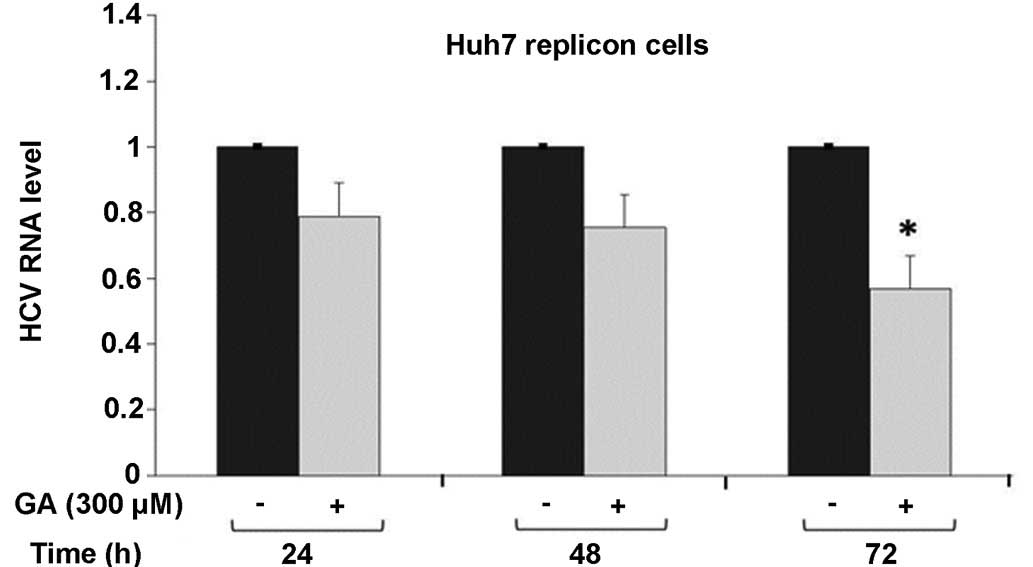
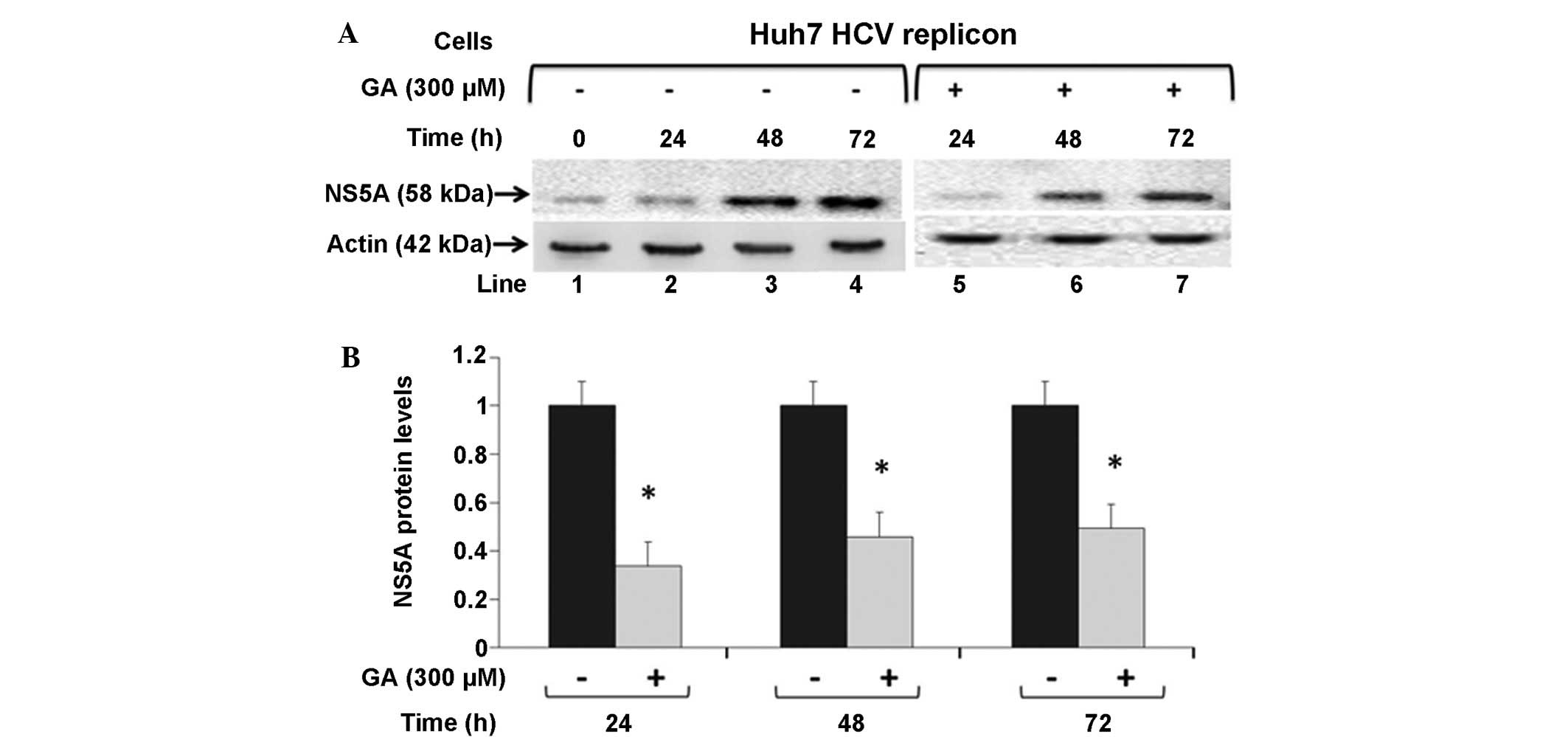
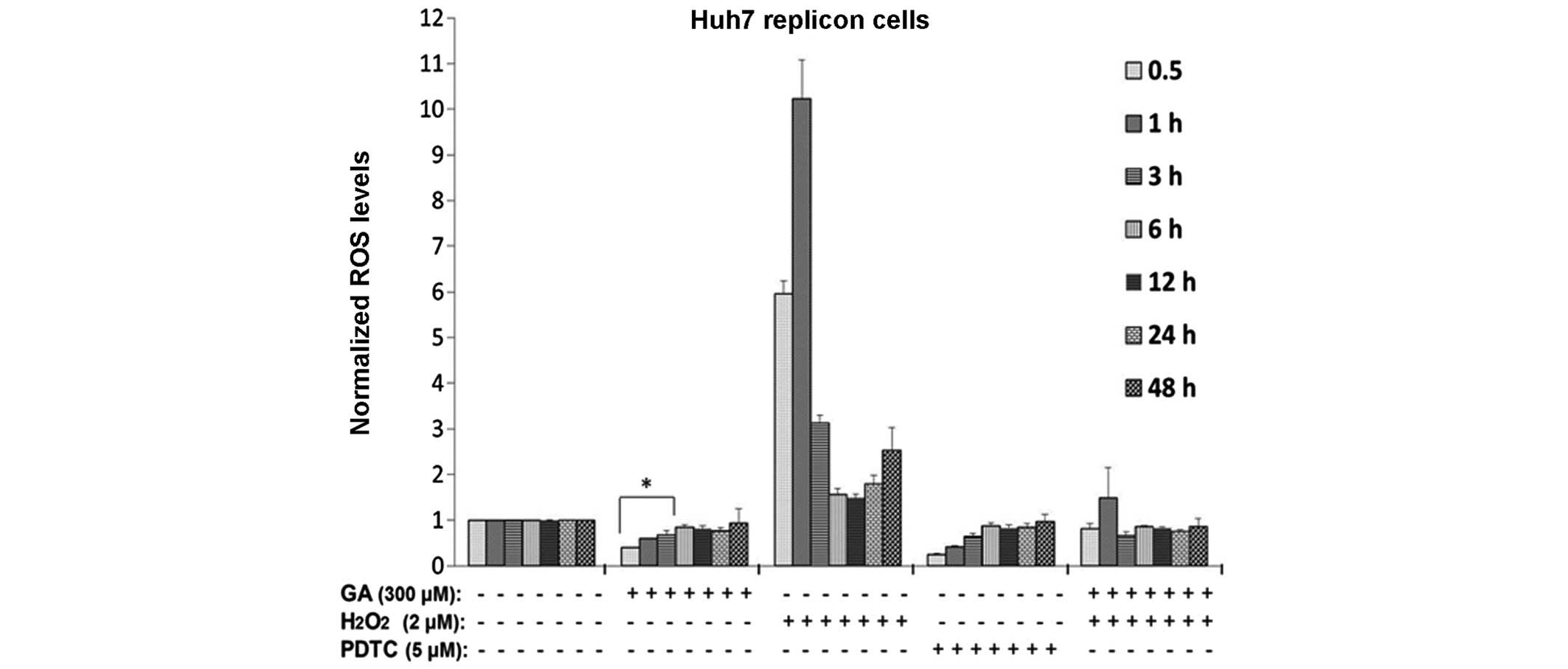
|
1
|
Pahl HL: Signal transduction from the
endoplasmic reticulum to the cell nucleus. Physiol Rev. 79:683–701.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Warris G and Siddiqui A: Hepatitis C virus
stimulates the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 via oxidative stress:
Role of prostaglandin E2 in RNA replication. J Virol. 79:9725–9734.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang H, Chen Y and Ye J: Inhibition of
hepatitis C virus replication by peroxidation of arachidonate and
restoration by vitamin E. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:18666–18670.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gong G, Waris G, Tanveer R and Siddiqui A:
Human hepatitis C virus NS5A protein alters intracellular calcium
