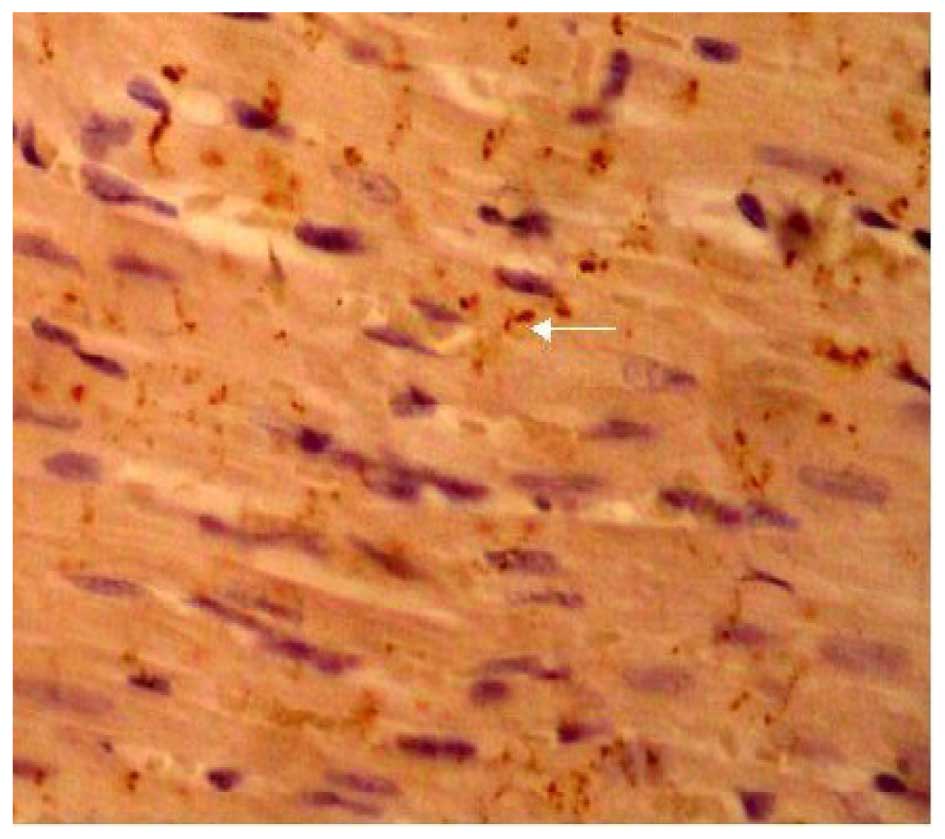
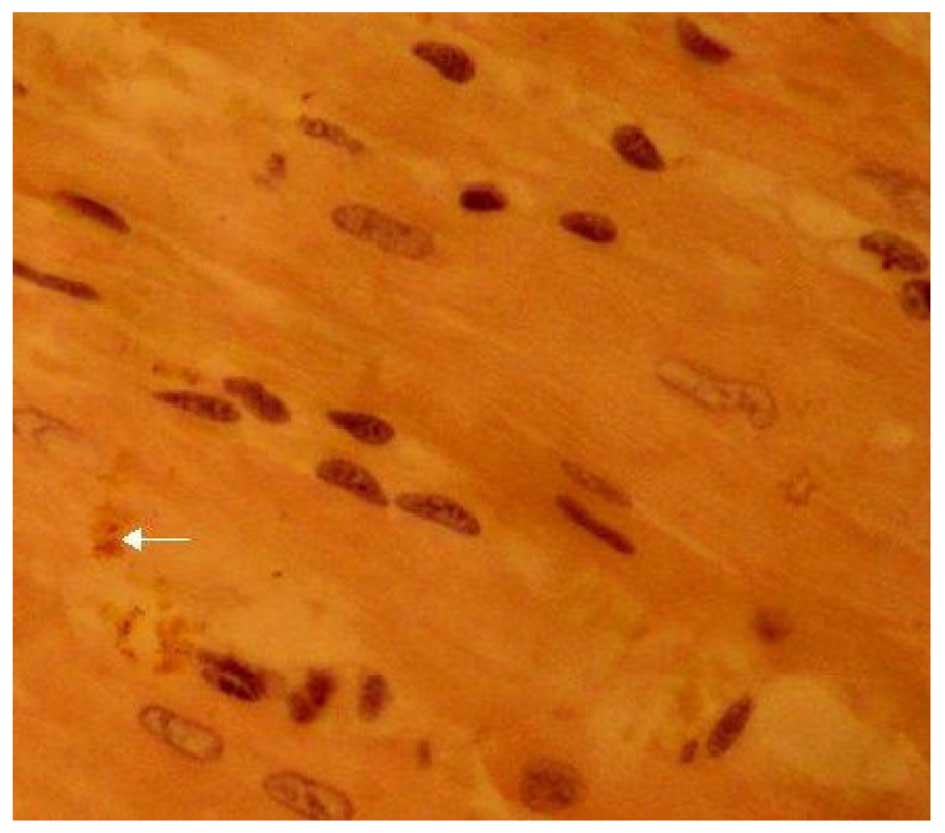
|
1
|
Sun R, Zhang D, Zhang J, Feng Q, Zhang Y,
Zhao C and Zhang W: Different effects of lysophosphatidic acid on
L-type calcium current in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes with
and without H2O2 treatment. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
118(119): 1–10. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharain K, Vasile VC and Jaffe AS: Does
cardiac rhythm monitoring in patients with elevated troponin levels
lead to changes in management. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care.
