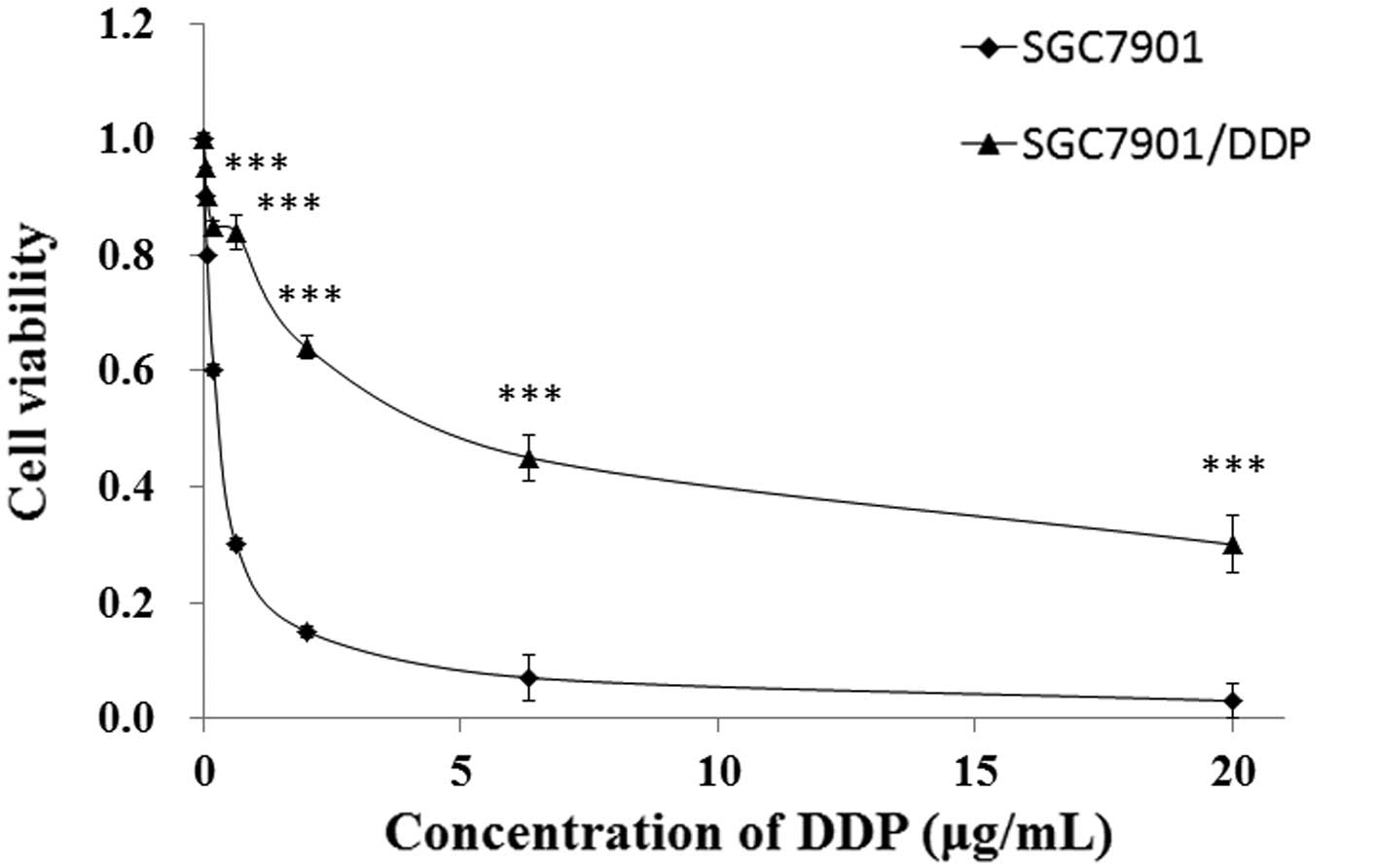
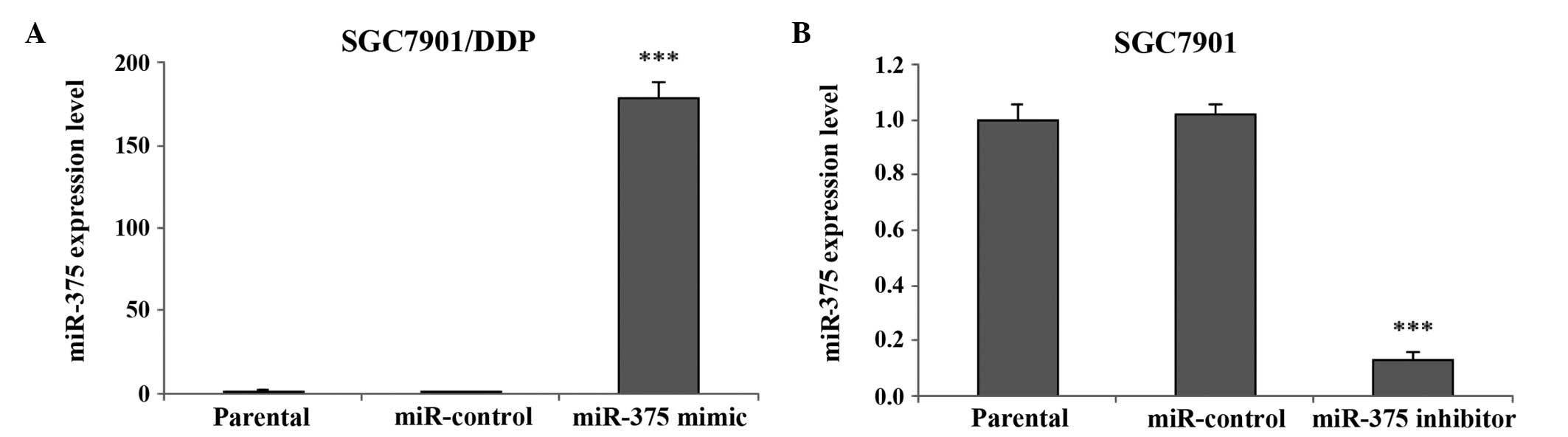
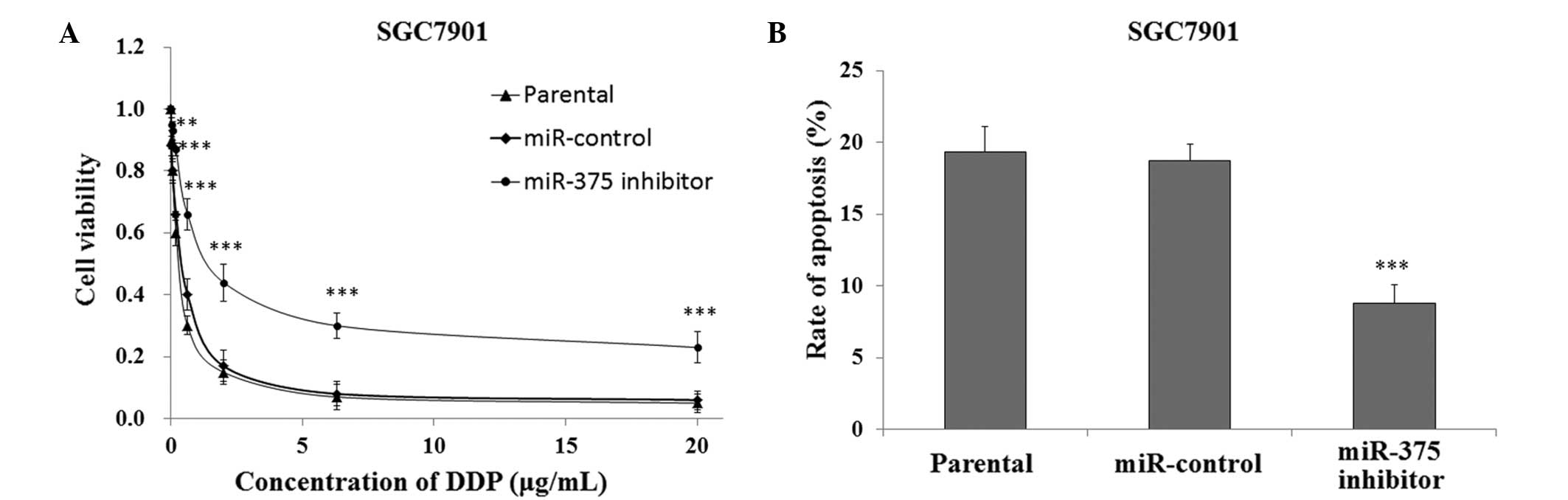
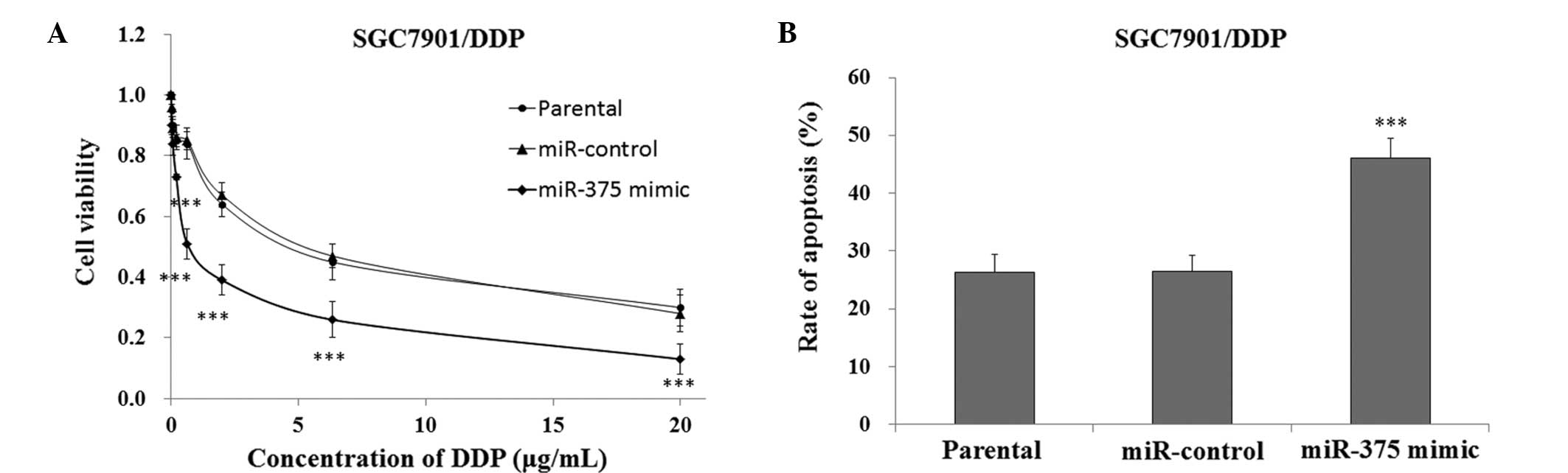
|
1
|
Roder DM: The epidemiology of gastric
cancer. Gastric Cancer. 5(Suppl 1): 5–11. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gallo A and Cha C: Updates on esophageal
and gastric cancers. World J Gastroenterol. 12:3237–3242.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gunderson LL: Gastric cancer - patterns of
relapse after surgical resection. Semin Radiat Oncol. 12:150–161.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP,
Thompson JN, Van de Velde CJ, Nicolson M, Scarffe JH, Lofts FJ,
Falk SJ, Iveson TJ, et al: MAGIC Trial Participants: Perioperative
chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable gastroesophageal
cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bang YJ, Kim YW, Yang HK, Chung HC, Park
