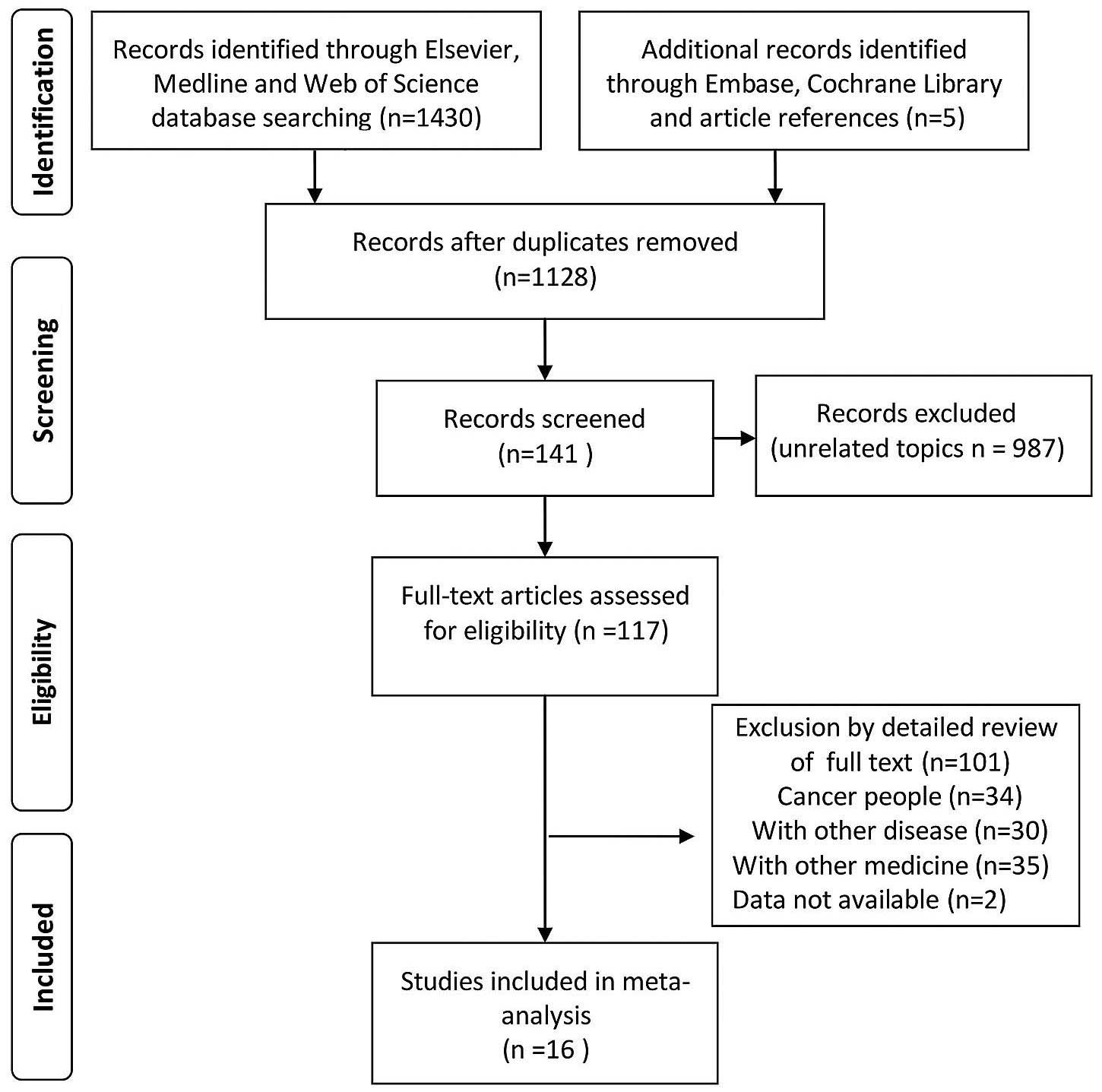
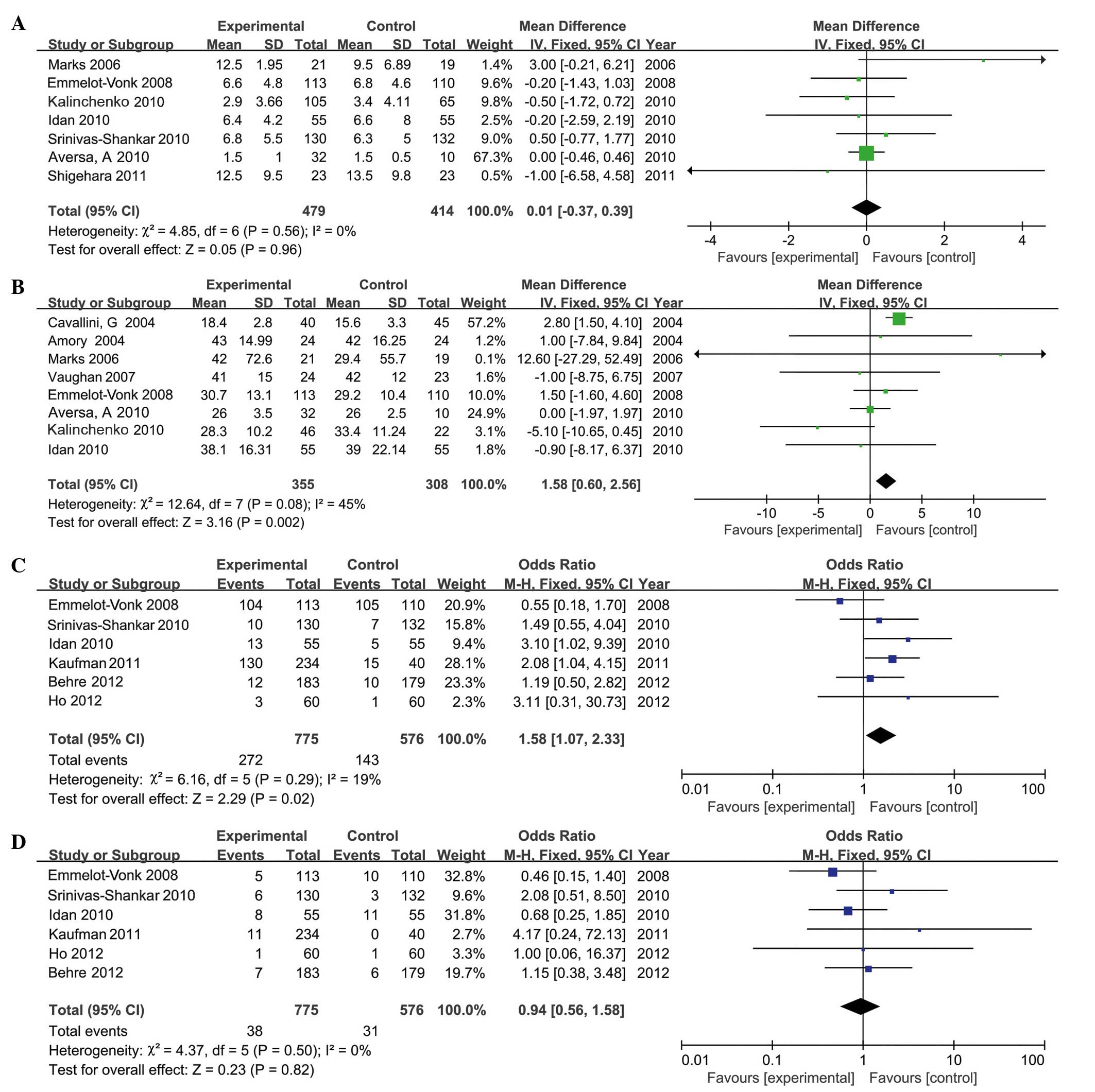
|
1
|
Cardarelli R, Singh M, Meyer J, Balyakina
E, Perez O and King M: The association of free testosterone levels
in men and lifestyle factors and chronic disease status: A North
Texas Healthy Heart Study. J Prim Care Community Health. 5:173–179.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferreira SR: Cushing and Arquivos
Brasileiros de Endocrinologia e Metabologia Award 2006. Arq Bras
Endocrinol Metabol. 51:11812007.(In Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cui Y, Zong H, Yan H and Zhang Y: The
effect of testosterone replacement therapy on prostate cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
17:132–143. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bassil N: Late-onset hypogonadism. Med
Clin North Am. 95:507–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Donatucci C, Cui Z, Fang Y and Muram D:
Long-term treatment patterns of testosterone replacement
medications. J Sex Med. 11:2092–2099. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Behre HM, Tammela TL, Arver S, Tolrá JR,
Bonifacio V, Lamche M, Kelly J, Hiemeyer F, Giltay EJ and Gooren
LJ: European Testogel Study Team: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial of testosterone gel on body composition
and health-related quality-of-life in men with hypogonadal to
low-normal levels of serum testosterone and symptoms of androgen
deficiency over 6 months with 12 months open-label follow-up. Aging
Male. 15:198–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Emmelot-Vonk MH, Verhaar HJ, Pour Nakhai
HR, Aleman A, Lock TM, Bosch JL, Grobbee DE and van der Schouw YT:
Effect of testosterone supplementation on functional mobility,
