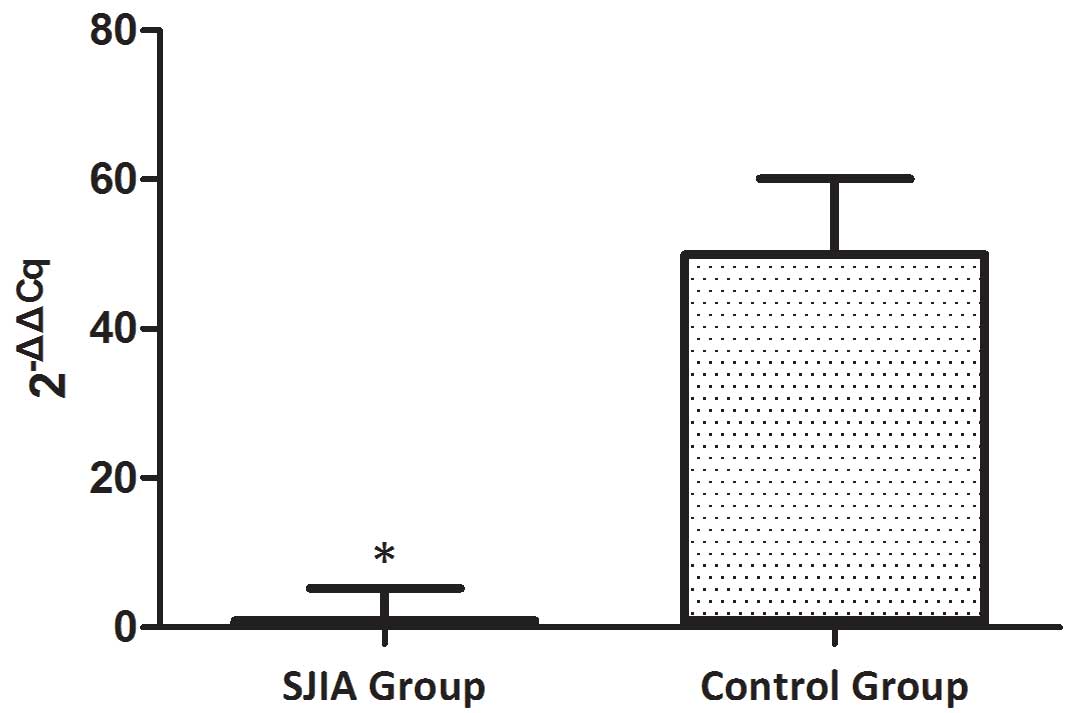
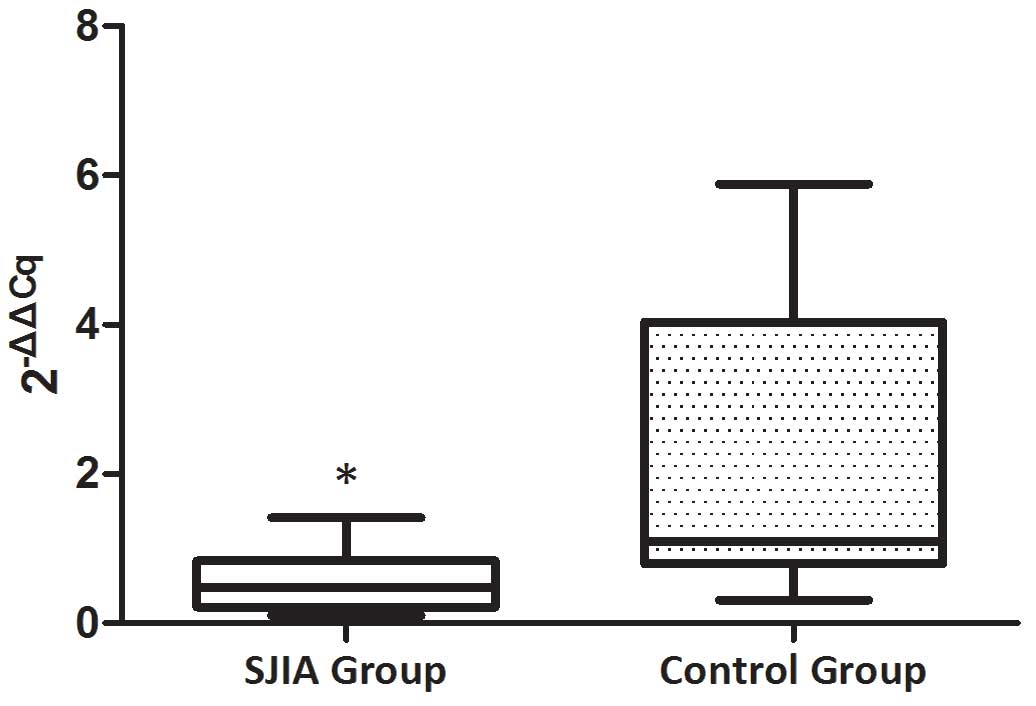
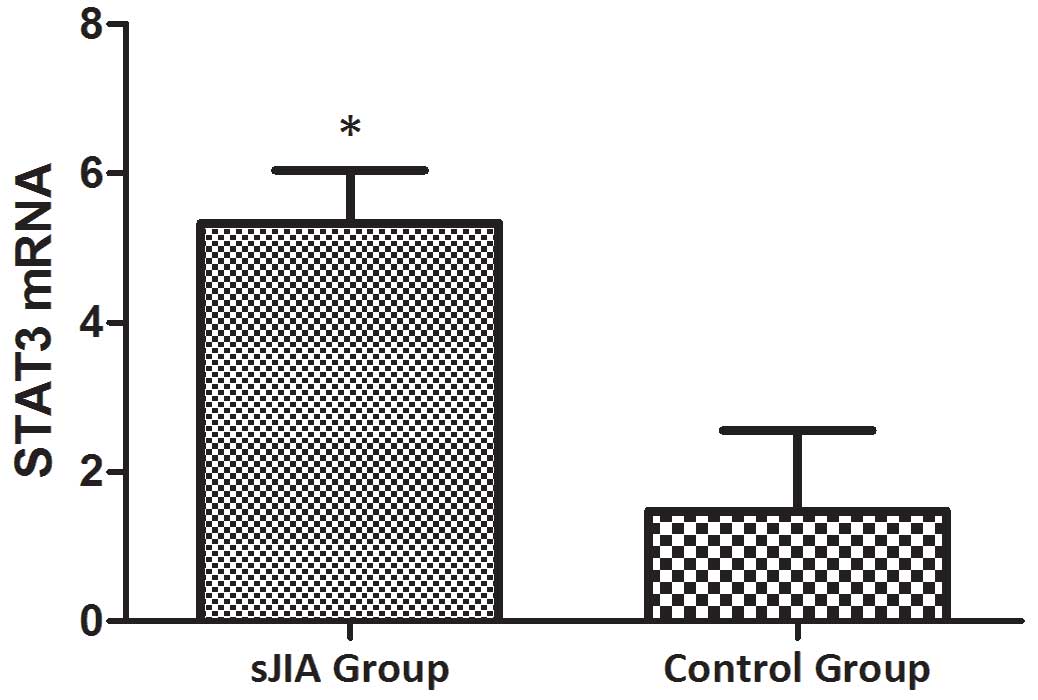
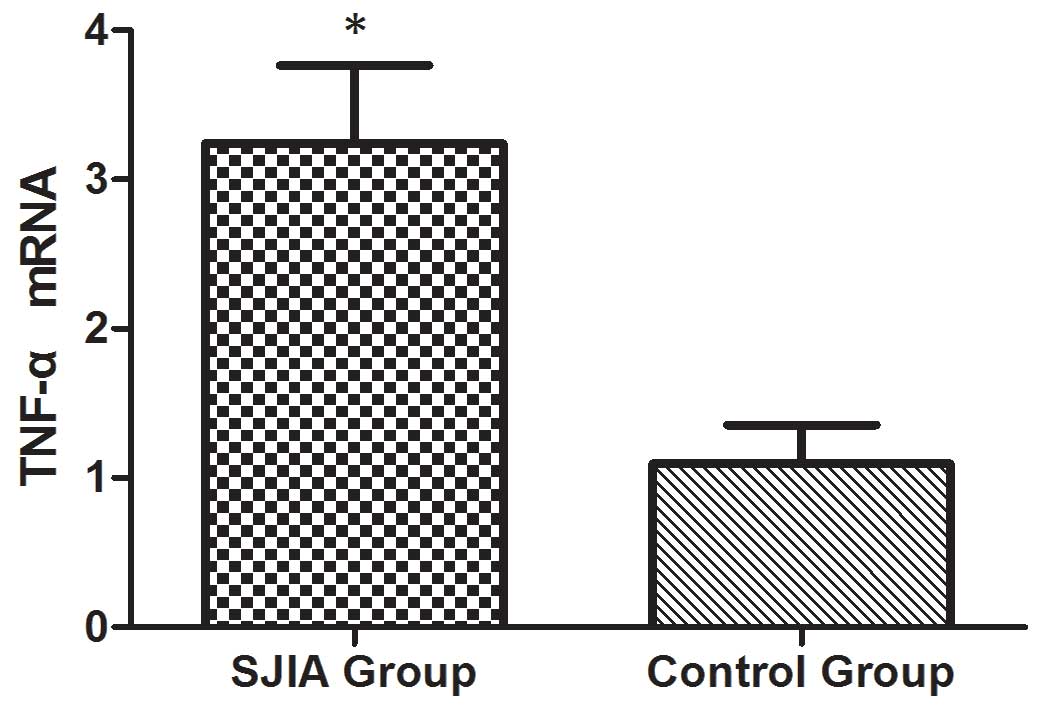
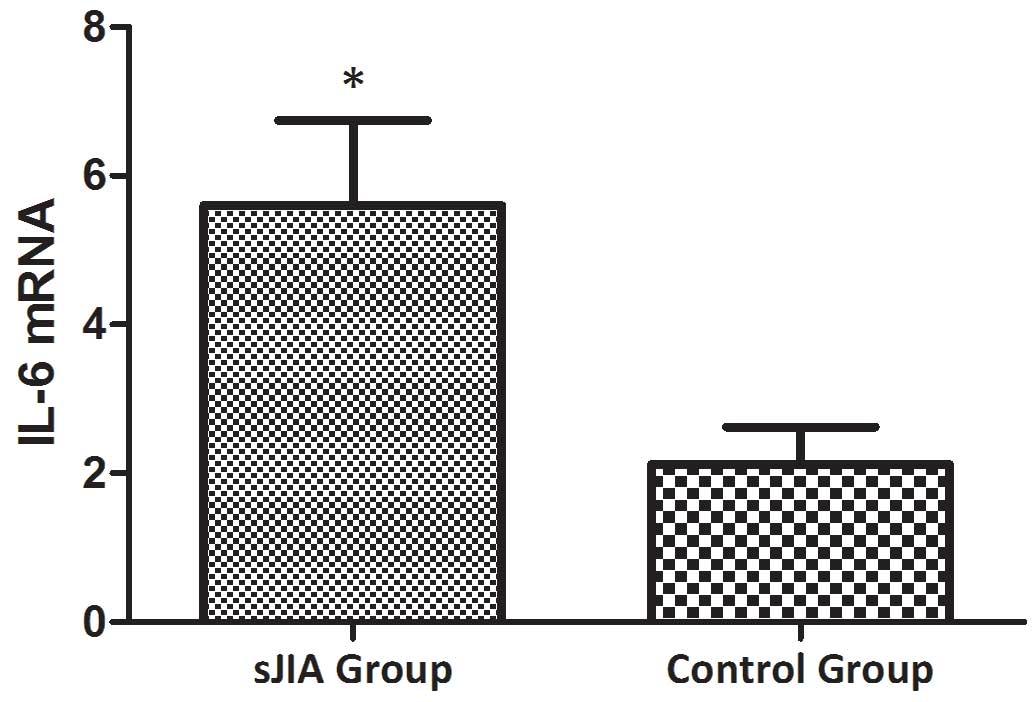
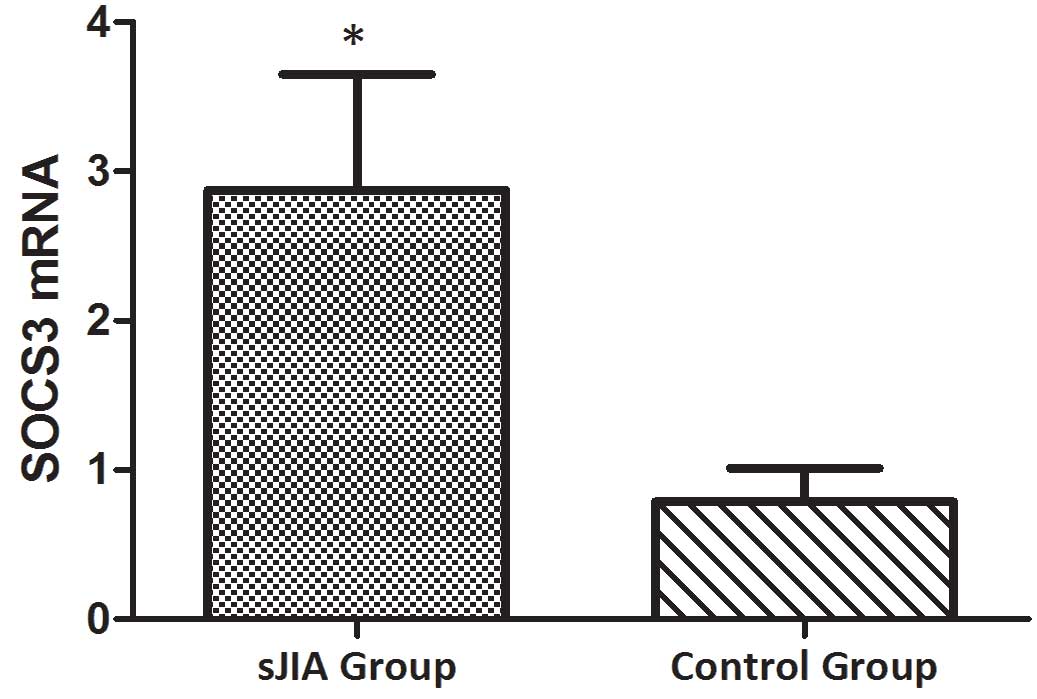
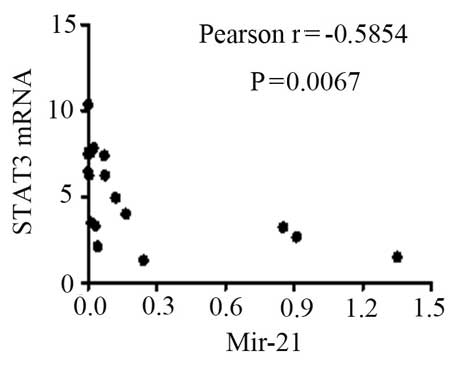
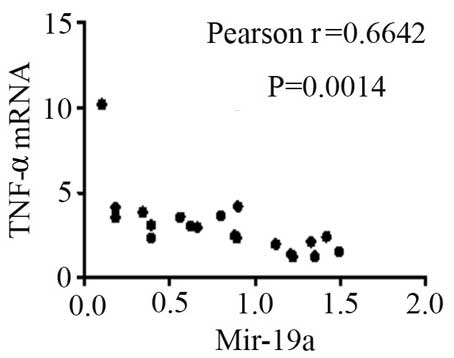
|
1
|
Beukelman T: Treatment advances in
systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. F1000Prime Rep. 6:212014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roderburg C and Luedde T: Circulating
microRNAs as markers of liver inflammation, fibrosis and cancer. J
Hepatol. 61:1434–1437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kemper AR, Van Mater HA, Coeytaux RR,
Williams JW Jr and Sanders GD: Systematic review of
disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for juvenile idiopathic