YK, Lee KH, Lee KW, Kim YH, Noh SI, Cho JY, et al: CLASSIC trial
investigators: Adjuvant capecitabine and oxaliplatin for gastric
cancer after D2 gastrectomy (CLASSIC): A phase 3 open-label,
randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 379:315–321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mesner PW Jr, Budihardjo II and Kaufmann
SH: Chemotherapy induced apoptosis. Adv Pharmacol. 41:461–499.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kaufmann SH and Earnshaw WC: Induction of
apoptosis by cancer chemotherapy. Exp Cell Res. 256:42–49. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hannun YA: Apoptosis and the dilemma of
cancer chemotherapy. Blood. 89:1845–1853. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kostova I: Platinum complexes as
anticancer agents. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 1:1–22. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics biogenesis,
mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
He H, Jazdzewski K, Li W, Liyanarachchi S,
Nagy R, Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Franssila K, Suster S, et al:
The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:19075–19080. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis
AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R, Liu YP, van Duijse J, Drost J, Griekspoor A,
et al: A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as
oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell. 124:1169–1181.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu L, Fan J and Belasco JG: MicroRNAs
direct rapid deadenylation of mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:4034–4039. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu ZW, Zhong LP, Ji T, Zhang P, Chen WT
and Zhang CP: MicroRNAs contribute to the chemoresistance of
cisplatin in tongue squamous cell carcinoma lines. Oral Oncol.