levels, induces oxidative stress, and activates STAT-3 and NF-kappa
B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:9599–9604. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Burra P and Hepatitis C: Semin Liver Dis.
29:53–65. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
do Kim Y, Ahn SH and Han KH: Emerging
therapies for hepatitis C. Gut Liver. 8:471–479. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Poordad F, McCone J Jr, Bacon BR, Bruno S,
Manns MP, Sulkowski MS, Jacobson IM, Reddy KR, Goodman ZD, Boparai
N, et al: Boceprevir for untreated chronic HCV genotype 1
infection. N Engl J Med. 364:1195–1206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patrick L and Hepatitis C: epidemiology
and review of complementary/alternative medicine treatments. Altern
Med Rev. 4:220–238. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Trujillo-Murillo K, Rincón-Sánchez AR,
Martinez-Rodriguez H, Bosques-Padilla F, Ramos-Jiménez J,
Barrera-Saldaña HA, Rojkind M and Rivas-Estilla AM: Acetylsalicylic
acid inhibits hepatitis C virus RNA and protein expression through
cyclooxygenase 2 signaling pathways. Hepatology. 47:1462–1472.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yano M, Ikeda M, Abe K, Dansako H, Ohkoshi
S, Aoyagi Y and Kato N: Comprehensive analysis of the effects of
ordinary nutrients on hepatitis C virus RNA replication in cell
culture. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 51:2016–2027. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Taitzoglou IA, Tsantarliotou M, Zervos I,
Kouretas D and Kokolis NA: Inhibition of human and ovine acrosomal
enzymes by tannic acid in vitro. Reproduction. 121:131–137.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Haslam E: Practical polyphenolics, From
structure to molecular recognition and physiological action.
