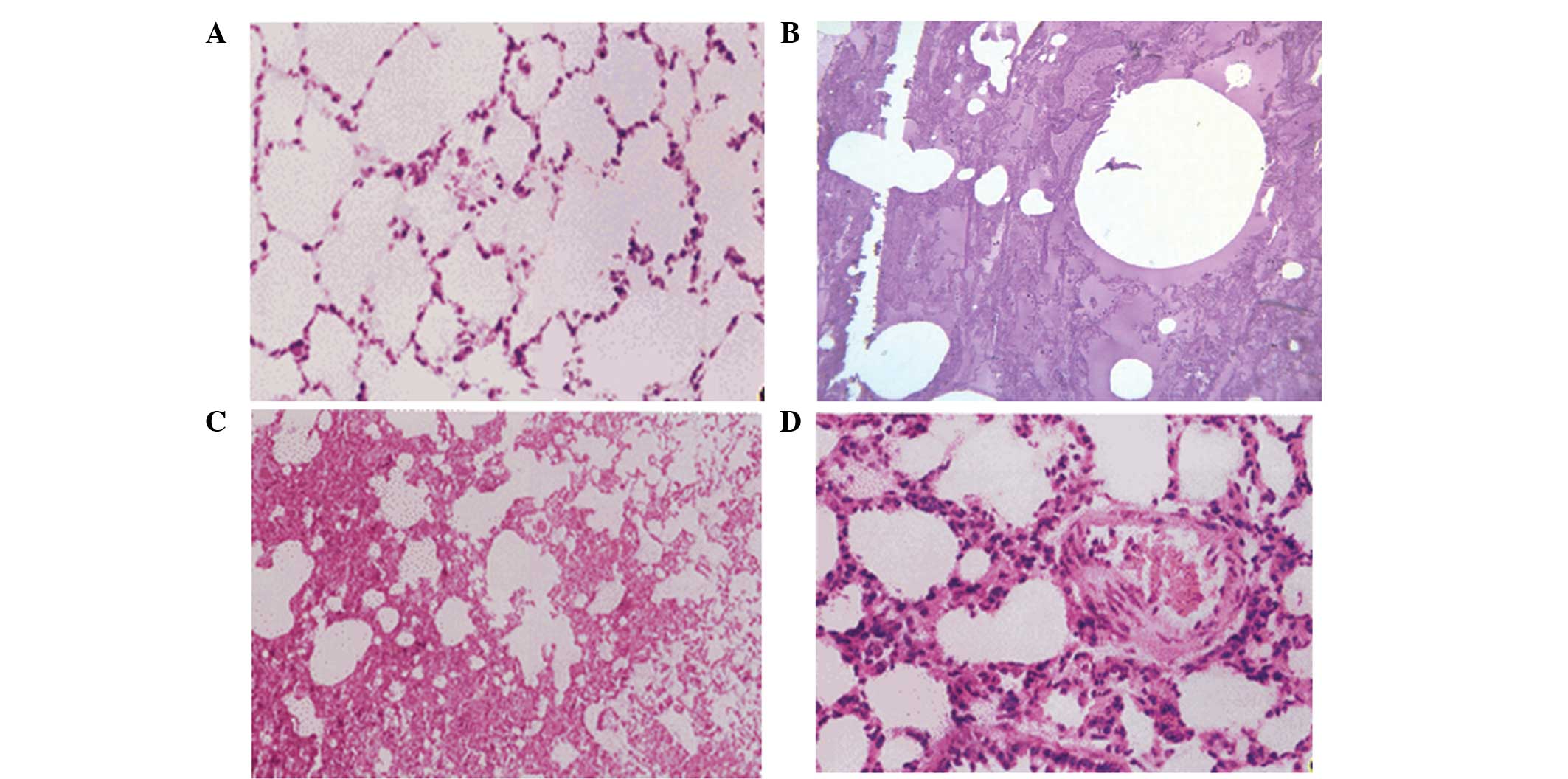
|
1
|
Obiagwu C, Paul V, Chadha S, Hollander G
and Shani J: Acute pulmonary edema secondary to hyperbaric oxygen
therapy. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2015:183–184. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith WS and Matthay MA: Evidence for a
hydrostatic mechanism in human neurogenic pulmonary edema. Chest.
