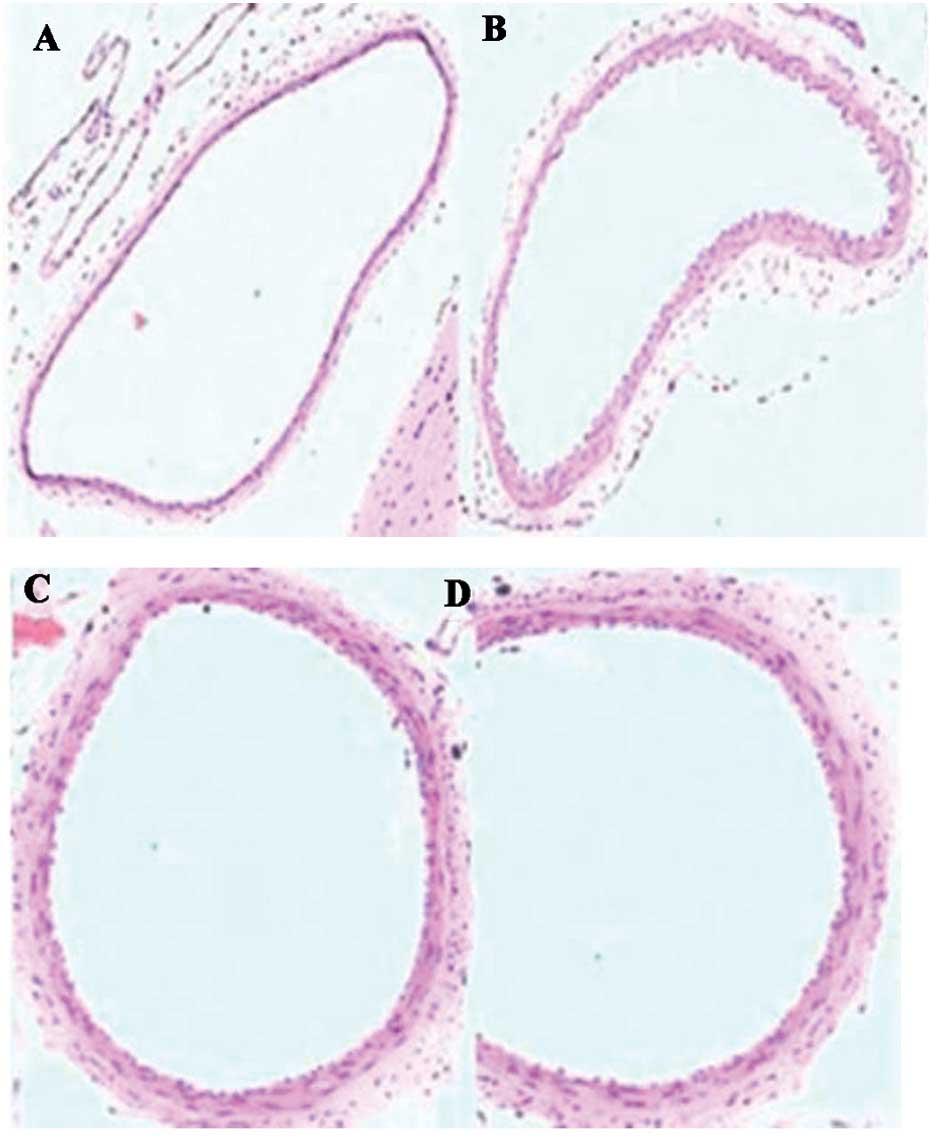
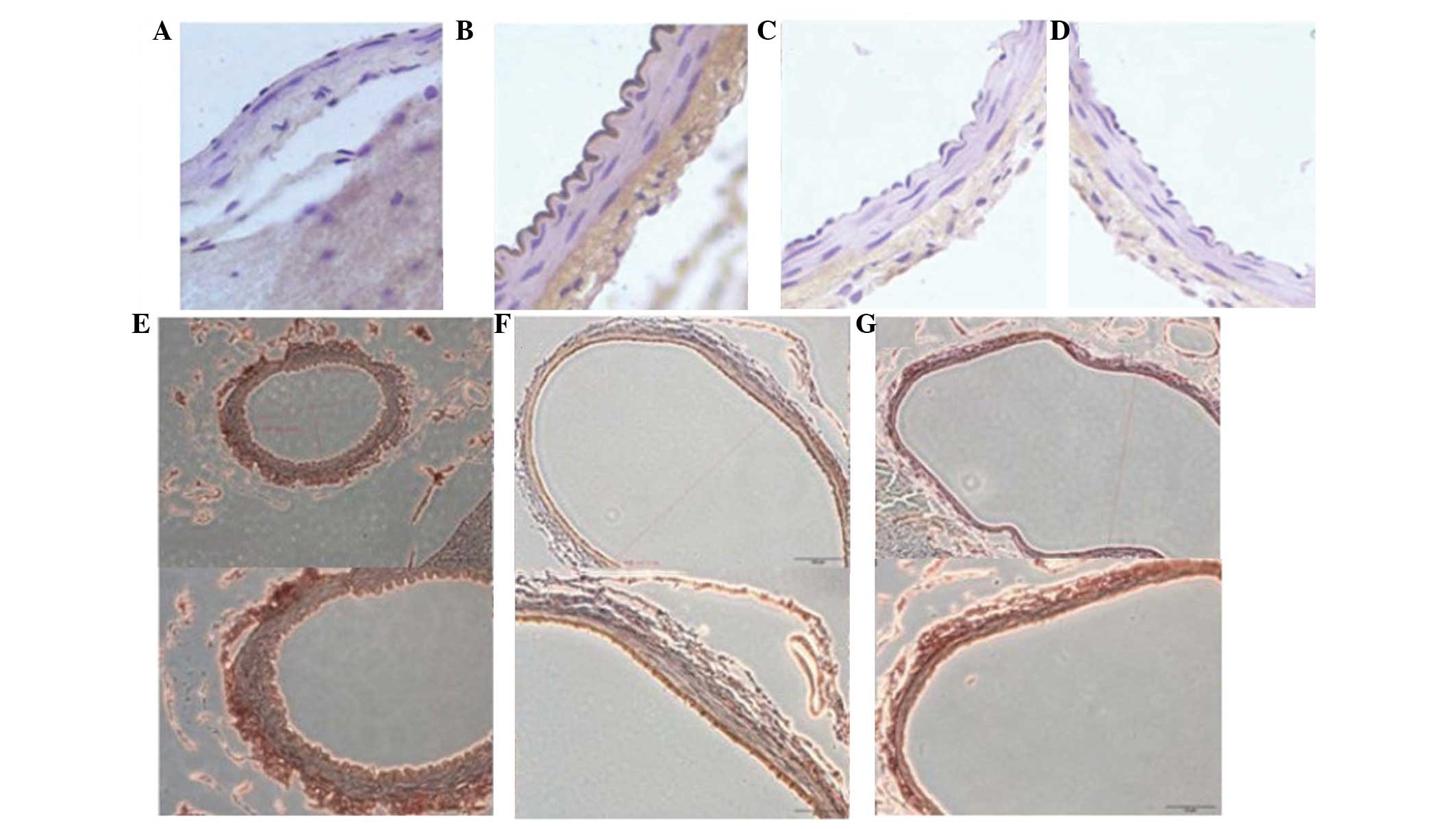
|
1
|
Kerz T, Victor A, Beyer C, Trapp I, Heid F
and Reisch R: A case control study of statin and magnesium
administration in patients after aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage: Incidence of delayed cerebral ischemia and mortality.
Neurol Res. 30:893–897. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Suzuki H, Kanamaru K, Shiba M, Fujimoto M,
Kawakita F, Imanaka-Yoshida K, Yoshida T and Taki W: Tenascin-C is
a possible mediator between initial brain injury and
vasospasm-related and -unrelated delayed cerebral ischemia after
aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl.
120:117–121. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
da Costa L, Fisher J, Mikulis DJ,
Tymianski M and Fierstra J: Early identification of brain tissue at
risk for delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 120:105–109. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hirashima Y, Endo S, Kato R and Takaku A:
Prevention of cerebrovasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage in
rabbits by the platelet-activating factor antagonist, E5880. J
Neurosurg. 84:826–830. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dumont AS, Dumont RJ, Chow MM, Lin CL,
Calisaneller T, Ley KF, Kassell NF and Lee KS: Cerebral vasospasm
after subarachnoid hemorrhage: putative role of inflammation.
