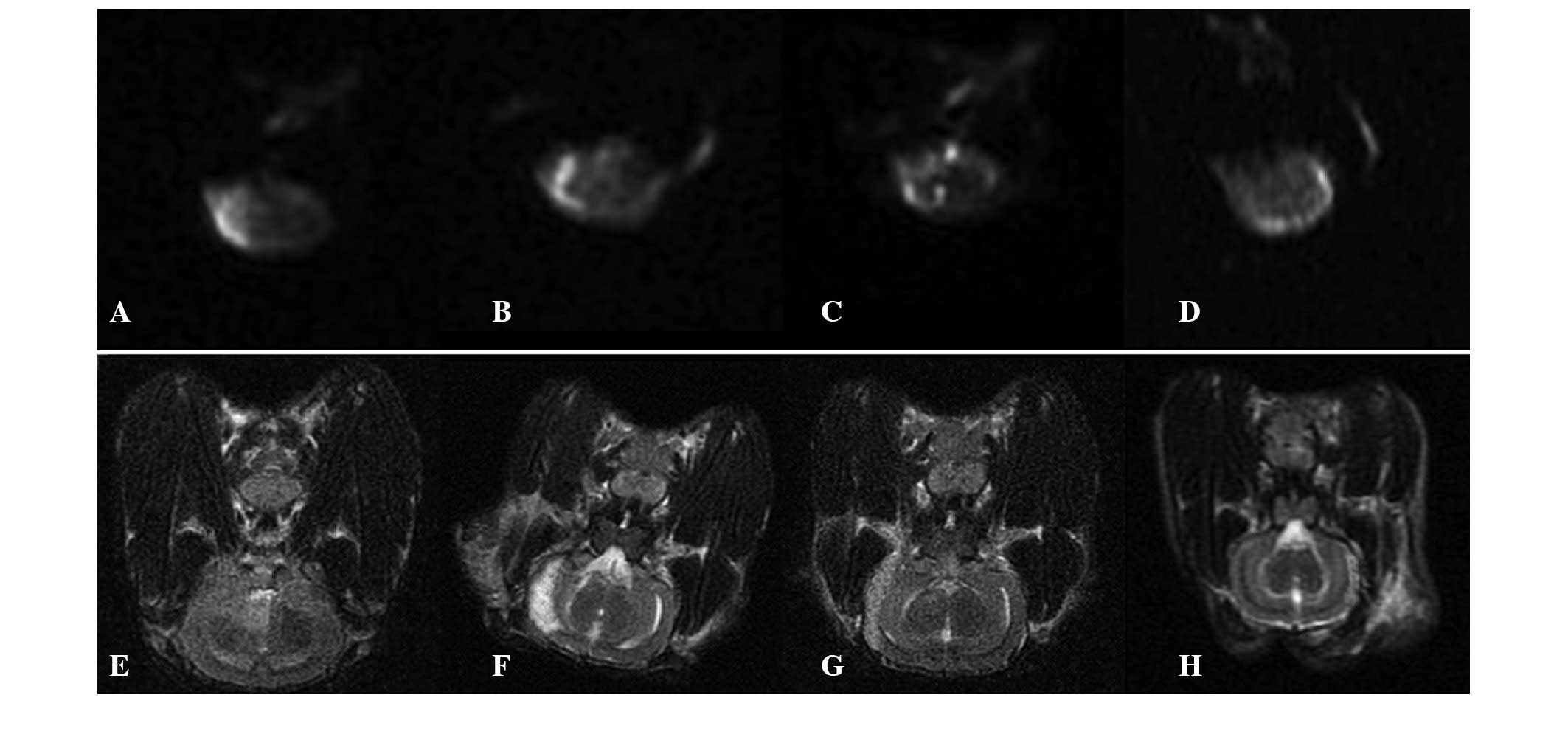
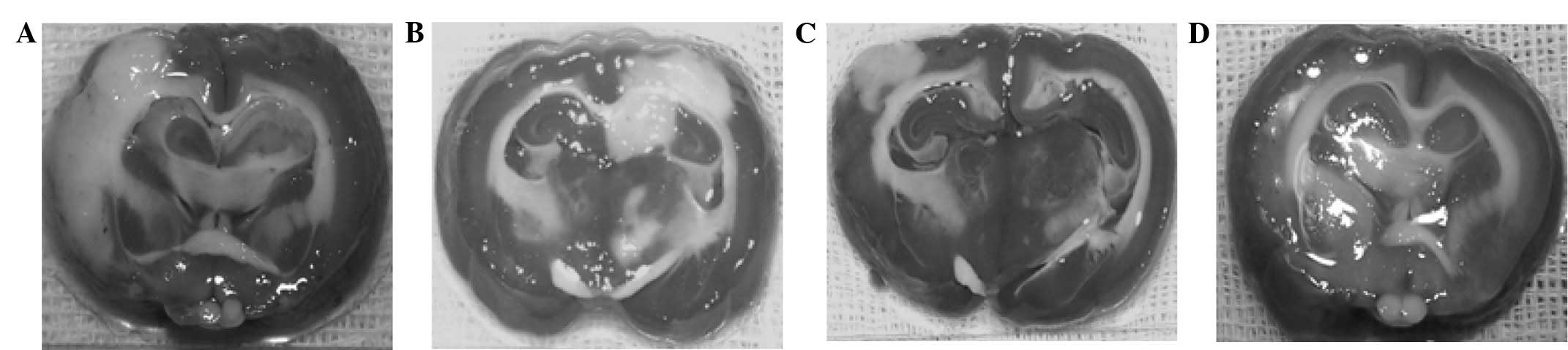
|
1
|
Gaillard N, Schmidt C, Costalat V, et al:
Hemorrhagic risk of recent silent cerebral infarct on
prethrombolysis MR imaging in acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
33:227–231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung SM, Lee TH, Cho HJ, Sol YL, Park KH,
Jung DS and Kim CW: Recanalization with Wingspan stent for acute
middle cerebral artery occlusion in failure or contraindication to
intravenous thrombolysis: A feasibility study. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 33:1156–1161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kellert L, Hametner C, Rohde S, Bendszus
M, Hacke W, Ringleb P and Stampfl S: Endovascular stroke therapy
tirofiban is associated with risk of fatal intracerebral hemorrhage
and poor outcome. Stroke. 44:1453–1455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mullen MT, Pisapia JM, Tilwa S, Messé SR
and Stein SC: Systematic review of outcome after ischemic stroke
due to anterior circulation occlusion treated with intravenous,
intra-arterial, or combined intravenous+intra-arterial
thrombolysis. Stroke. 43:2350–2355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xu XQ, Zu QQ, Lu SS, et al: Use of FLAIR
imaging to identify onset time of cerebral ischemia in a canine
model. ANJR Am J Neuroradiol. 35:311–316. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Siebler M, Hennerici MG, Schneider D, et
al: Safety of Tirofiban in acute ischemic Stroke: The SaTIS trial.
Stroke. 42:2388–2392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Georgiadis AL, Memon MZ, Shah QA, Vazquez
G, Suri MF, Lakshminarayan K and Qureshi AI: Comparison of partial
(6 mg/kg) versus full-dose (9 mg/kg) intravenous recombinant tissue
plasminogen activator followed by endovascular treatment for acute
ischemic stroke: A meta-analysis. J Neuroimaging. 21:113–120. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Zhang R, Morris D, Lu
M, Coller BS and Chopp M: Adjuvant treatment with a glycoprotein
IIb/IIIa receptor inhibitor increases the therapeutic window for
low-dose tissue plasminogen activator administration in a rat model
of embolic stroke. Circulation. 107:2837–2843. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Junghans U, Seitz R, Ritzl A, Wittsack HJ,
Fink GR, Freund HJ and Siebler M: Ischemic brain tissue salvaged
from infarction by the GP II b/III a platelet antagonist tirofiban.