46:317–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sorrentino A, Liu CG, Addario A, Peschle
C, Scambia G and Ferlini C: Role of microRNAs in drug-resistant
ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 111:478–486. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Avissar M, Christensen BC, Kelsey KT and
Marsit CJ: MicroRNA expression ratio is predictive of head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2850–2855. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mathé EA, Nguyen GH, Bowman ED, Zhao Y,
Budhu A, Schetter AJ, Braun R, Reimers M, et al: MicroRNA
expression in squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of the
esophagus: Associations with survival. Clin Cancer Res.
15:6192–6200. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu AM, Poon RT and Luk JM: microRNA-375
targets Hippo-signaling effector YAP in liver cancer and inhibits
tumor properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:623–627. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen ZY, Zhang ZZ, Liu H, Zhao EH and Cao
H: miR-375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by
repressing ERBB2 expression. Exp Ther Med. 7:1757–1761.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding L, Xu Y, Zhang W, Deng Y, Si M, Du Y,
Yao H, Liu X, Ke Y, Si J and Zhou T: MiR-375 frequently
downregulated in gastric cancer inhibits cell proliferation by
targeting JAK2. Cell Res. 20:784–793. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tsukamoto Y, Nakada C, Noguchi T, Tanigawa
M, Nguyen LT, Uchida T, Hijiya N, Matsuura K, Fujioka T, Seto M and
Moriyama M: MicroRNA-375 is downregulated in gastric carcinomas and
regulates cell survival by targeting PDK1 and 14-3-3zeta. Cancer
Res. 70:2339–2349. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hanapi NA, Ismail S and Mansor SM:
Inhibitory effect of mitragynine on human cytochrome P450 enzyme
activities. Pharmacognosy Res. 5:241–246. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Krauskopf J, Caiment F, Claessen SM,
Johnson KJ, Warner RL, Schomaker SJ, Burt DA, Aubrecht J and
Kleinjans JC: Application of high-throughput sequencing to
circulating microRNAs reveals novel biomarkers for drug-induced
liver injury. Toxicol Sci. 143:268–276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Knuefermann C, Lu Y, Liu B, Jin W, Liang
K, Wu L, Schmidt M, Mills GB, Mendelsohn J and Fan Z:
HER2/PI-3K/Akt activation leads to a multidrug resistance in human
breast adenocarcinoma cells. Oncogene. 22:3205–3212. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ding J, Huang S, Wu S, Zhao Y, Liang L,
Yan M, Ge C, Yao J, Chen T, Wan D, et al: Gain of miR-151 on
chromosome 8q24.3 facilitates tumour cell migration and spreading
through downregulating RhoGDIA. Nat Cell Biol. 12:390–399. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jay C, Nemunaitis J, Chen P, Fulgham P and
Tong AW: miRNA profiling for diagnosis and prognosis of human
cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 26:293–300. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang H, Kong W, He L, Zhao JJ, O’Donnell
JD, Wang J, Wenham RM, Coppola D, Kruk PA, Nicosia SV and Cheng JQ:
MicroRNA expression profiling in human ovarian cancer, miR-214
induces cell survival and cisplatin resistance by targeting PTEN.
Cancer Res. 68:425–433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J,
Ilnytskyy Y, Tryndyak VP, Chekhun VF and Pogribny IP: Involvement
of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast cancer cells to
chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2152–2159.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li T, Li D, Sha J, Sun P, Huang Y and Li
TI: MicroRNA-21 directly targets MARCKS and promotes apoptosis
resistance and invasion in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 383:280–285. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, Pan Y, Zhao L, Sun
S, Hong L, Liu J and Fan D: MiR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug
resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 123:372–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miller TE, Ghoshal K, Ramaswamy B, Roy S,
Datta J, Shapiro CL, Jacob S and Majumder S: MicroRNA-221/222
confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer by targeting p27Kip1.
J Biol Chem. 283:29897–29903. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang SM, Huang C, Li XF, Yu MZ, He Y and
Li J: miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells
by regulating PTEN. Toxicology. 306:162–168. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cao W, Yang W, Fan R, Li H, Jiang J, Geng
M, Jin Y and Wu Y: miR-34a regulates cisplatin-induce gastric
cancer cell death by modulating PI3K/AKT/survivin pathway. Tumour
Biol. 35:1287–1295. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M,
Taccioli C, Rossi S, Alder H, Liu CG, Oue N, et al: Relation
between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis of
gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bang YJ: Advances in the management of HER
2-positive advanced gastric and gastroesophageal junction cancer. J
Clin Gastroenterol. 46:637–648. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|