cognition, and other parameters in older men: A randomized
controlled trial. JAMA. 299:39–52. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Amory JK, Watts NB, Easley KA, Sutton PR,
Anawalt BD, Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ and Tenover JL: Exogenous
testosterone or testosterone with finasteride increases bone
mineral density in older men with low serum testosterone. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 89:503–510. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cavallini G, Caracciolo S, Vitali G,
Modenini F and Biagiotti G: Carnitine versus androgen
administration in the treatment of sexual dysfunction, depressed
mood, and fatigue associated with male aging. Urology. 63:641–646.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Page ST, Amory JK, Bowman FD, Anawalt BD,
Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ and Tenover JL: Exogenous testosterone (T)
alone or with finasteride increases physical performance, grip
strength, and lean body mass in older men with low serum T. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 90:1502–1510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marks LS, Mazer NA, Mostaghel E, Hess DL,
Dorey FJ, Epstein JI, Veltri RW, Makarov DV, Partin AW, Bostwick
DG, et al: Effect of testosterone replacement therapy on prostate
tissue in men with late-onset hypogonadism: A randomized controlled
trial. JAMA. 296:2351–2361. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vaughan C, Goldstein FC and Tenover JL:
Exogenous testosterone alone or with finasteride does not improve
measurements of cognition in healthy older men with low serum