Neurology. 58:474–476. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baik SK, Oh SJ, Park KP and Lee JH:
Intra-arterial tirofiban infusion for partial recanalization with
stagnant flow in hyperacute cerebral ischemic stroke. Interv
Neuroradiol. 17:442–451. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ottani F, La Vecchia L, De Vita M,
Catapano O, Tarantino F and Galvani M: Comparison by meta-analysis
of eptifibatide and tirofiban to abciximab in patients with
ST-elevation myocardial infarction treated with primary
percutaneous coronary intervention. Am J Cardiol. 106:167–174.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schiariti M, Saladini A, Cuturello D,
Missiroli B and Puddu PE: Long-term efficacy of high-dose tirofiban
versus double-bolus eptifibatide in patients undergoing
percutaneous coronary intervention. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown).
12:29–36. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura
MC, Davis RL and Bartkowksi H: Rat middle cerebral artery
occlusion: Evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic
examination. Stroke. 17:472–476. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bhatia R, Hill MD, Shobha N, et al: Low
rates of acute recanalization with intravenous recombinant tissue
plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke: Real-world experience and
a call for action. Stroke. 41:2254–2258. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zangerle A, Kiechl S, Spiegel M, et al:
Recanalization after thrombolysis in stroke patients: Predictors
and prognostic implications. Neurology. 68:39–44. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rha JH and Saver JL: The impact of
recanalization on ischemic stroke outcome: A meta-analysis. Stroke.
38:967–973. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mangiafico S, Cellerini M, Nencini P,
Gensini G and Inzitari D: Intravenous glycoprotein IIb/IIIa
inhibitor (tirofiban) followed by intra-arterial urokinase and
mechanical thrombolysis in stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
26:2595–2601. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shuaib A, Yang Y, Nakada MT, Li Q and Yang
T: Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist, murine 7E3 F (ab') 2 and
tissue plasminogen activator in focal ischemia: Evaluation of
efficacy and risk of hemorrhage with combination therapy. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 22:215–222. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jeon JS, Sheen SH, Hwang G, Kang SH, Heo
DH and Cho YJ: Intraarterial tirofiban thrombolysis for
thromboembolisms during coil embolization for ruptured intracranial
aneurysms. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 14:5–10. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jeong HW and Jin SC: Intra-arterial
infusion of a glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonist for the treatment of
thromboembolism during coil embolization of intracranial aneurysm:
A comparison of abciximab and tirofiban. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
34:1621–1625. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen MH, Wu SL, Lo MC, Chen WL and Wang
WF: Basilar artery occlusion in a teenaged boy treated with
intra-arterial thrombolysis. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 19:281–286.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kwon BJ, Seo DH, Ha YS and Lee KC:
Endovascular treatment of wide-necked cerebral aneurysms with an
acute angle branch incorporated into the Sac: Novel methods of
branch access in 8 aneurysms. Neurointervention. 7:93–101. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rho MH, Kim BM, Suh SH, Kim DJ and Kim DI:
Initial experience with the new double-lumen scepter balloon
catheter for treatment of wide-necked aneurysms. Korean J Radiol.
14:832–840. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cho YD, Lee JY, Seo JH, Kang HS, Kim JE,
Jung KH and Han MH: Intra-arterial tirofiban infusion for
thromboembolic complication during coil embolization of ruptured
intracranial aneurysms. Eur J Radiol. 81:2833–2838. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Won YS, Rho MH, Kim BM, Park HJ, Kwag HJ
and Chung EC: Various techniques of stent-assisted coil
embolization of wide-necked or fusiform middle cerebral artery
aneurysms: initial and mid-term results. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
53:274–280. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lang SH, Manning N, Armstrong N, Misso K,
Allen A, Di Nisio M and Kleijnen J: Treatment with tirofiban for
acute coronary syndrome (ACS): A systematic review and network
analysis. Curr Med Res Opin. 28:351–370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Syfret DA, Mitchell P, Dowling R and Yan
B: Does intra-arterial thrombolysis have a role as first-line
intervention in acute ischaemic stroke. Intern Med J. 41:220–226.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|