arthritis. BMC Pediatr. 12:292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tian TJ, Wang J and Zhou X: A review:
microRNA detection methods. Org Biomol Chem. 13:2226–2238. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Alivernini S,
Ballantine LE, Asquith DL, Millar NL, Gilchrist DS, Reilly J, Ierna
M, Fraser AR, Stolarski B, et al: MicroRNA-155 as a proinflammatory
regulator in clinical and experimental arthritis. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 108:11193–11198. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou Q, Haupt S, Kreuzer JT, Hammitzsch A,
Proft F, Neumann C, Leipe J, Witt M, Schulze-Koops H and Skapenko
A: Decreased expression of miR-146a and miR-155 contributes to an
abnormal Treg phenotype in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann
Rheum Dis. 74:1265–1274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xie Q, Wang SC, Zhong J and Li J:
MicroRNA-146a, a good biomarker and potential therapeutic target
for rheumatoid arthritis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 17:91–92.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Long L, Yu P, Liu Y, Wang S, Li R, Shi J,
Zhang X, Li Y, Sun X, Zhou B, et al: Upregulated microRNA-155
expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and
fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Dev
Immunol. 2013:2961392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen SY: MicroRNA-223: A double-edged
sword in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 34:285–286. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dong L, Wang X, Tan J, Li H, Qian W, Chen
J, Chen Q, Wang J, Xu W, Tao C and Wang S: Decreased expression of
