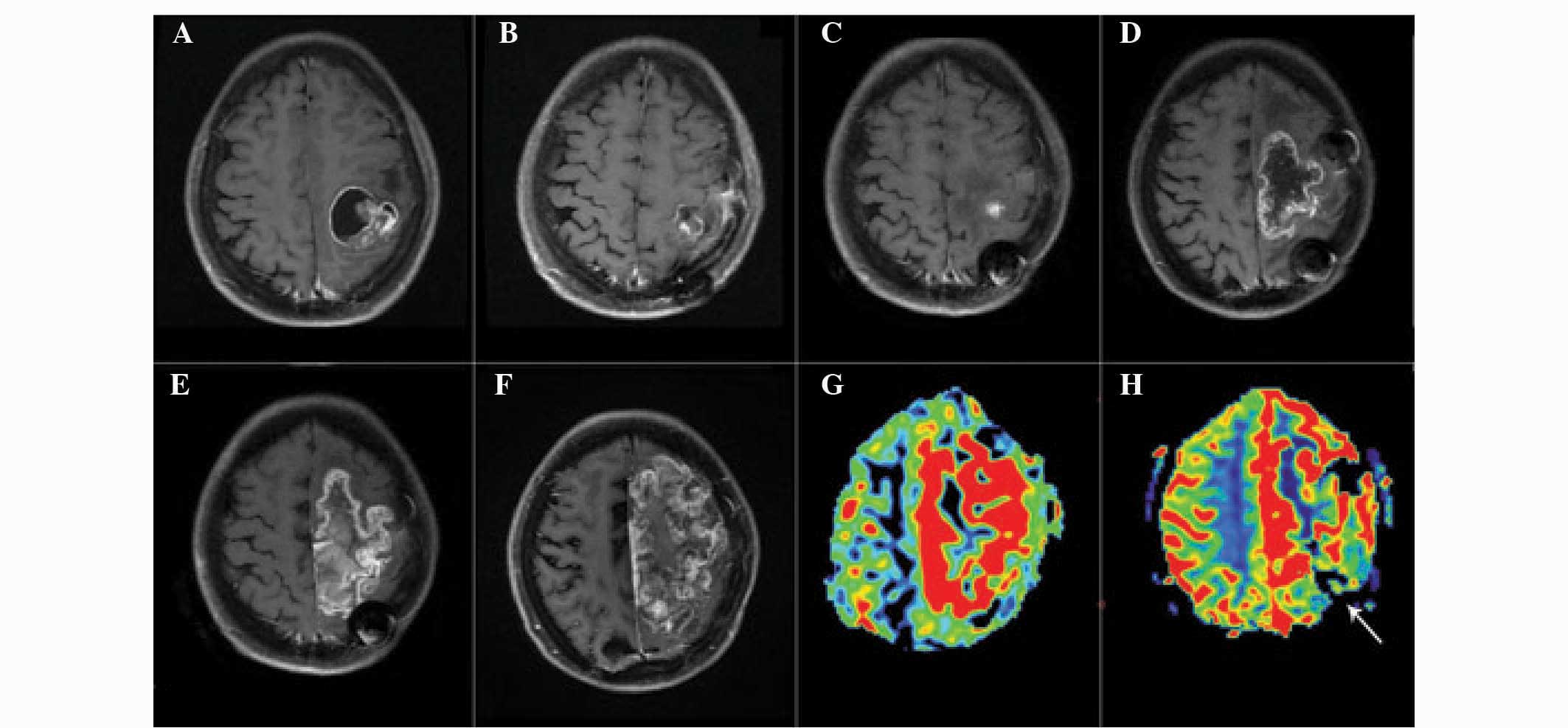
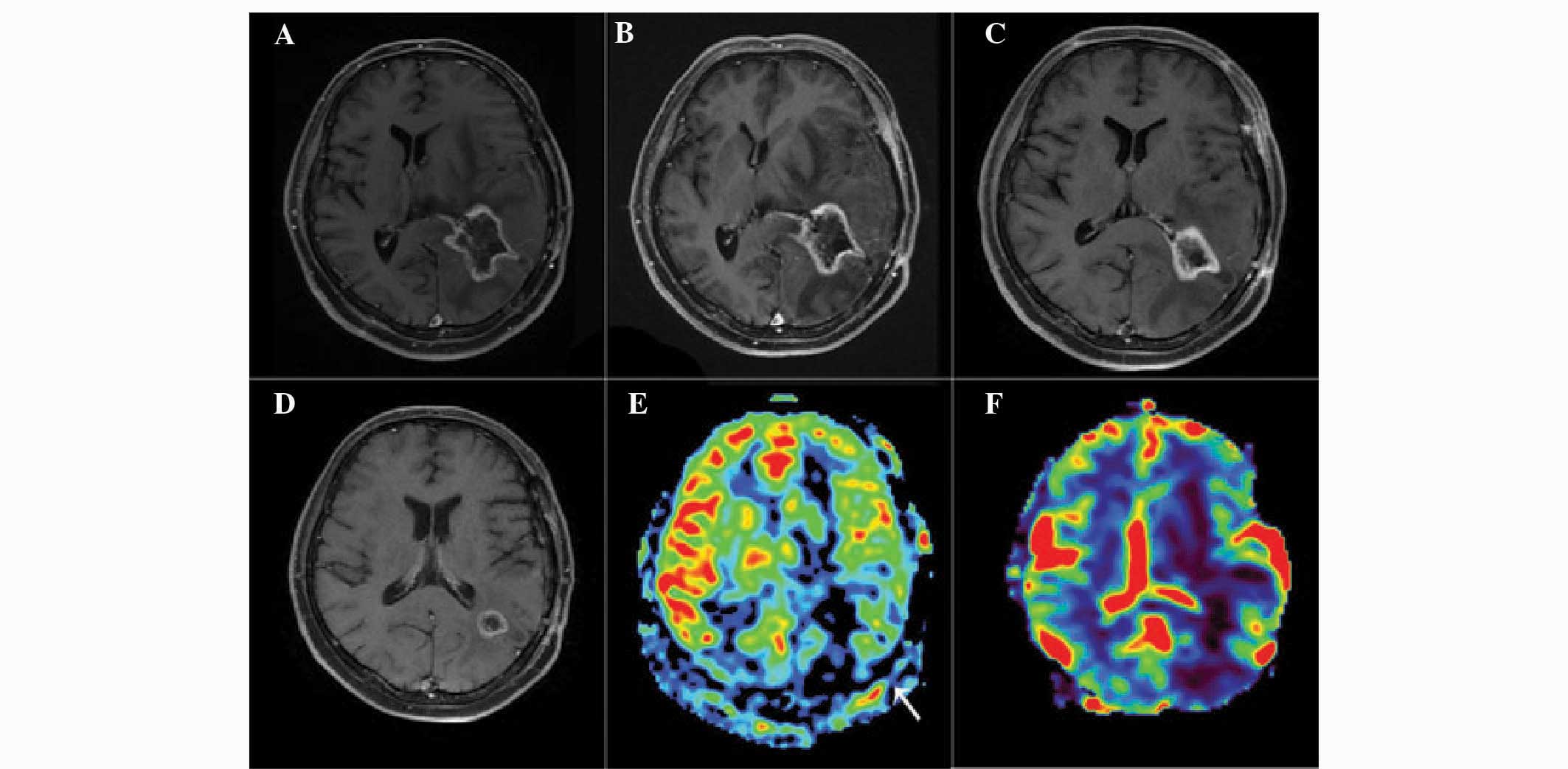
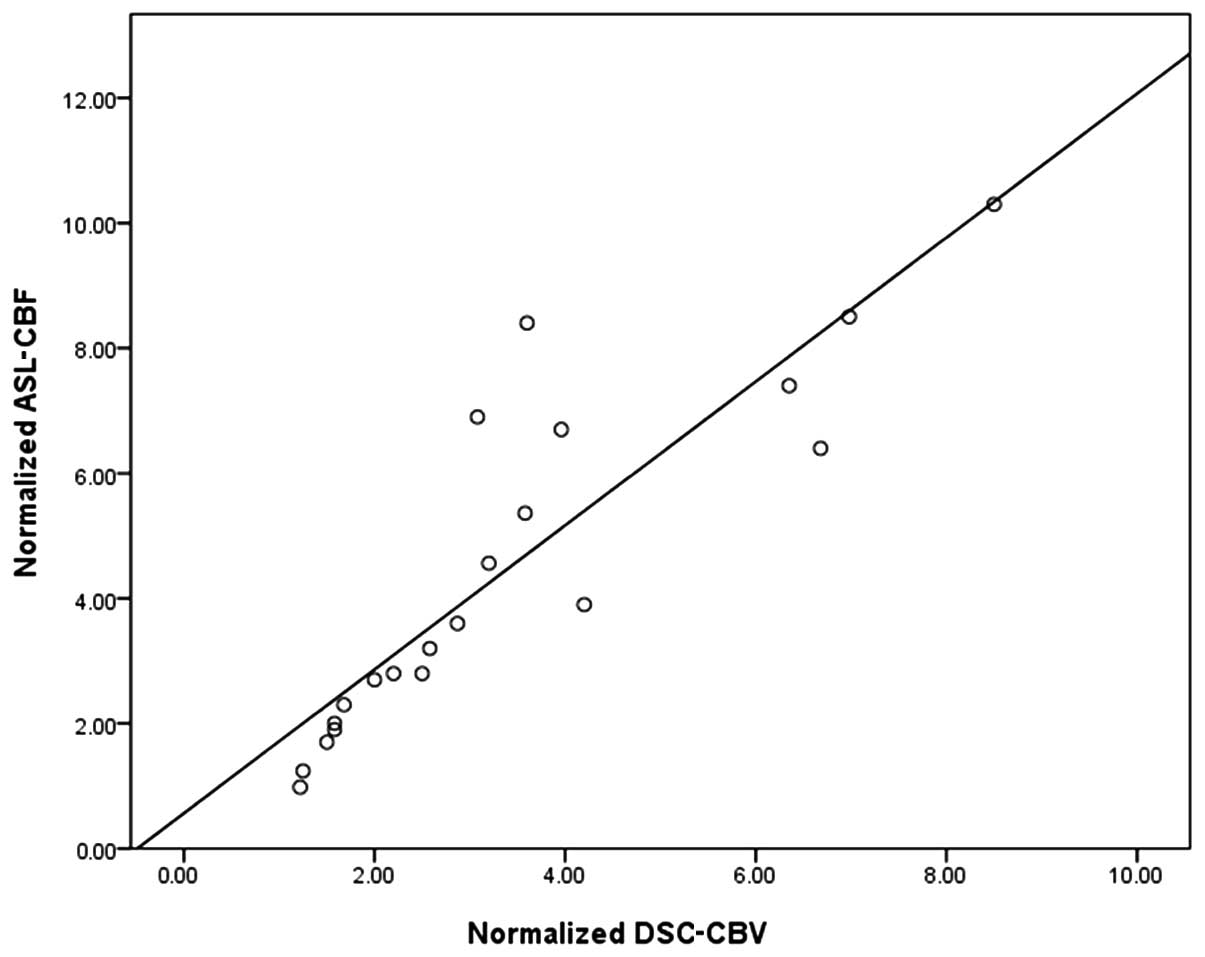
|
1
|
Tsuruda JS, Kortman KE, Bradley WG,
Wheeler DC, Van Dalsem W and Bradley TP: Radiation effects on
cerebral white matter: MR evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
149:165–171. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Remler MP, Marcussen WH and Tiller-Borsich
J: The late effects of radiation on the blood brain barrier. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 12:1965–1969. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leon SP, Folkerth RD and Black PM:
Microvessel density is a prognostic indicator for patients with
astroglial brain tumors. Cancer. 77:362–372. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang AP, Tsai JC, Kuo LT, Lee CW, Lai HS,
Tsai LK, Huang SJ, Chen CM, Chen YS, Chuang HY and Wintermark M:
Clinical application of perfusion computed tomography in
neurosurgery. J Neurosurg. 120:473–488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mullins ME, Barest GD, Schaefer PW,
Hochberg FH, Gonzalez RG and Lev MH: Radiation necrosis versus
glioma recurrence: Conventional MR imaging clues to diagnosis. AJNR
Am J Neuroradiol. 26:1967–1972. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Spagnolli F, Frezza
G, Leonardi M, Calbucci F and Franceschi E: Disease progression or
pseudoprogression after concomitant radiochemotherapy treatment:
Pitfalls in neurooncology. Neuro Oncol. 10:361–367. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kumar AJ, Leeds NE, Fuller GN, Van Tassel
P, Maor MH, Sawaya RE and Levin VA: Malignant gliomas: MR imaging
spectrum of radiation therapy- and chemotherapy-induced necrosis of
the brain after treatment. Radiology. 217:377–384. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cha S, Knopp EA, Johnson G, Wetzel SG,
Litt AW and Zagzag D: Intracranial mass lesions: Dynamic