111:1326–1333. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang XT, Liu DW, Zhang HM and Chai WZ:
Integrated cardiopulmonary sonography: a useful tool for assessment
of acute pulmonary edema in the intensive care unit. J Ultrasound
Med. 33:1231–1239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
MacIver DH and Clark AL: The vital role of
the right ventricle in the pathogenesis of acute pulmonary edema.
Am J Cardiol. 115:992–1000. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Theodore J and Robin ED: Pathogenesis of
neurogenic pulmonary oedema. Lancet. 2:749–751. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mammoto T, Jiang E, Jiang A, Lu Y, Juan
AM, Chen J and Mammoto A: Twist1 controls lung vascular
permeability and endotoxin-induced pulmonary edema by altering Tie2
expression. PLoS One. 8:e734072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Minnear FL, Kite C, Hill LA and van der
Zee H: Endothelial injury and pulmonary congestion characterize
neurogenic pulmonary edema in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985).
63:335–341. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang XM, Sun DY, Tang L and Yuan YJ:
Preliminary experimental research on glucocorticoid for treatment
of nitrogen dioxide induced acute pulmonary edema in rats. Zhonghua
Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 28:822–826. 2010.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Viswanathan S, Muthu V and Remalayam B:
Pulmonary edema in near hanging. J Trauma Acute Care Surg.
72:297–301. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hamdy O, Maekawa H, Shimada Y, Feng GG and
Ishikawa N: Role of central nervous system nitric oxide in the
development of neurogenic pulmonary edema in rats. Crit Care Med.
29:1222–1228. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lionte C, Sorodoc L and Laba V:
Respiratory syndromes in acute poisoning. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat
Iasi. 108:544–548. 2004.(In Romanian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ekman I, Ekstrand L and Schaufelberger M:
Pulmonary oedema - a life threatening disease. Eur J Cardiovasc
Nurs. 6:259–264. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Greenbaum R, Bay J, Hargreaves MD, Kain
ML, Kelman GR, Nunn JF, Prys-Roberts C and Siebold K: Effects of
higher oxides of nitrogen on the anaesthetized dog. Br J Anaesth.
39:393–404. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lavie L: Oxidative stress in obstructive
sleep apnea and intermittent hypoxia - revisited - the bad ugly and
good: Implications to the heart and brain. Sleep Med Rev. 20:27–45.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wojtczak L and Slyshenkov VS: Protection
by pantothenic acid against apoptosis and cell damage by oxygen
free radicals - the role of glutathione. Biofactors. 17:61–73.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Prys-Roberts C: Principles of treatment of
poisoning by higher oxides of nitrogen. Br J Anaesth. 39:432–439.
1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mansuroğlu B, Derman S, Yaba A and
Kizilbey K: Protective effect of chemically modified SOD on lipid
peroxidation and antioxidant status in diabetic rats. Int J Biol
Macromol. 72:79–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li K, Gao B, Li J, Chen H, Li Y, Wei Y,
Gong D, Gao J, Zhang J, Tan W, et al: ZNF32 protects against
oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by modulating C1QBP
transcription. Oncotarget. 6:38107–38126. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Parsons PE: Respiratory failure as a
result of drugs, overdoses, and poisonings. Clin Chest Med.
15:93–102. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fang LL and Ye JJ: Investigated progress
of expression of interleukin-6,-10 in herniated disc. Yi Xue Zong
Shu. 13:569–572. 2007.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Rassler B: Role of α- and β-adrenergic
mechanisms in the pathogenesis of pulmonary injuries characterized
by edema, inflammation and fibrosis. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug
Targets. 13:197–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sarada S, Himadri P, Mishra C, Geetali P,
Ram MS and Ilavazhagan G: Role of oxidative stress and NFkB in
hypoxia-induced pulmonary edema. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
233:1088–1098. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chatterjee K and Parmley WW: The role of
vasodilator therapy in heart failure. Prog Cardiovasc Dis.
19:301–325. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sonnenblick EH, Mancini DM and LeJemtel
TH: New positive inotropic drugs for the treatment of congestive
heart failure. Am J Cardiol. 55:41A–44A. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Francois G, Faizende J and Reboul J:
Pulmonary edemas due to acute heroin poisoning. Ann Anesthesiol Fr.
16:77–83. 1975.(In French). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hamdy O, Maekawa H, Shimada Y, Feng GG and
Ishikawa N: Role of central nervous system nitric oxide in the
development of neurogenic pulmonary edema in rats. Crit Care Med.
29:1222–1228. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|