microRNA-21 correlates with the imbalance of Th17 and Treg cells in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2213–2224.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shibuya H, Nakasa T, Adachi N, Nagata Y,
Ishikawa M, Deie M, Suzuki O and Ochi M: Overexpression of
microRNA-223 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium controls osteoclast
differentiation. Mod Rheumatol. 23:674–685. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng ZT, Li J, Ren J and Lv Z: Expression
of miR-146a and miR-16 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of
patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their correlation to the
disease activity. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 31:320–323.
2011.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stanczyk J, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Filer
A, Raza K, Kolling C, Gay R, Buckley CD, Tak PP, Gay S and Kyburz
D: Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis
synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation.
Arthritis Rheum. 63:373–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu S, Pan W, Song X, Liu Y, Shao X, Tang
Y, Liang D, He D, Wang H, Liu W, et al: The microRNA miR-23b
suppresses IL-17-associated autoimmune inflammation by targeting
TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-α. Nat Med. 18:1077–1086. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
ILAR 2001. Abstracts of the 20th Congress
of the International League of Associations for Rheumatology.
Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. August 26–30, 2001. J Rheumatol Suppll.
63:1–120. 2001.
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao W, Dong Y, Wu C, Ma Y, Jin Y and Ji
Y: MiR-21 overexpression improves osteoporosis by targeting RECK.
