat SK, Bakhshi R, Vishnubhatla S,
Gupta R and Bakhshi S: BAX/BCL2 RMFI ratio predicts better
induction response in pediatric patients with acute myeloid
leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 60:E63–E66. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sjöström J, Blomqvist C, von Boguslawski
K, Bengtsson NO, Mjaaland I, Malmström P, Ostenstadt B, Wist E,
Valvere V, Takayama S, Reed JC and Saksela E: The predictive value
of bcl-2, bax, bcl-xL, bag-1, fas and fasL for chemotherapy
response in advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 8:811–816.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dent P: Crosstalk between ERK AKT and cell
survival. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:245–246. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Briest F and Grabowski P:
PI3K-AKT-mTOR-signaling and beyond: The complex network in
gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Theranostics.
4:336–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Polivka J: Jr andJ anku F: Molecular
targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol
Ther. 142:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Kempf CR,
Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Stivala F, Malaponte G, Nicoletti F, Libra
M, Bäsecke J, et al: Therapeutic resistance resulting from
mutations in Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways.
J Cell Physiol. 226:2762–2781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Infante JR, Fecher LA, Falchook GS,
Nallapareddy S, Gordon MS, Becerra C, DeMarini DJ, Cox DS, Xu Y,
Morris SR, et al: Safety, pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and
efficacy data for the oral MEK inhibitor trametinib: A phase 1
dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:773–781. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|