testosterone. J Androl. 28:875–882. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aversa A, Bruzziches R, Francomano D,
Rosano G, Isidori AM, Lenzi A and Spera G: Effects of testosterone
undecanoate on cardiovascular risk factors and atherosclerosis in
middle-aged men with late-onset hypogonadism and metabolic
syndrome: Results from a 24-month, randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. J Sex Med. 7:3495–3503. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aversa A, Bruzziches R, Francomano D,
Spera G and Lenzi A: Efficacy and safety of two different
testosterone undecanoate formulations in hypogonadal men with
metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol Invest. 33:776–783. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Idan A, Griffiths KA, Harwood DT, Seibel
MJ, Turner L, Conway AJ and Handelsman DJ: Long-term effects of
dihydrotestosterone treatment on prostate growth in healthy,
middle-aged men without prostate disease: A randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 153:621–632. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kalinchenko SY, Tishova YA, Mskhalaya GJ,
Gooren LJ, Giltay EJ and Saad F: Effects of testosterone
supplementation on markers of the metabolic syndrome and
inflammation in hypogonadal men with the metabolic syndrome: The
double-blinded placebo-controlled Moscow study. Clin Endocrinol
(Oxf). 73:602–612. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Srinivas-Shankar U, Roberts SA, Connolly
MJ, O'Connell MD, Adams JE, Oldham JA and Wu FC: Effects of
testosterone on muscle strength, physical function, body
composition, and quality of life in intermediate-frail and frail
elderly men: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study.