Mol Cell Biochem. 405:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sasi W, Sharma AK and Mokbel K: The role
of suppressors of cytokine signalling in human neoplasms. Mol Biol
Int. 2014:6307972014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ju JH, Heo YJ, Cho ML, Jhun JY, Park JS,
Lee SY, Oh HJ, Moon SJ, Kwok SK, Park KS, et al: Modulation of
STAT3 in rheumatoid synovial T cells suppresses Th17
differentiation and increases the proportion of Treg cells.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:3543–3552. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Garbers C, Aparicio-Siegmund S and
Rose-John S: The IL-6/gp130/STAT3 signaling axis: Recent advances
towards specific inhibition. Curr Opin Immunol. 34:75–82. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kotake S, Udagawa N, Takahashi N,
Matsuzaki K, Itoh K, Ishiyama S, Saito S, Inoue K, Kamatani N,
Gillespie MT, et al: IL-17 in synovial fluids from patients with
rheumatoid arthritis is a potent stimulator of osteoclastogenesis.
J Clin Invest. 103:1345–1352. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sawant DV, Wu H, Kaplan MH and Dent AL:
The Bcl6 target gene microRNA-21 promotes Th2 differentiation by a
T cell intrinsic pathway. Mol Immunol. 54:435–442. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu TX, Hartner J, Lim EJ, Fabry V, Mingler
MK, Cole ET, Orkin SH, Aronow BJ and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA-21
limits in vivo immune response-mediated activation of the
IL-12/IFN-gamma pathway, Th1 polarization and the severity of
delayed-type hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 187:3362–3373. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iliopoulos D, Jaeger SA, Hirsch HA, Bulyk
ML and Struhl K: STAT3 activation of miR-21 and miR-181b-1 via PTEN
and CYLD are part of the epigenetic switch linking inflammation to
cancer. Mol Cell. 39:493–506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Park HK, Jo W, Choi HJ, Jang S, Ryu JE,
Lee HJ, Lee H, Kim H, Yu ES and Son WC: Time-course changes in the
expression levels of miR-122, −155, and −21 as markers of liver
cell damage, inflammation, and regeneration in
acetaminophen-induced liver injury in rats. J Vet Sci. 4:64–71.
2015.
|
|
26
|
Peacock O, Lee AC, Cameron F, Tarbox R,
Vafadar-Isfahani N, Tufarelli C and Lund JN: Inflammation and
MiR-21 pathways functionally interact to downregulate PDCD4 in
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1102672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang YY, Sun G, Luo H, Wang XF, Lan FM,
Yue X, Fu LS, Pu PY, Kang CS, Liu N and You YP: MiR-21 modulates
hTERT through a STAT3-dependent manner on glioblastoma cell growth.
CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:722–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Collins AS, McCoy CE, Lloyd AT, O'Farrelly
C and Stevenson NJ: miR-19a: An effective regulator of SOCS3 and
enhancer of JAK-STAT signalling. PLoS One. 8:e690902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin S, Ai F, Ji WF, Rao W, Zhang HC and
Yao WJ: miR-19a promotes cell growth and tumorigenesis through
targeting SOCS1 in gastric cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:835–840. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Philippe L, Alsaleh G, Suffert G, Meyer A,
Georgel P, Sibilia J, Wachsmann D and Pfeffer S: TLR2 expression is
regulated by MicroRNA miR-19 in rheumatoid fibroblast-like
synoviocytes. J Immunol. 188:454–461. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gantier MP, Stunden HJ, McCoy CE, Behlke
MA, Wang D, Kaparakis-Liaskos M, Sarvestani ST, Yang YH, Xu D, Corr
SC, et al: A miR-19 regulon that controls NF-kB signaling. Nucleic
Acids Res. 40:8048–8058. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen B, She S, Li D, Liu Z, Yang X, Zeng Z
and Liu F: Role of miR-19a targeting TNF-α in mediating ulcerative
colitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 48:815–824. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou P, Chen B, Hu P and Sun Y: Role of
miR-19a in ulcerative colitis in mice. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue
Bao. 33:1325–1328. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR,
Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Notebook J, O'Brian
KC, et al: Circulating microRNAs as stableblood-based markers for
cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10513–10518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|