Neurosurgery. 53:123–133; discussion 133–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin CL, Dumont AS, Calisaneller T, Kwan
AL, Hwong SL and Lee KS: Monoclonal antibody against E selectin
attenuates subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced cerebral vasospasm. Surg
Neurol. 64:201–205; discussion 205–206. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim E, Kim HC, Park SY, Lim YJ, Ro SH, Cho
WS, Jeon YT, Hwang JW and Park HP: Effect of red blood cell
transfusion on unfavorable neurological outcome and symptomatic
vasospasm in patients with cerebral aneurysmal rupture: Old versus
fresh blood. World Neurosurg. Aug 28–2015.(Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
8
|
Nickele C, Muro K, Getch CC, Walker MT and
Bernstein RA: Severe reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome
mimicking aneurysmal rupture and vasospasm. Neurocrit Care.
7:81–85. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Salunke P, Patra DP and Mukherjee KK:
Delayed cerebral vasospasm and systemic inflammatory response
syndrome following intraoperative rupture of cerebral hydatid cyst.
Acta Neurochir (Wien). 156:613–614. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li W, Zheng T, Altura BT and Altura BM:
Antioxidants prevent elevation in [Ca(2+)](i) induced by low
extracellular magnesium in cultured canine cerebral vascular smooth
muscle cells: Possible relationship to Mg(2+) deficiency-induced
vasospasm and stroke. Brain Res Bull. 52:151–154. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heffren J, McIntosh AM and Reiter PD:
Nimodipine for the prevention of cerebral vasospasm after
subarachnoid hemorrhage in 12 children. Pediatr Neurol. 52:356–360.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Munakata A, Ohkuma H and Shimamura N:
Effect of a free radical scavenger, edaravone, on free radical
reactions: Related signal transduction and cerebral vasospasm in
the rabbit subarachnoid hemorrhage model. Acta Neurochir Suppl.
110:17–22. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nishziawa S: Roles of signal transduction
mechanisms in cerebral vasospasm following subarachnoid hemorrhage:
Overview. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 110:27–30. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zubkov AY, Nanda A and Zhang JH: Signal
transduction pathways in cerebral vasospasm. Pathophysiology.
9:47–61. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jośko J, Hendryk S, Jedrzejowska-Szypułka
H, Słowiński J, Gwóźdź B, Lange D, Snietura M, Zwirska-Korczala K
and Jochem J: Cerebral angiogenesis after subarachnoid hemorrhage
(SAH) and endothelin receptor blockage with BQ-123 antagonist in
rats. J Physiol Pharmacol. 52:237–248. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou ML, Zhu L, Wang J, Hang CH and Shi
JX: The inflammation in the gut after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage. J Surg Res. 137:103–108. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sarrafzadeh A, Copin JC, Bengualid DJ,
Turck N, Vajkoczy P, Bijlenga P, Schaller K and Gasche Y: Matrix
metalloproteinase-9 concentration in the cerebral extracellular
fluid of patients during the acute phase of aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Neurol Res. 34:455–461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Martin R, Hoeth M, Hofer-Warbinek R and
Schmid JA: The transcription factor NF-kappa B and the regulation
of vascular cell function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
20:E83–E88. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Song YS, Lee YS and Chan PH: Oxidative
stress transiently decreases the IKK complex (IKKalpha, beta, and
gamma), an upstream component of NF-kappaB signaling, after
transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 25:1301–1311. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang CY, Fujimura M, Noshita N, Chang YY
and Chan PH: SOD1 down-regulates NF-kappaB and c-Myc expression in
mice after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 21:163–173. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu W, Guan Y, Zhao G, Fu XJ, Guo TZ, Liu
YT, Ren XL, Wang W, Liu HR and Li YQ: Elevated IL-6 and TNF-α
levels in cerebrospinal fluid of subarachnoid hemorrhage patients.