contrast-enhanced susceptibility-weighted echo-planar perfusion MR
imaging. Radiology. 223:11–29. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paulson ES and Schmainda KM: Comparison of
dynamic susceptibility-weighted contrast-enhanced MR methods:
Recommendations for measuring relative cerebral blood volume in
brain tumors. Radiology. 249:601–613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thomsen H, Steffensen E and Larsson EM:
Perfusion MRI (dynamic susceptibility contrast imaging) with
different measurement approaches for the evaluation of blood flow
and blood volume in human gliomas. Acta Radiol. 53:95–101. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barajas RF Jr, Chang JS, Segal MR, Parsa
AT, McDermott MW, Berger MS and Cha S: Differentiation of recurrent
glioblastoma multiforme from radiation necrosis after external beam
radiation therapy with dynamic susceptibility-weighted
contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging. Radiology. 253:486–496.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsumura T, Hayakawa M, Shimada F, Yabuki
M, Dohanish S, Palkowitsch P and Yoshikawa K: Safety of
gadopentetate dimeglumine after 120 million administrations over 25
years of clinical use. Magn Reson Med Sci. 12:297–304. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang L, Krefting I, Gorovets A, Marzella
L, Kaiser J, Boucher R and Rieves D: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
and class labeling of gadolinium-based contrast agents by the food
and drug administration. Radiology. 265:248–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bjornerud A and Emblem KE: A fully
automated method for quantitative cerebral hemodynamic analysis
using DSC-MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1066–1078. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carlsson A, Starck G, Ljungberg M, Ekholm
