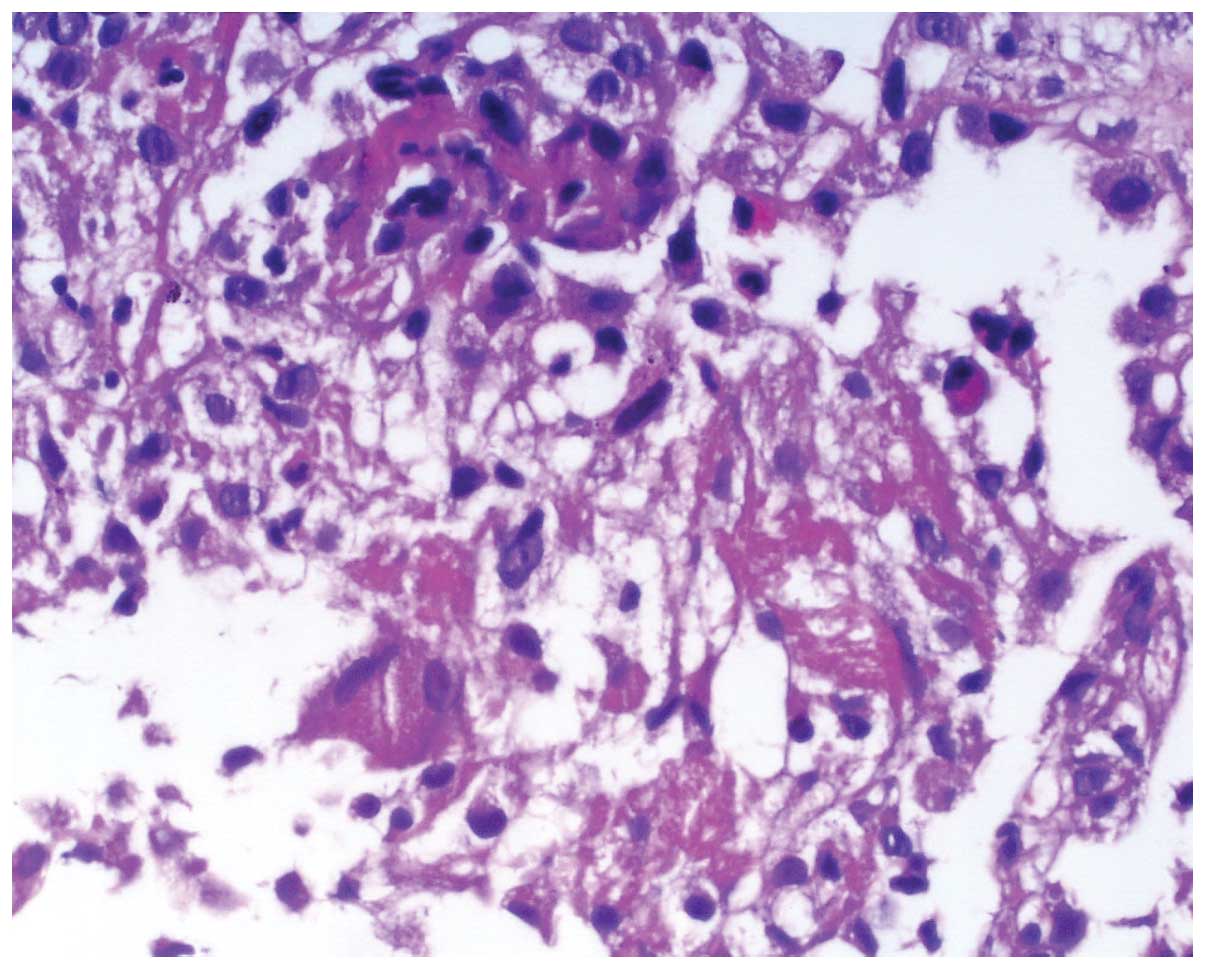
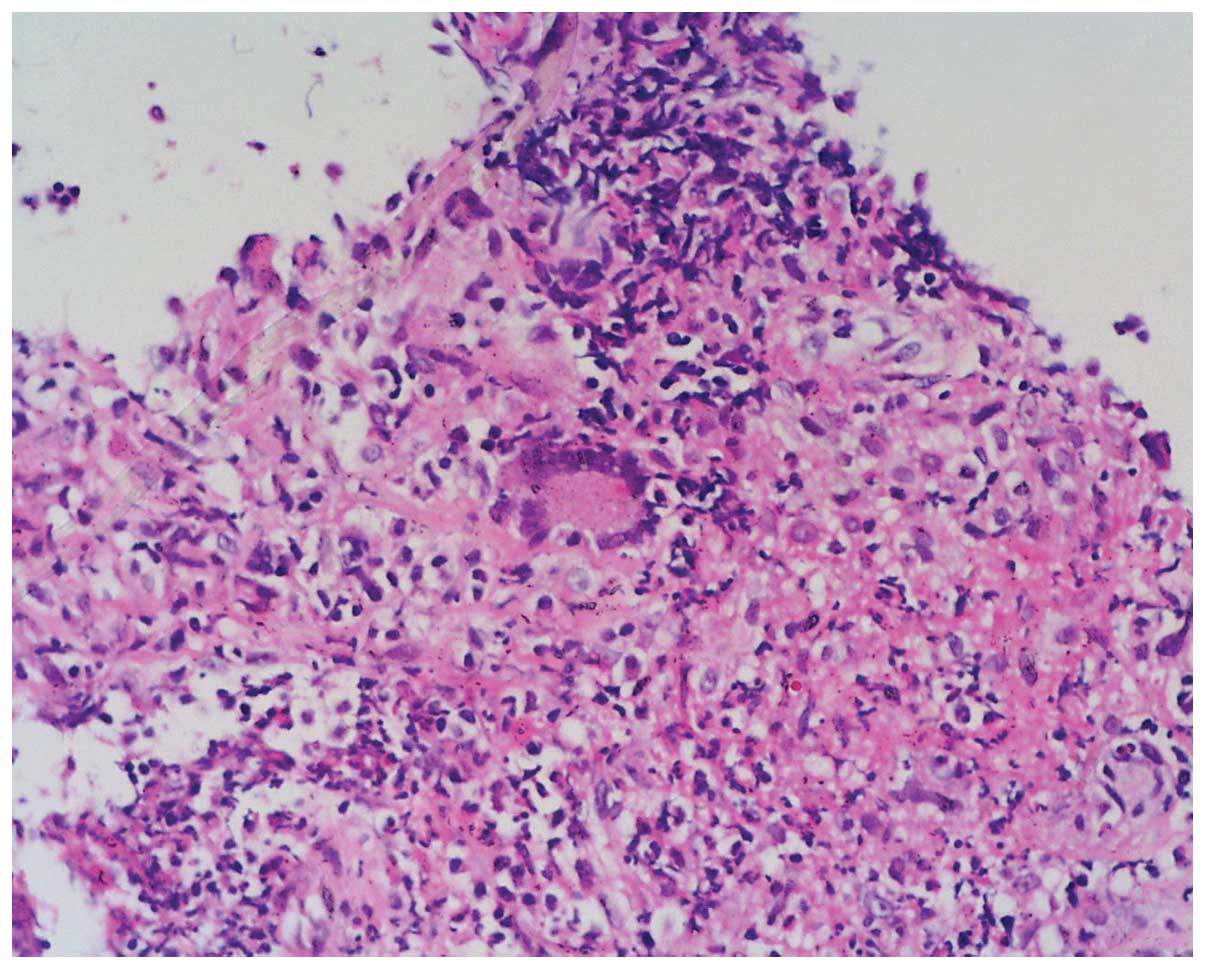
|
1
|
Hoffman GS, Kerr GS, Leavitt RY, Hallahan
CW, Lebovics RS, Travis WD, Rottem M and Fauci AS: Wegener
granulomatosis: an analysis of 158 patients. Ann Intern Med.
116:488–498. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Klinger H: Grenzformen der periarteritis
nodosa. Frankf Z Pathol. 42:455–480. 1931.(In German).
|
|
3
|
Wegener F: Über generalisierte, septische
Efäberkrankungen. Verh Dtsch Pathol Ges. 29:202–210. 1936.(In
German).
|
|
4
|
Lu ZY and Zhong NS: Internal Medicine.
Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House. 884–885. 2011.
|
|
5
|
Gadó KI, Zszabó L, Csákó L and Domján G:
Wegener's granulomatosis. Orv Hetil. 154:1083–1095. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen DY, Liang LQ and Zhan ZP: Limited and
severe Wegener's granulomatosis: clinical features. Chin Remedies
Clin. 10:489–492. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Yu SY and Sun B: Clinical Diagnosis and
Treatment of Respiratory Department of Internal Medicine. Beijing:
Union Medical College Press. 2010.
|
|
8
|
Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, Bloch DA, Michel BA,
Hunder GG, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, Fries JF, Lie JT, Lightfoot RW
Jr, et al: The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for
the classification of Wegener's granulomatosis. Arthritis Rheum.
33:1101–1107. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vassilopoulos D, Niles JL, Villa-Forte A,
Arroliga AC, Sullivan EJ, Merkel PA and Hoffman GS: Prevalence of
antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in patients with various
pulmonary diseases or multiorgan dysfunction. Arthritis Rheum.
49:151–155. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zak-Gołab A, Hrycek A, Holecki M and
Chudek J: Diagnostic value of antineutophil cytoplasmic antibodies.