Mol Neurobiol. Jun 11–2015.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Young AM, Karri SK, You W and Ogilvy CS:
Specific TNF-alpha inhibition in cerebral aneurysm formation and
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Curr Drug Saf. 7:190–196. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hanafy KA, Grobelny B, Fernandez L, Kurtz
P, Connolly ES, Mayer SA, Schindler C and Badjatia N: Brain
interstitial fluid TNF-alpha after subarachnoid hemorrhage. J
Neurol Sci. 291:69–73. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pinchuk TV, Fedulaev YN, Khairetdinova GA,
Denisova NN, Chura OV and Logunova IY: Anti-inflammatory effects of
simvastatin in patients with chronic heart failure. Bull Exp Biol
Med. 157:552–554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun M, Zhao Y, Gu Y and Xu C:
Anti-inflammatory mechanism of taurine against ischemic stroke is
related to down-regulation of PARP and NF-κB. Amino Acids.
42:1735–1747. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Seiyama A, Yoshikawa N and Imamura Y:
Ischemic pretreatment delays ischemic brain vasospasm injury in
gerbils. Adv Exp Med Biol. 812:247–252. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang H, Zhang B and Li S, Liang C, Xu K
and Li S: Whole brain CT perfusion combined with CT angiography in
patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage and cerebral vasospasm. Clin
Neurol Neurosurg. 115:2496–2501. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Suarez JI, Tarr RW and Selman WR:
Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 354:387–396.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Miyazaki T and Matsuzaki Y: Taurine and
liver diseases: A focus on the heterogeneous protective properties
of taurine. Amino Acids. 46:101–110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Juvela S: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory
drugs as risk factors for spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage and
aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 34:e34–e36. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Joo K, Lee Y, Choi D, Han J, Hong S, Kim
YM and Jung Y: An anti-inflammatory mechanism of taurine conjugated
5-aminosalicylic acid against experimental colitis: Taurine
chloramine potentiates inhibitory effect of 5-aminosalicylic acid
on IL-1beta-mediated NFkappaB activation. Eur J Pharmacol.
618:91–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Marcinkiewicz J, Kurnyta M, Biedroń R,
Bobek M, Kontny E and Maśliński W: Anti-inflammatory effects of
taurine derivatives (taurine chloramine, taurine bromamine, and
taurolidine) are mediated by different mechanisms. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 583:481–492. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Quinn MR, Barua M, Liu Y and Serban V:
Taurine chloramine inhibits production of inflammatory mediators
and iNOS gene expression in alveolar macrophages; a tale of two
pathways: Part I, NF-kappaB signaling. Adv Exp Med Biol.
526:341–348. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Buechler C, Ullrich H, Aslanidis C, Bared
SM, Lingenhel A, Ritter M and Schmitz G: Lipoprotein (a)
downregulates lysosomal acid lipase and induces interleukin-6 in
human blood monocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1642:25–31. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Coppack SW: Pro-inflammatory cytokines and
adipose tissue. Proc Nutr Soc. 60:349–356. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF,
Atkinson RL and Spiegelman BM: Increased adipose tissue expression
of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin
resistance. J Clin Invest. 95:2409–2415. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Asahi M, Huang Z, Thomas S, Yoshimura S,
Sumii T, Mori T, Qiu J, Amin-Hanjani S, Huang PL, Liao JK, et al:
Protective effects of statins involving both eNOS and tPA in focal
cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 25:722–729. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kramer AH: Statins in the management of
aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: An overview of animal research,
observational studies, randomized controlled trials and
meta-analyses. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 110:193–201. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sabri M and Macdonald RL: Statins: A
potential therapeutic addition to treatment for aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage? World Neurosurg. 73:646–653. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rasmussen LM, Hansen PR, Nabipour MT,
Olesen P, Kristiansen MT and Ledet T: Diverse effects of inhibition
of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase on the expression of
VCAM-1 and E-selectin in endothelial cells. Biochem J. 360:363–370.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zelvyte I, Dominaitiene R, Crisby M and
Janciauskiene S: Modulation of inflammatory mediators and PPARgamma
and NFkappaB expression by pravastatin in response to lipoproteins
in human monocytes in vitro. Pharmacol Res. 45:147–154. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kaji H, Kanatani M, Sugimoto T and Chihara
K: Statins modulate the levels of osteoprotegerin/receptor
activator of NFkappaB ligand mRNA in mouse bone-cell cultures. Horm
Metab Res. 37:589–592. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ahn KS, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB: Reversal
of chemoresistance and enhancement of apoptosis by statins through
down-regulation of the NF-kappaB pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
75:907–913. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|