Cambridge University Press Cambridge. 84–177. 1998.
|
|
13
|
Lekha PK and Lonsane BK: Production and
application of tannin acyl hydrolase: State of the art. Adv Appl
Microbiol. 44:215–260. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hocman G: Chemoprevention of cancer: P
henolic antioxidants (BHT, BHA). Int J Biochem. 20:639–651. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sharma S, Wyatt GP and Steele VE: A
carcinogen-DNA binding assay as a biomarker screen for identifying
potential chemopreventive agents. Methods Cell Sci. 19:45481997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim YJ: Antimelanogenic and antioxidant
properties of gallic acid. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:1052–1055. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ji BC, Hsu WH, Yang JS, Hsia TC, Lu CC,
Chiang JH, Yang JL, Lin CH, Lin JJ, Suen LJ, et al: Gallic acid
induces apoptosis via caspase-3 and mitochondrion-dependent
pathways in vitro and suppresses lung xenograft tumor growth
in vivo. J Agric Food Chem. 57:7596–7604. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Inoue M, Suzuki R, Sakaguchi N, Li Z,
Takeda T, Ogihara Y, Jiang BY and Chen Y: Selective induction of
cell death in cancer cells by gallic acid. Biol Pharm Bull.
18:1526–1530. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen HM, Wu YC, Chia YC, Chang FR, Hsu HK,
Hsieh YC, Chen CC and Yuan SS: Gallic acid, a major component of
Toona sinensis leaf extracts, contains a ROS-mediated
anti-cancer activity in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
286:161–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
You BR and Park WH: The effects of
mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors or small interfering
RNAs on gallic acid induced HeLa cell death in relation to reactive
oxygen species and glutathione. J Agric Food Chem. 59:763–771.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Choi HJ, Song JH, Bhatt LR and Baek SH:
Anti-Human Rhinovirus activity of gallic acid possessing
antioxidant capacity. Phytother Res. 24:1292–1296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kratz JM, Andrighetti-Frohner CR, Kolling
DJ, Leal PC, Cirne-Santos CC, Yunes RA, Nunes RJ, Trybala E,
Bergström T, Frugulhetti IC, et al: Anti-HSV-1 and anti-HIV-1
activity of gallic acid and pentyl gallate. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz.
103:437–442. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cuzzocrea S, Chatterjee PK, Mazzon E,
Serraino I, Britti D, Dugo L, Mazzullo G, Caputi AP and Thiemermann
C: Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates the development of acute
and chronic inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 135:496–510. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lohmann V, Körner F, Koch J, Herian U,
Theilmann L and Bartenschlager R: Replication of subgenomic
hepatitis C virus RNAs in a hepatoma cell line. Science.
285:110–113. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Devasagayam TP, Maurya DK and Nandakumar
N: Anticancer property of gallic acid in A549, a human lung
adenocarcinoma cell line and possible mechanisms. J Clin Biochem
Nutr. 48:85–90. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: A pplications to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yedjou CG and Tchounwou PB: In
vitro cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of arsenic trioxide on
human leukemia (HL-60) cells using the MTT and alkaline single cell
gel electrophoreis (Comet) assays. Mol Cell Biochem. 301:123–130.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rivas-Estilla AM, Svitkin Y, Lastra Lopez
M, Hatzoglou M, Sherker A and Koromilas AE: PKR-dependent
mechanisms of gene expression from a subgenomic hepatitis C virus
clone. J Virol. 76:10637–10653. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rivas-Estilla AM, Bryan-Marrugo OL,
Trujillo-Murillo K, Pérez-Ibave D, Charles-Niño C, Pedroza-Roldan
C, RíosIbarra C, Ramírez-Valles E, Ortíz-López R, Islas-Carbajal
MC, et al: Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) induction is
implicated in the antioxidative and antiviral activity of
acetylsalicylic acid in HCV-expressing cells. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 302:G1264–G1273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kopff M, Kopff A and Kowalczyk E: The
effect of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on
oxidative/antioxidative balance. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 23:184–187.