Wiad Lek. 64:37–42. 2011.(In Polish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen M, Yu F, Zhang Y and Zhao MH:
Antineutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibody-associated vasculitis in
older patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 87:203–209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kallenberg CG: Key advances in the
clinical approach to ANCA-associated vasculitis. Nat Rev Rheumatol.
10:484–493. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stierna P and Carlsöö B: Histopathological
observations in chronic maxillary sinusitis. Acta Otolaryngol.
110:450–458. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chubachi A, Imai H, Nishimura S, Saitoh M
and Miura AB: Nasal T-cell lymphoma associated with hemophagocytic
syndrome. Immunohistochemical and genotypic studies. Arch Pathol
Lab Med. 116:1209–1212. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sweany HC and Seiler HH: The pathology and
bacteriology of resected lesions in pulmonary. Dis Chest.
29:119–152. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Feng RE, Liu HR, Liu TH, Chen J, Ling Q,
Shi XH, Zhong DR, Luo YF and Cao JL: Pulmonary lymphomatoid
granulomatosis: An immunohistochemical and gene rearrangement
study. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 40:460–464. 2011.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chinese Medical Association of
Rheumatology: Microscopic polyangiitis diagnosis and treatment
guidelines. Chin J Rheumatol. 15:259–261. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Jones RB, Tervaert JW, Hauser T, Luqmani
R, Morgan MD, Peh CA, Savage CO, Segelmark M, Tesar V, van Paassen
P, et al: European Vasculitis Study Group: Rituximab versus
cyclophosphamide in ANCA-associated renal vasculitis. N Engl J Med.
363:211–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|