Jan 27–2016.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aaltonen N, Laitinen JT and Lehtonen M:
Quantification of lysophosphatidic acids in rat brain tissue by
liquid chromatography-electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J
Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 878:1145–1152. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei Y, Zhao LQ, Qi BZ, Xiao X, He L, Zhou
GQ, Chen SW, Li HL, Ruan L, Zhang CT and Liu SW: Lysophosphatidic
acid increases the electrophysiological instability of adult rabbit
ventricular myocardium by augmenting L-type calcium current. PLoS
One. 7:e458622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim Do Y, Song HJ, Jeong JH, Suh JS and
Sohn UD: Regulation of lysophosphatidic acid-induced COX-2
expression by ERK1/2 activation in cultured feline esophageal
epithelial cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:1331–1338. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Latet SC, Hoymans VY, Van Herck PL and
Vrints CJ: The cellular immune system in the post-myocardial
infarction repair process. Int J Cardiol. 179:240–247. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Laskarin G, Zaputovic L, Persic V, Ruzic A
and Tokmadzic Sotosek V: Harmful immune reactions during acute
myocardial infarction. Med Hypotheses. 78:703–706. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hansson GK: Inflammatory mechanisms in
atherosclerosis. J Thromb Haemostasis. 7(Suppl 1): 328–331. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hansson GK, Robertson AK and
Söderberg-Nauclér C: Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Ann Rev
Pathol. 1:297–329. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lin CC, Lin CE, Lin YC, Ju TK, Huang YL,
Lee MS, Chen JH and Lee H: Lysophosphatidic acid induces reactive
oxygen species generation by activating protein kinase C in PC-3
human prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
440:564–569. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chang CL, Lin ME, Hsu HY, Yao CL, Hwang
SM, Pan CY, Hsu CY and Lee H: Lysophosphatidic acid-induced
interleukin-1 beta expression is mediated through Gi/Rho and the
generation of reactive oxygen species in macrophages. J Biomed Sci.
15:357–363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karliner JS: Lysophospholipids and the
cardiovascular system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1582:216–221. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources
(US). Committee on Care, Use of Laboratory Animals, and National
Institutes of Health (US). Division of Research Resources: Guide
for the care and use of laboratory animals (8th). National
Academies Press. (Washington, DC). 2011.
|
|
14
|
Bocksteins E, Raes AL, Van de Vijver G,
Bruyns T, Van Bogaert PP and Snyders DJ: Kv2.1 and silent Kv
subunits underlie the delayed rectifier K+ current in
cultured small mouse DRG neurons. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
296:C1271–C1278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moreno C, Prieto P, Macías A,
Pimentel-Santillana M, de la Cruz A, Través PG, Boscá L and
Valenzuela C: Modulation of Voltage-Dependent and Inward Rectifier
Potassium Channels by 15-Epi-Lipoxin-A4 in Activated Murine
Macrophages: Implications in Innate Immunity. J Immunol.
191:6136–6146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakasaki T, Tanaka T, Okudaira S, Hirosawa
M, Umemoto E, Otani K, Jin S, Bai Z, Hayasaka H, Fukui Y, et al:
Involvement of the lysophosphatidic acid-generating enzyme
autotaxin in lymphocyte-endothelial cell interactions. Am J Pathol.
173:1566–1576. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng HY, Dong A, Panchatcharam M, Mueller
P, Yang F, Li Z, Mills G, Chun J, Morris AJ and Smyth SS:
Lysophosphatidic acid signaling protects pulmonary vasculature from
hypoxia-induced remodeling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
32:24–32. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pamuklar Z, Lee JS, Cheng HY,
Panchatcharam M, Steinhubl S, Morris AJ, Charnigo R and Smyth SS:
Individual heterogeneity in platelet response to lysophosphatidic
acid: Evidence for a novel inhibitory pathway. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 28:555–561. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kempf K, Haltern G, Füth R, Herder C,
Müller-Scholze S, Gülker H and Martin S: Increased TNF-alpha and
decreased TGF-beta expression in peripheral blood leukocytes after
acute myocardial infarction. Horm Metab Res. 38:346–351. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie Y, Gibbs TC and Meier KE:
Lysophosphatidic acid as an autocrine and paracrine mediator.