2007.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Polat A and Emre MH: Effects of melatonin
or acetylsalicylic acid on gastric oxidative stress after bile duct
ligation in rats. J Gastroenterol. 41:433–439. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chatel-Chaix L, Baril M and Lamarre D:
Hepatitis C Virus NS3/4A Protease inhibitors, A light at the end of
the Tunnel. Viruses. 2:1752–1765. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ivanov AV, Bartosh B, Smirnova OA,
Isaguliants MG and Kochetkov SN: HCV and oxidative stress in the
liver. Viruses. 5:439–469. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mehrab-Mohseni M, Sendi H, Steuerwald N,
Ghosh S, Schrum LW and Bonkovsky HL: Legalon-SIL down regulates HCV
core and NS5A in human hepatocytes expressing full-length HCV.
World J Gastroenterol. 17:1694–1700. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Choi HJ, Song JH, Park KS and Baek SH:
In vitro anti-enterovirus 71 activity of gallic acid from
Woodfordia fruticosa flowers. Lett Appl Microbiol.
50:438–440. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sriwilaijaroen N, Fukumoto S, Kumagai K,
Hiramatsu H, Odagiri T, Tashiro M and Suzuki Y: Antiviral effect of
Psidium guajava Linn (guava) tea on the growth of clinical
isolated H1N1 viruses: Its role in viral hemagglutination and
neuraminidase inhibition. Antiviral Res. 94:139–146. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
de Oliveira A, Adams SD, Lee LH, Murray
SR, Hsu SD, Hammond JR, Dickinson D, Chen P and Chu TC: Inhibition
of herpes simplex virus type 1 with the modified green tea
polyphenol palmitoyl-epigallocatechin gallate. Food Chem Toxicol.
52:207–215. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
You BR, Moon HJ, Han YH and Park WH:
Gallic acid inhibits the growth of HeLa cervical cancer cells via
apoptosis and/or necrosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:1334–1340. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Polyak SJ, Morishima C, Lohmann V, Pal S,
Lee DYW, Liu Y, Graf TN and Oberlies NH: Identification of
hepatoprotective flavonolignans from silymarin. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:5595–5599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee JC, Chen WC, Wu SF, Tseng CK, Chiou
CY, Chang FR, Hsu SH and Wu YC: Anti-hepatitis C virus of Acacia
confusa extract via suppressing cyclooxygenase-2. Antiviral
Res. 89:35–42. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ravikumar YS, Ray U, Nandhitha M, Perween
A, Naika Raja HR, Khanna N and Das S: Inhibition of hepatitis C
virus replication by herbal extract. Phyllanthus amarus as potent
natural source. Virus Res. 158:89–97. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Manvar D, Mishra M, Kumar S and Pandey VN:
Identification and evaluation of anti Hepatitis C virus
phytochemicals from Eclipta alba. J Ethnopharmacology.
144:545–554. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ahn MJ, Kim CY, Lee JS, Kim TG, Kim SH,
Lee CK, Lee BB, Shin CG, Huh H and Kim J: Inhibition of HIV-1
integrase by galloyl glucoses from Terminalia chebula and
flavonol glycoside gallates from Euphorbia pekinensis.
Planta Med. 68:457–459. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Duan D, Li Z, Luo H, Zhang W, Chen L and
Xu X: Antiviral compounds from traditional Chinese medicines Galla
Chinese as inhibitors of HCV NS3 protease. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
14:6041–6044. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Uosaki M, Yamasaki H, Katsuyama Y, Higuchi
M, Higuti T and Koyama AH: Antiviral effect of octyl gallate
against DNA and RNA viruses. Antiviral Res. 73:85–91. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nutan Modi M, Goel T, Das T, Malik S, Suri
S, Rawat AK, Srivastava SK, Tuli R, Malhotra S and Gupta SK:
Ellagic acid & gallic acid from Lagerstroemia speciosa
L. inhibit HIV-1 infection through inhibition of HIV-1 protease
& reverse transcriptase activity. Indian J Med Res.
137:540–548. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu G, Xiong S, Xiang YF, Guo CW, Ge F,
Yang CR, Zhang YJ, Wang YF and Kitazato K: Antiviral activity and
possible mechanisms of action of pentagalloylglucose (PGG) against
influenza A virus. Arch Virol. 156:1359–1369. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|