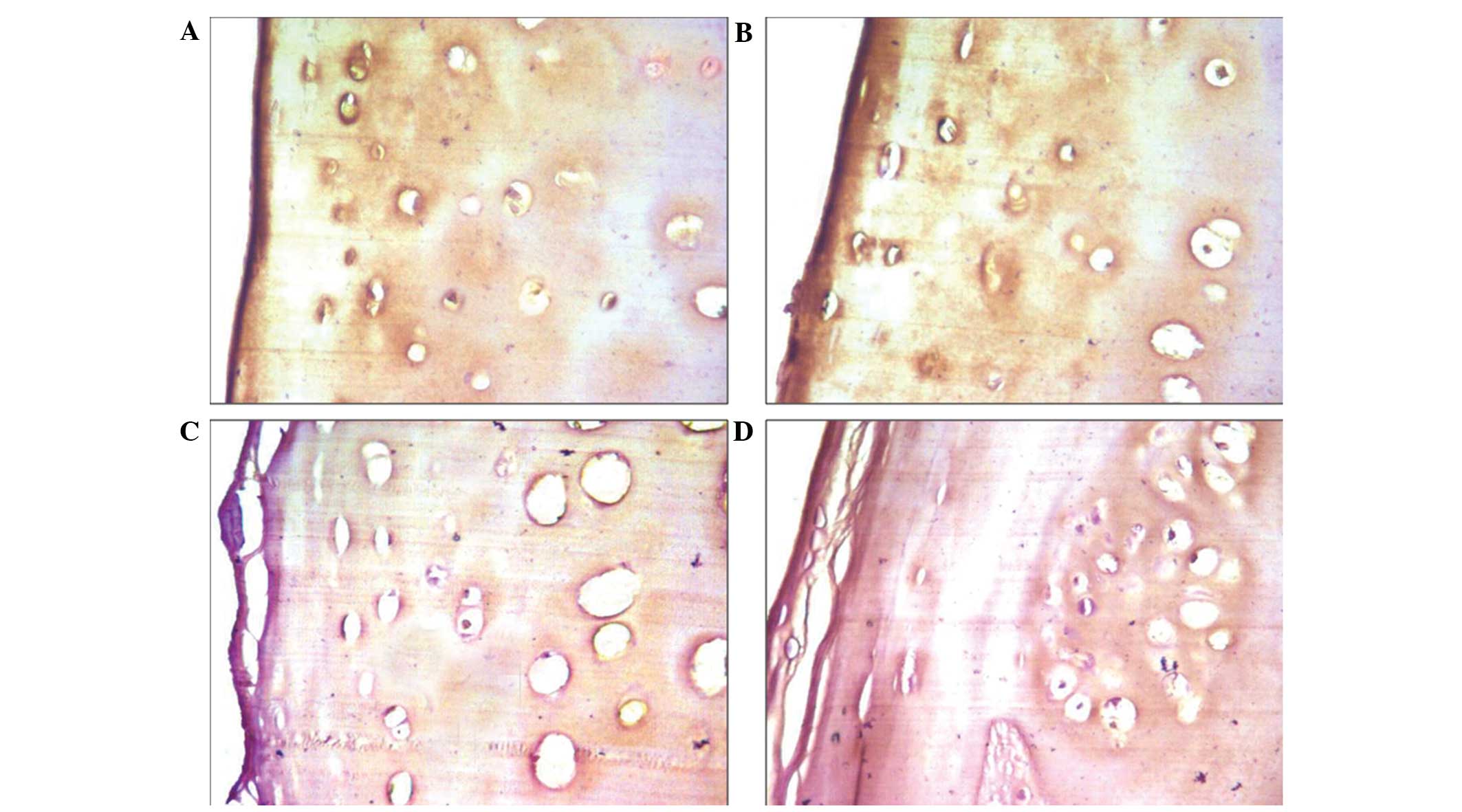
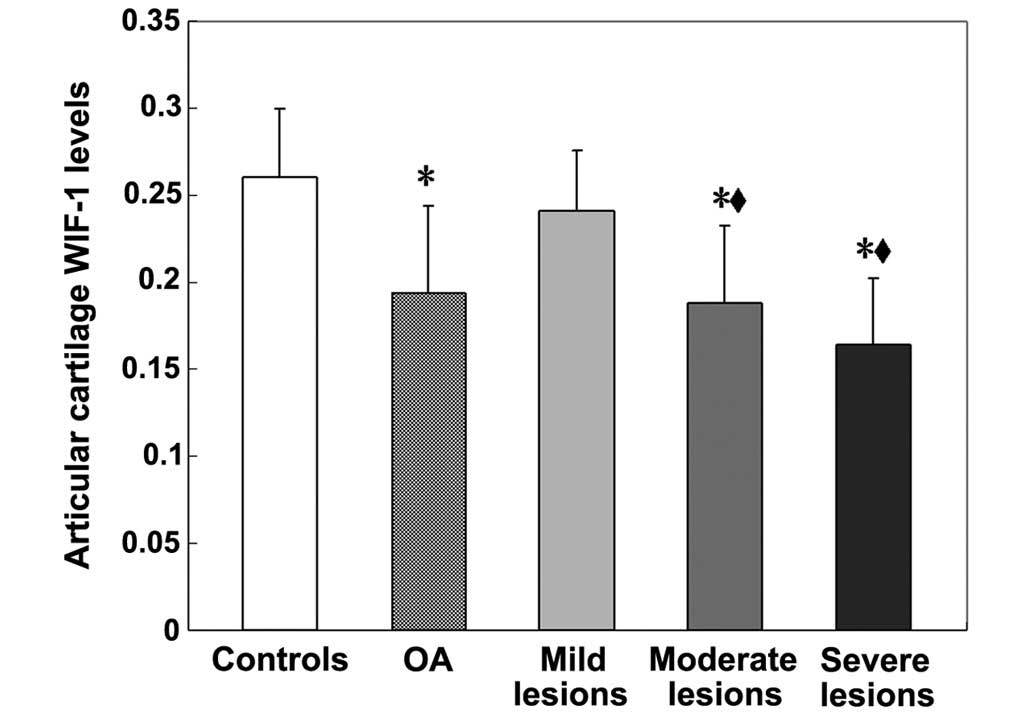
|
1
|
Arden NK and Leyland KM: Osteoarthritis
year 2013 in review: Clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
21:1409–1413. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao SG, Li KH, Zeng KB, Tu M, Xu M and Lei
GH: Elevated osteopontin level of synovial fluid and articular
cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee
osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:82–87. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lawrence RC, Felson DT, Helmick CG, Arnold
LM, Choi H, Deyo RA, Gabriel S, Hirsch R, Hochberg MC, Hunder GG,
et al: Estimates of the prevalence of arthritis and other rheumatic
conditions in the United States. Part II. Arthritis Rheum.