J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 95:639–650. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kaufman JM, Miller MG, Garwin JL,
Fitzpatrick S, McWhirter C and Brennan JJ: Efficacy and safety
study of 1.62% testosterone gel for the treatment of hypogonadal
men. J Sex Med. 8:2079–2089. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shigehara K, Sugimoto K, Konaka H, Iijima
M, Fukushima M, Maeda Y, Mizokami A, Koh E, Origasa H, Iwamoto T
and Namiki M: Androgen replacement therapy contributes to improving
lower urinary tract symptoms in patients with hypogonadism and
benign prostate hypertrophy: A randomised controlled study. Aging
Male. 14:53–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Frederiksen L, Højlund K, Hougaard DM,
Brixen K and Andersen M: Testosterone therapy increased muscle mass
and lipid oxidation in aging men. Age (Dordr). 34:145–156. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ho CC, Tong SF, Low WY, Ng CJ, Khoo EM,
Lee VK, Zainuddin ZM and Tan HM: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial on the effect of long-acting testosterone
treatment as assessed by the Aging Male Symptoms scale. BJU Int.
110:260–265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morgentaler A: Testosterone and prostate
cancer: An historical perspective on a modern myth. Eur Urol.
50:935–939. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Moher D, Cook DJ, Eastwood S, Olkin I,
Rennie D and Stroup F: Improving the Quality of Reports of
Meta-Analyses of Randomised Controlled Trials: The QUOROM
Statement. Onkologie. 23:597–602. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Oxman AD and Guyatt GH: The science of
reviewing research. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 703:125–134. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bhasin S and Buckwalter JG: Testosterone
supplementation in older men: A rational idea whose time has not
yet come. J Androl. 22:718–731. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smith MR: Changes in fat and lean body
mass during androgen-deprivation therapy for prostate cancer.
Urology. 63:742–745. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mittan D, Lee S, Miller E, Perez RC,
Basler JW and Bruder JM: Bone loss following hypogonadism in men
with prostate cancer treated with GnRH analogs. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 87:3656–3661. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hackett G, Cole N, Bhartia M, Kennedy D,
Raju J and Wilkinson P: BLAST Study Group: Testosterone replacement
therapy improves metabolic parameters in hypogonadal men with type
2 diabetes but not in men with coexisting depression: The BLAST
study. J Sex Med. 11:840–856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Roehrborn CG, Siami P, Barkin J, Damião R,
Major-Walker K, Nandy I, Morrill BB, Gagnier RP and Montorsi F:
CombAT Study Group: The effects of combination therapy with
dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men with
symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from the
CombAT study. Eur Urol. 57:123–131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kaplan SA: Re: The effects of combination
therapy with dutasteride and tamsulosin on clinical outcomes in men
with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia: 4-year results from
the CombAT study. J Urol. 185:1384–1385. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hsing AW, Reichardt JK and Stanczyk FZ:
Hormones and prostate cancer: Current perspectives and future
directions. Prostate. 52:213–235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khera M, Bhattacharya RK, Blick G, Kushner
H, Nguyen D and Miner MM: Changes in prostate specific antigen in
hypogonadal men after 12 months of testosterone replacement
therapy: Support for the prostate saturation theory. J Urol.
186:1005–1011. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liao CH, Li HY, Chung SD, Chiang HS and Yu
HJ: Significant association between serum dihydrotestosterone level
and prostate volume among Taiwanese men aged 40–79 years. Aging
Male. 15:28–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Raynaud JP, Gardette J, Rollet J and
Legros JJ: Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) concentrations in
hypogonadal men during 6 years of transdermal testosterone
treatment. BJU Int. 111:880–890. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ozata M, Bulur M, Beyhan Z, Sengül A,
Saglam M, Turan M, Corakci A and Gundogan Ali M: Effects of
gonadotropin and testosterone treatments on prostate volume and
serum prostate specific antigen levels in male hypogonadism. Endocr
J. 44:719–724. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Calof OM, Singh AB, Lee ML, Kenny AM,
Urban RJ, Tenover JL and Bhasin S: Adverse events associated with
testosterone replacement in middle-aged and older men: A
meta-analysis of randomized, placebo-controlled trials. J Gerontol
A Biol Sci Med Sci. 60:1451–1457. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|