Biochim Biophysiolo Acta. 1582:270–281. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Okudaira S, Yukiura H and Aoki J:
Biological roles of lysophosphatidic acid signaling through its
production by autotaxin. Biochimie. 92:698–706. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Putko BN, Wang Z, Lo J, Anderson T, Becher
H, Dyck JR, Kassiri Z and Oudit GY: Alberta HEART Investigators:
Circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor 2 are
increased in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction
relative to heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Evidence
for a divergence in pathophysiology. PLoS One. 9:e994952014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Meilleur MA, Akpovi CD, Pelletier RM and
Vitale ML: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced anterior pituitary
folliculostellate TtT/GF cell uncoupling is mediated by connexin 43
dephosphorylation. Endocrinology. 148:5913–5924. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Blancke F, Claeys MJ, Jorens P, Vermeiren
G, Bosmans J, Wuyts FL and Vrints CJ: Systemic inflammation and
reperfusion injury in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Mediators Inflamm. 2005:385–389. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moreira DM, da Silva RL, Vieira JL, Fattah
T, Lueneberg ME and Gottschall CA: Role of vascular inflammation in
coronary artery disease: Potential of anti-inflammatory drugs in
the prevention of atherothrombosis. Inflammation and
anti-inflammatory drugs in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiovasc
Drugs. 15:1–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wit AL and Duffy HS: Drug development for
treatment of cardiac arrhythmias: Targeting the gap junctions. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 294:H16–H18. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Y, Zhang Q, Liao YH, Cao Z, Du YM,
Xia JD, Yang H and Chen ZJ: Effect of tumor necrosis factor-α on
neutralization of ventricular fibrillation in rats with acute
myocardial infarction. Mediators Inflamm. 2011:5652382011.
|
|
28
|
Chang WT, Wang YC, Chen CC, Zhang SK, Liu
CH, Chang FH and Hsu LS: The −308G/A of tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-α and 825C/T of guanidine nucleotide binding protein 3 (GNB3)
are associated with the onset of acute myocardial infarction and
obesity in Taiwan. Int J Mol Sci. 13:1846–1857. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Petkova-Kirova PS, London B, Salama G,
Rasmusson RL and Bondarenko VE: Mathematical modeling mechanisms of
arrhythmias in transgenic mouse heart overexpressing TNF-α. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302:H934–H952. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lawrence MC, Naziruddin B, Levy MF,
Jackson A and McGlynn K: Calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T
cells and MAPK signaling induce TNF-{alpha} gene expression in
pancreatic islet endocrine cells. J Biol Chem. 286:1025–1036. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kazama I, Tamada T and Tachi M: Usefulness
of targeting lymphocyte Kv1.3-channels in the treatment of
respiratory diseases. Inflamma Res. 64:753–765. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kazama I: Physiological significance of
delayed rectifier K+ channels (Kv1.3) expressed in T
lymphocytes and their pathological significance in chronic kidney
disease. J Physiol Sci. 65:25–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Csordás G, Thomas AP and Hajnóczky G:
Calcium signal transmission between ryanodine receptors and
mitochondria in cardiac muscle. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 11:269–275.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vinogradova TM, Lyashkov AE, Zhu W,
Ruknudin AM, Sirenko S, Yang D, Deo S, Barlow M, Johnson S, Caffrey
JL, et al: High basal protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation
drives rhythmic internal Ca2+ store oscillations and
spontaneous beating of cardiac pacemaker cells. Circulation Res.
98:505–514. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hirata N, Kanaya N, Kamada N, Kimura S and
Namiki A: Differential effects of propofol and sevoflurane on
ischemia-induced ventricular arrhythmias and phosphorylated
connexin 43 protein in rats. Anesthesiology. 110:50–57. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dhein S, Polontehouk L, Salameh A and
Haefliger JA: Pharmacological modulation and differential
regulation of the cardiac gap junction proteins connexin 43 and
connexin 40. Biol Cell. 94:409–422. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
De Vuyst E, Decrock E, De Bock M, Yamasaki
H, Naus CC, Evans WH and Leybaert L: Connexin hemichannels and gap
junction channels are differentially influenced by
lipopolysaccharide and basic fibroblast growth factor. Mol Biol
Cell. 18:34–46. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nielsen MS, Axelsen LN, Sorgen PL, Verma
V, Delmar M and Holstein-Rathlou NH: Gap junctions. Compr Physiol.
2:1981–2035. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Palatinus JA, Rhett JM and Gourdie RG: The
connexin 43 carboxyl terminus and cardiac gap junction
organization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1818:1831–1843. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gendaszewska-Darmach E: Lysophosphatidic
acids, cyclic phosphatidic acids and autotaxin as promising targets
in therapies of cancer and other diseases. Acta Biochim Pol.
55:227–240. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chan LC, Peters W, Xu Y, Chun J, Farese RV
Jr and Cases S: LPA3 receptor mediates chemotaxis of immature
murine dendritic cells to unsaturated lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).
J Leukoc Biol. 82:1193–1200. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|