58:26–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu M and Hu C: Association of MIF in
serum and synovial fluid with severity of knee osteoarthritis. Clin
Biochem. 45:737–739. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Holt HL, Katz JN, Reichmann WM, Gerlovin
H, Wright EA, Hunter DJ, Jordan JM, Kessler CL and Losina E:
Forecasting the burden of advanced knee osteoarthritis over a
10-year period in a cohort of 60–64 year-old US adults.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 19:44–50. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bay-Jensen AC, Reker D, Kjelgaard-Petersen
CF, Mobasheri A, Karsdal MA, Ladel C, Henrotin Y and Thudium CS:
Osteoarthritis year in review: 2015 soluble biomarkers and the
BIPED criteria. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24:9–20. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ai L, Tao Q, Zhong S, Fields CR, Kim WJ,
Lee MW, Cui Y, Brown KD and Robertson KD: Inactivation of Wnt
inhibitory factor-1 (WIF1) expression by epigenetic silencing is a
common event in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 27:1341–1348. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsieh JC, Kodjabachian L, Rebbert ML,
Rattner A, Smallwood PM, Samos CH, Nusse R, Dawid IB and Nathans J:
A new secreted protein that binds to Wnt proteins and inhibits
their activities. Nature. 398:431–436. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu YA, Gu X, Liu J, Yang Y, Yan Y and Zhao
C: Expression pattern of Wnt inhibitor factor 1(Wif1) during the
development in mouse CNS. Gene Expr Patterns. 8:515–522. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hunter DD, Zhang M, Ferguson JW, Koch M
and Brunken WJ: The extracellular matrix component WIF-1 is
expressed during and can modulate, retinal development. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 27:477–488. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Surmann-Schmitt C, Sasaki T, Hattori T,
Eitzinger N, Schett G, von der Mark K and Stock M: The Wnt
antagonist Wif-1 interacts with CTGF and inhibits CTGF activity. J
Cell Physiol. 227:2207–2216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stock M, Böhm C, Scholtysek C, Englbrecht
M, Fürnrohr BG, Klinger P, Gelse K, Gayetskyy S, Engelke K,
Billmeier U, et al: Wnt inhibitory factor 1 deficiency uncouples
cartilage and bone destruction in tumor necrosis factor α-mediated
experimental arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 65:2310–2322. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Altman R, Asch E, Bloch D, Bole G,
Borenstein D, Brandt K, Christy W, Cooke TD, Greenwald R and
Hochberg M: Development of criteria for the classification and
reporting of osteoarthritis: Classification of osteoarthritis of
the knee Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria of the American
Rheumatism Association. Arthritis Rheum. 29:1039–1049. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kellgren JH and Lawrence JS: Radiological
assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 16:494–502. 1957.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, van der
Linden AJ, Bulstra SK, Kuyer R and Drukker J: The reliability of
the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 10:58–61. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang W, Gao SG, Chen XG, Xu XC, Xu M, Luo
W, Tu M, Zhang FJ, Zeng C and Lei GH: Expression of synovial fluid
and articular cartilage VIP in human osteoarthritic knee: A new
indicator of disease severity? Clin Biochem. 45:1607–1612. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang FJ, Luo W, Gao SG, Su DZ, Li YS,
Zeng C and Lei GH: Expression of CD44 in articular cartilage is
associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis. Mod
Rheumatol. 23:1186–1191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Surmann-Schmitt C, Widmann N, Dietz U,
Saeger B, Eitzinger N, Nakamura Y, Rattel M, Latham R, Hartmann C,
von der Mark H, et al: Wif-1 is expressed at cartilage-mesenchyme
interfaces and impedes Wnt3a-mediated inhibition of chondrogenesis.
J Cell Sci. 122:3627–3637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Herman JG and Baylin SB: Gene silencing in
cancer in association with promoter hypermethylation. N Engl J Med.
349:2042–2054. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jones PA and Baylin SB: The fundamental
role of epigenetic events in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 3:415–428.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Urakami S, Shiina H, Enokida H, Kawakami
T, Tokizane T, Ogishima T, Tanaka Y, Li LC, Ribeiro-Filho LA,
Terashima M, et al: Epigenetic inactivation of Wnt inhibitory
factor-1 plays an important role in bladder cancer through aberrant
canonical Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Clin Cancer Res.
12:383–391. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang Z and Wang Y, Fang J, Chen F, Liu J,
Wu J and Wang Y: Expression and aberrant promoter methylation of
Wnt inhibitory factor-1 in human astrocytomas. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 29:262010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mazieres J, He B, You L, Xu Z, Lee AY,
Mikami I, Reguart N, Rosell R, McCormick F and Jablons DM: Wnt
inhibitory factor-1 is silenced by promoter hypermethylation in
human lung cancer. Cancer Res. 64:4717–4720. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|