S and Forssell-Aronsson E: Accurate and sensitive measurements of
magnetic susceptibility using echo planar imaging. Magn Reson
Imaging. 24:1179–1185. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Detre JA, Rao H, Wang DJ, Chen YF and Wang
Z: Applications of arterial spin labeled MRI in the brain. J Magn
Reson Imaging. 35:1026–1037. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Detre JA, Wang J, Wang Z and Rao H:
Arterial spin-labeled perfusion MRI in basic and clinical
neuroscience. Curr Opin Neuro. 22:348–355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chawla S, Wang S, Wolf RL, Woo JH, Wang J,
O'Rourke DM, Judy KD, Grady MS, Melhem ER and Poptani H: Arterial
spin-labeling and MR spectroscopy in the differentiation of
gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 28:1683–1689. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr and
Cairncross JG: Response criteria for phase II studies of
supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol. 8:1277–1280.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan H, Chen L, Guan Y and Lin X:
Comparison of MRI, F-18 FDG and 11C-choline PET/CT for their
potentials in differentiating brain tumor recurrence from brain
tumor necrosis following radiotherapy. Clin Nucl Med. 36:978–981.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Tomiguchi S,
Shigematsu Y, Ikushima I, Kira T, Liang L, Ushio Y and Takahashi M:
Posttherapeutic intraaxial brain tumor: The value of
perfusion-sensitive contrast-enhanced MR imaging for
differentiating tumor recurrence from nonneoplastic
contrast-enhancing tissue. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 21:901–909.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Warmuth C, Gunther M and Zimmer C:
Quantification of blood flow in brain tumors: Comparison of
arterial spin labeling and dynamic susceptibility-weighted
contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 228:523–532. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
White CM, Pope WB, Zaw T, Qiao J, Naeini
KM, Lai A, Nghiemphu PL, Wang JJ, Cloughesy TF and Ellingson BM:
Regional and voxel-wise comparisons of blood flow measurements
between dynamic susceptibility contrast magnetic resonance imaging
(DSC-MRI) and arterial spin labeling (ASL) in brain tumors. J
Neuroimaging. 24:23–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ozsunar Y, Mullins ME, Kwong K, Hochberg
FH, Ament C, Schaefer PW, Gonzalez RG and Lev MH: Glioma recurrence
versus radiation necrosis? A pilot comparison of arterial
spin-labeled, dynamic susceptibility contrast enhanced MRI and
FDG-PET imaging. Acad Radiol. 17:282–290. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Choi YJ, Kim HS, Jahng GH, Kim SJ and Suh
DC: Pseudoprogression in patients with glioblastoma: Added value of
arterial spin labeling to dynamic susceptibility contrast perfusion
MR imaging. Acta Radiol. 54:448–454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu LS, Baxter LC, Smith KA, Feuerstein BG,
Karis JP, Eschbacher JM, Coons SW, Nakaji P, Yeh RF, Debbins J and
Heiserman JE: Relative cerebral blood volume values to
differentiate high-grade glioma recurrence from posttreatment
radiation effect: Direct correlation between image-guided tissue
histopathology and localized dynamic susceptibility-weighted
contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging measurements. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 30:552–558. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Larsen VA, Simonsen HJ, Law I, Larsson HB
and Hansen AE: Evaluation of dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted
perfusion MRI in the differentiation of tumor recurrence from
radiation necrosis. Neuroradiology. 55:361–369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|